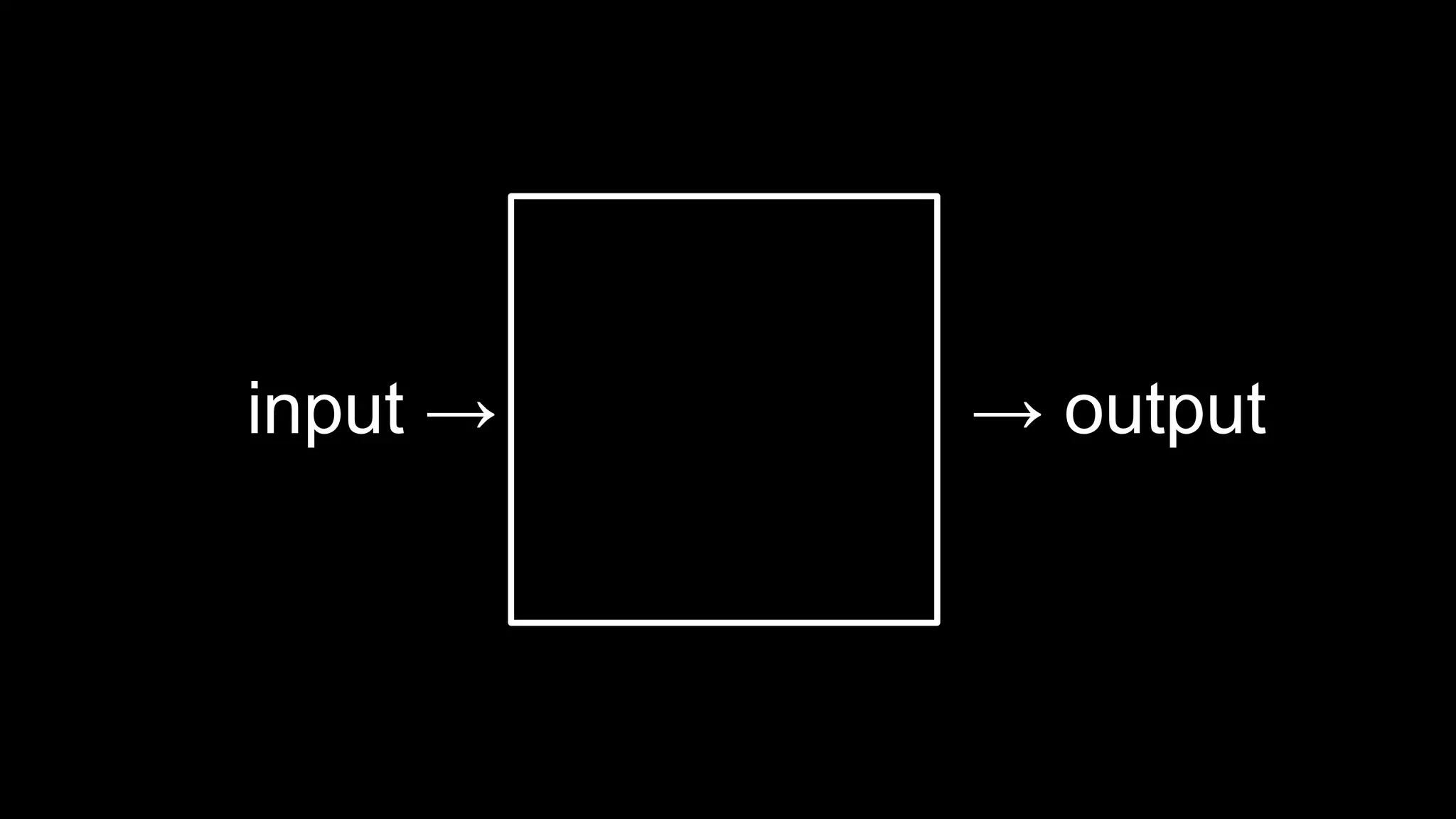
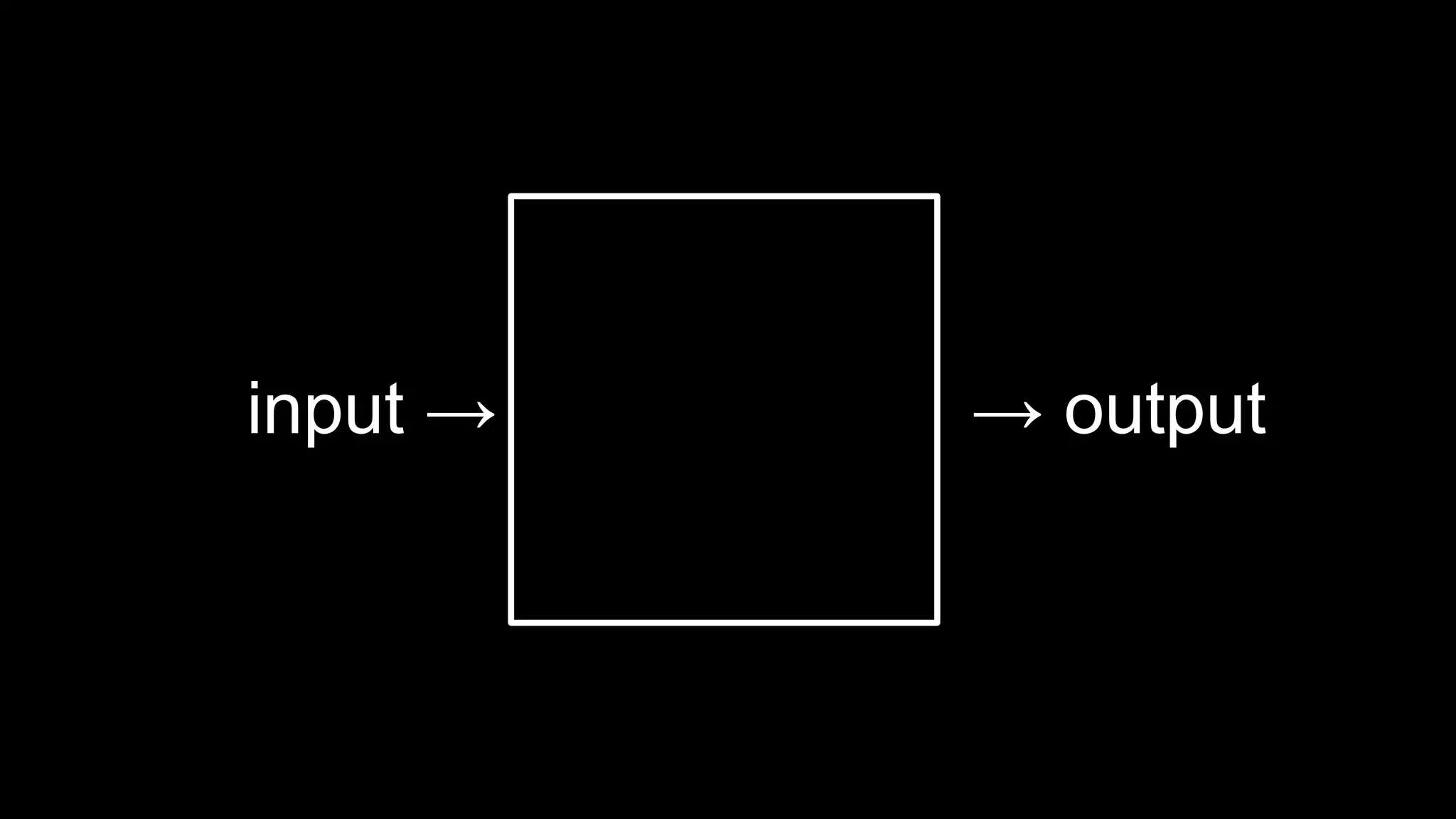
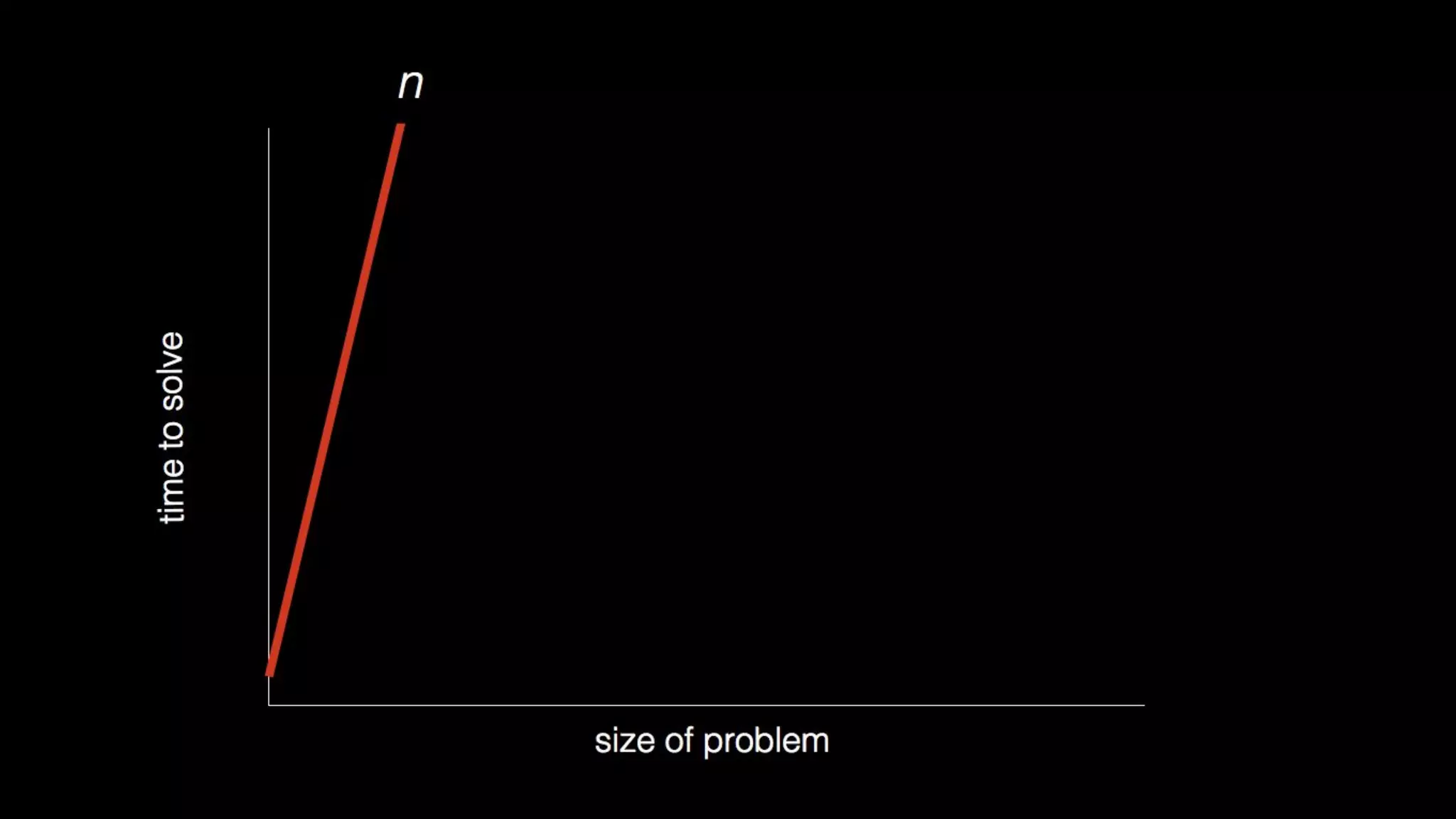
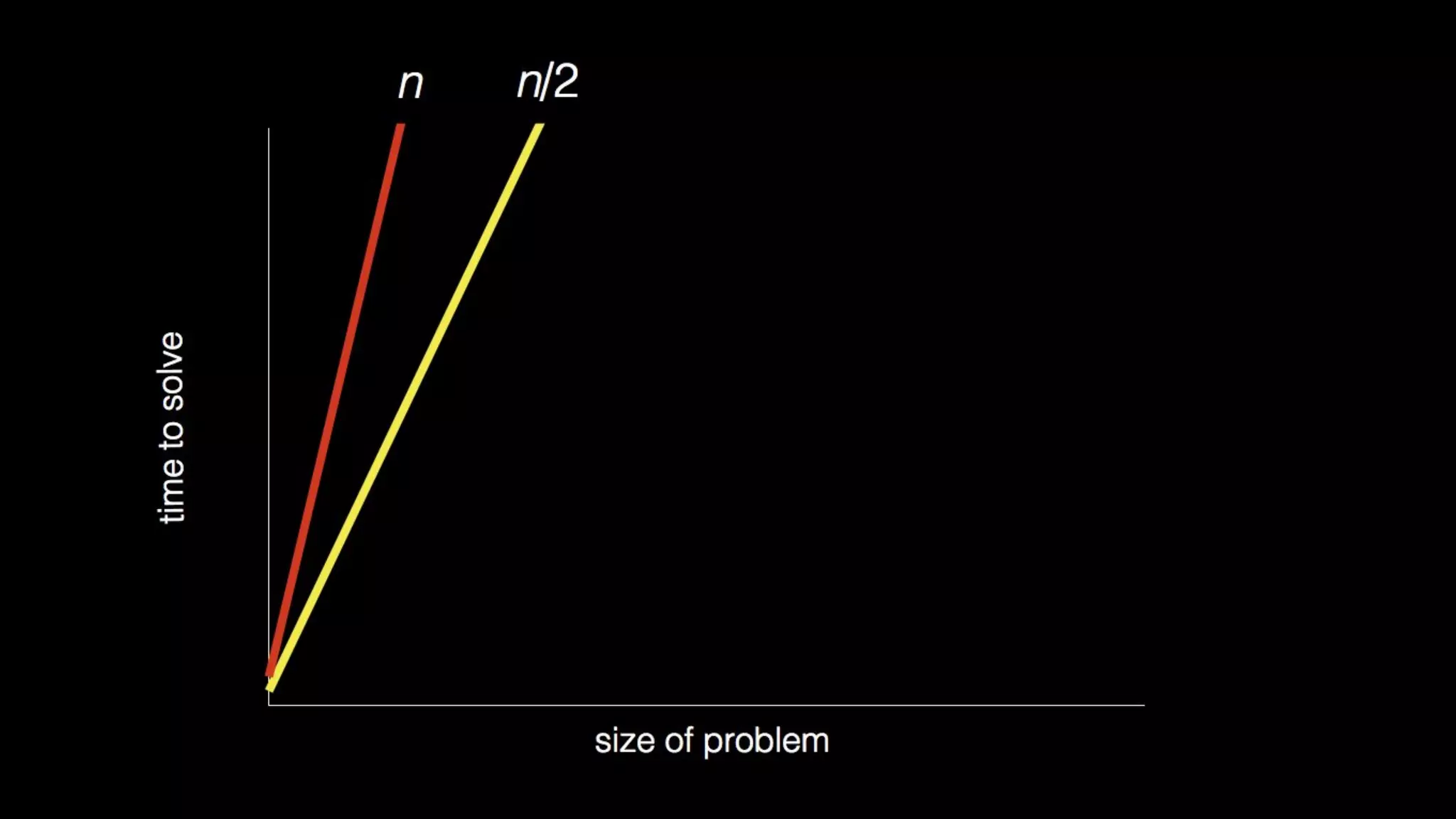
