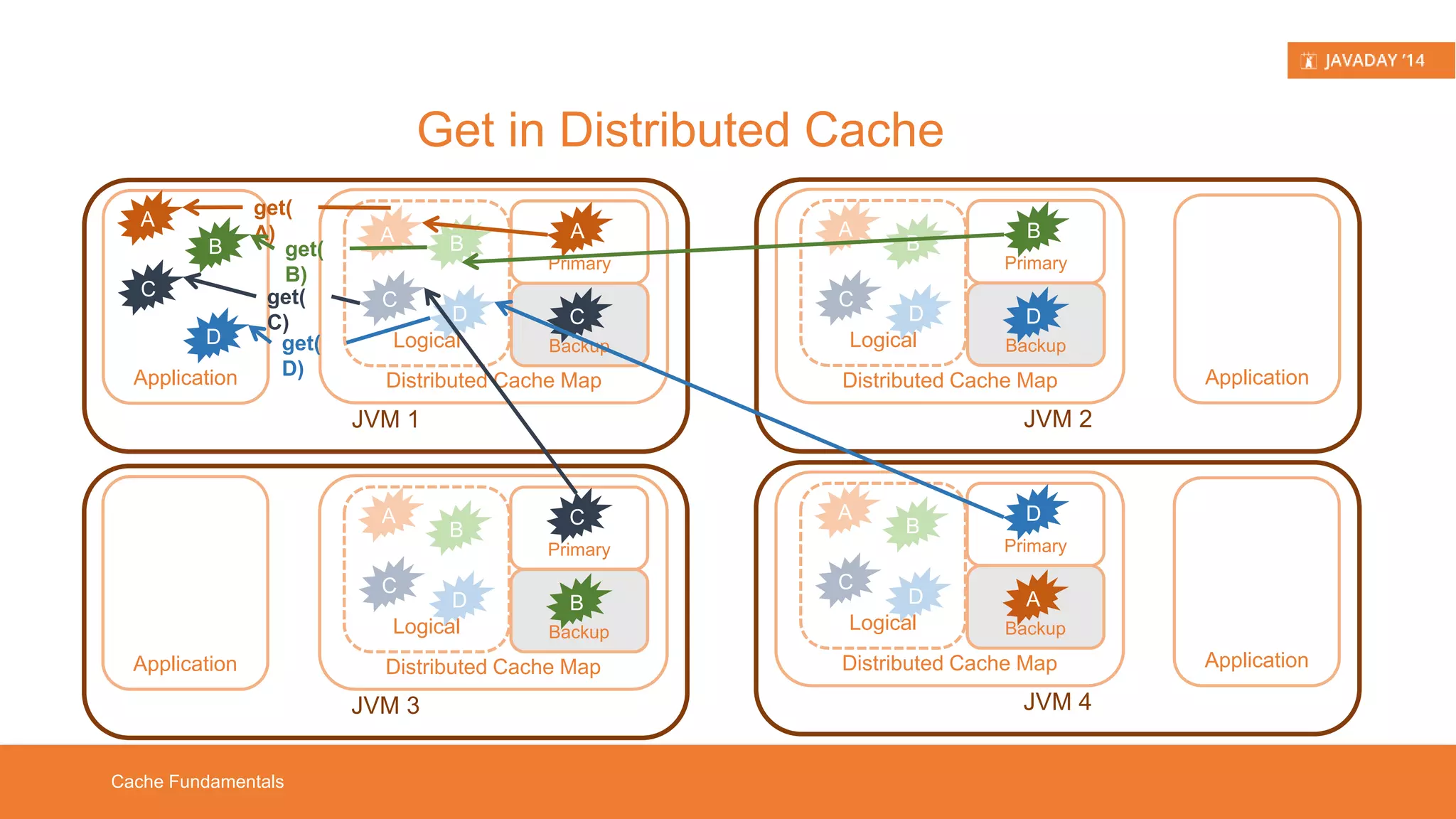
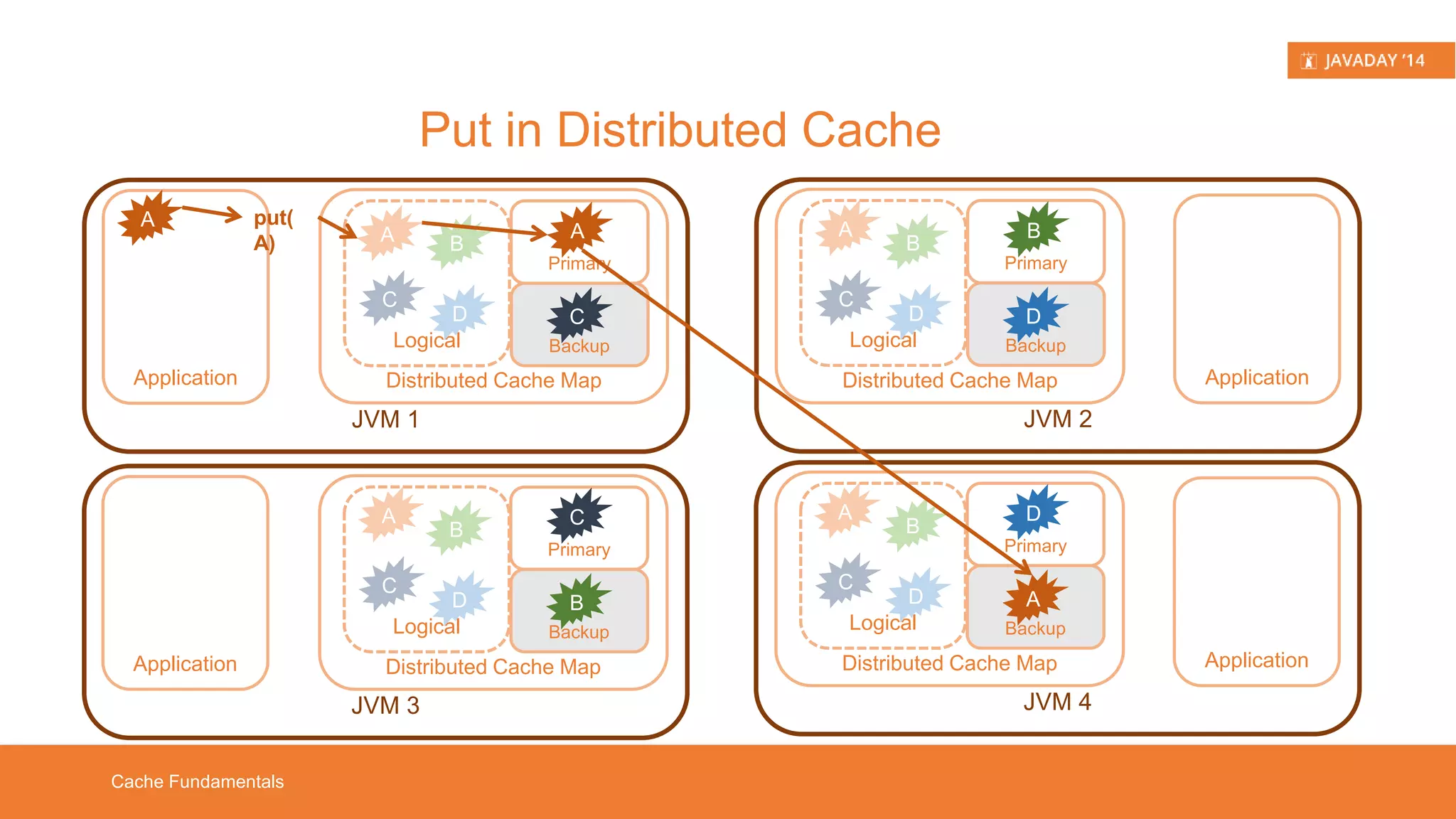
