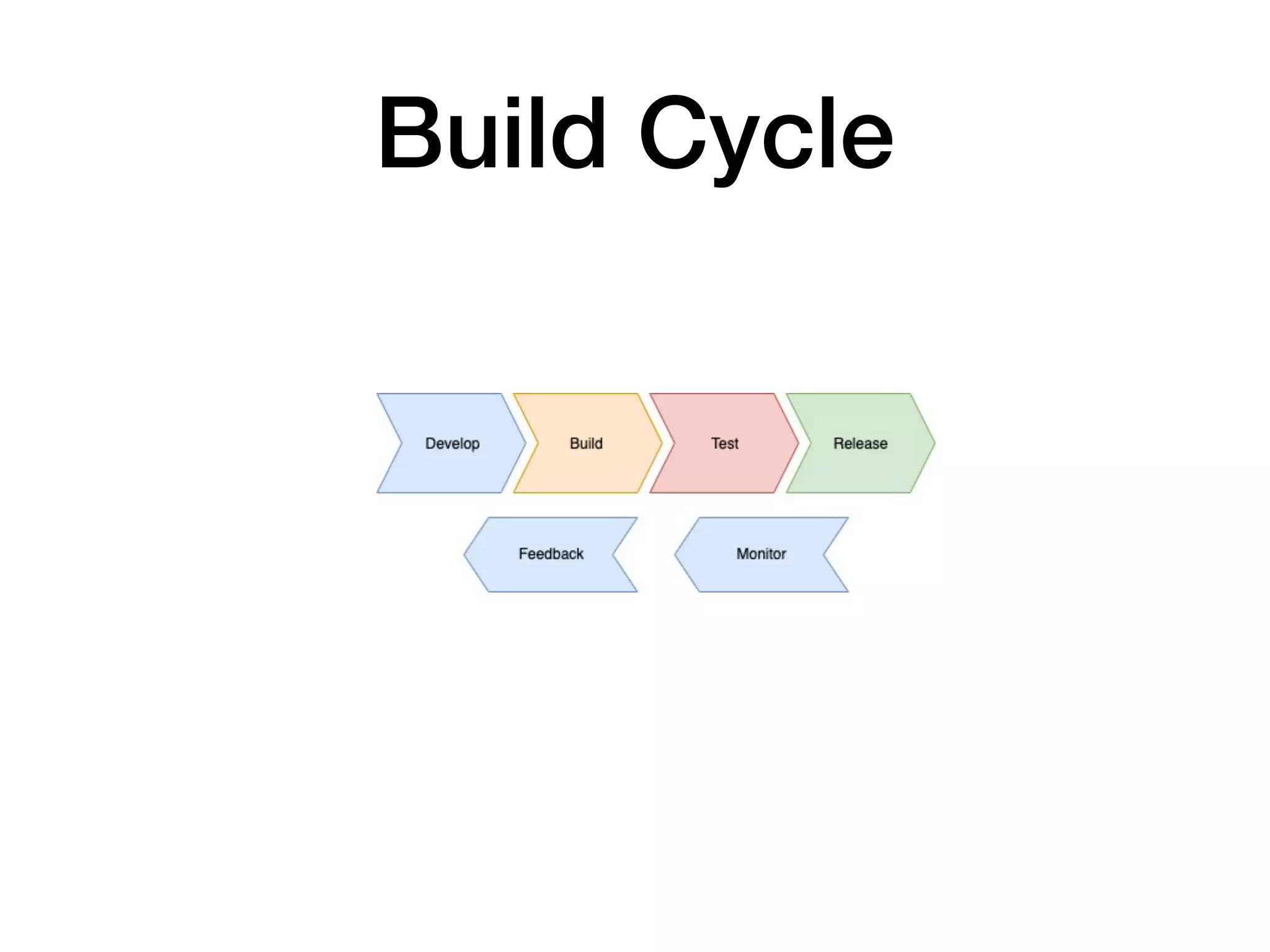
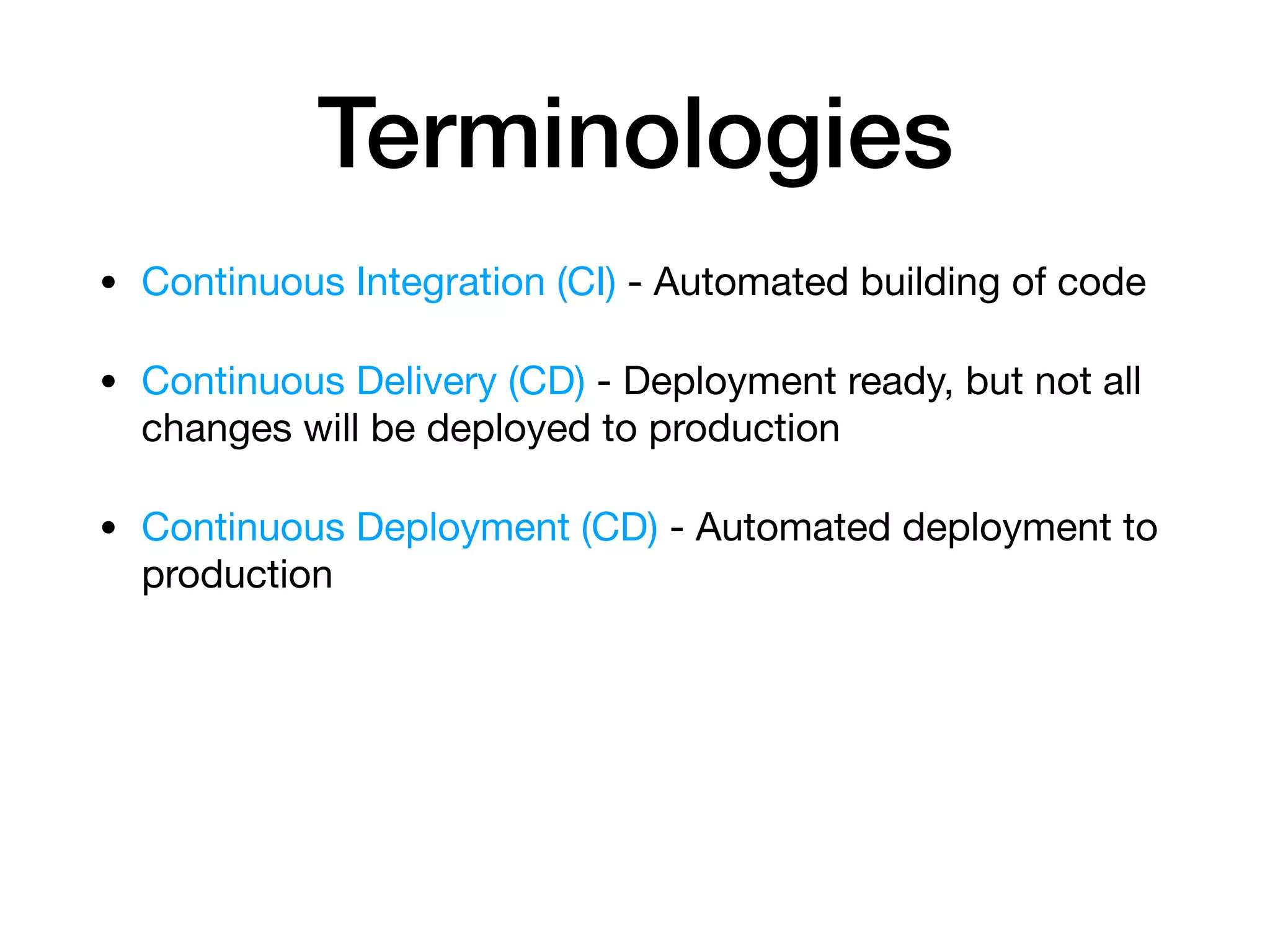
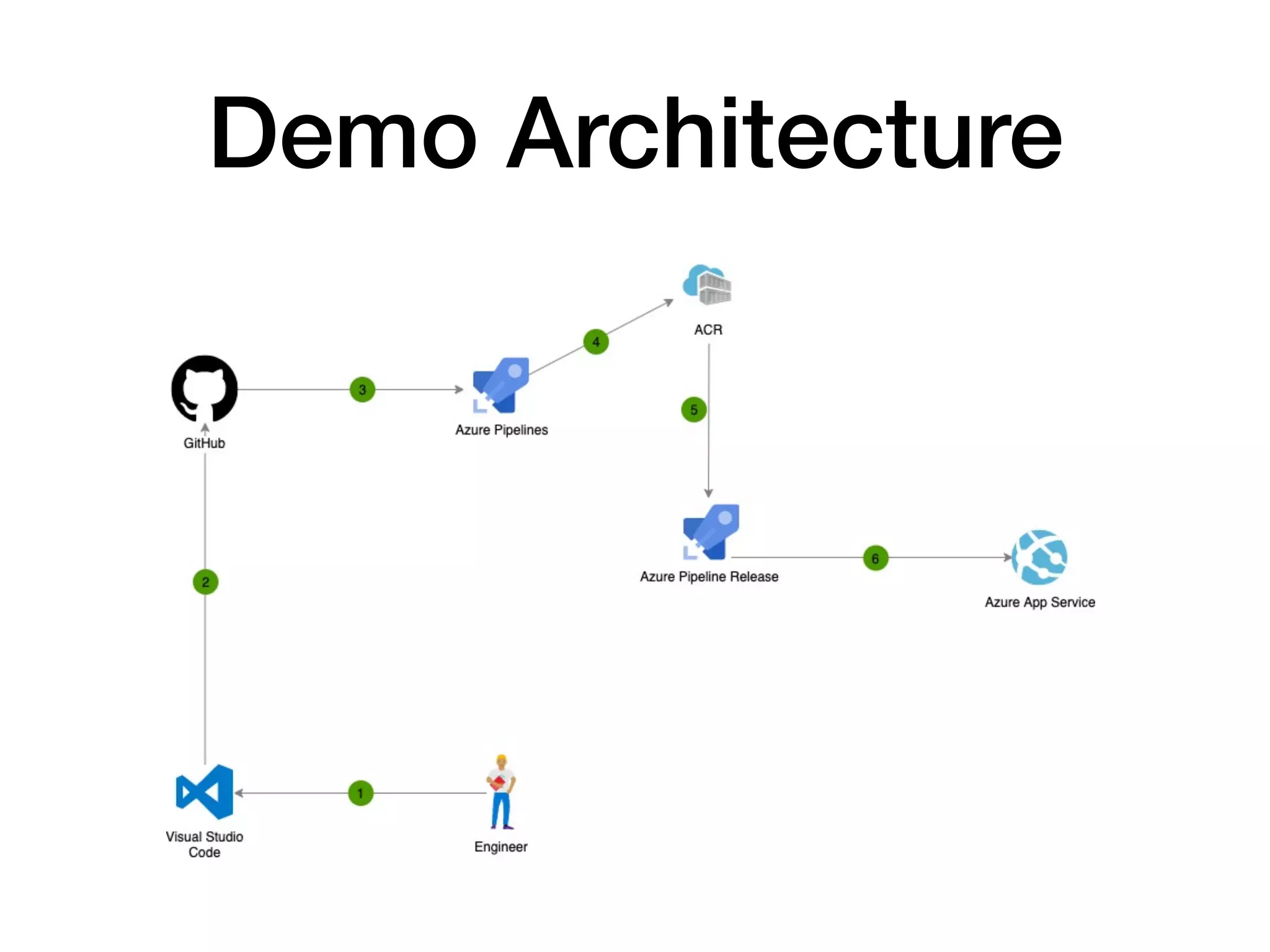