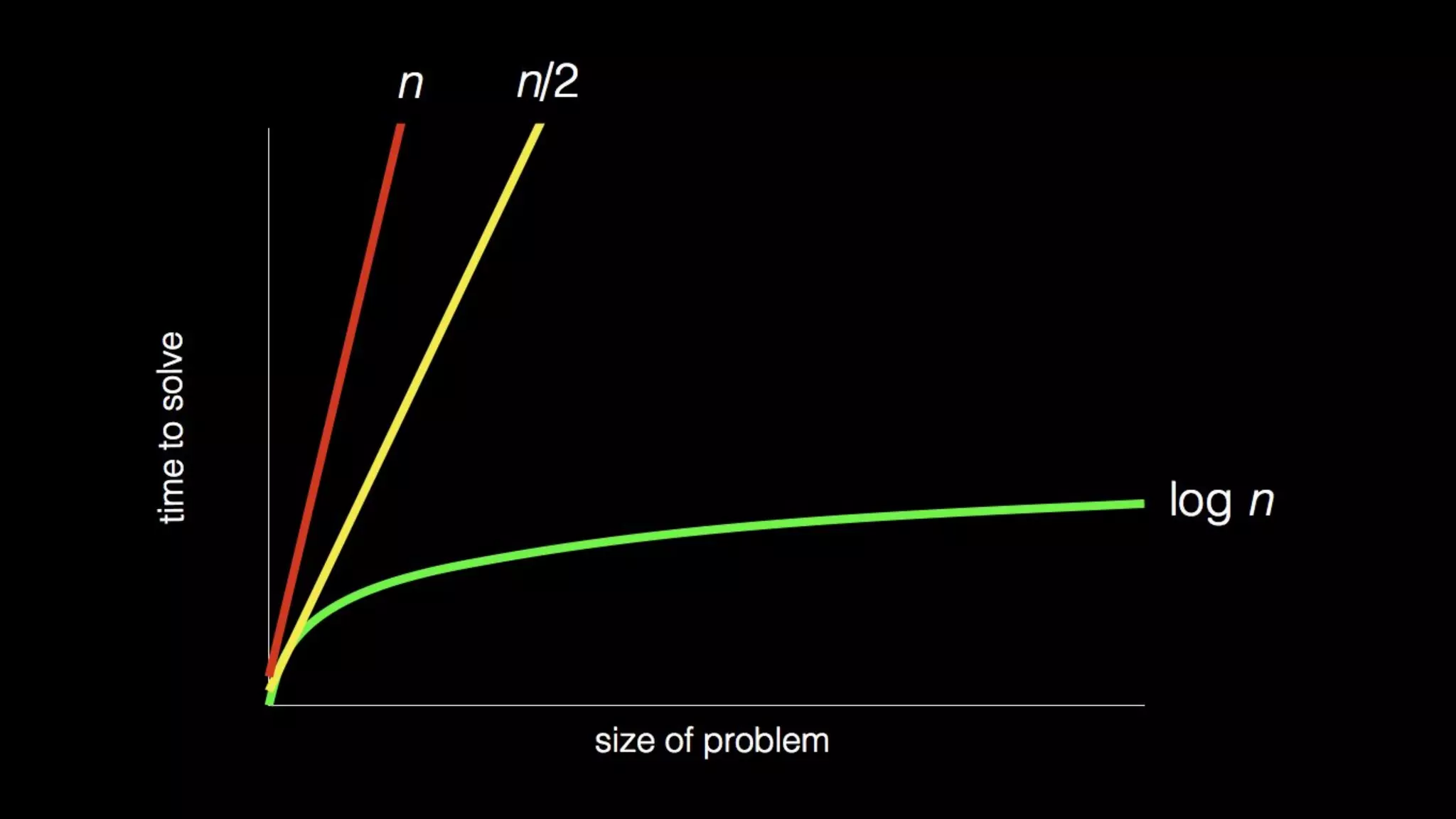
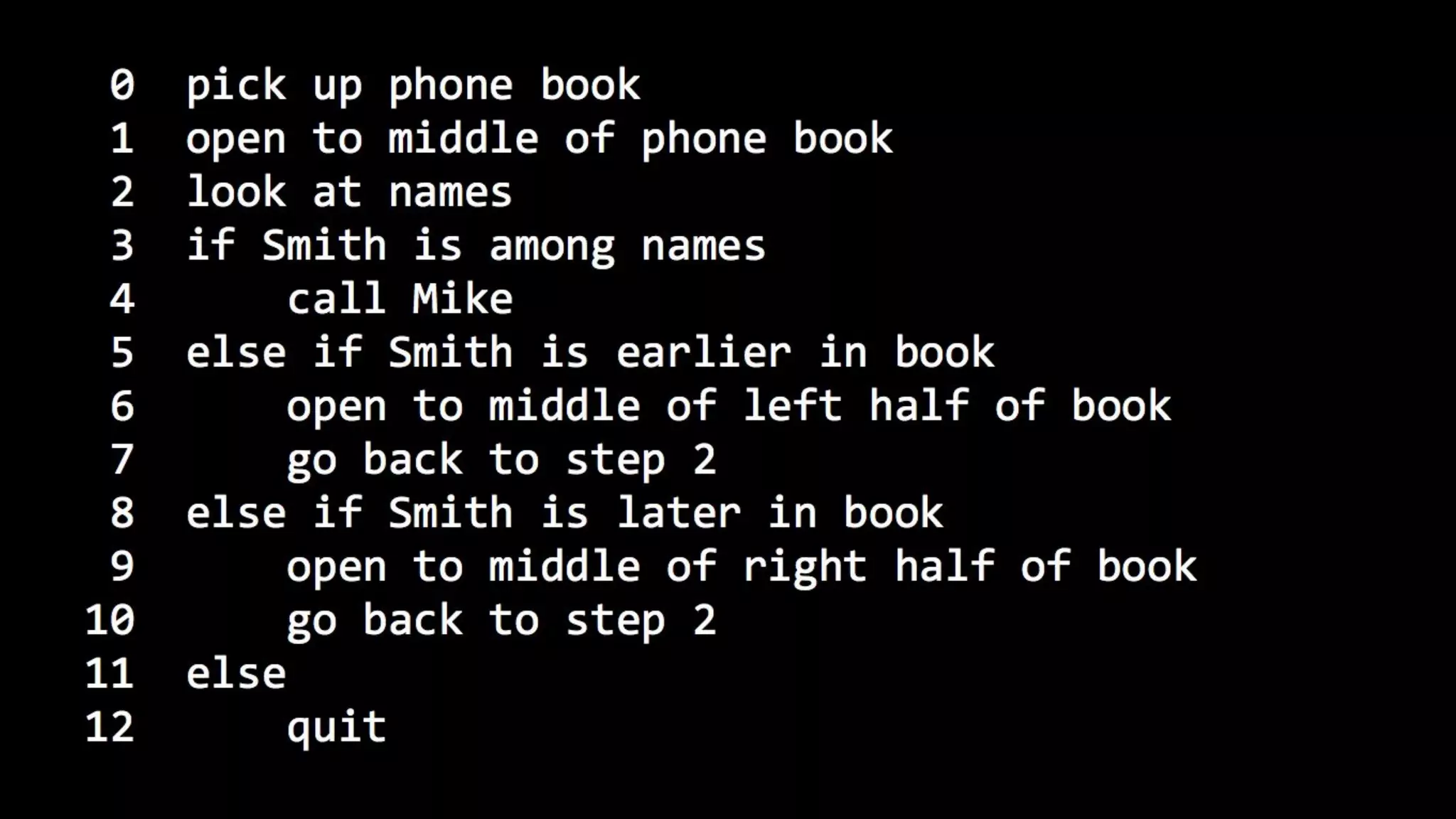
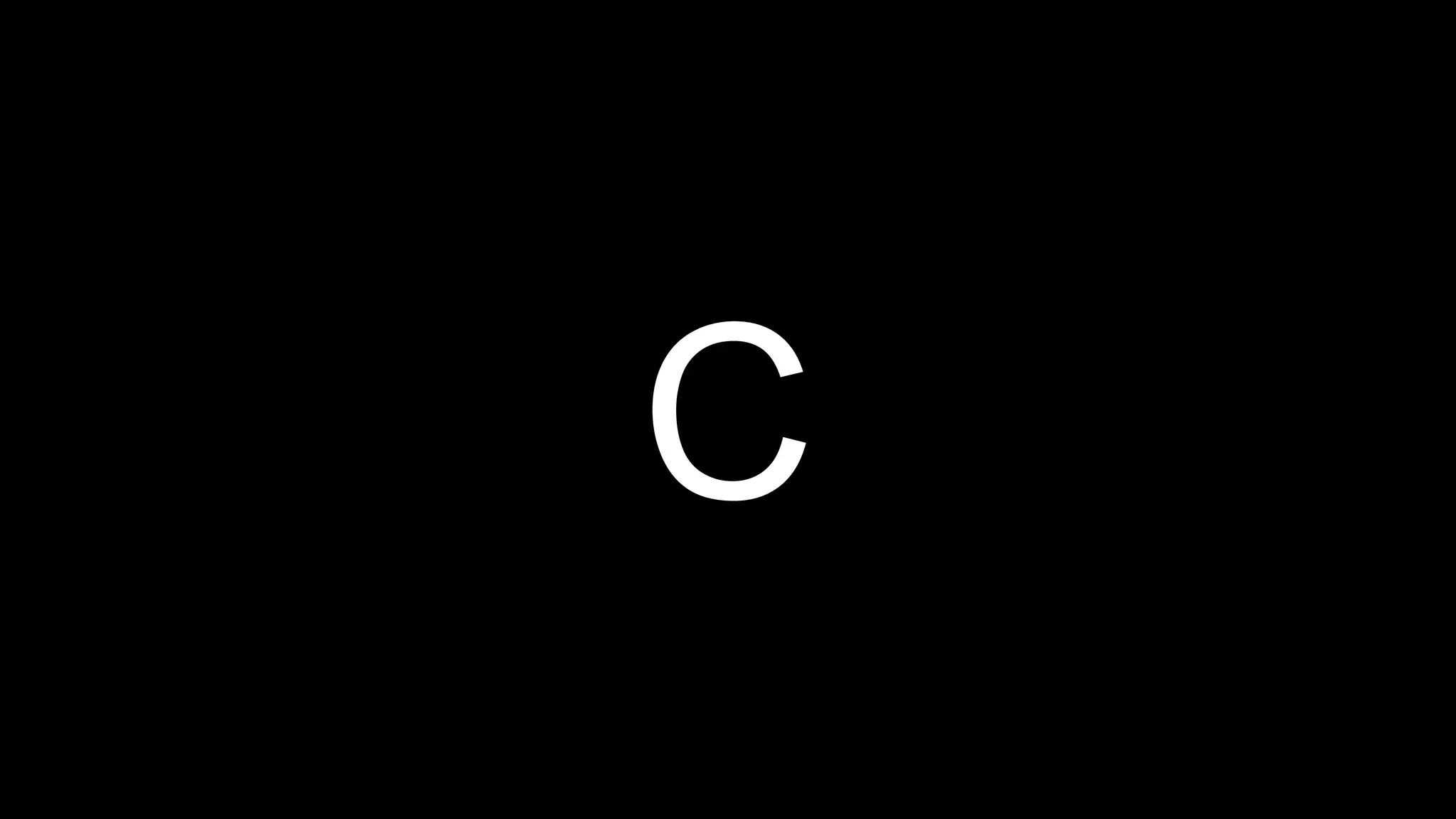
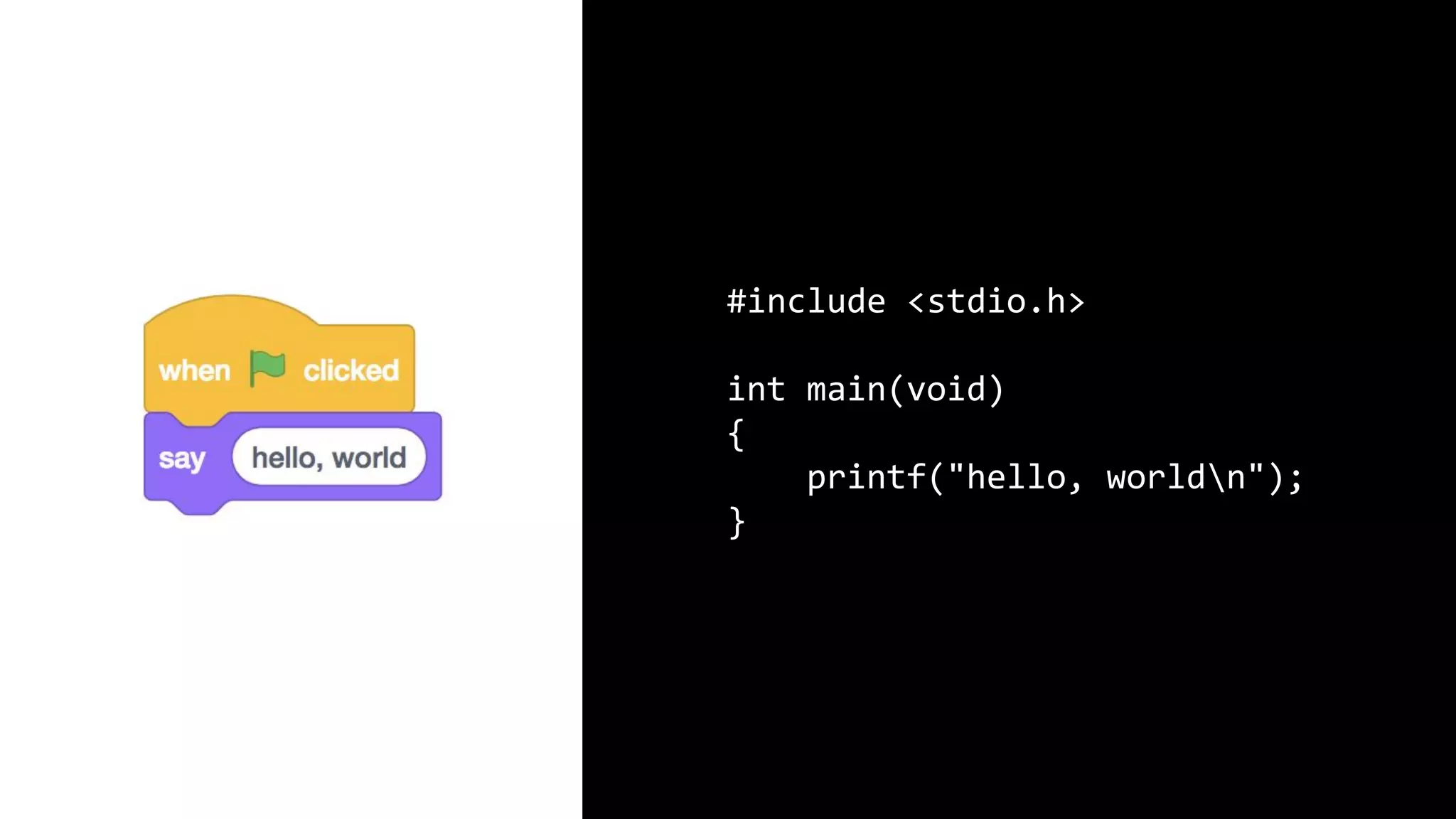
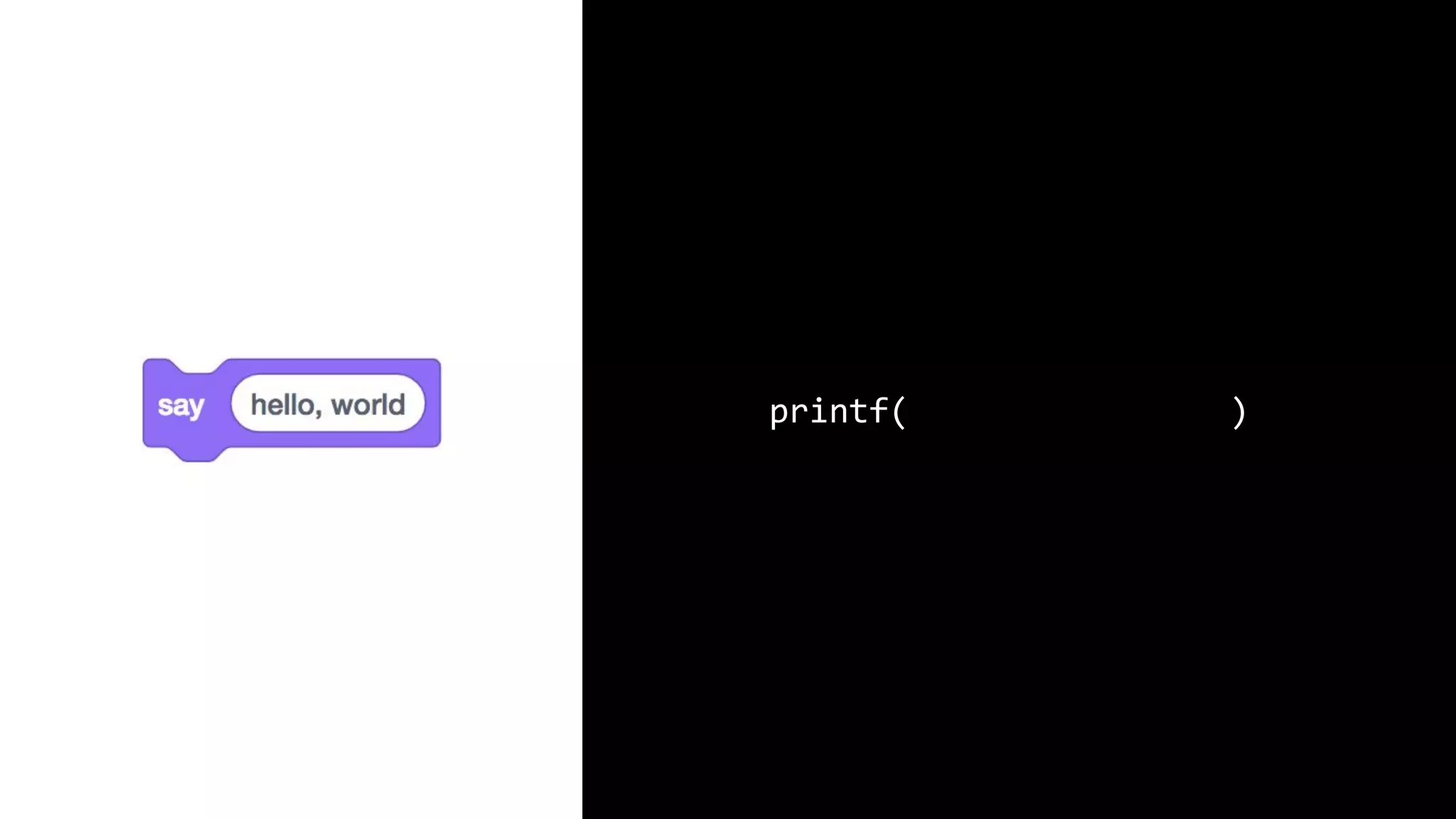