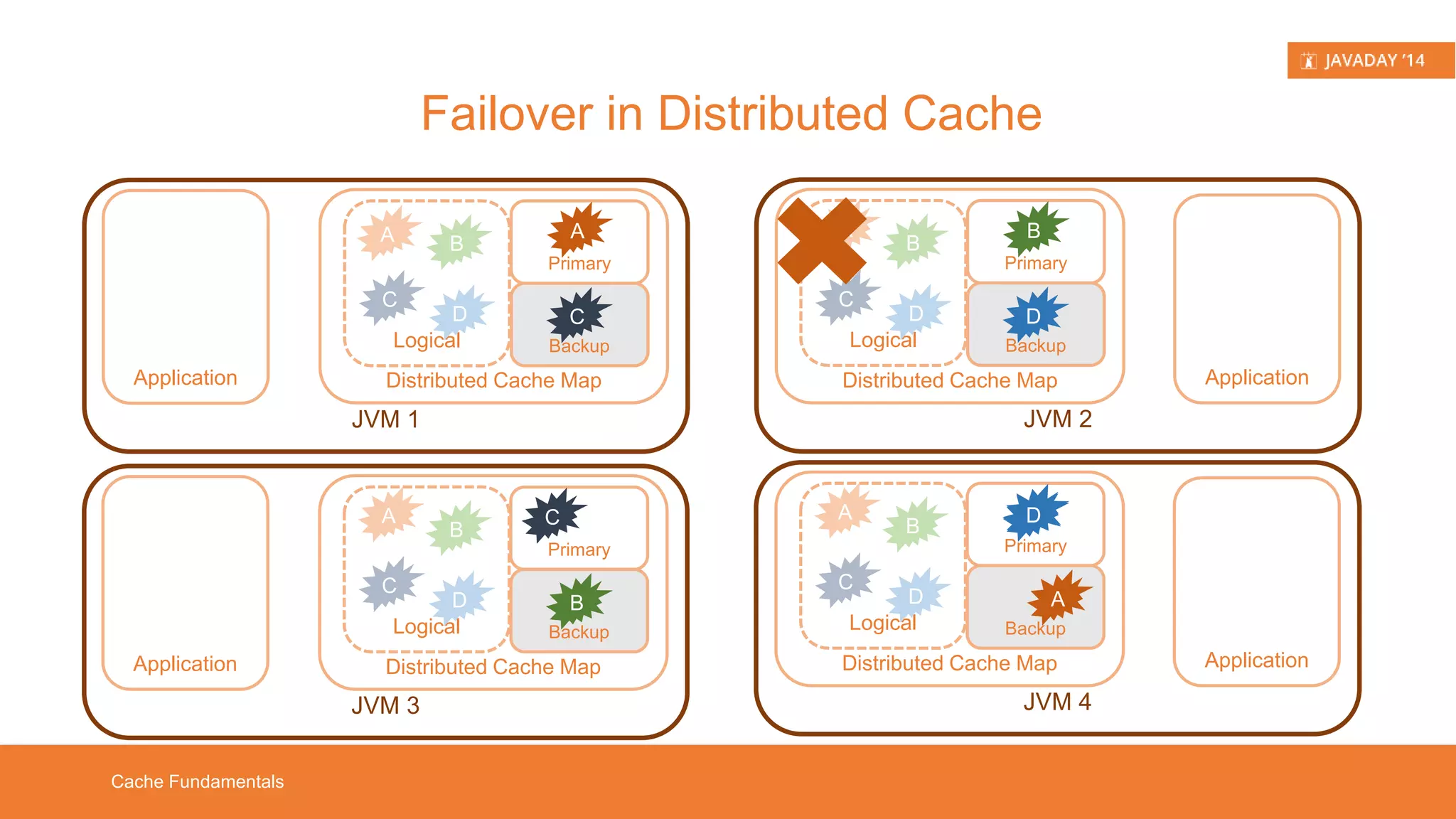
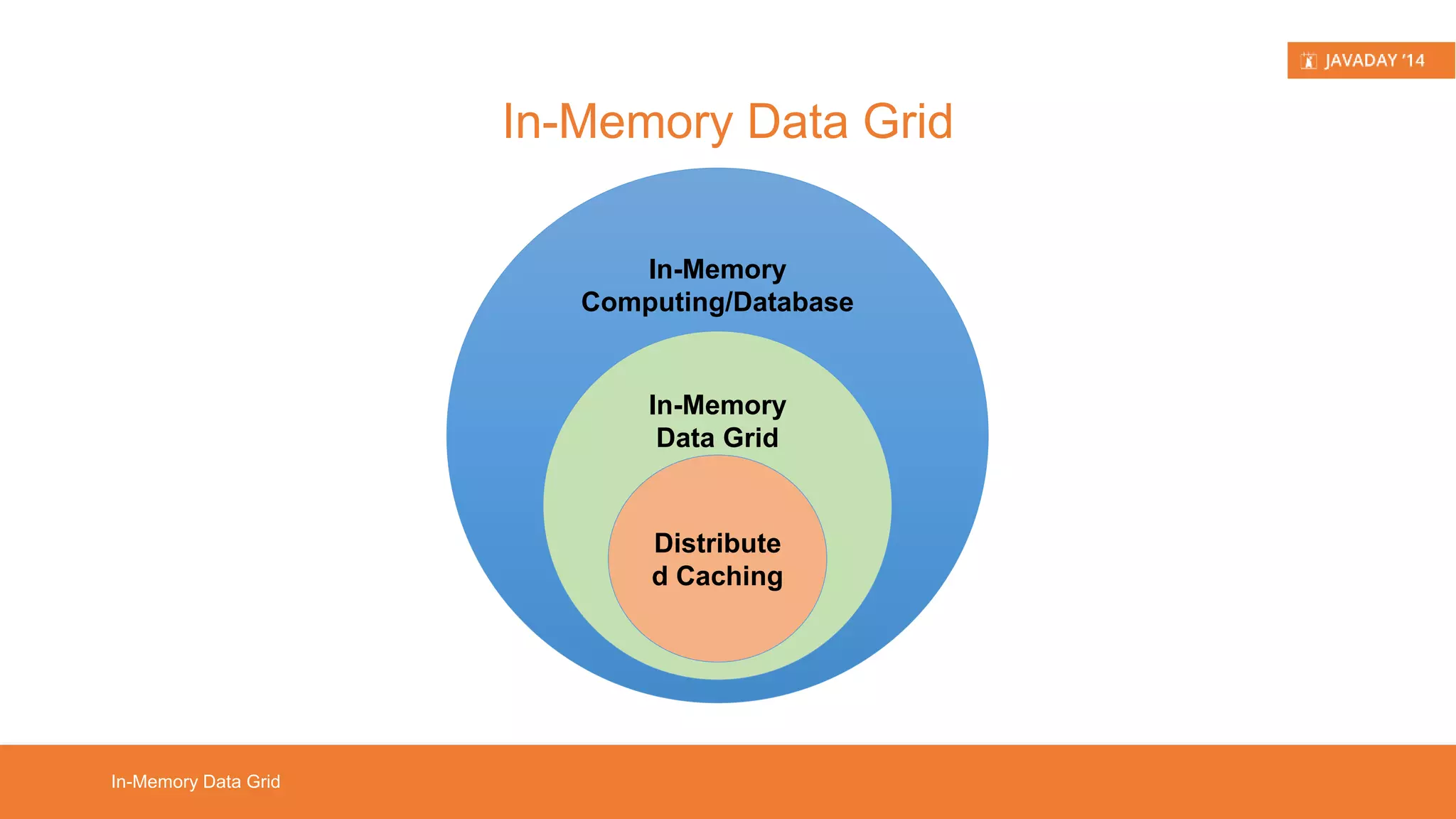
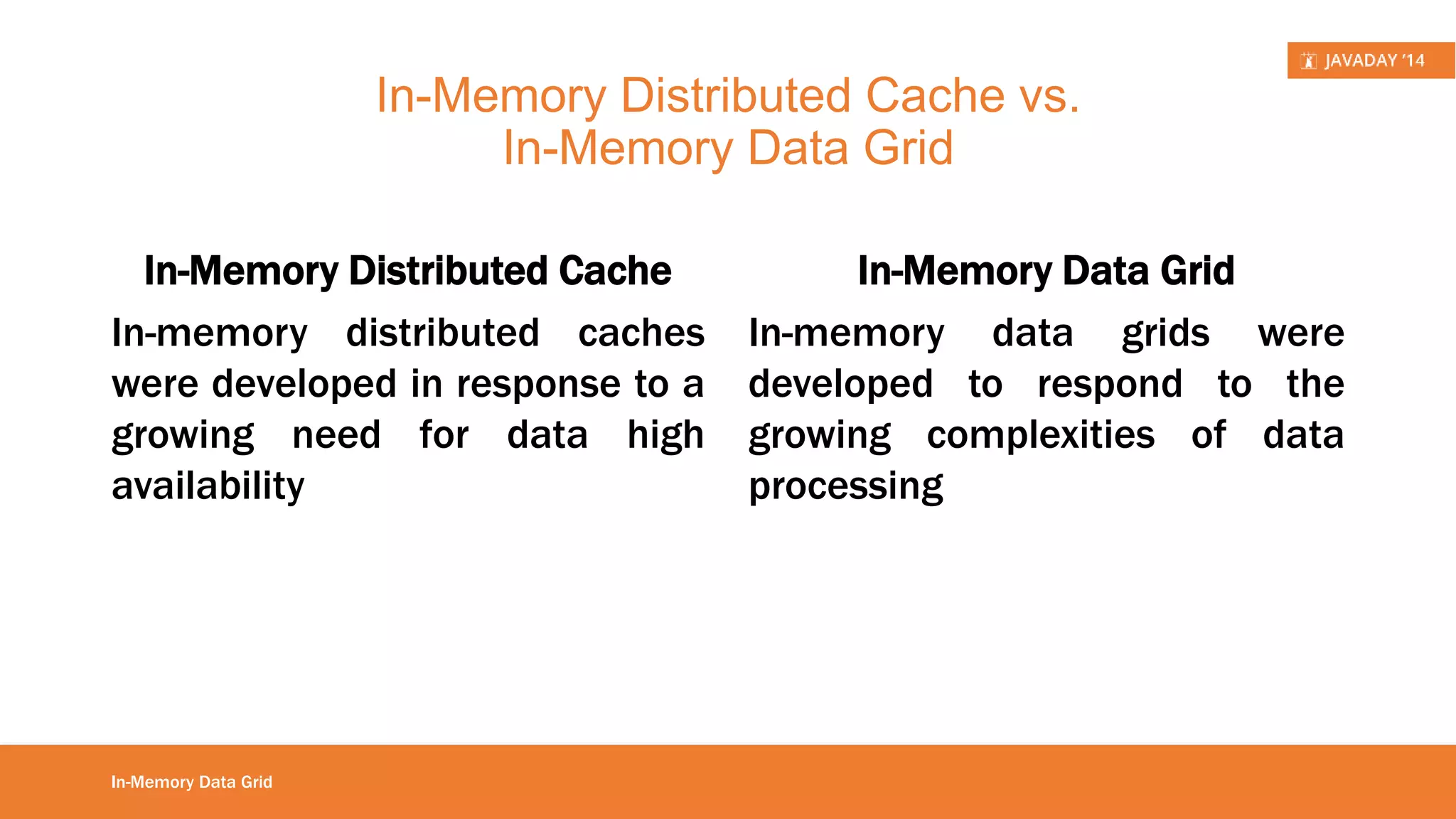
