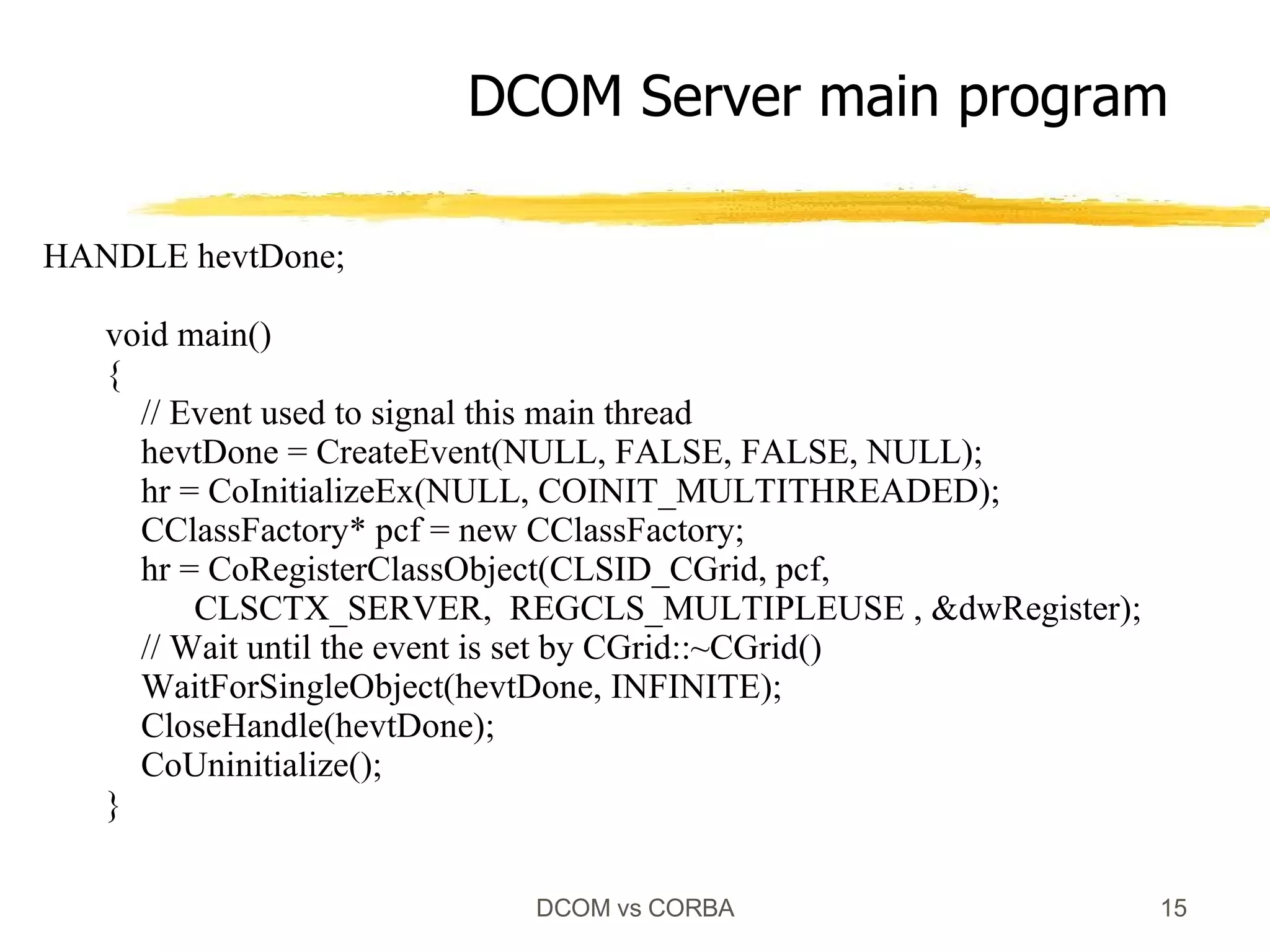
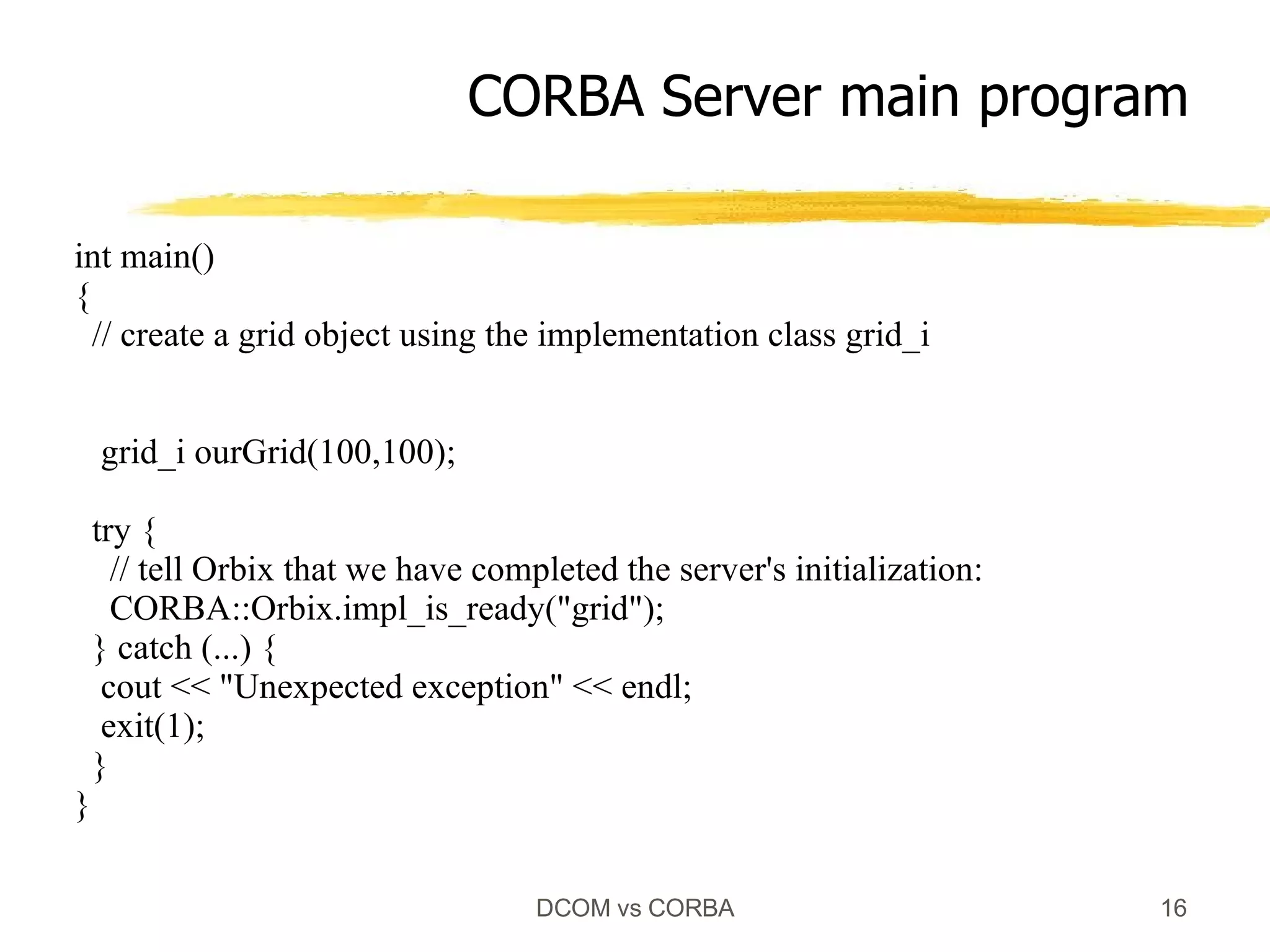
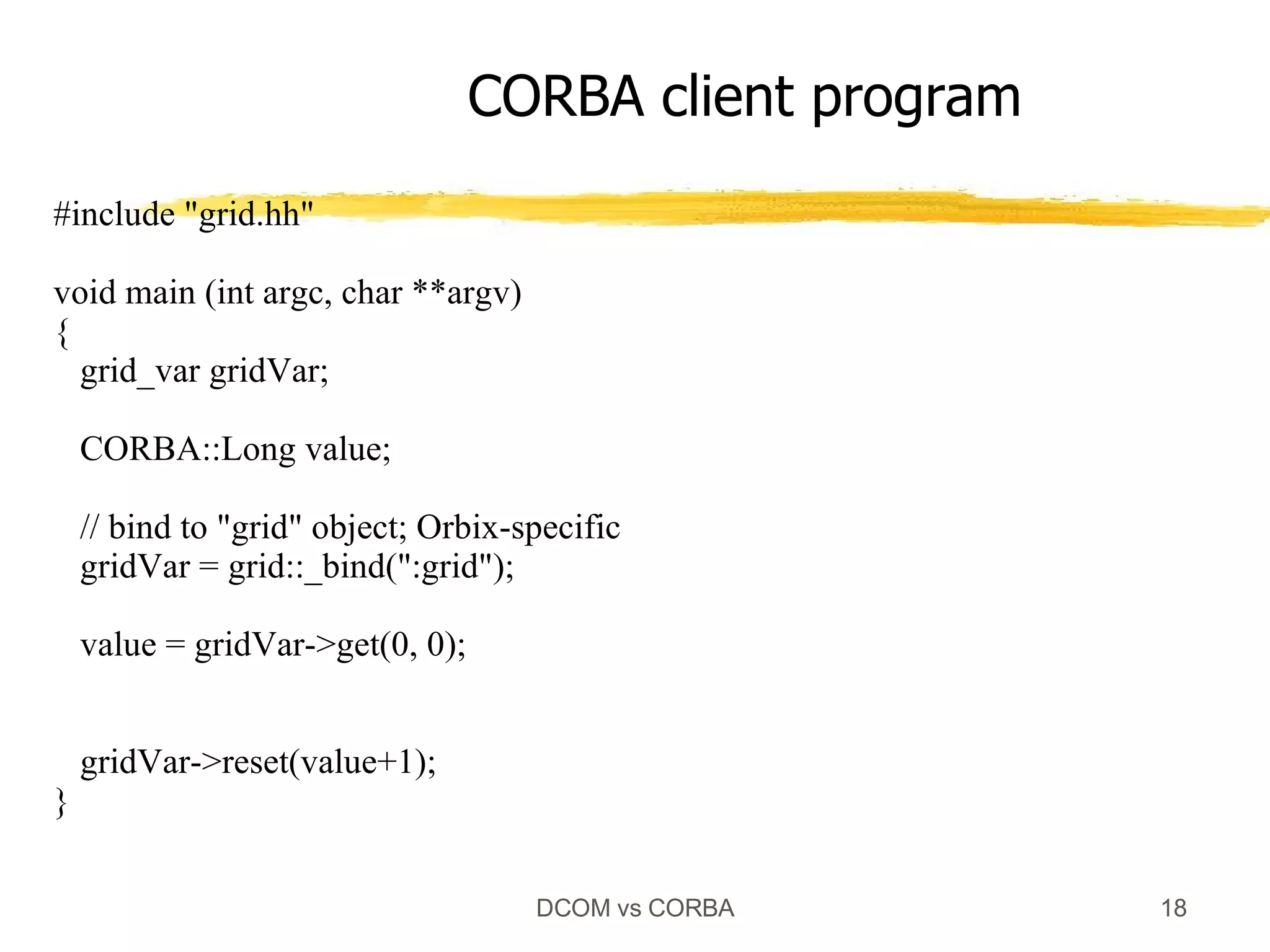