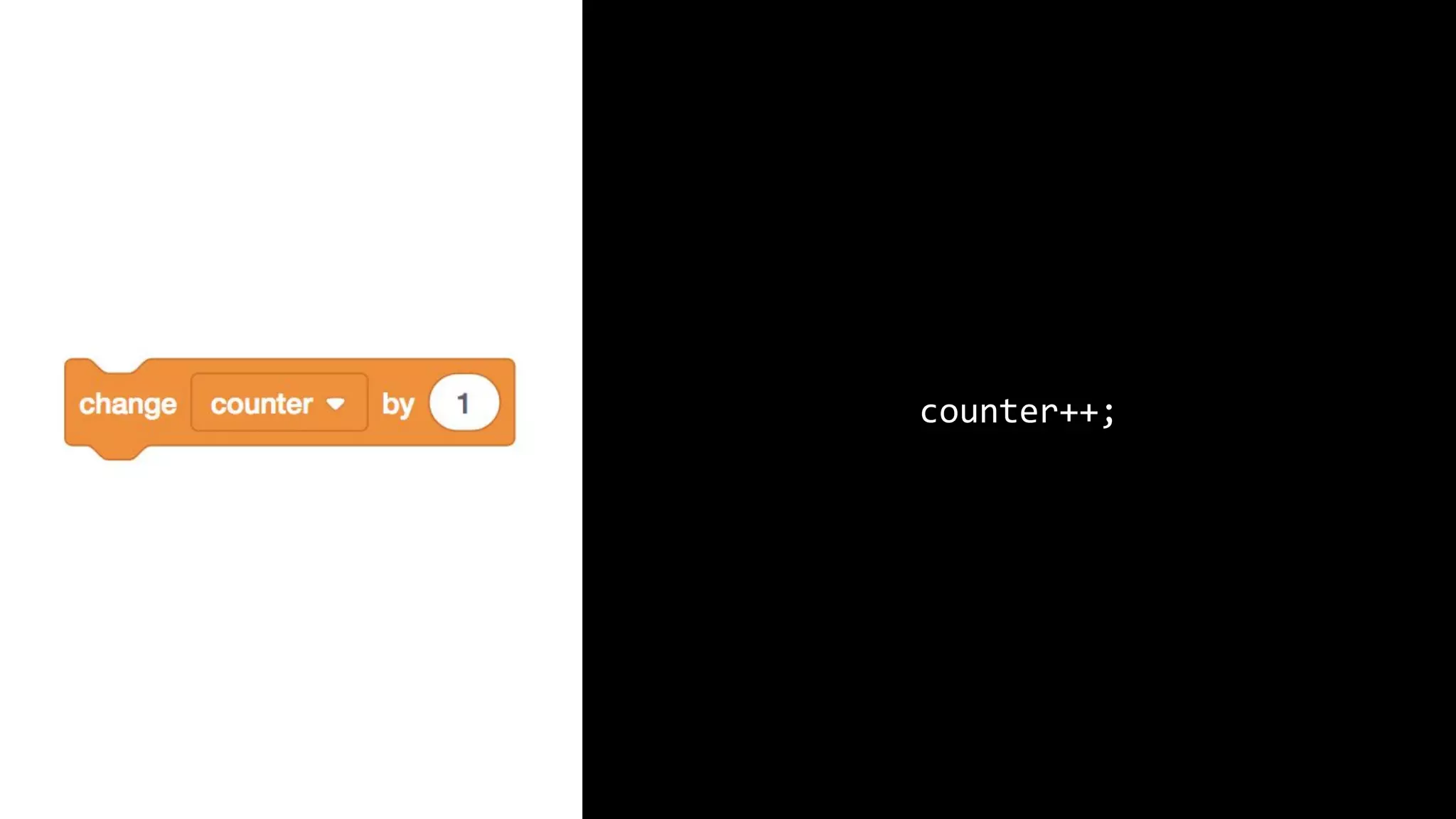
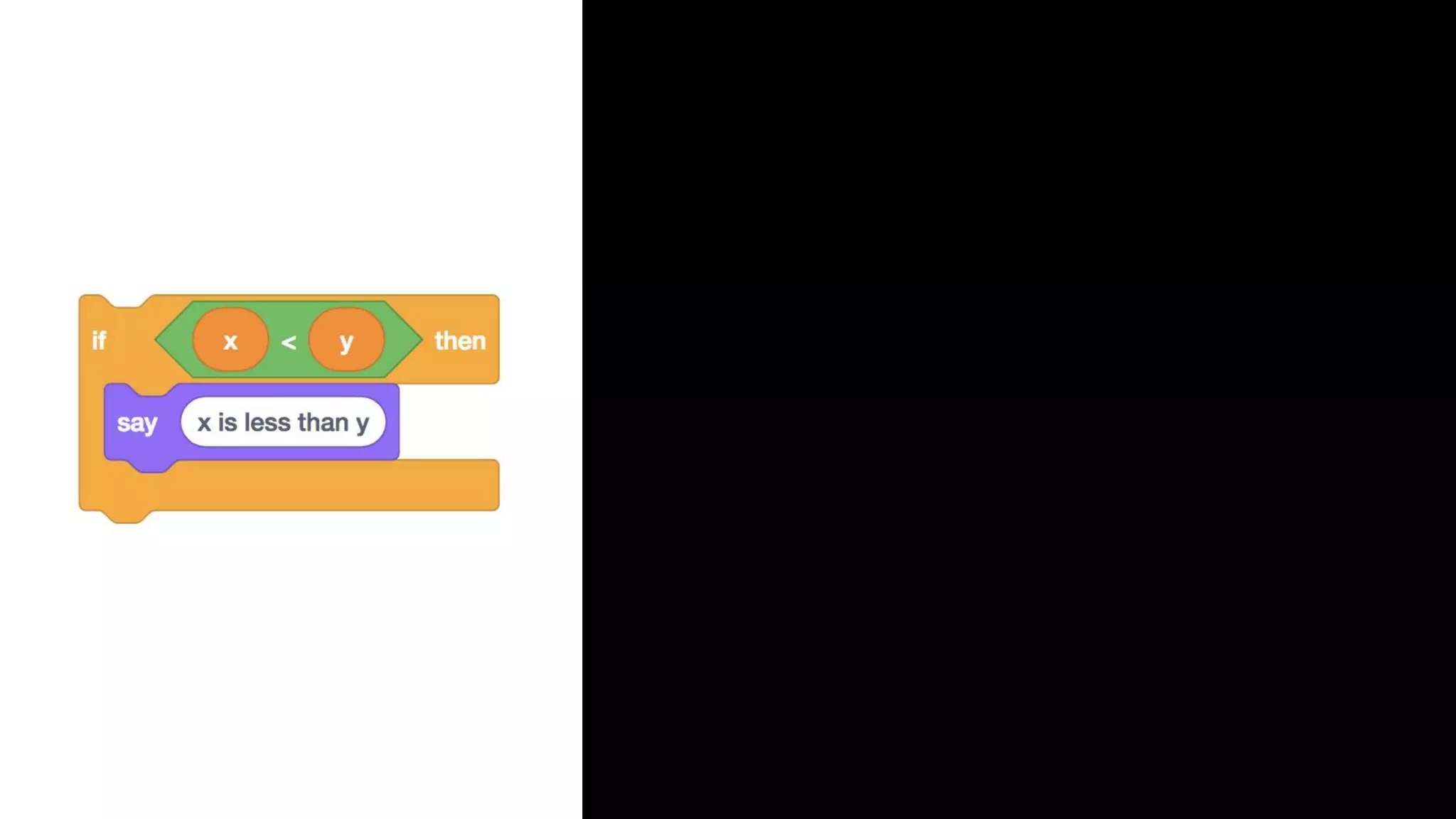
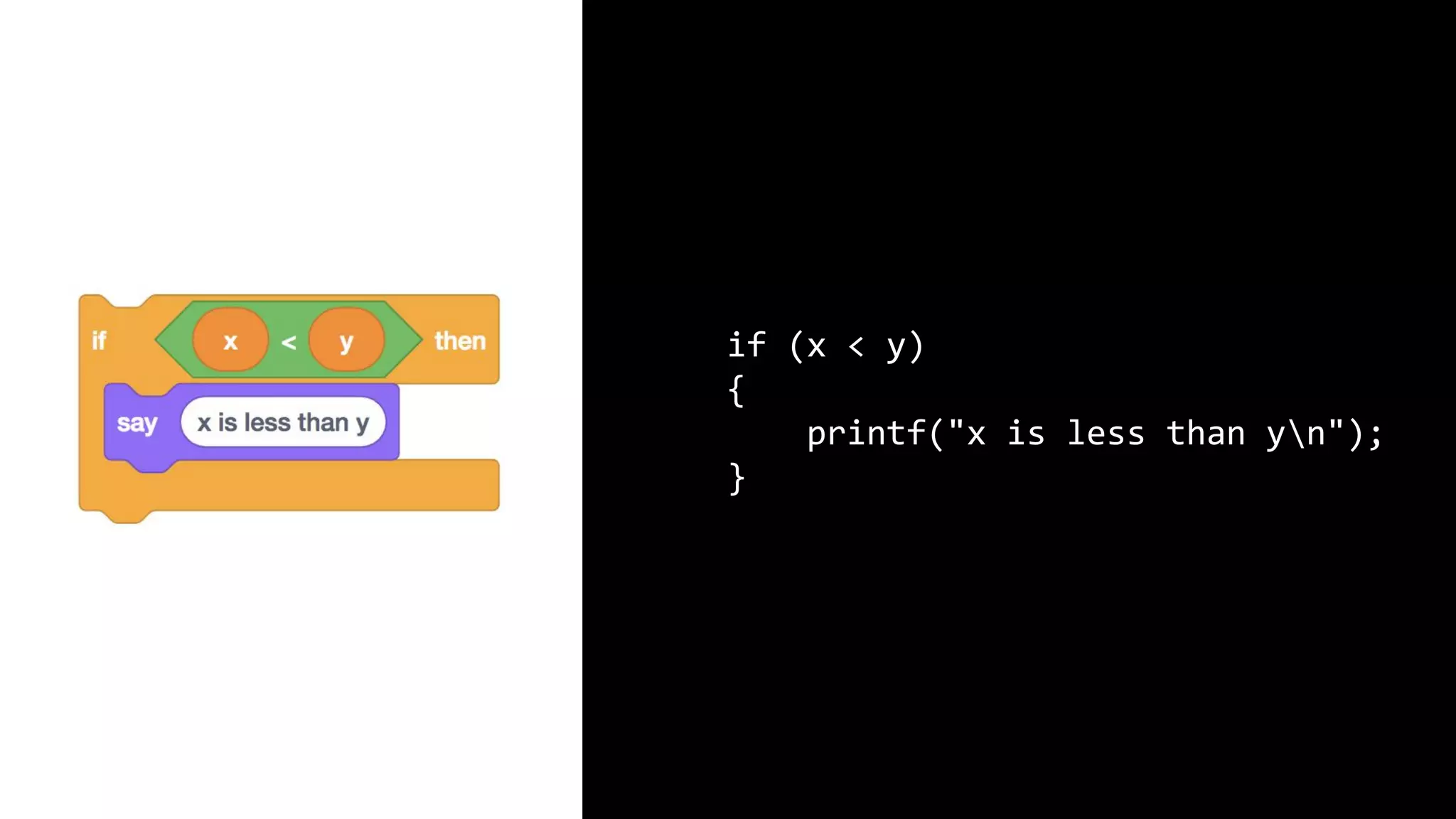
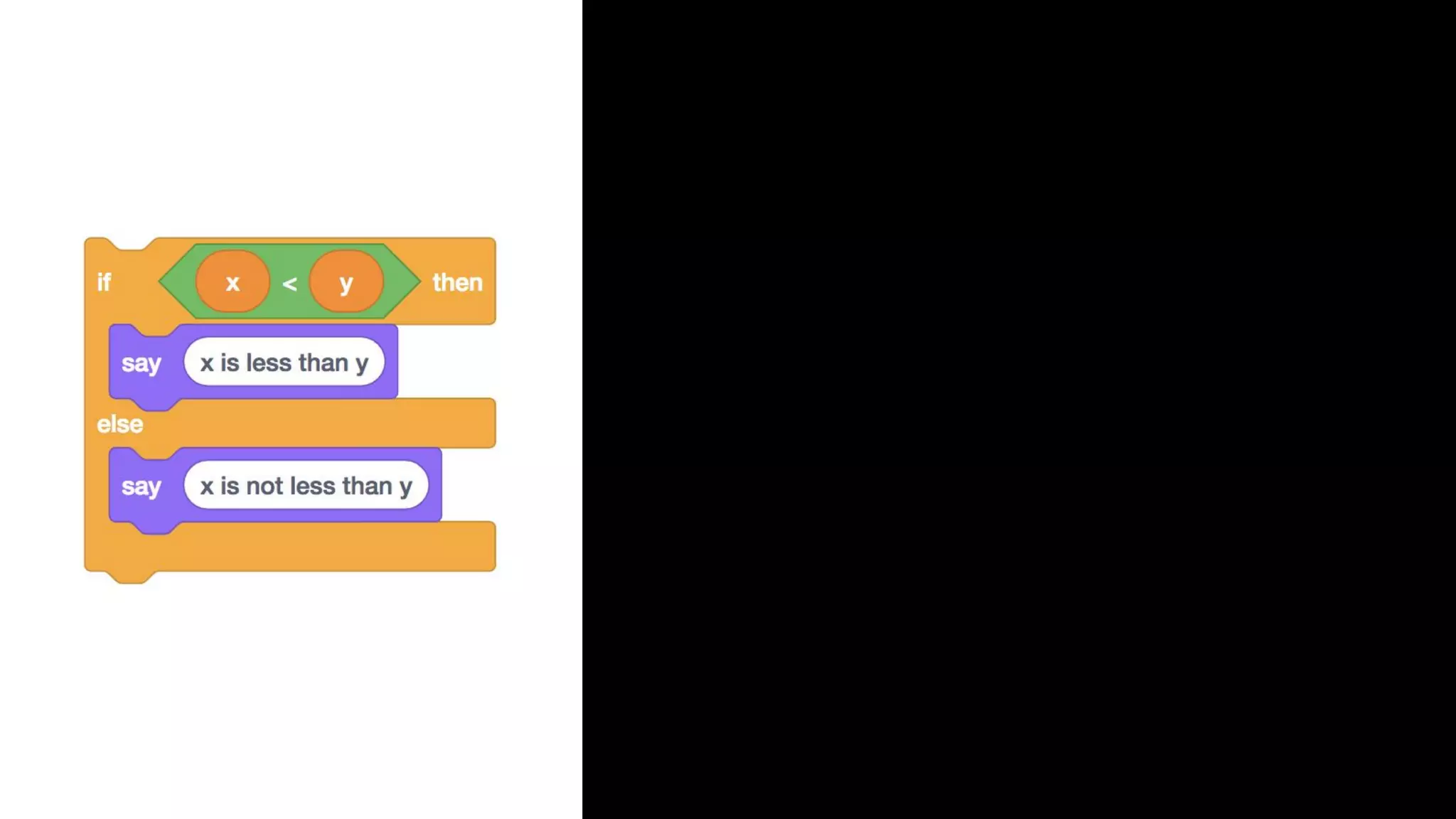