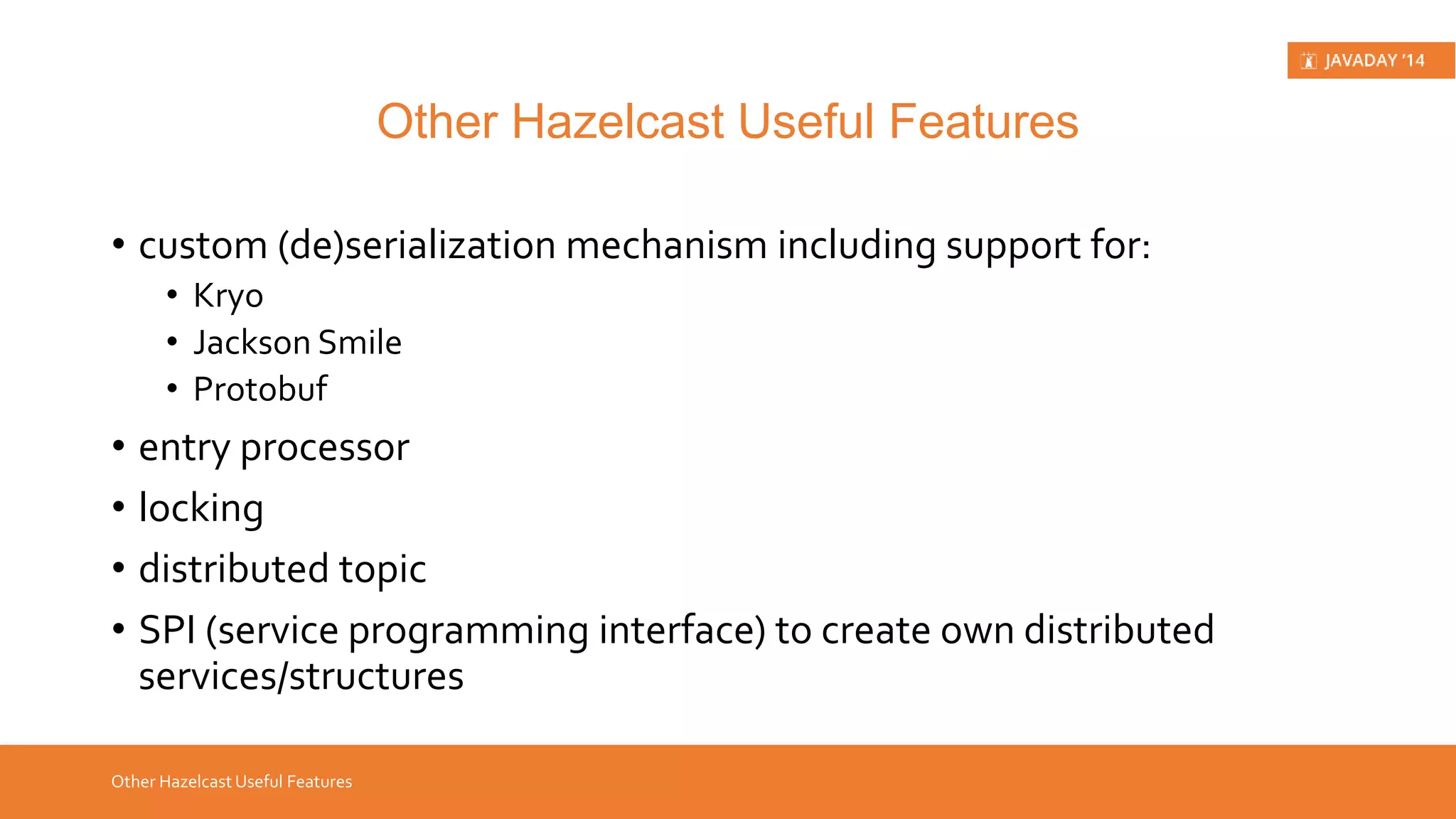
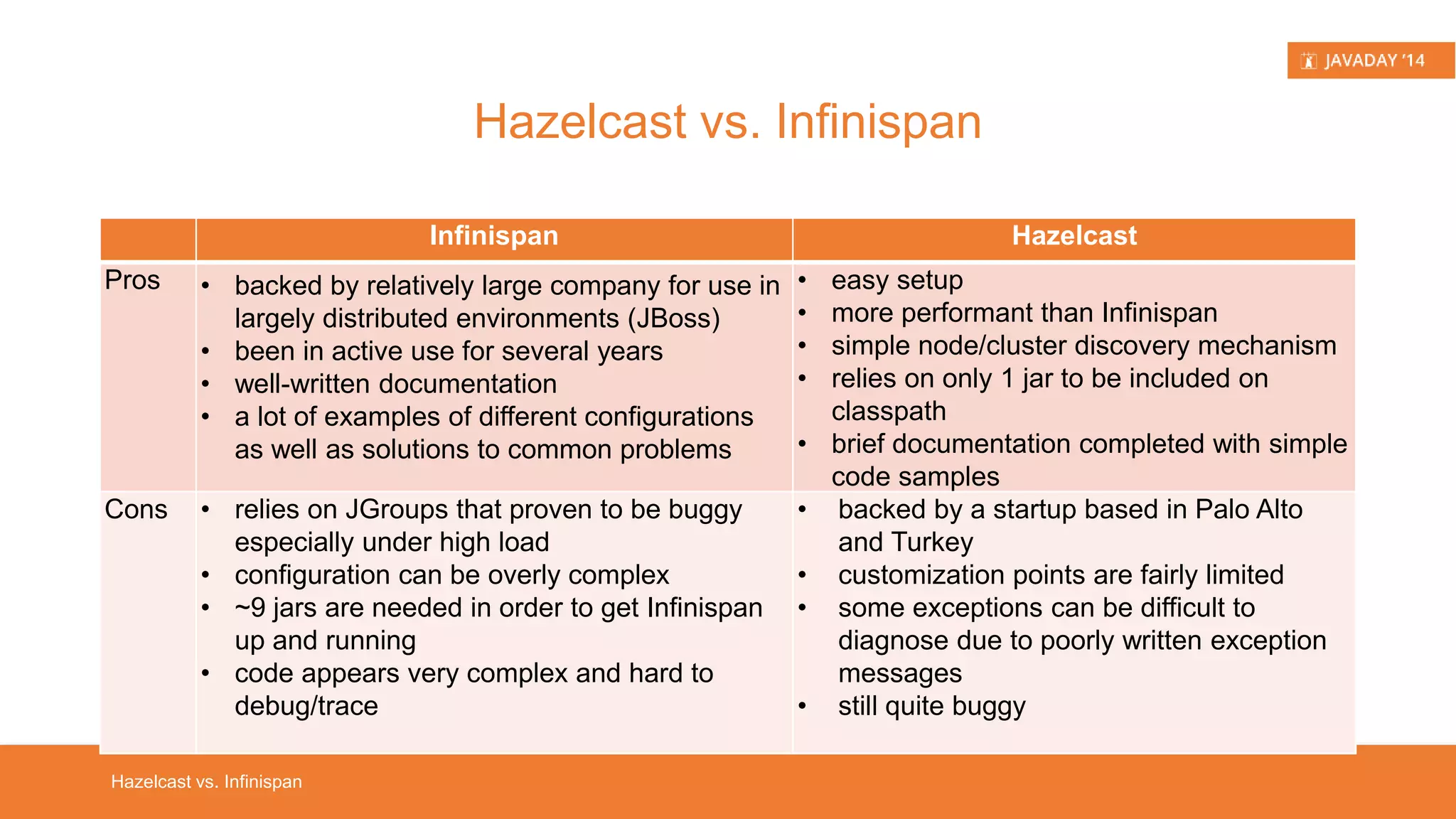
This presentation provides an overview of Hazelcast, highlighting its key features and use cases for distributed applications. It includes live demos and a comparison between distributed caching and in-memory data grids while not promoting Hazelcast as the ultimate solution. Targeted at developers, it aims to deepen understanding of Hazelcast's capabilities, such as dynamic clustering and data partitioning.