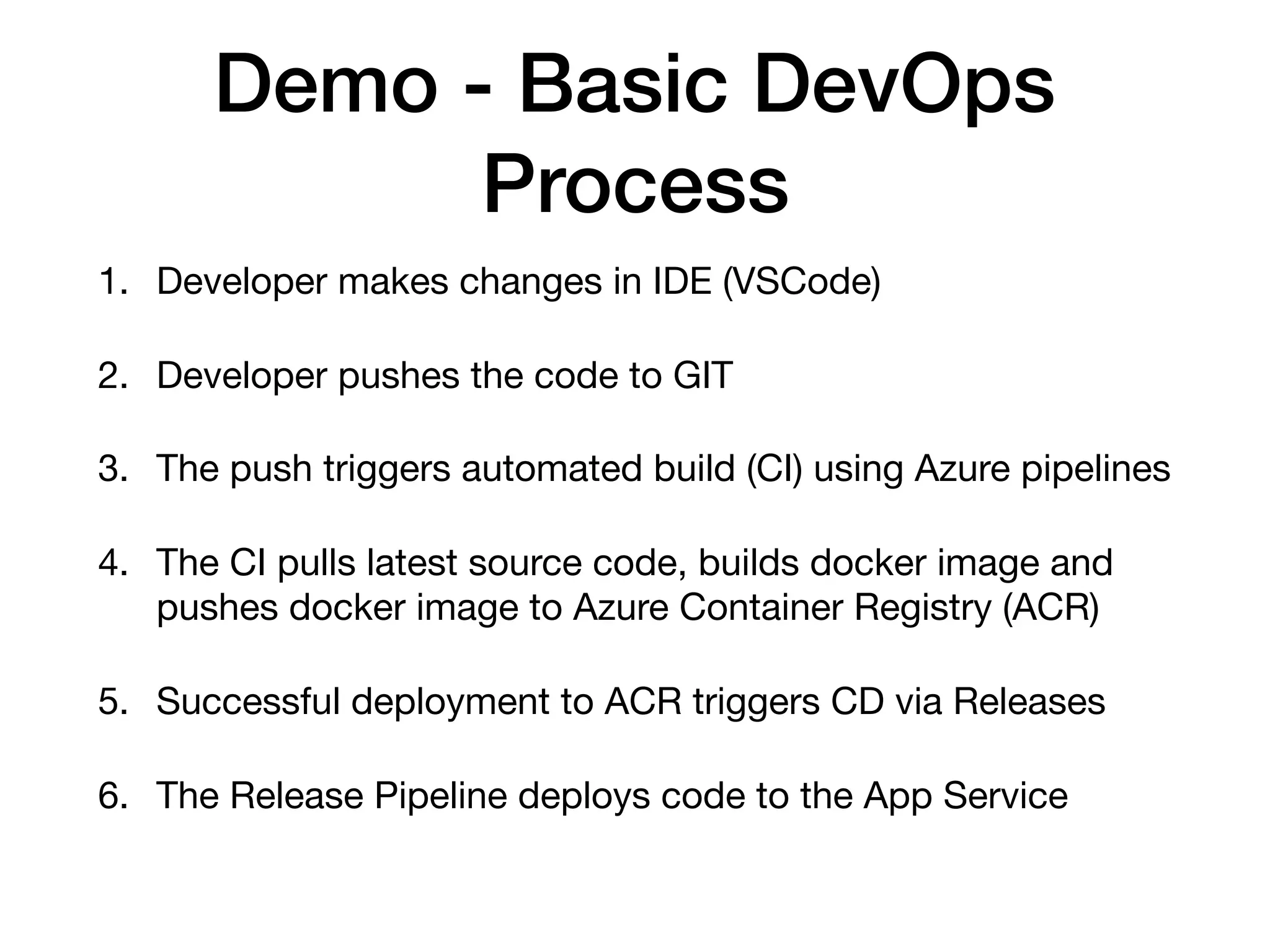
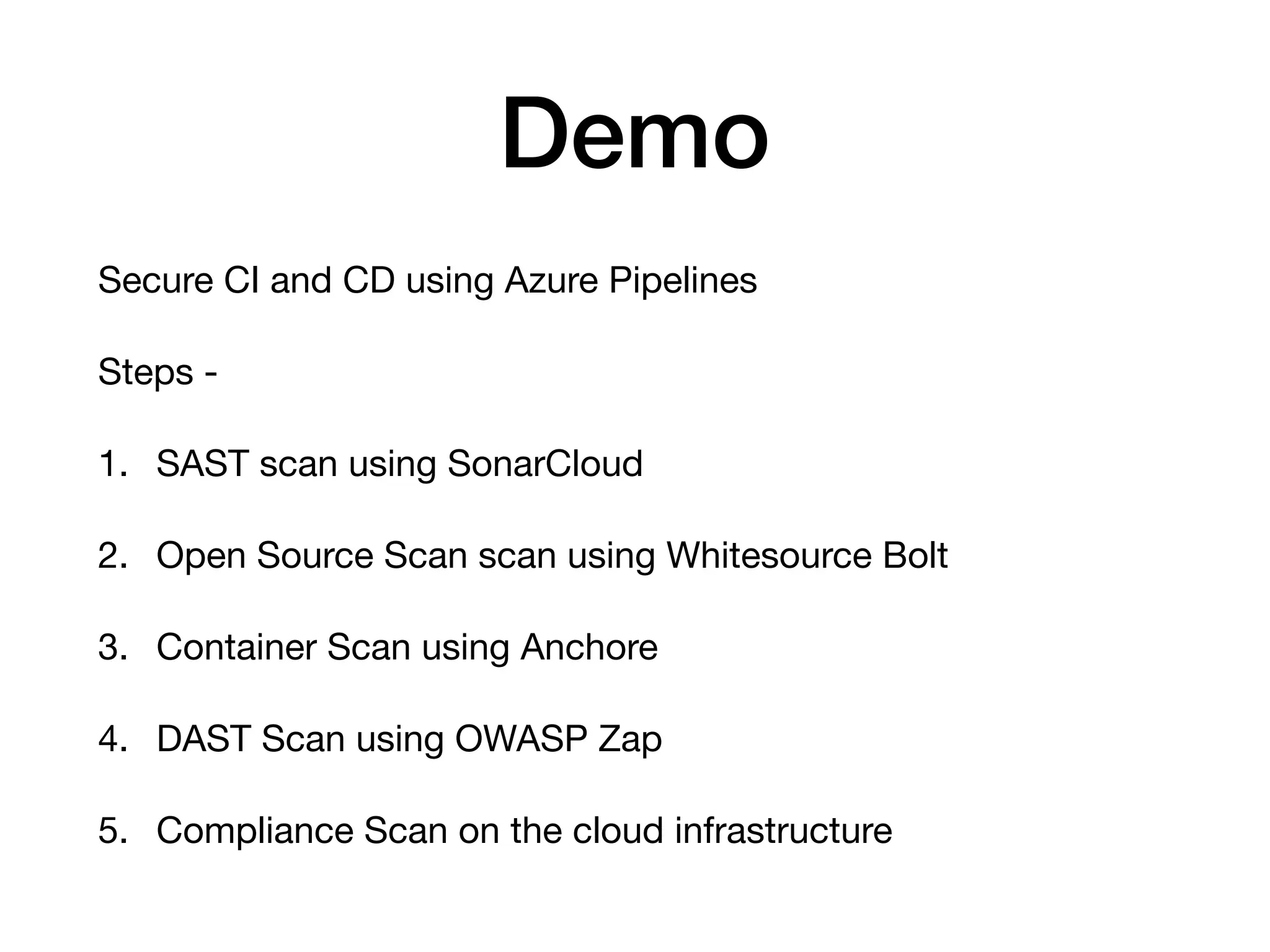
This document discusses DevSecOps, which integrates security practices into DevOps workflows to securely develop software through continuous integration and delivery. It outlines the basic DevOps process using Azure Pipelines for CI/CD and defines DevSecOps. The document then discusses challenges with security, benefits of DevSecOps for businesses, and common tools used, before concluding with an example DevSecOps demo using Azure Pipelines with security scans at various stages.