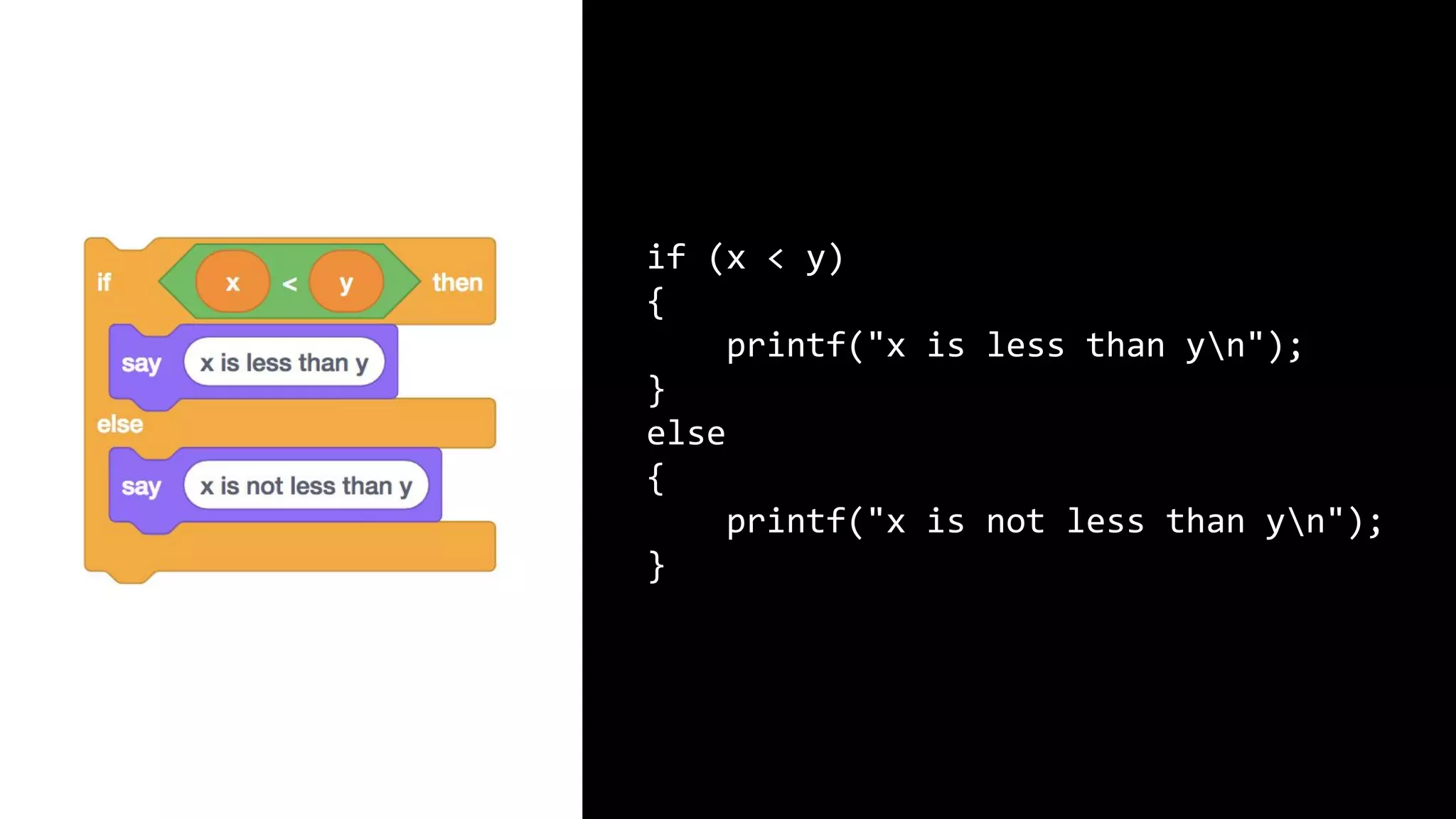
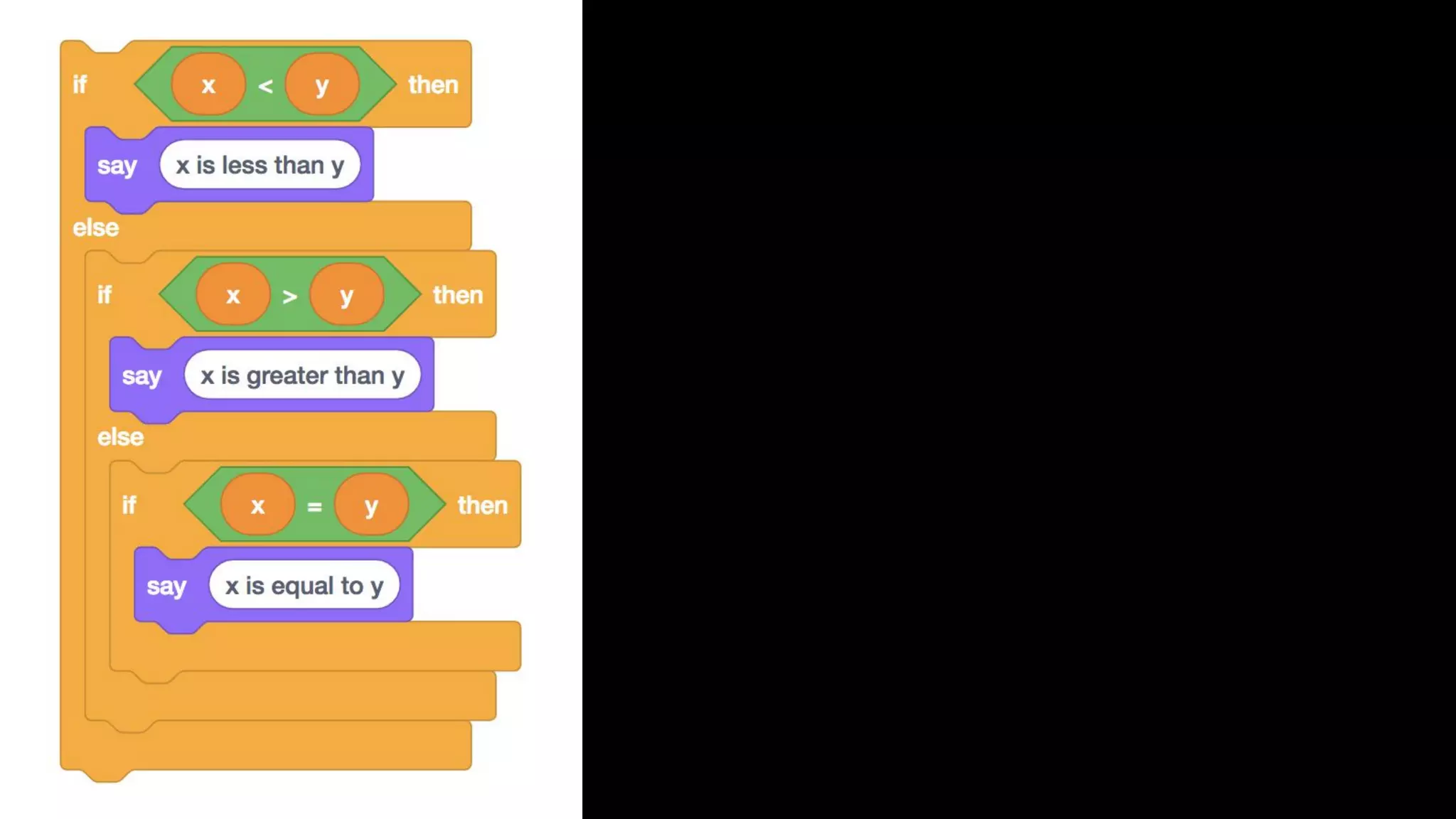
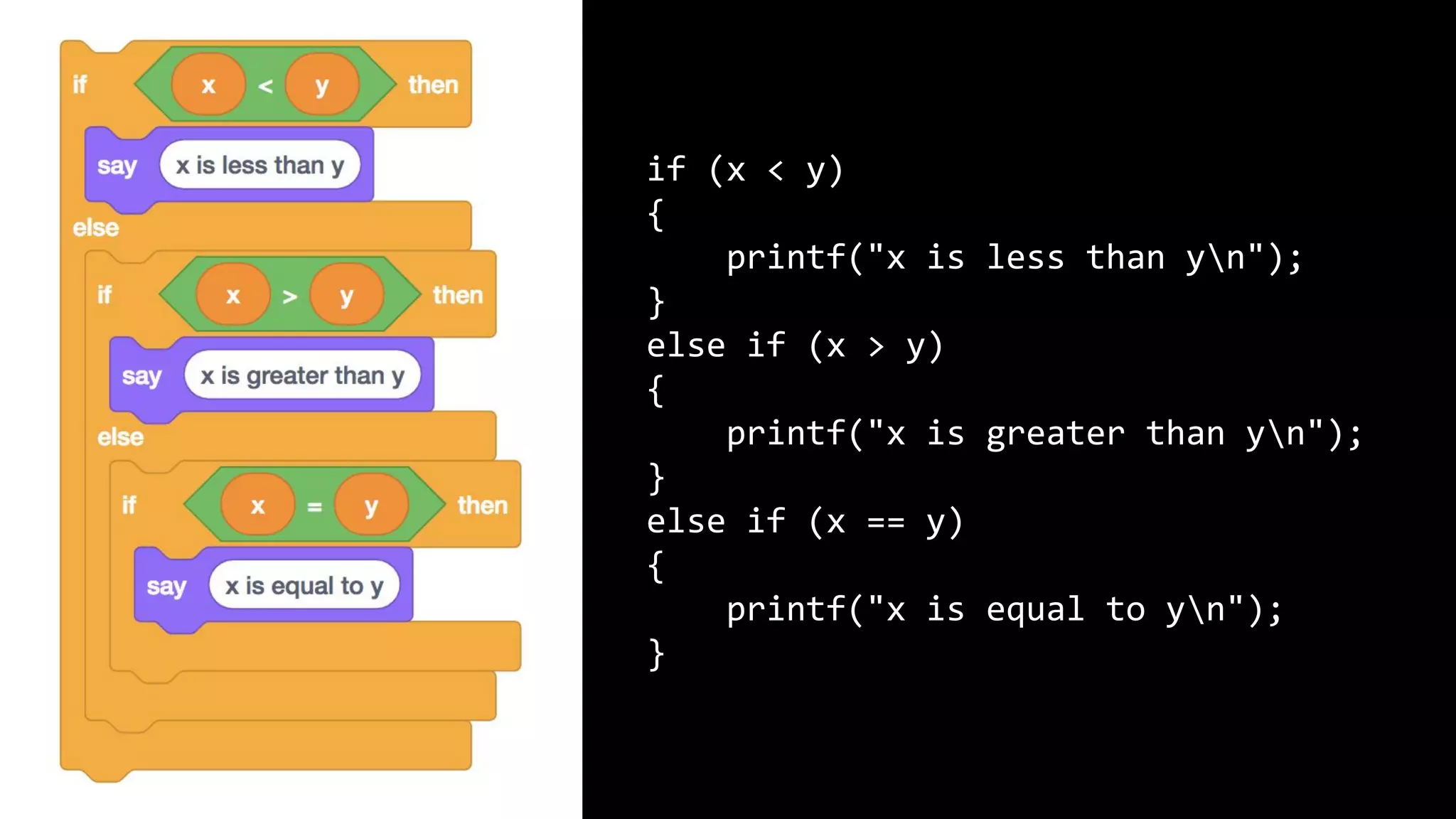
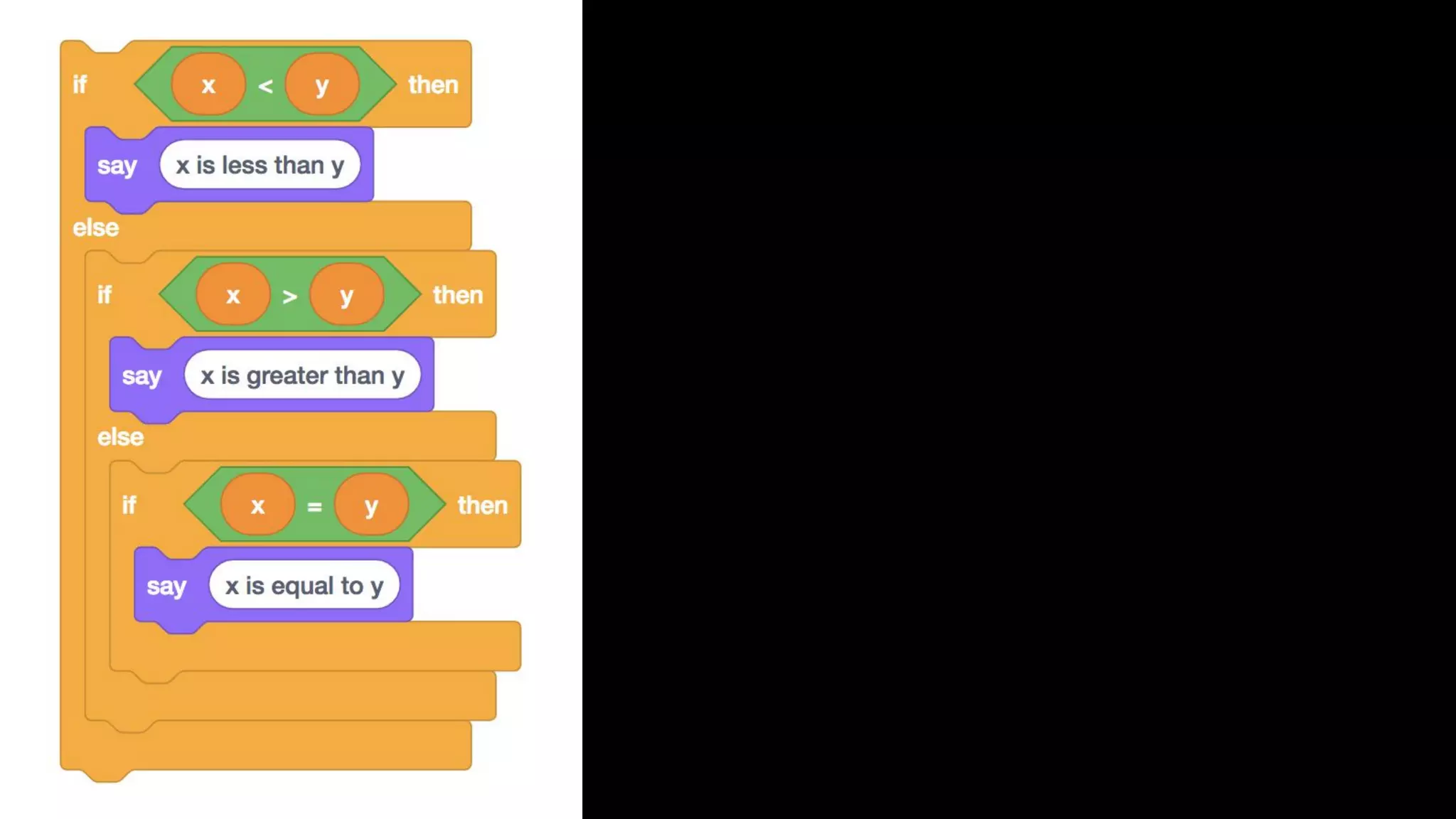