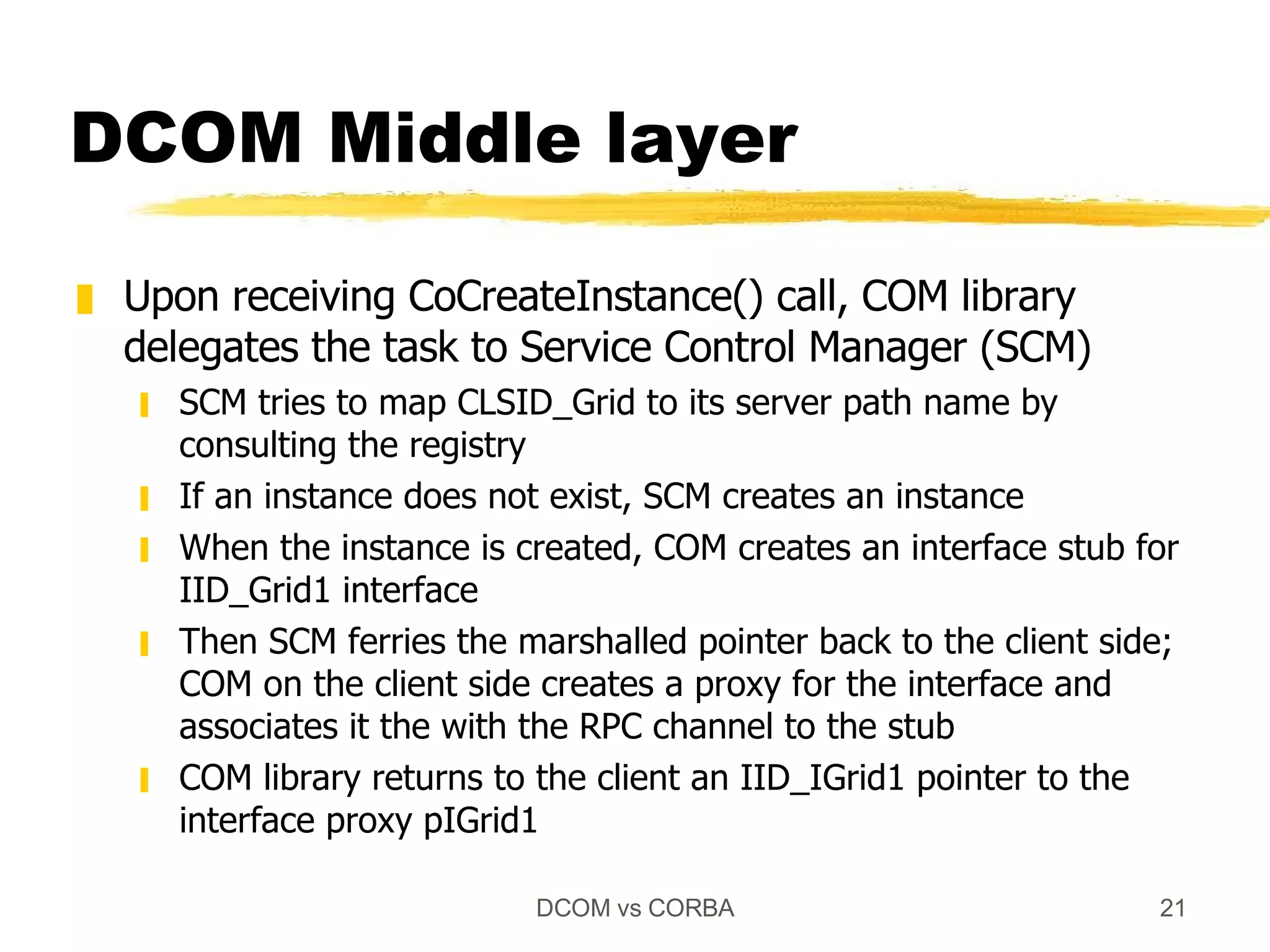
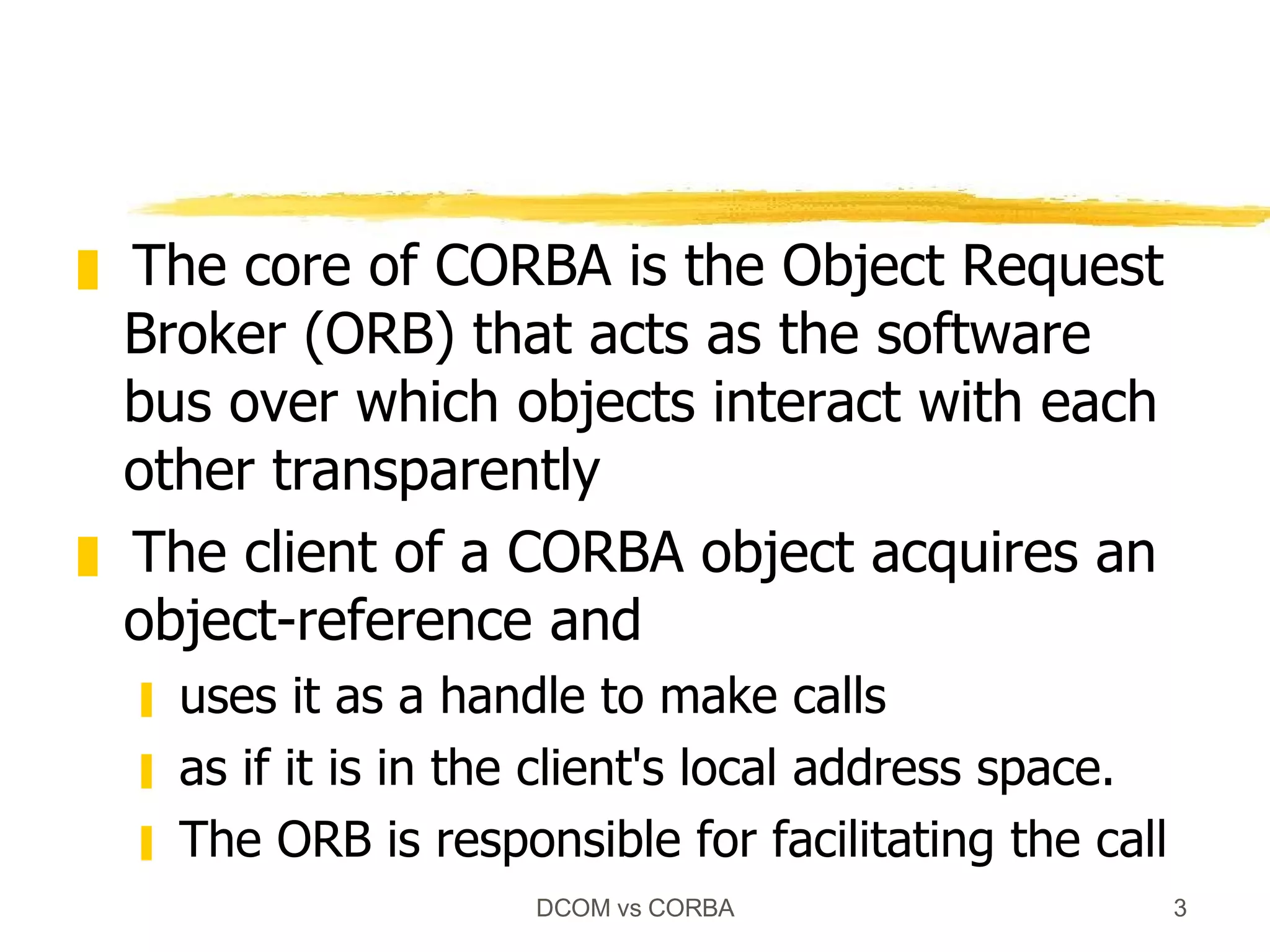
Both DCOM and CORBA provide client-server relationships between objects by allowing clients to access server objects remotely. DCOM uses COM interfaces and the Windows registry for registration, while CORBA uses IDL interfaces and an implementation repository. When a client calls CoCreateInstance() in DCOM or bind() in CORBA, middleware layers look up the server implementation and return a proxy that allows remote method calls to appear local to the client.


