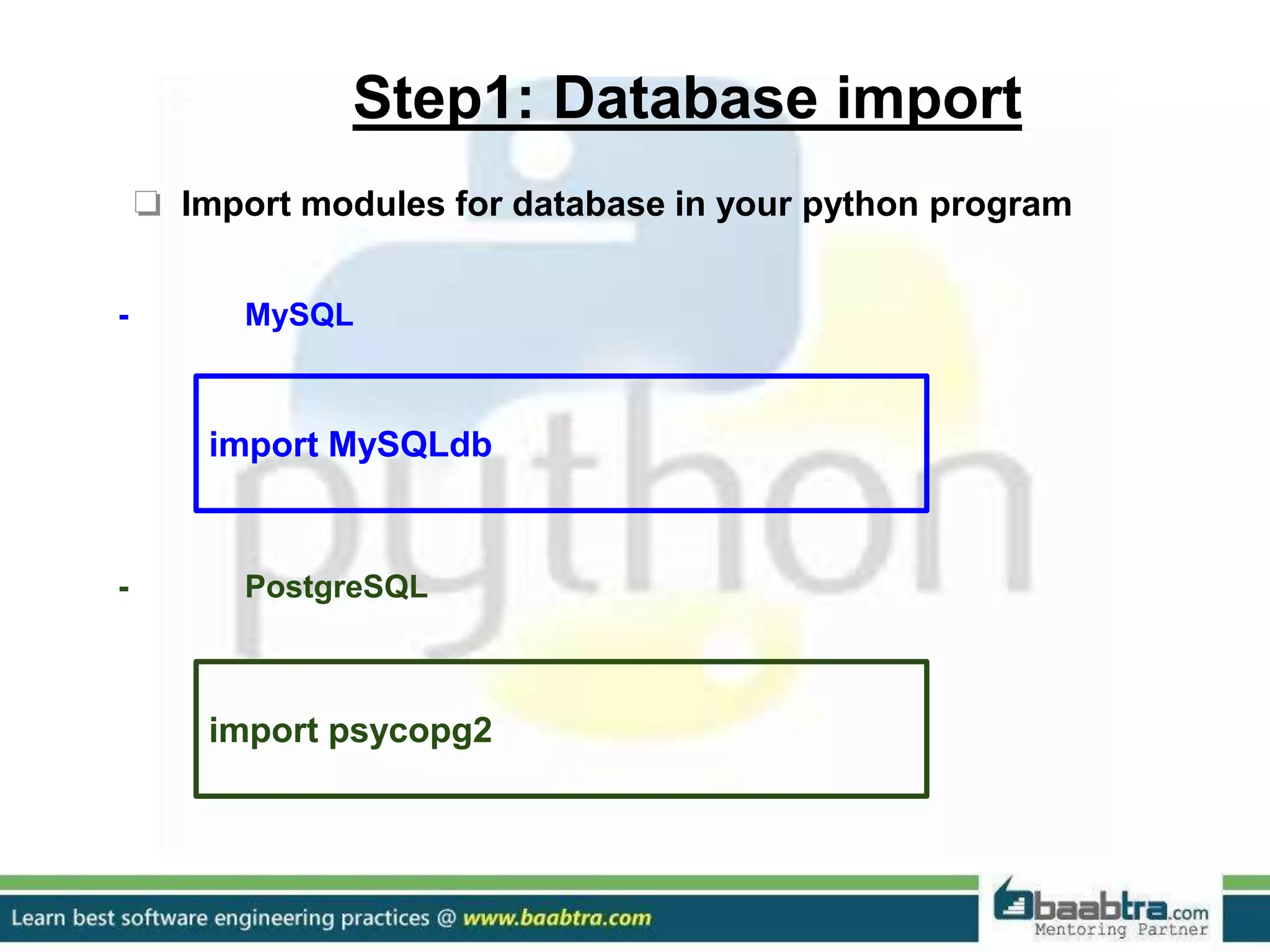
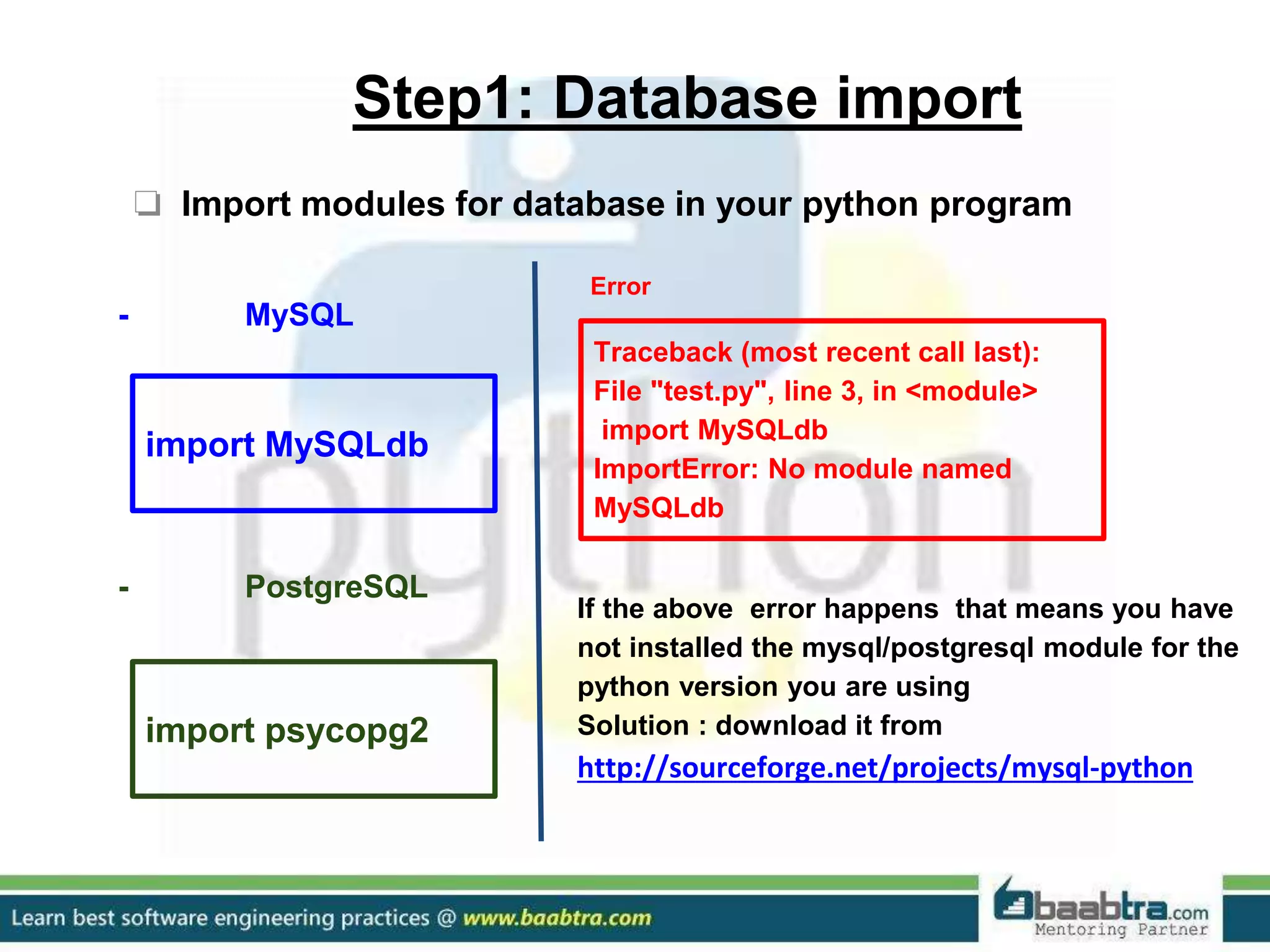
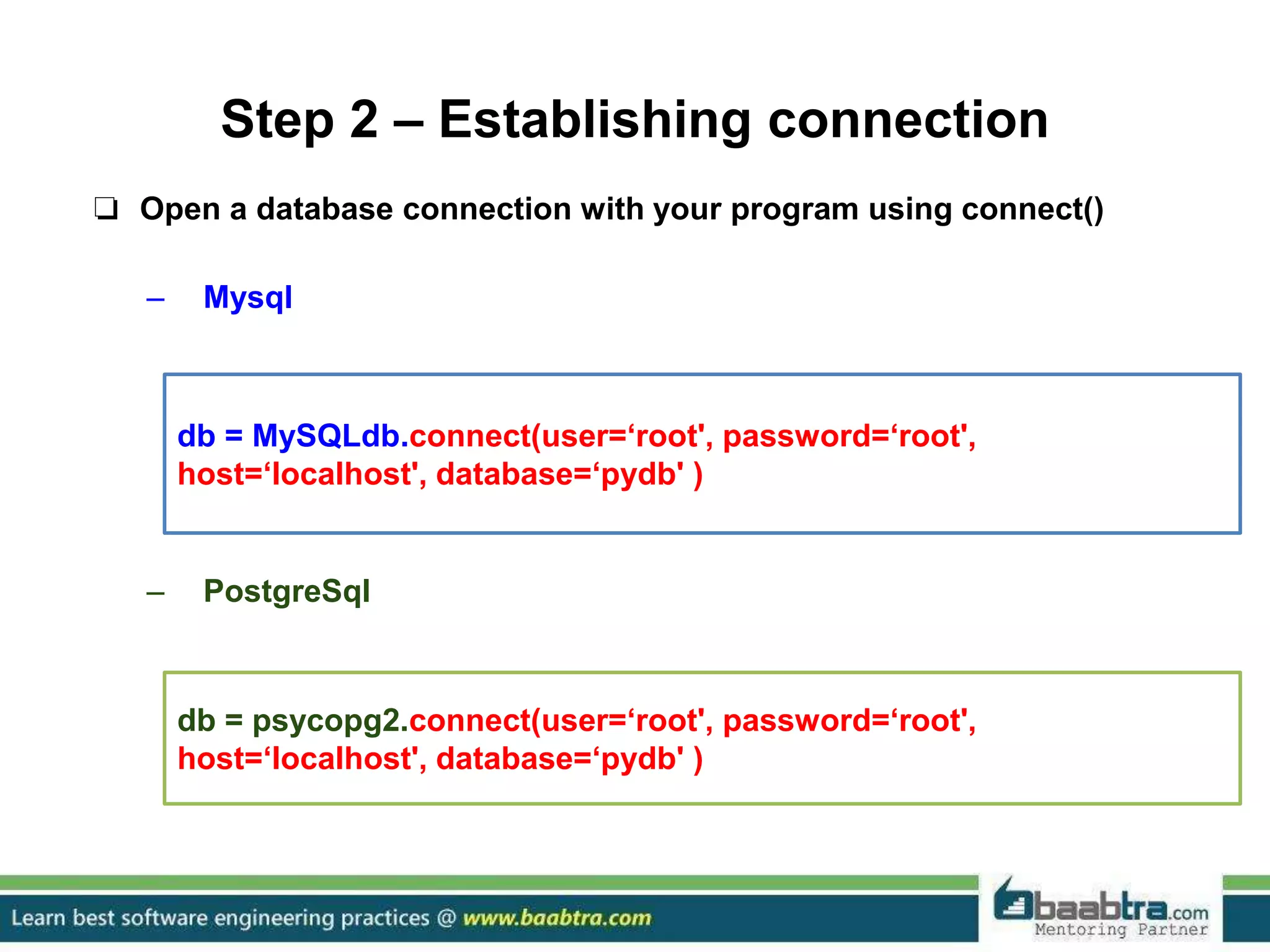
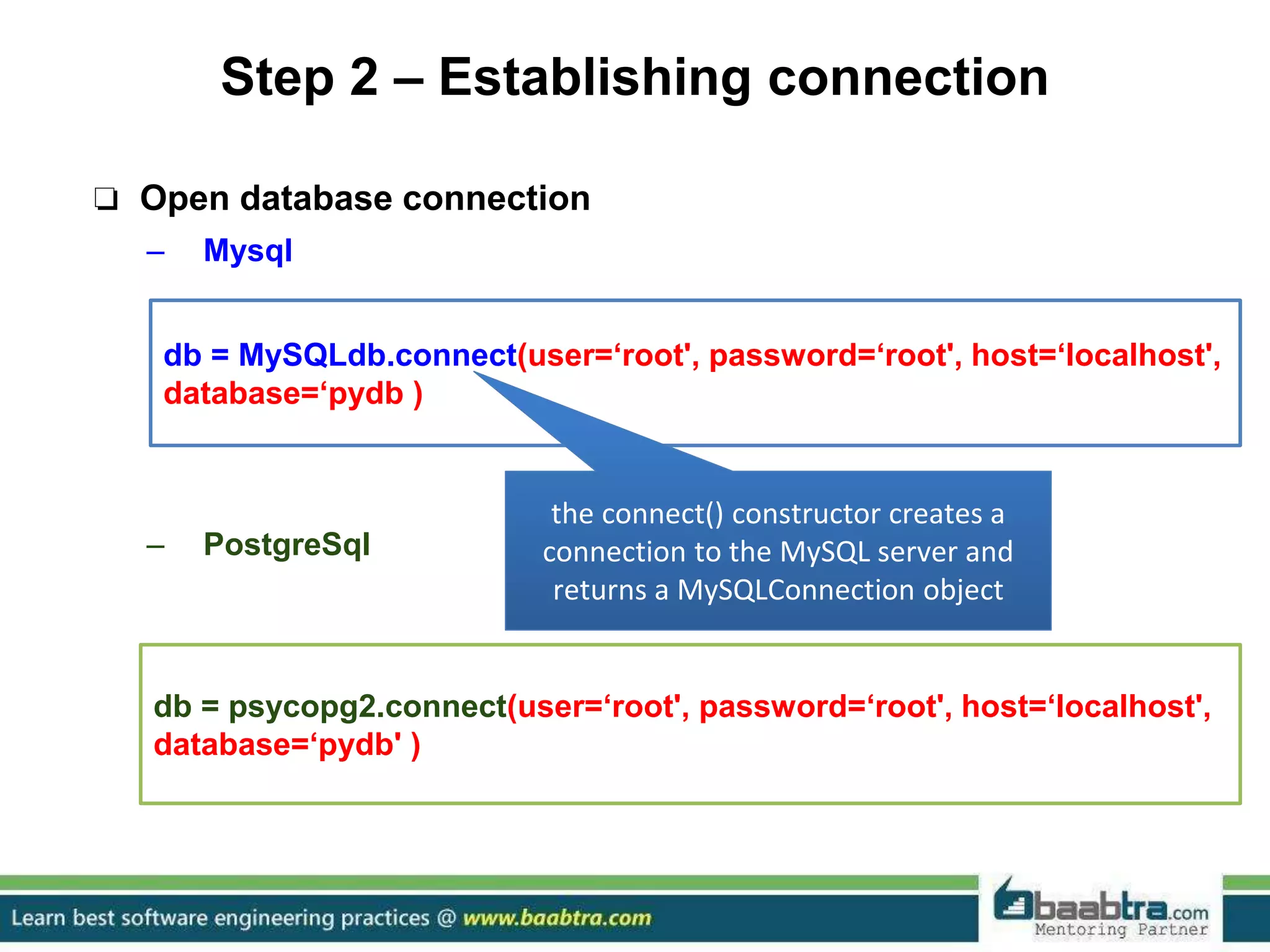
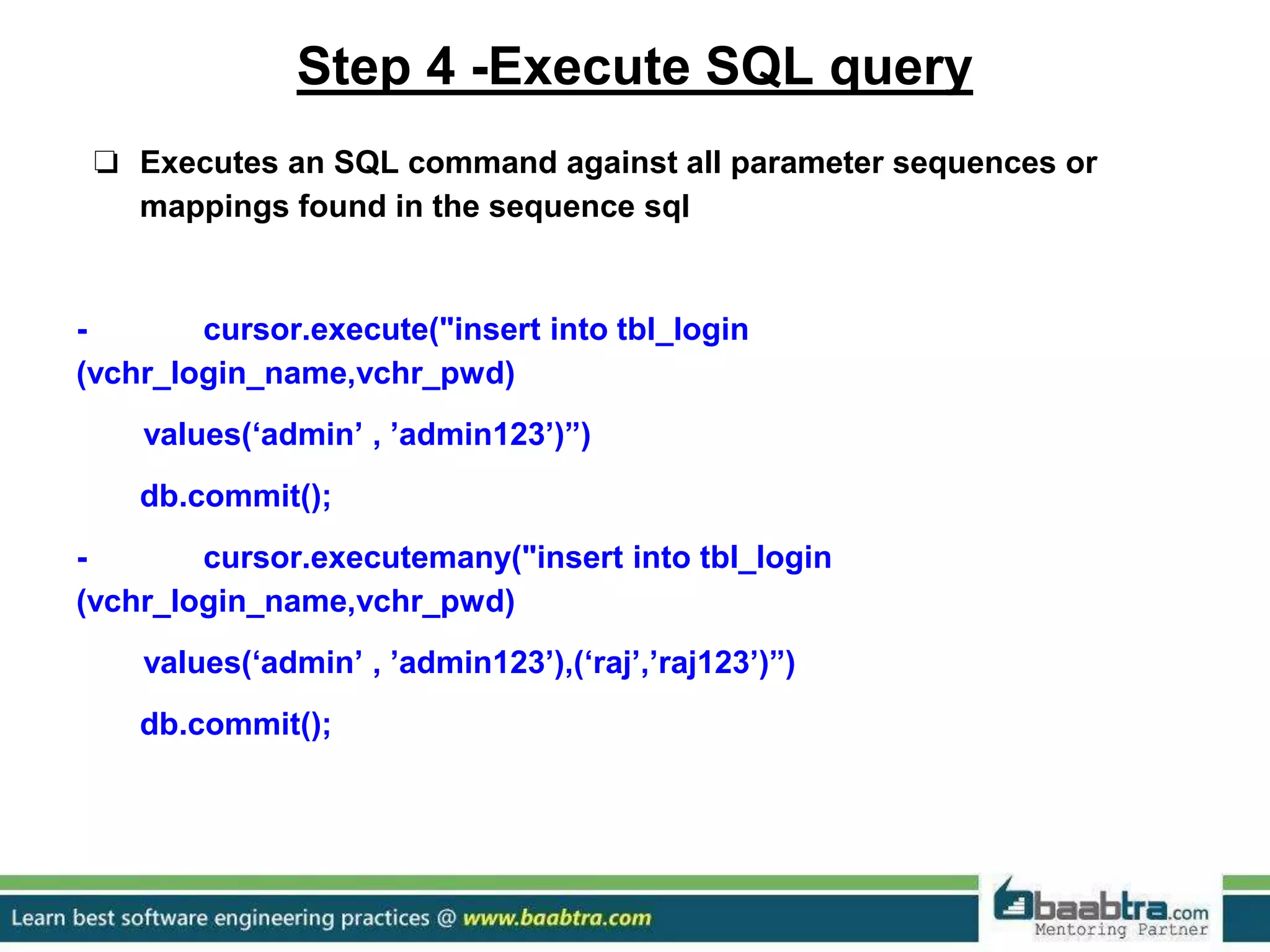
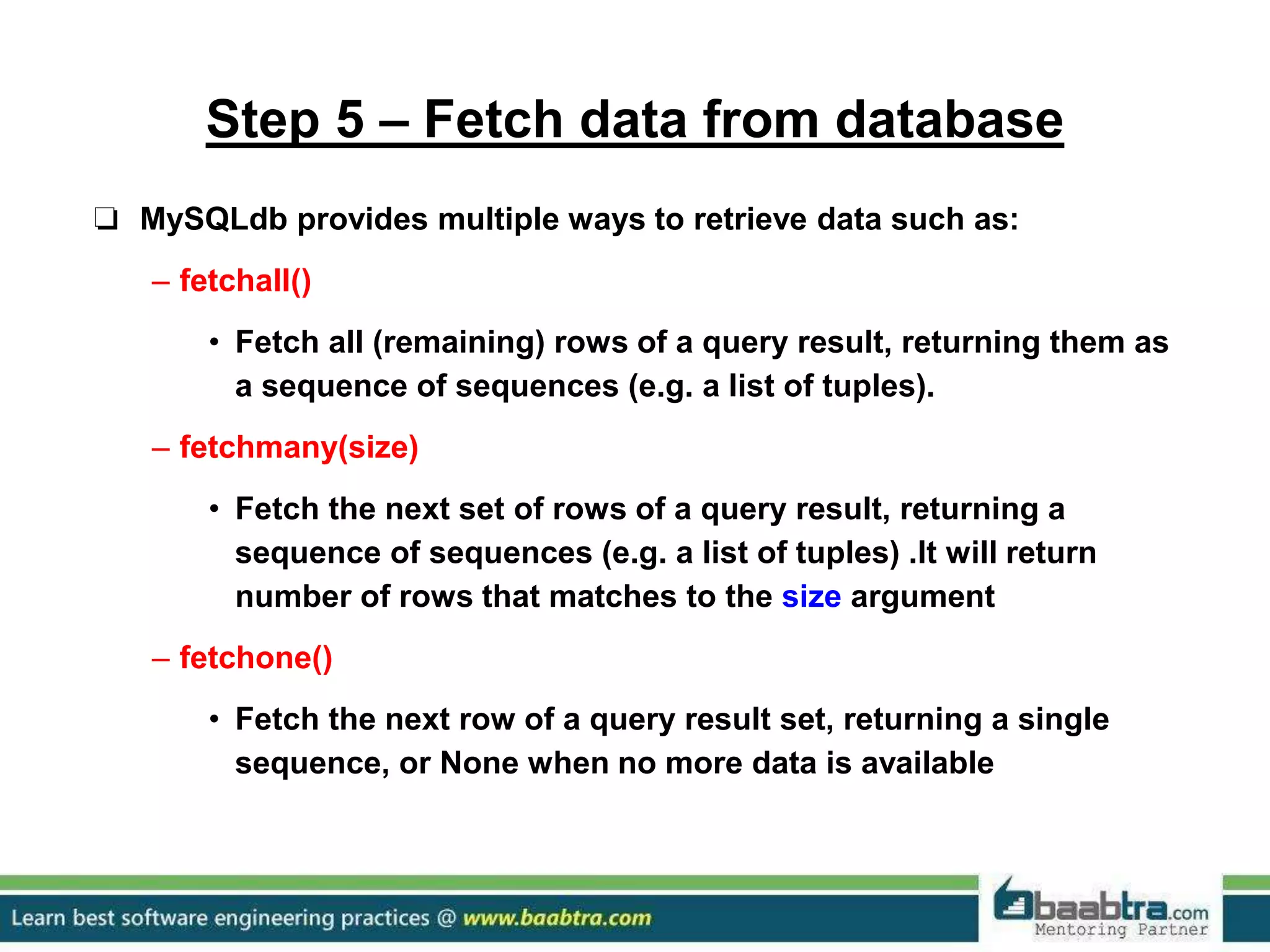
This document discusses connecting Python programs to databases. It covers: 1. Importing database modules for MySQL and PostgreSQL. 2. Establishing a connection to the database using connect() and handling connection errors. 3. Creating a cursor object to execute SQL commands. 4. Executing SQL queries like SELECT and INSERT using the cursor's execute() method. 5. Fetching data from the database using cursor methods like fetchall(), fetchmany(), and fetchone().




![Example import MySQLdb def insertEmp(str_name,str_pwd): db=MySQLdb.connect( 'localhost' ,' root' , ' ' , 'pydb' ) cursor=db.cursor() cursor.execute("insert into tbl_login (vchr_login_name,vchr_pwd) values(%s,%s);",(str_name,str_pwd)) db.commit() cursor.execute("select * from tbl_login") result=cursor.fetchall() db.close() print "loginidtnametpassword" for row in result: login=row[0] name=row[1] password=row[2] print "%dt%st%s"%(login,name,password) str_name=raw_input("enter user name : ") str_pwd=raw_input("Enter password : ") insertEmp(str_name,str_pwd)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databaseconnectivityinpython-150220233937-conversion-gate02/75/Database-connectivity-in-python-12-2048.jpg)