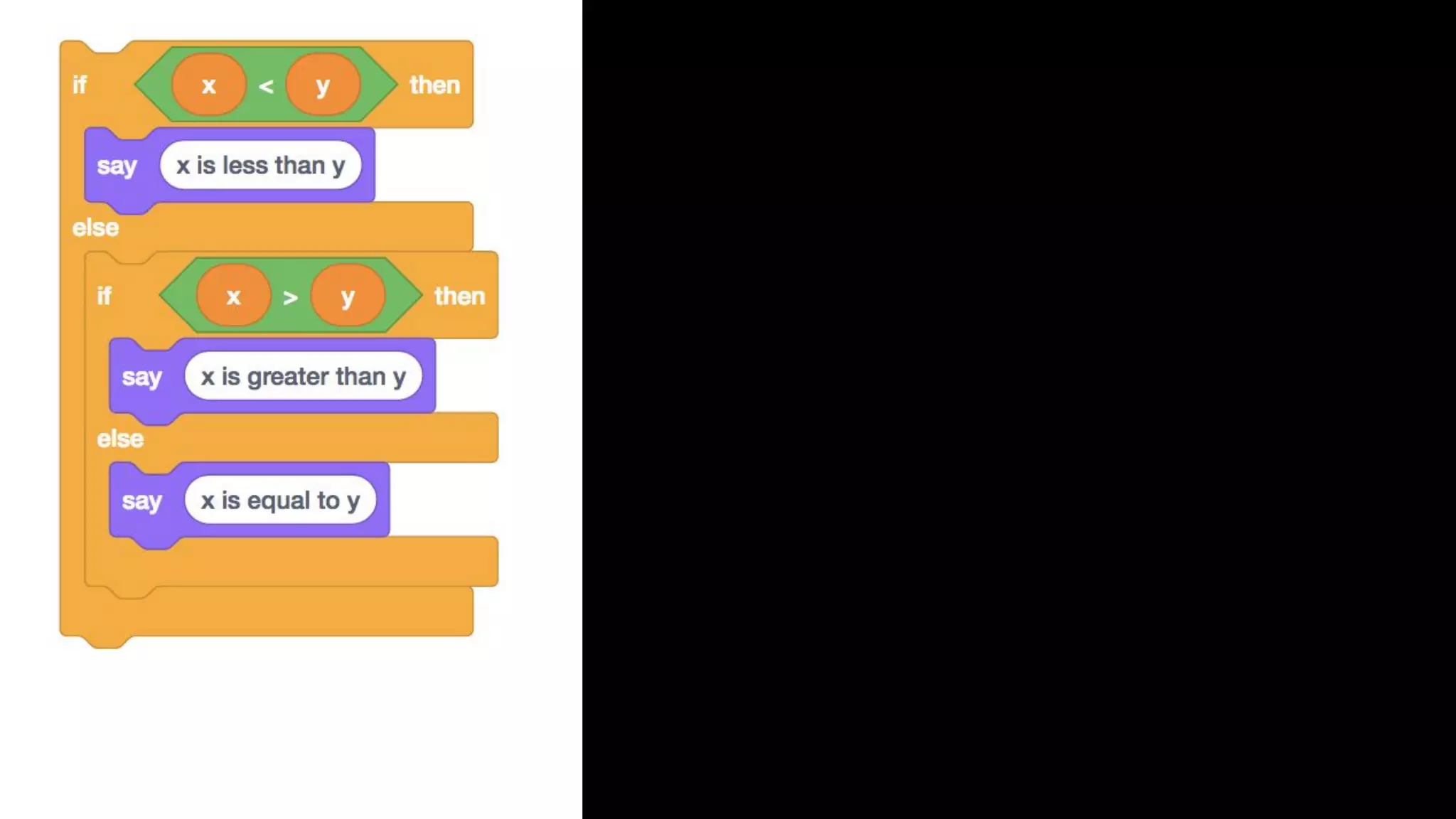
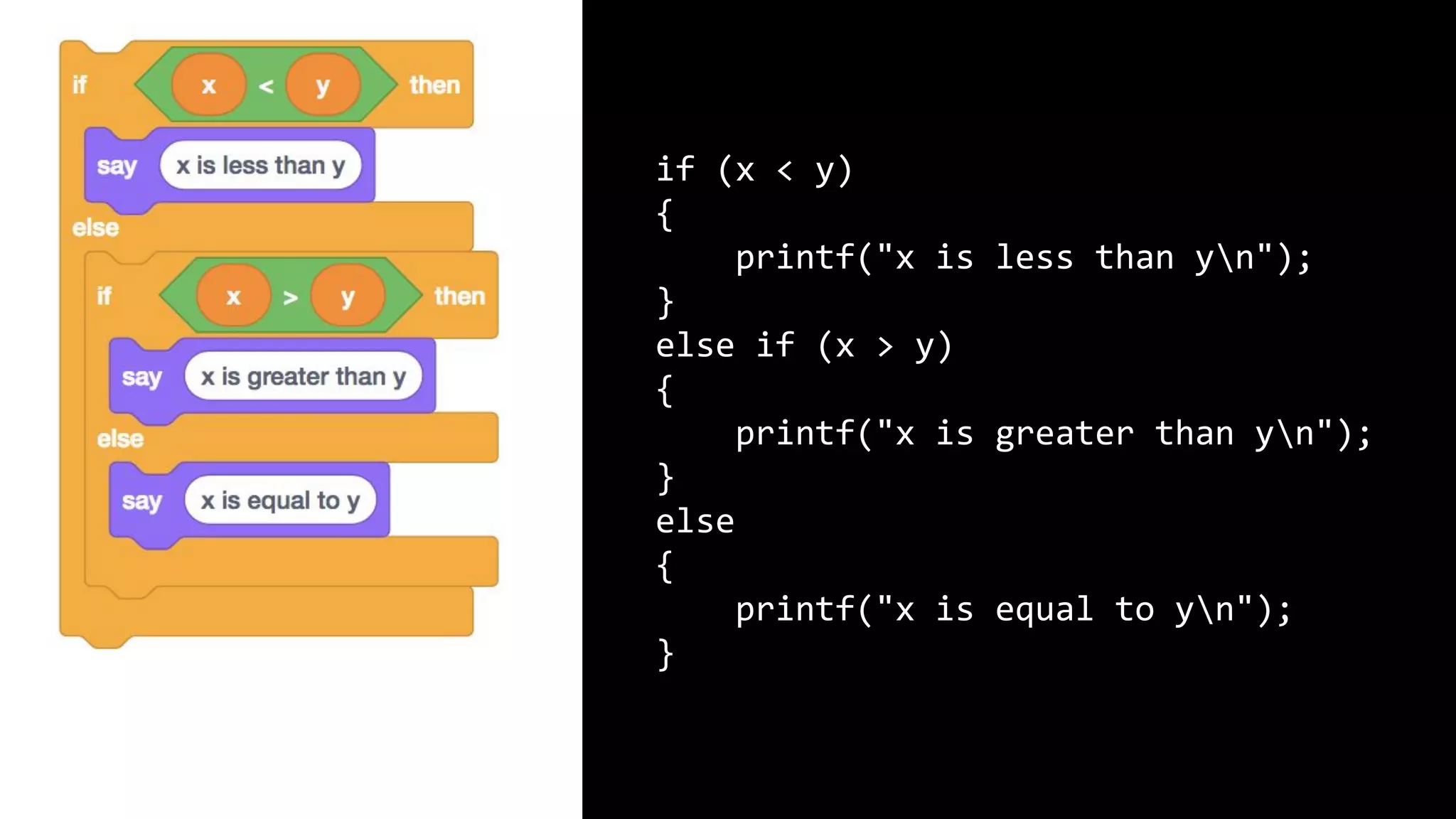
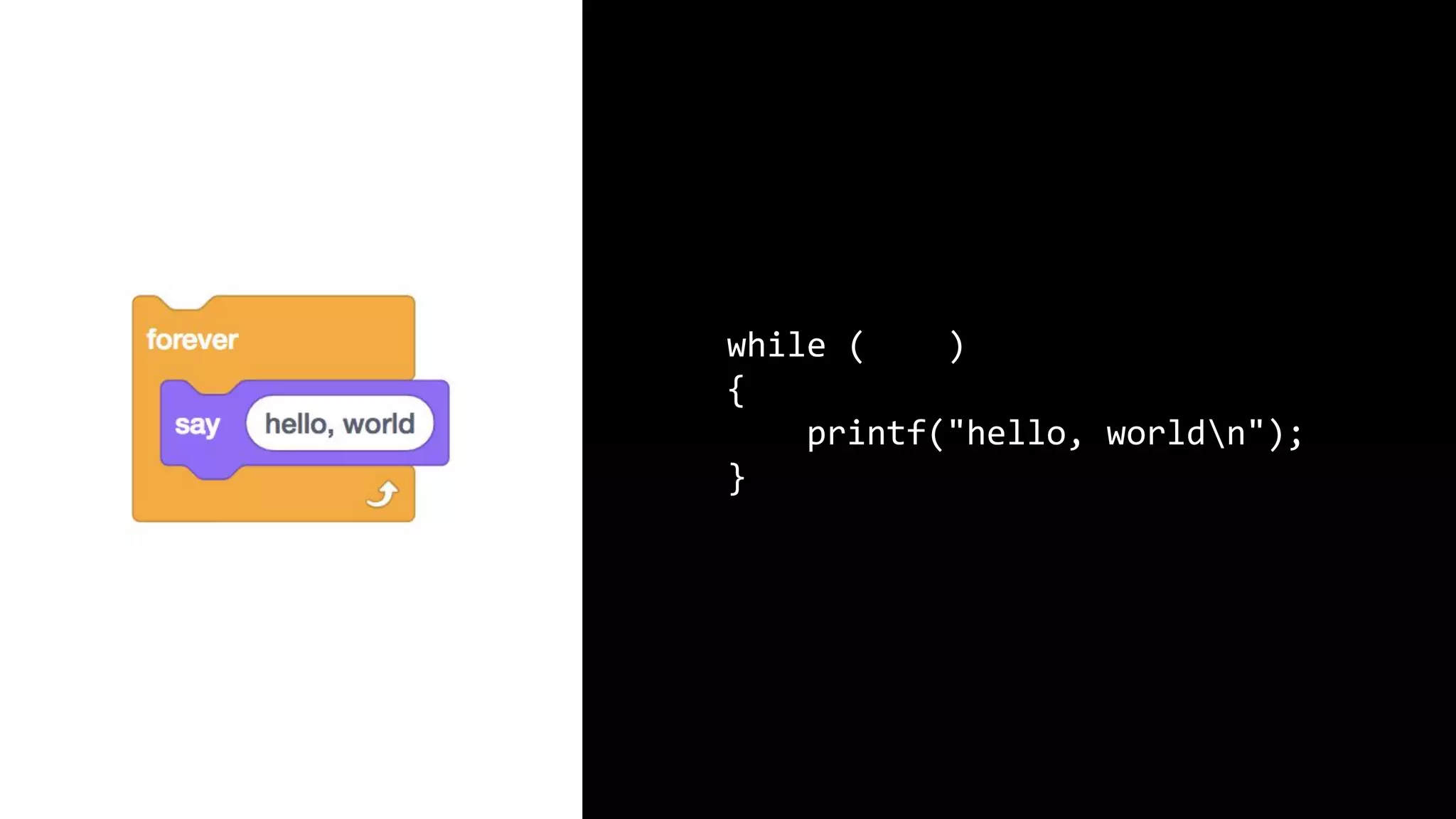
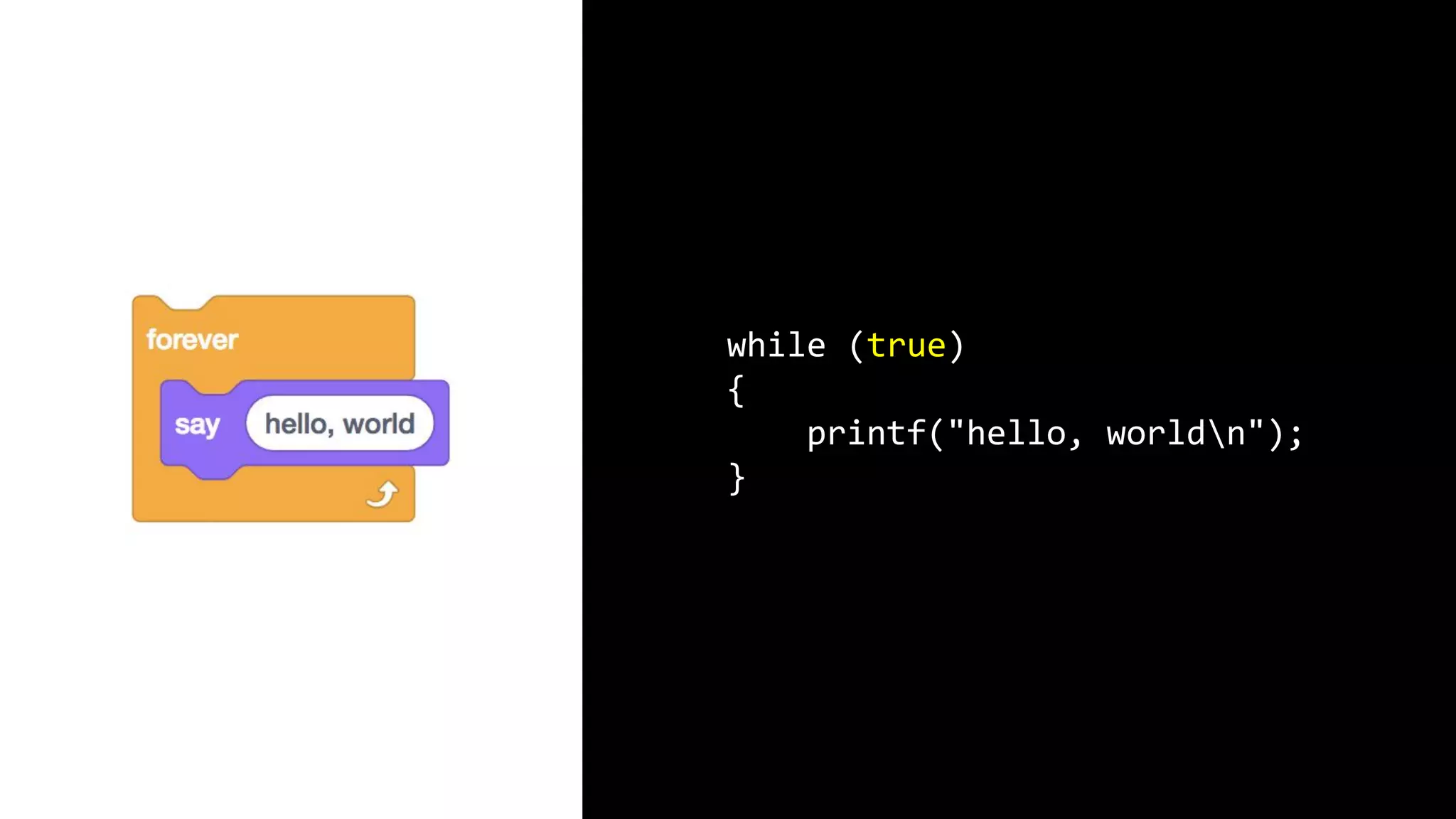
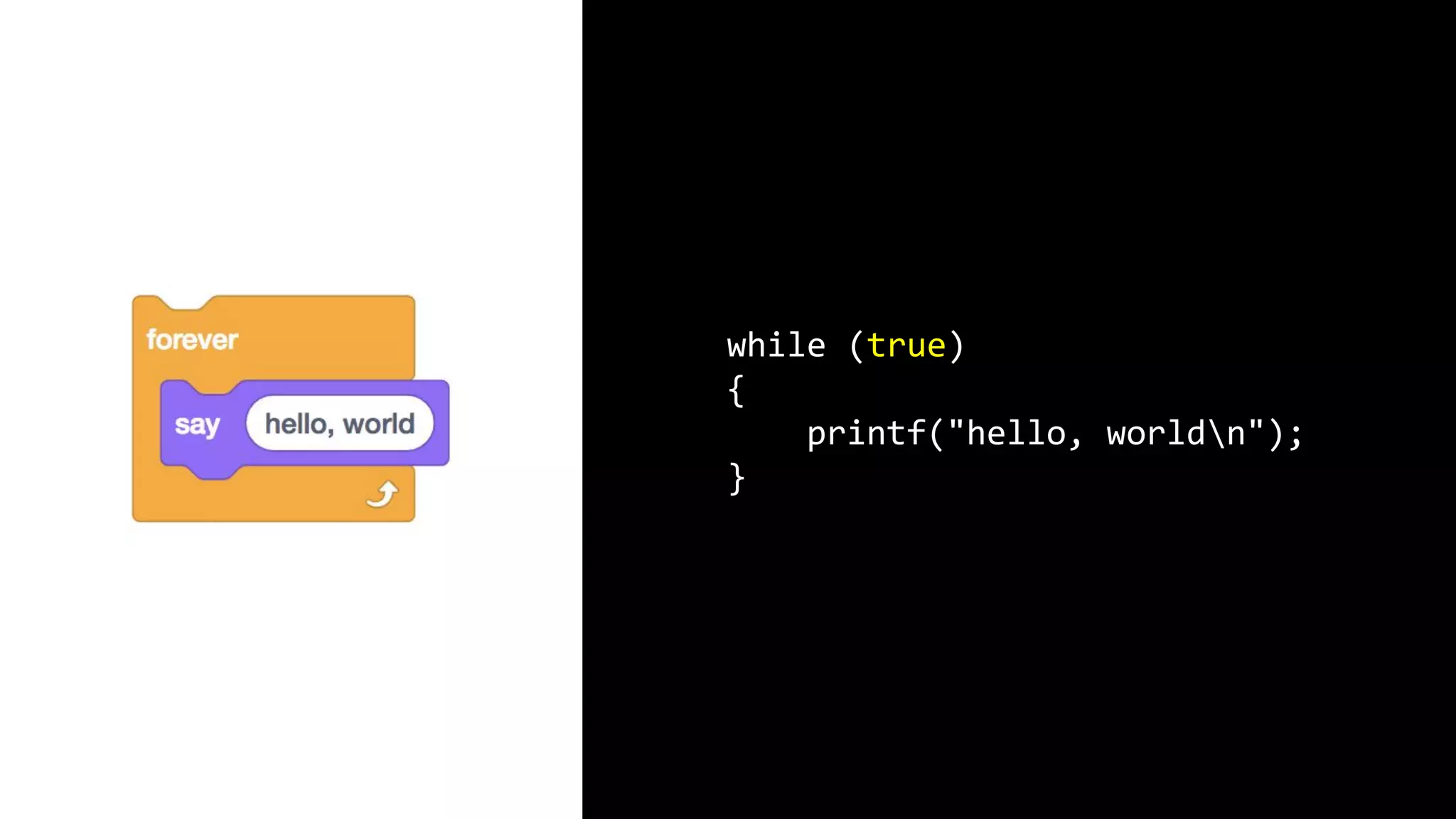