![// uuid and definition of IGrid1 [ object, uuid(3CFDB283-CCC5-11D0-BA0B-00A0C90DF8BC), helpstring("IGrid1 Interface"), pointer_default(unique) ] interface IGrid1 : IUnknown { import "unknwn.idl"; HRESULT get([in] SHORT n, [in] SHORT m, [out] LONG *value); HRESULT set([in] SHORT n, [in] SHORT m, [in] LONG value); }; // uuid and definition of IGrid2 [ object, uuid(3CFDB284-CCC5-11D0-BA0B-00A0C90DF8BC), helpstring("IGrid2 Interface"), pointer_default(unique) ] interface IGrid2 : IUnknown { import "unknwn.idl"; HRESULT reset([in] LONG value); }; DCOM IDL Each interface and class has GUIDs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcom-comparison-1207056819446761-4/75/DCOM-Comparison-8-2048.jpg)
![// uuid and definition of type library [ uuid(3CFDB281-CCC5-11D0-BA0B-00A0C90DF8BC), version(1.0), helpstring("grid 1.0 Type Library) ] library GRIDLib { importlib("stdole32.tlb"); // uuid and definition of class [ uuid(3CFDB287-CCC5-11D0-BA0B-00A0C90DF8BC), helpstring("Grid Class") ] // multiple interfaces coclass CGrid { [default] interface IGrid1; interface IGrid2; }; }; DCOM IDL (continued) multiple views for Grid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcom-comparison-1207056819446761-4/75/DCOM-Comparison-9-2048.jpg)

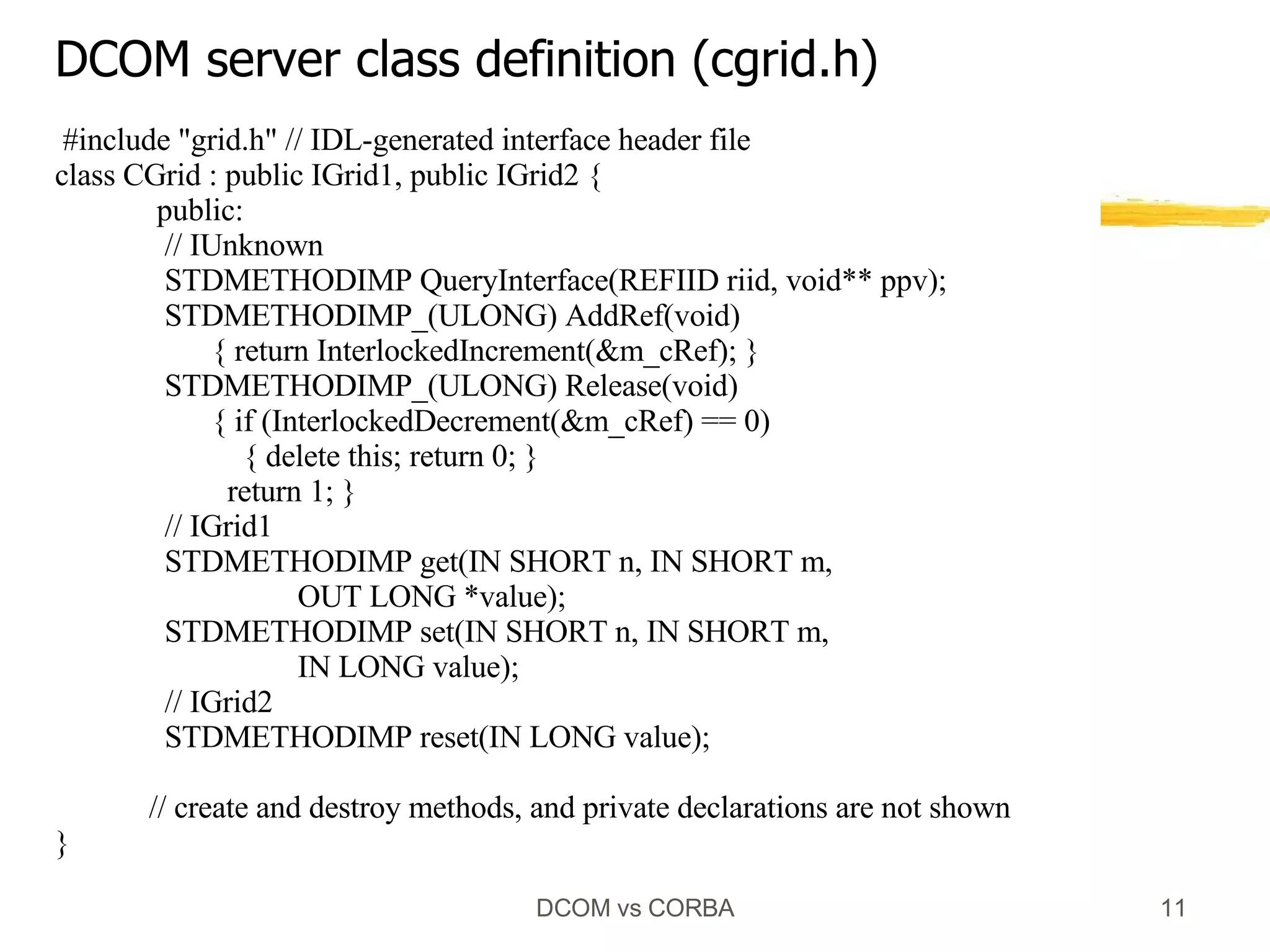
![#include "cgrid.h" STDMETHODIMP CGrid::QueryInterface(REFIID riid, void** ppv) { if (riid == IID_IUnknown || riid == IID_IGrid1) *ppv = (IGrid1*) this; else if (riid == IID_IGrid2) *ppv = (IGrid2*) this; else { *ppv = NULL; return E_NOINTERFACE; } AddRef(); return S_OK; } STDMETHODIMP CGrid::get(IN SHORT n, IN SHORT m, OUT LONG* value) { *value = m_a[n][m]; return S_OK; } extern HANDLE hevtDone; CGrid::~CGrid () { for (int i=0; i < m_height; i++) delete[] m_a[i]; delete[] m_a; SetEvent(hevtDone); } DCOM Server Implementation create, set, reset method implementations are not shown](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcom-comparison-1207056819446761-4/75/DCOM-Comparison-13-2048.jpg)
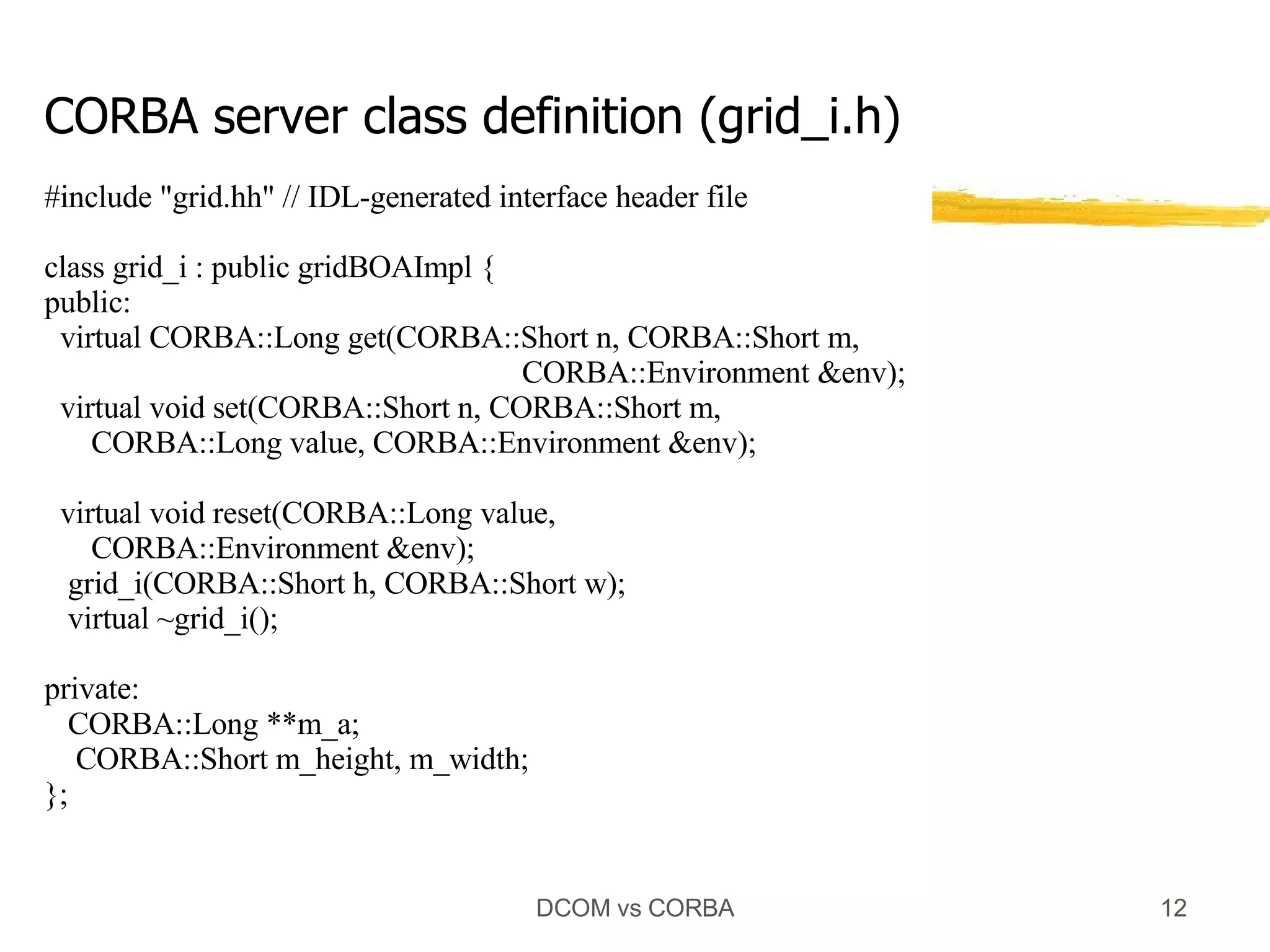
![#include "grid_i.h" CORBA::Long grid_i::get(CORBA::Short n, CORBA::Short m, CORBA::Environment &) { return m_a[n][m]; } void grid_i::set(CORBA::Short n, CORBA::Short m, CORBA::Long value, CORBA::Environment &) { m_a[n][m] = value; } void grid_i::reset(CORBA::Long value, CORBA::Environment &) { short n, m; for (n = 0; n < m_height; n++) for (m = 0; m < m_width; m++) m_a[n][m]=value; return; } // create and delete not shown CORBA Server Implementation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcom-comparison-1207056819446761-4/75/DCOM-Comparison-14-2048.jpg)