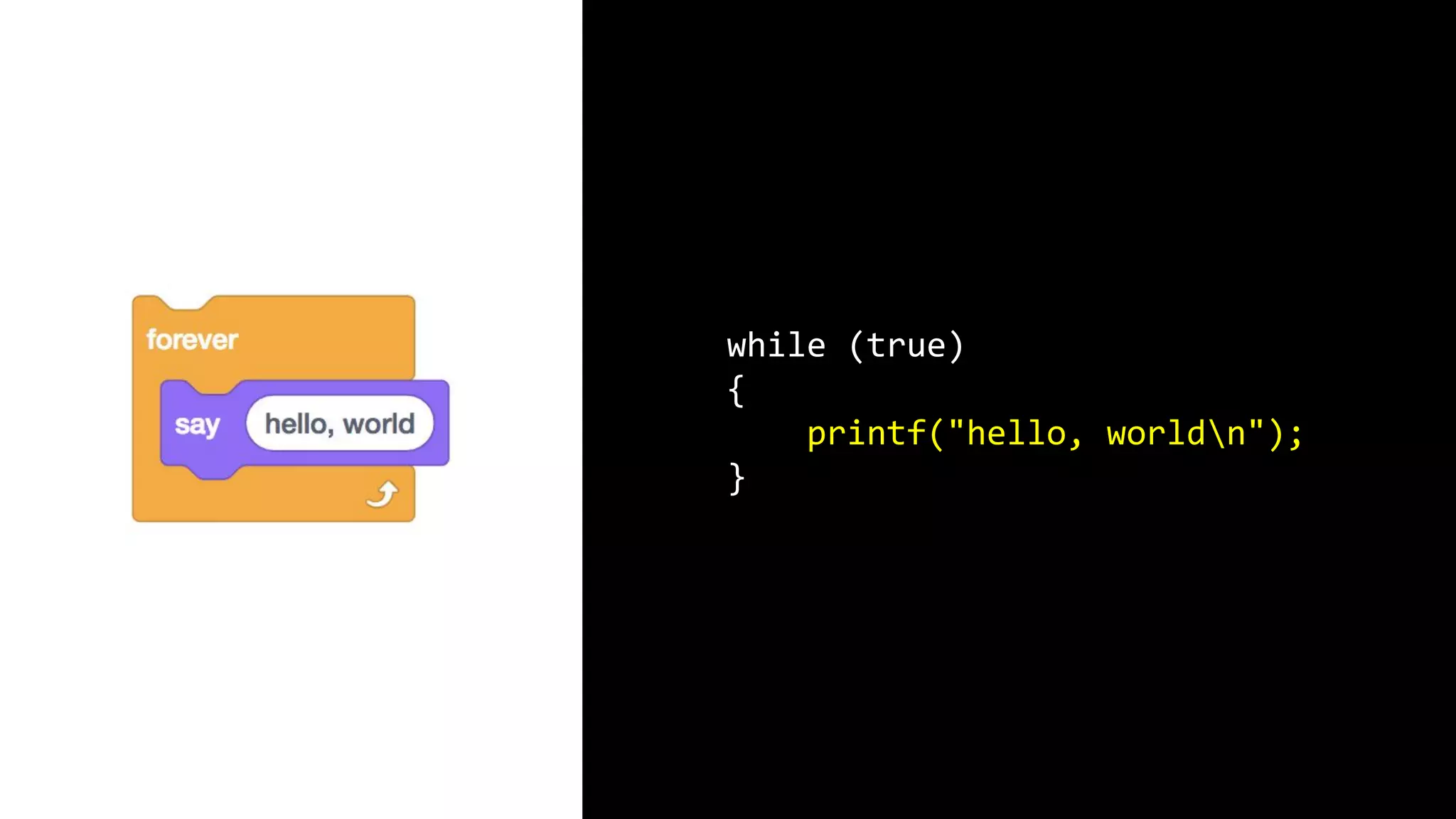
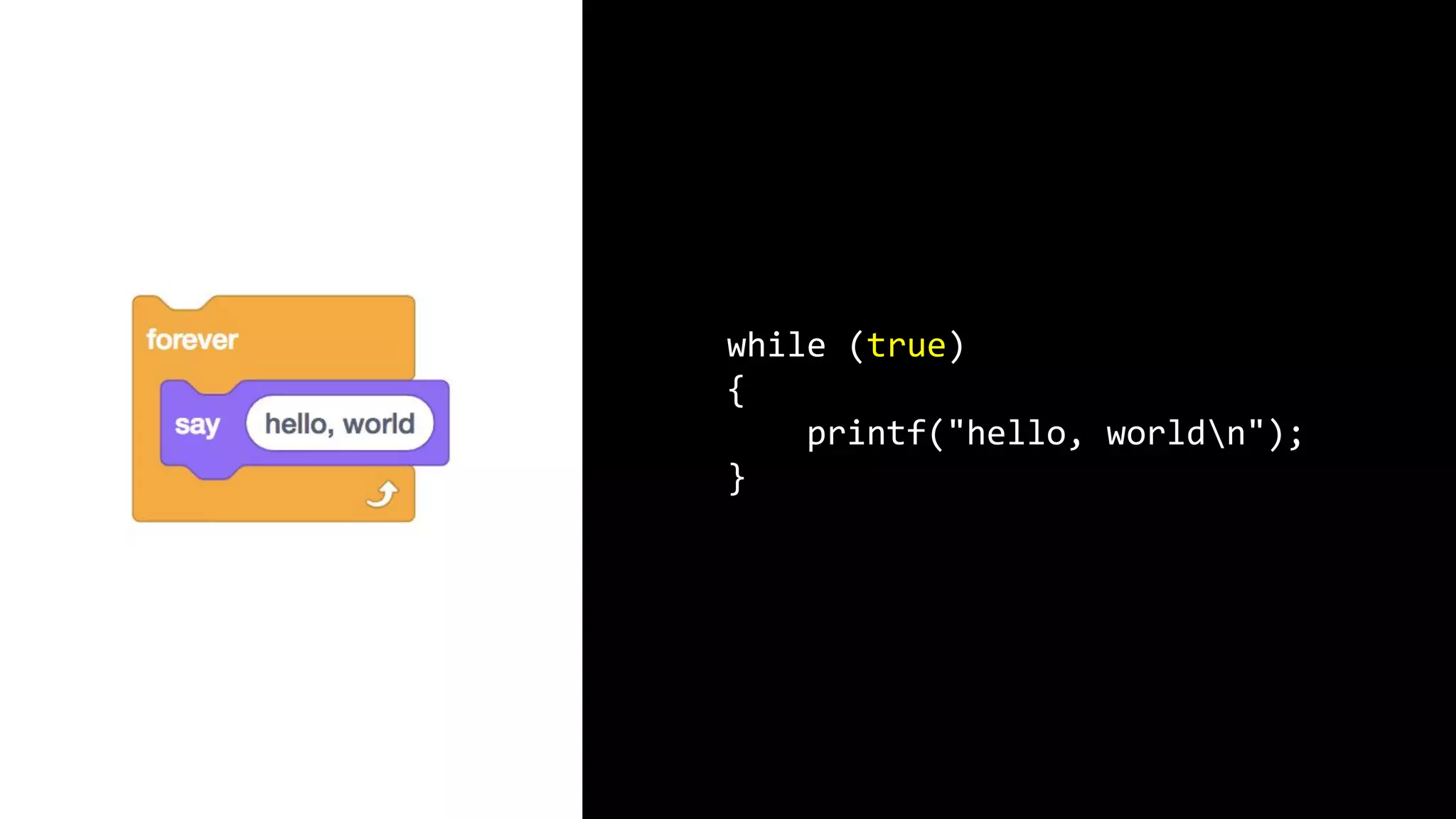
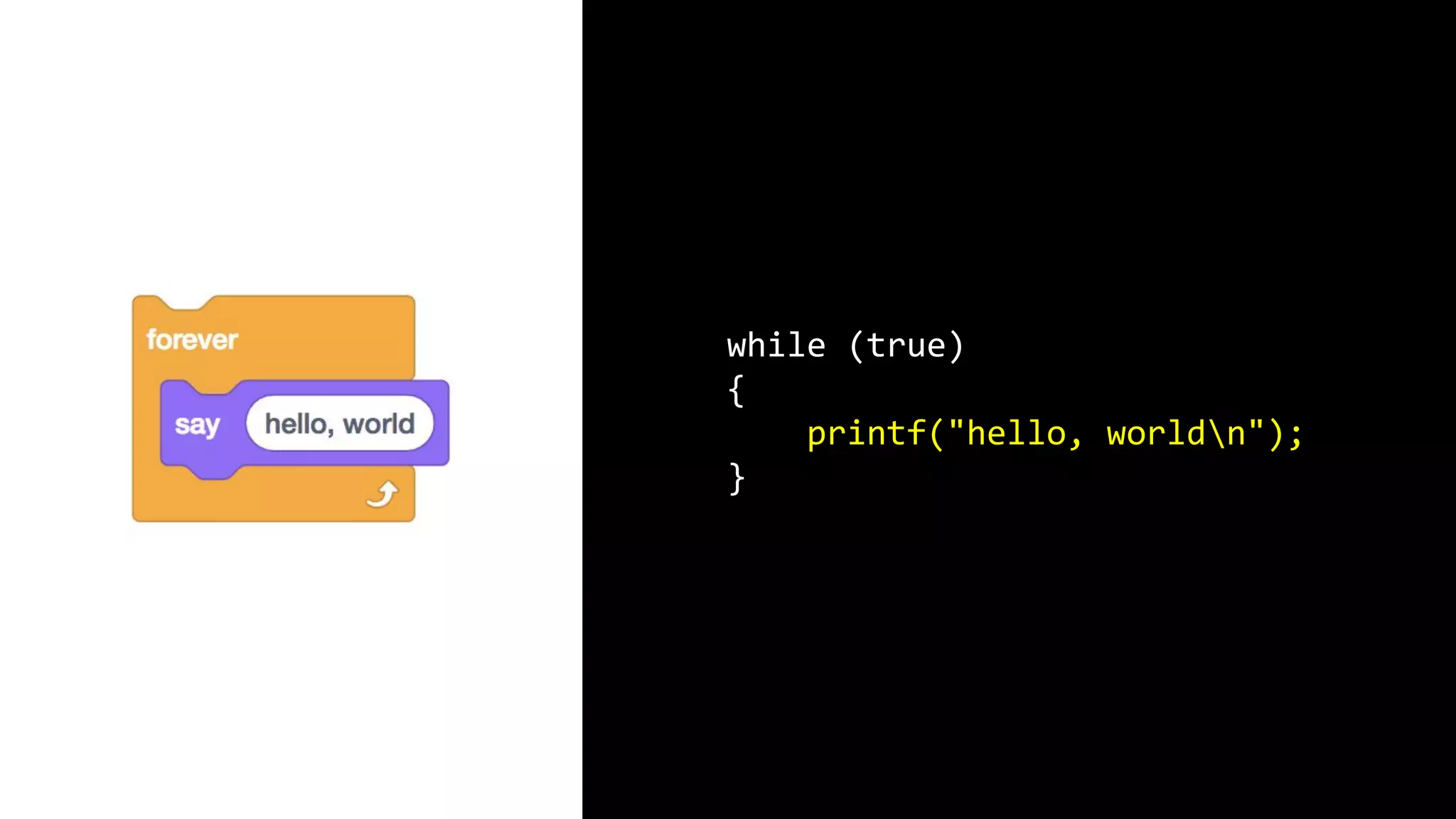
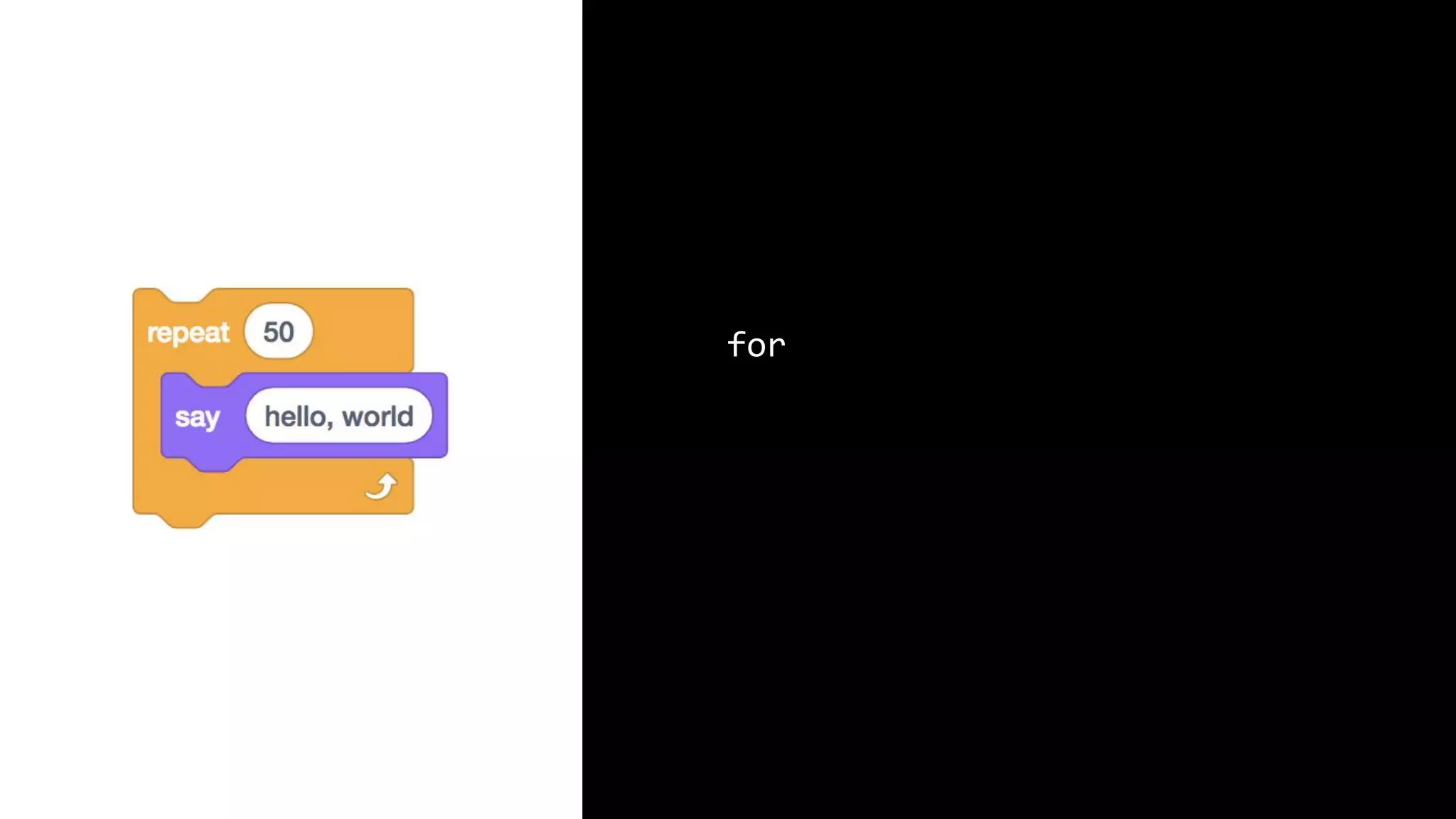
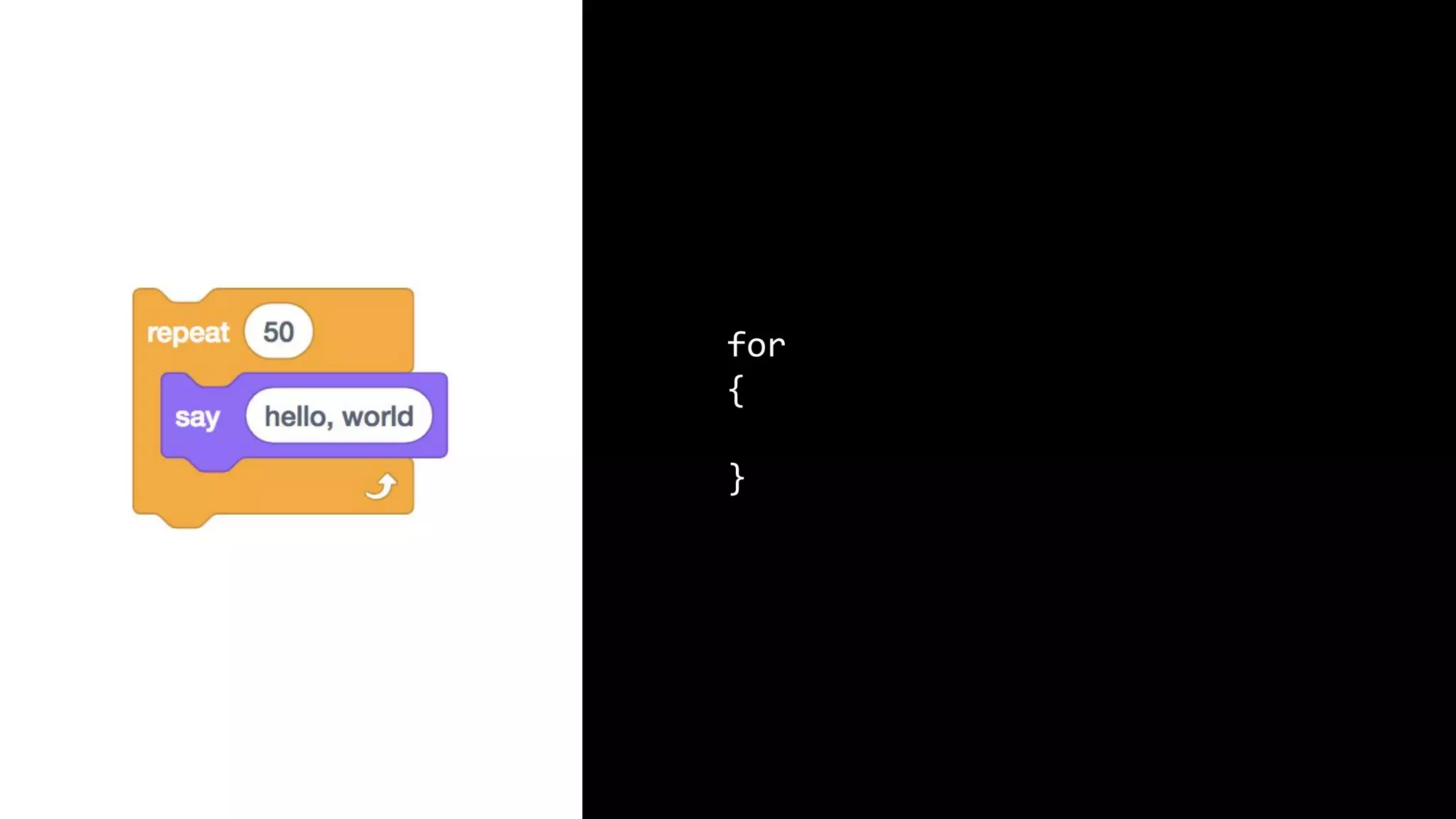
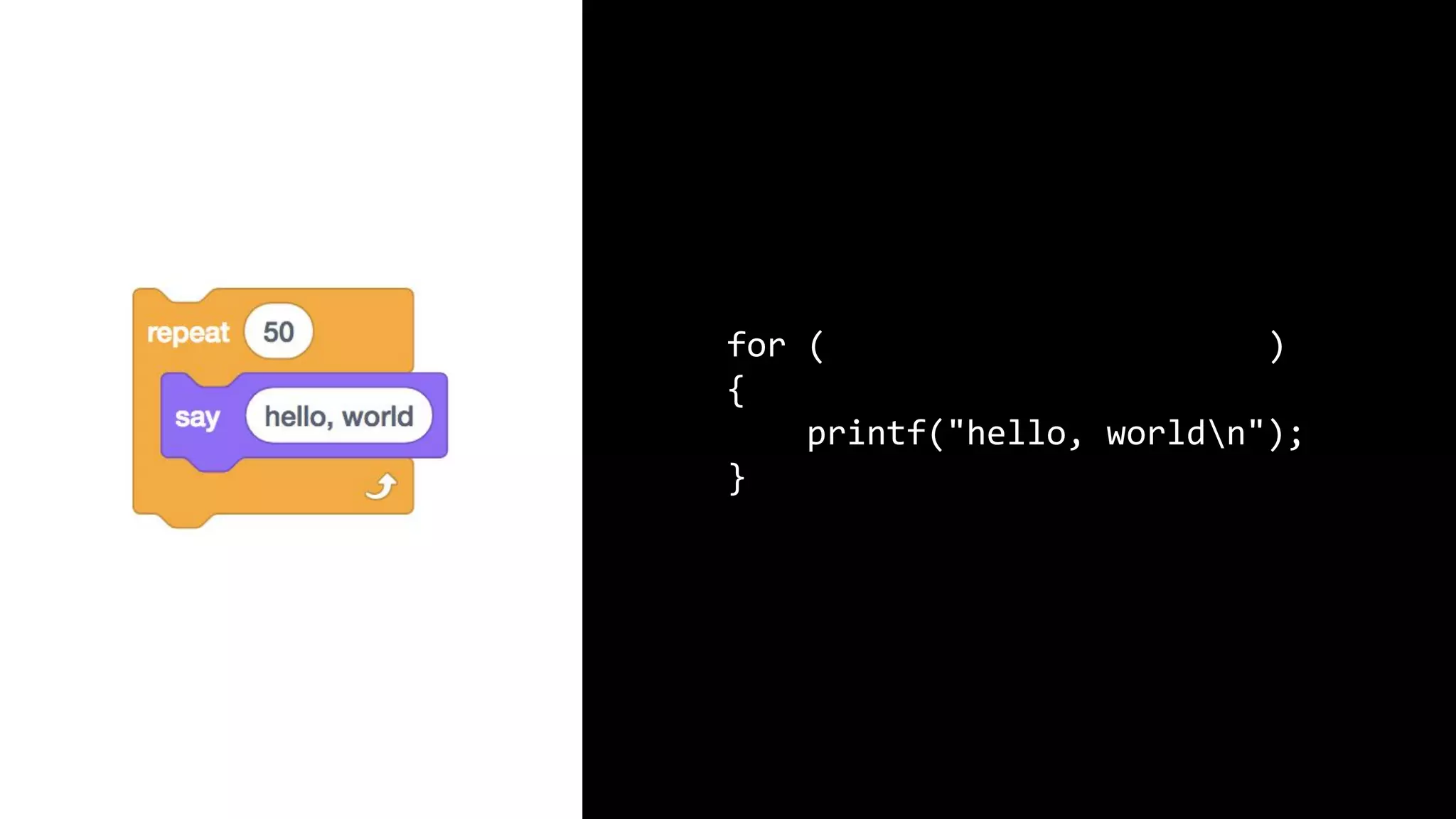
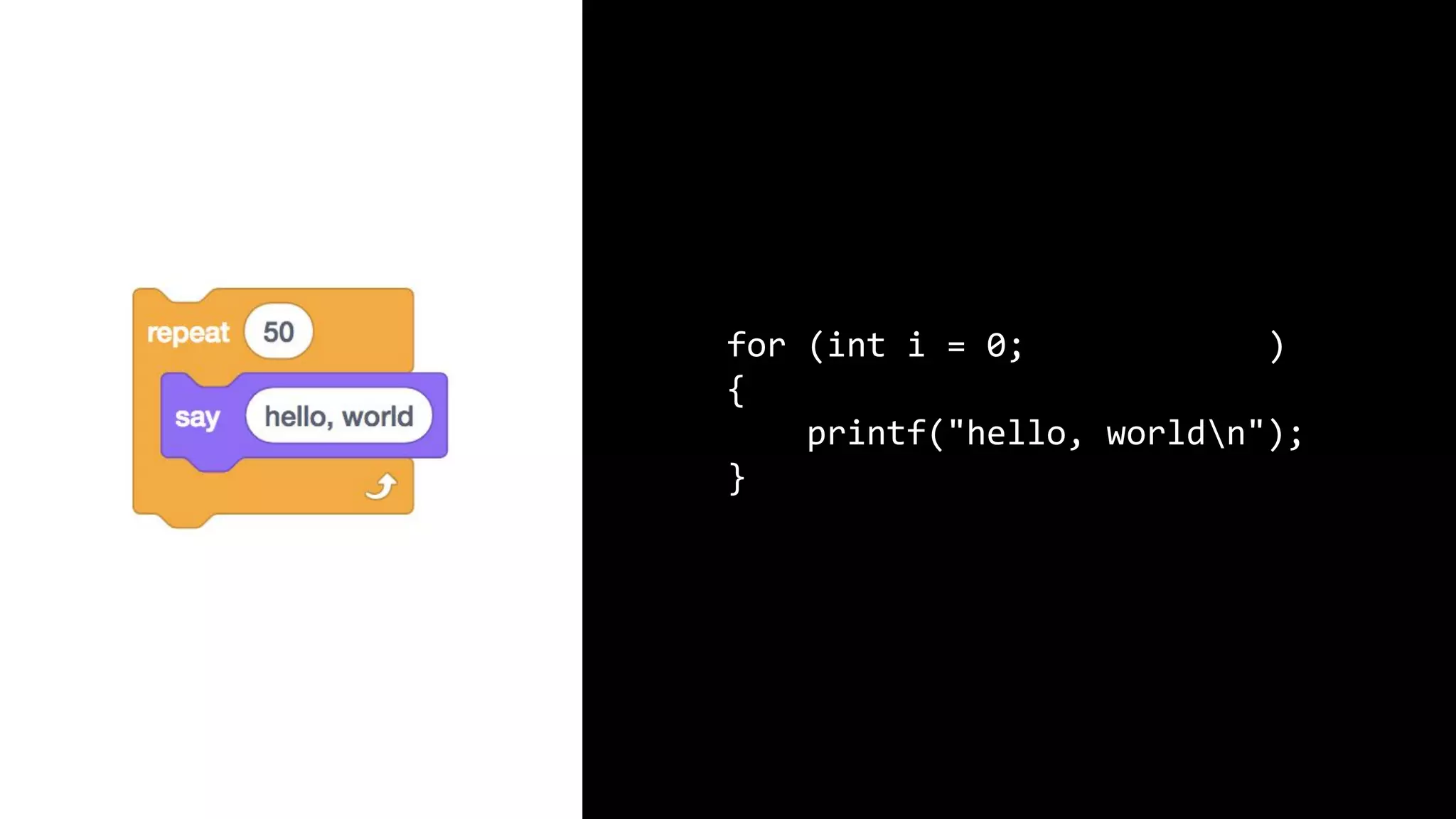
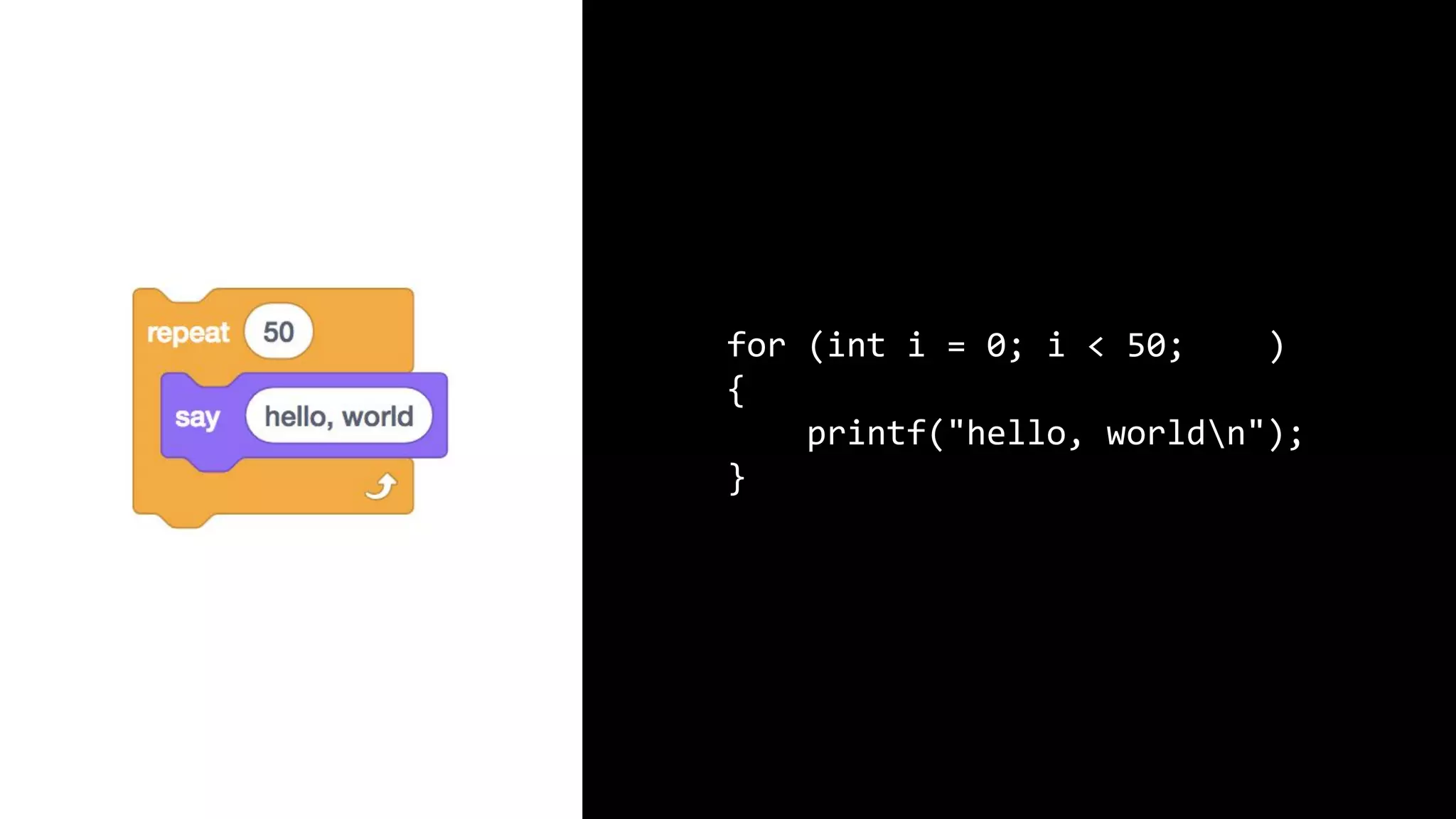
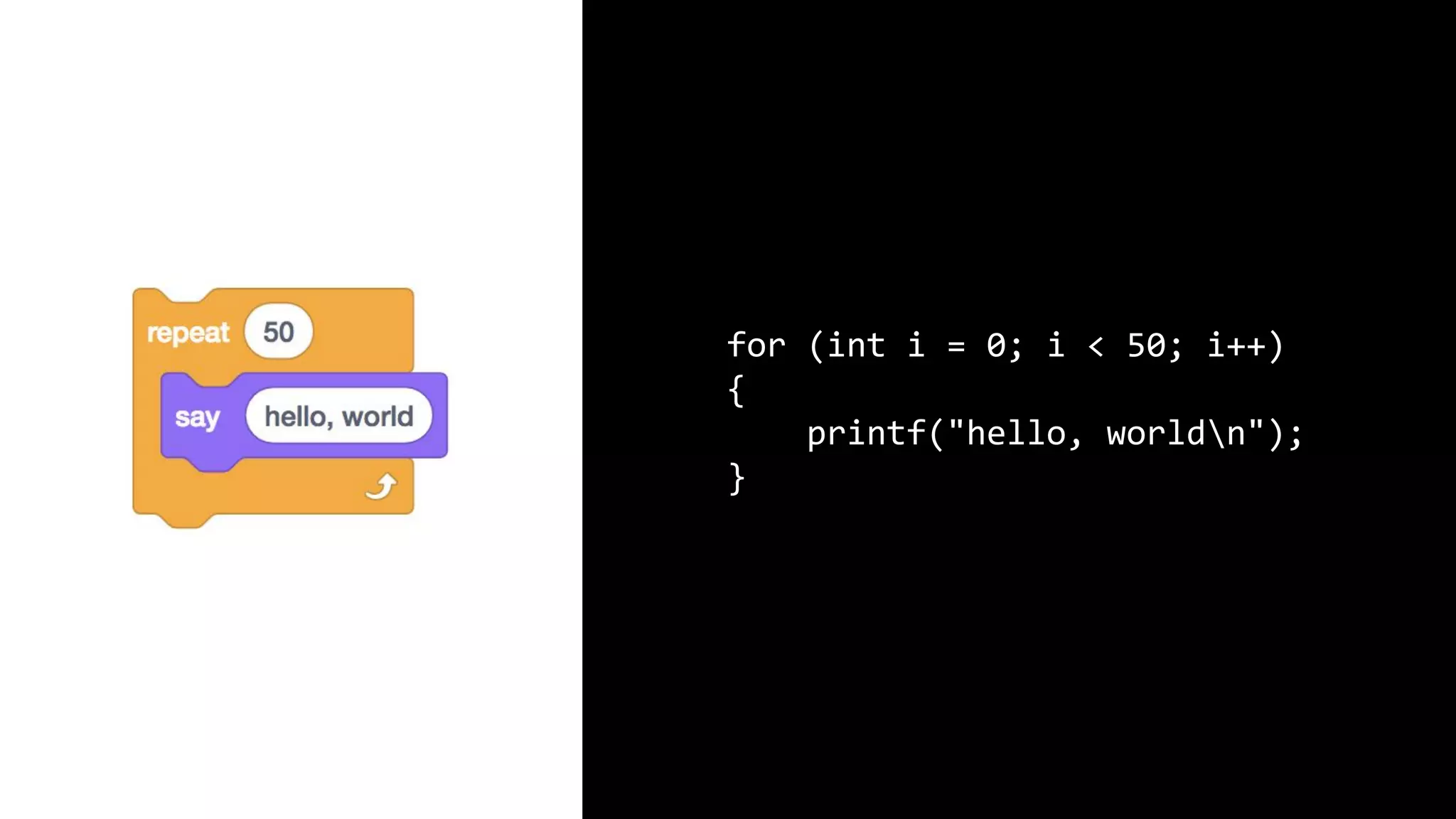
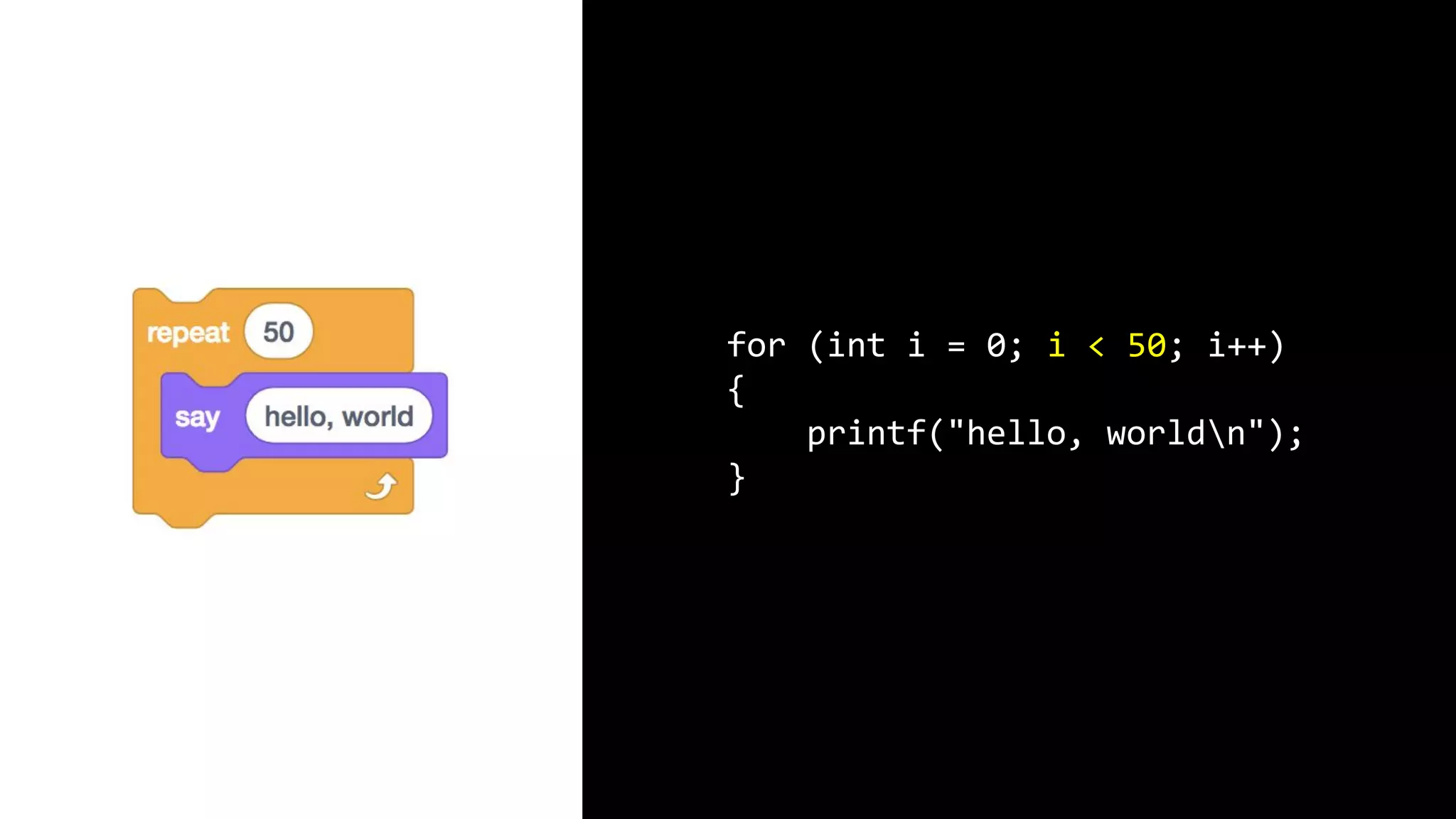
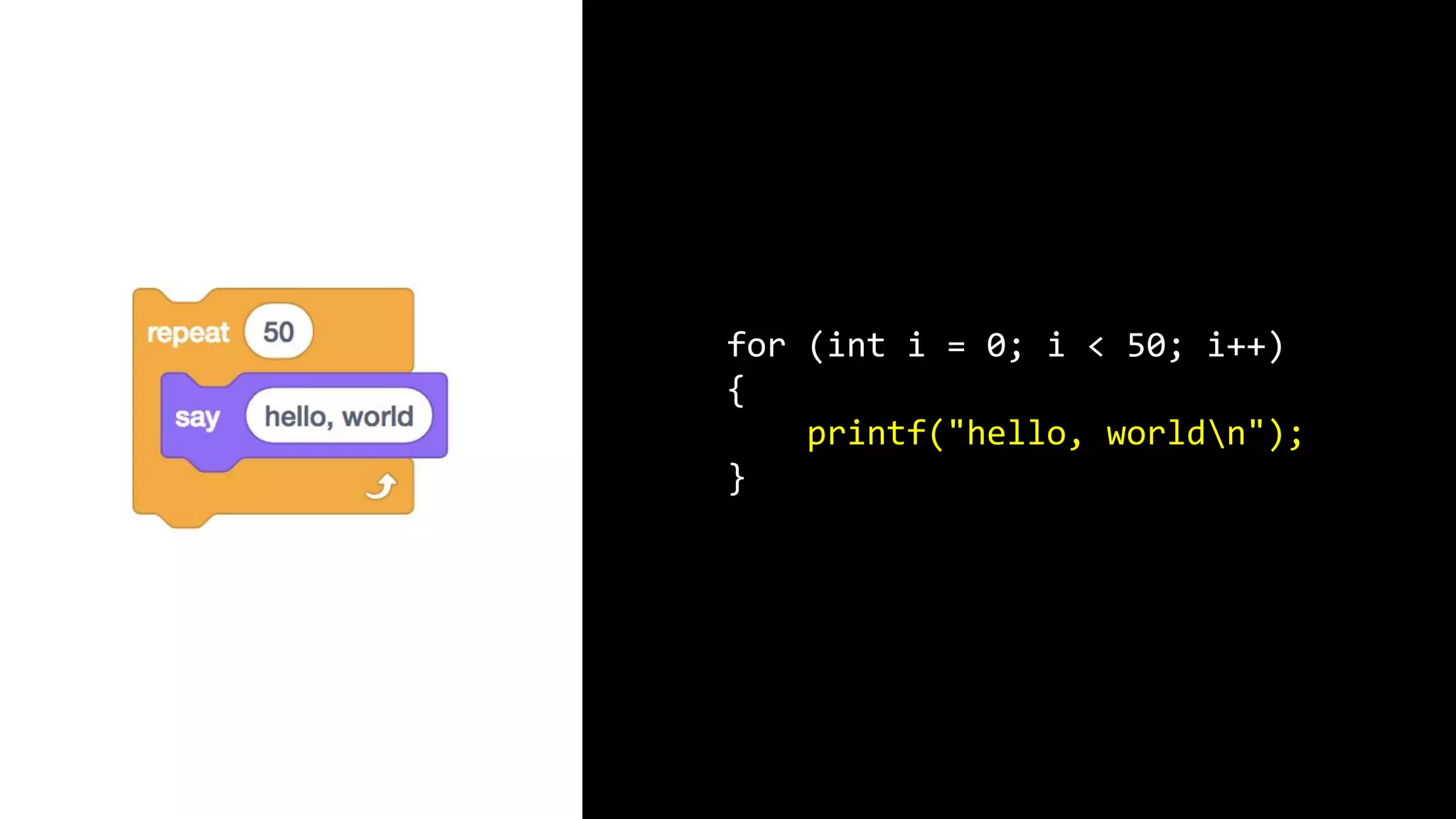
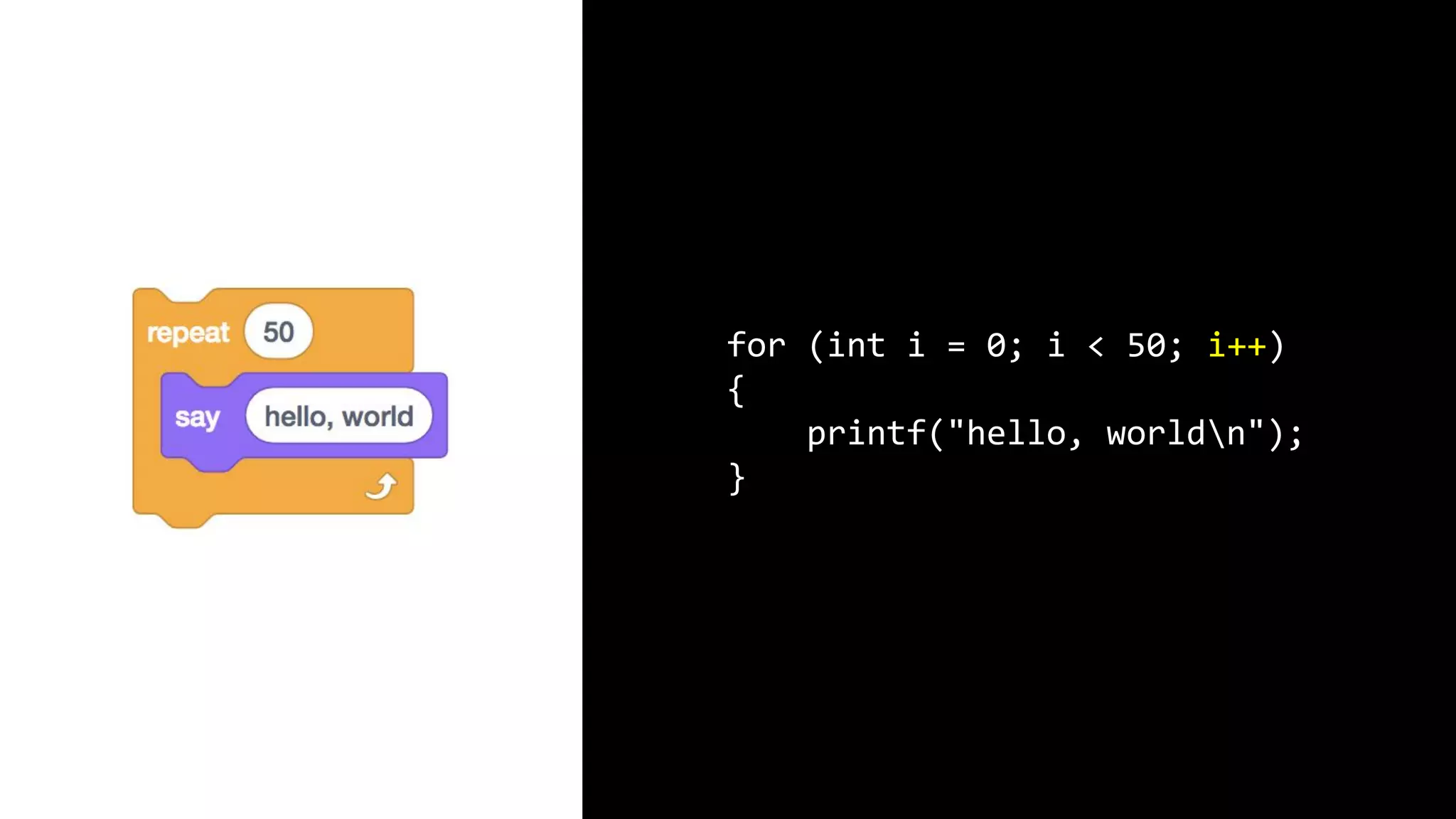
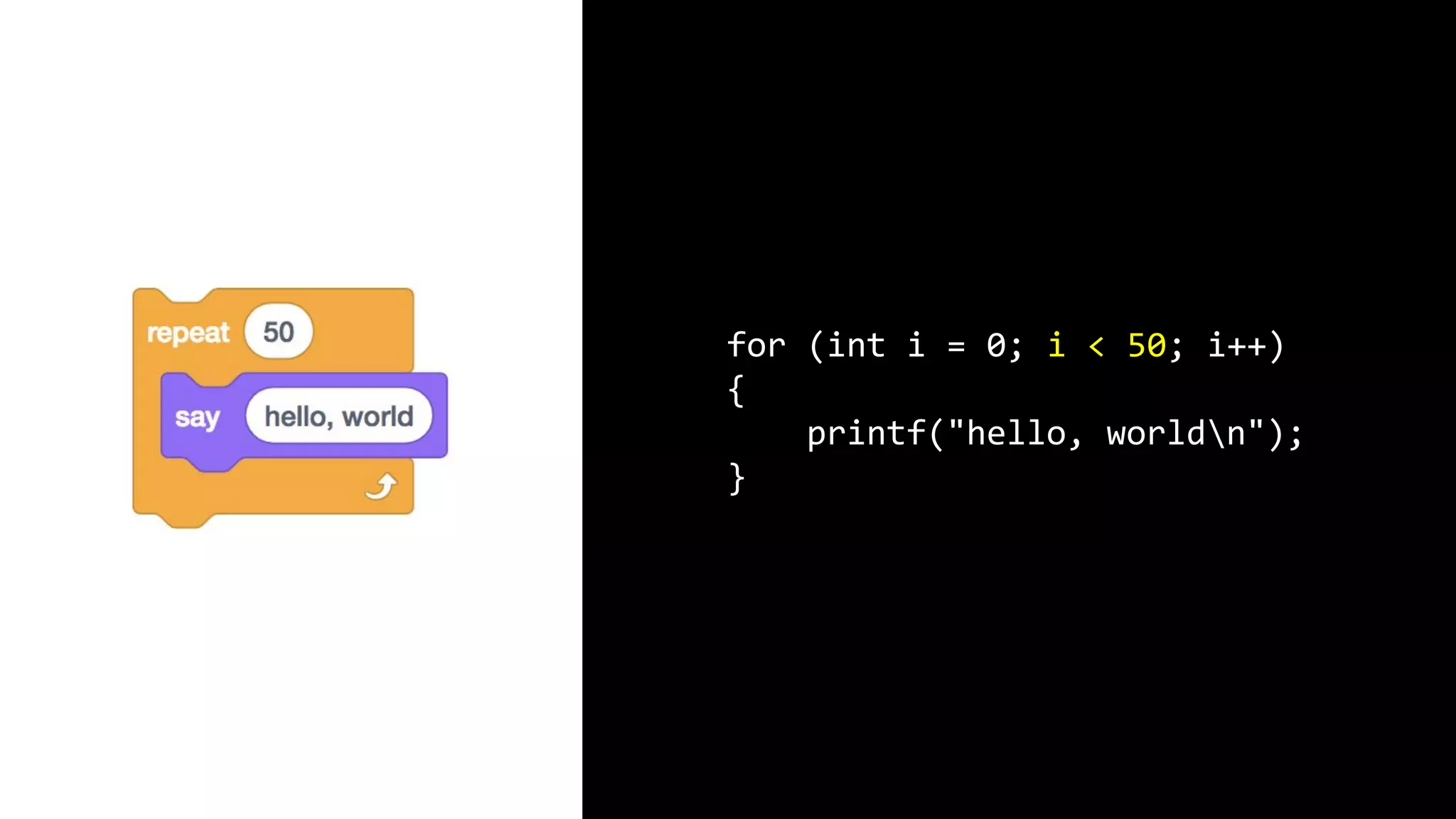
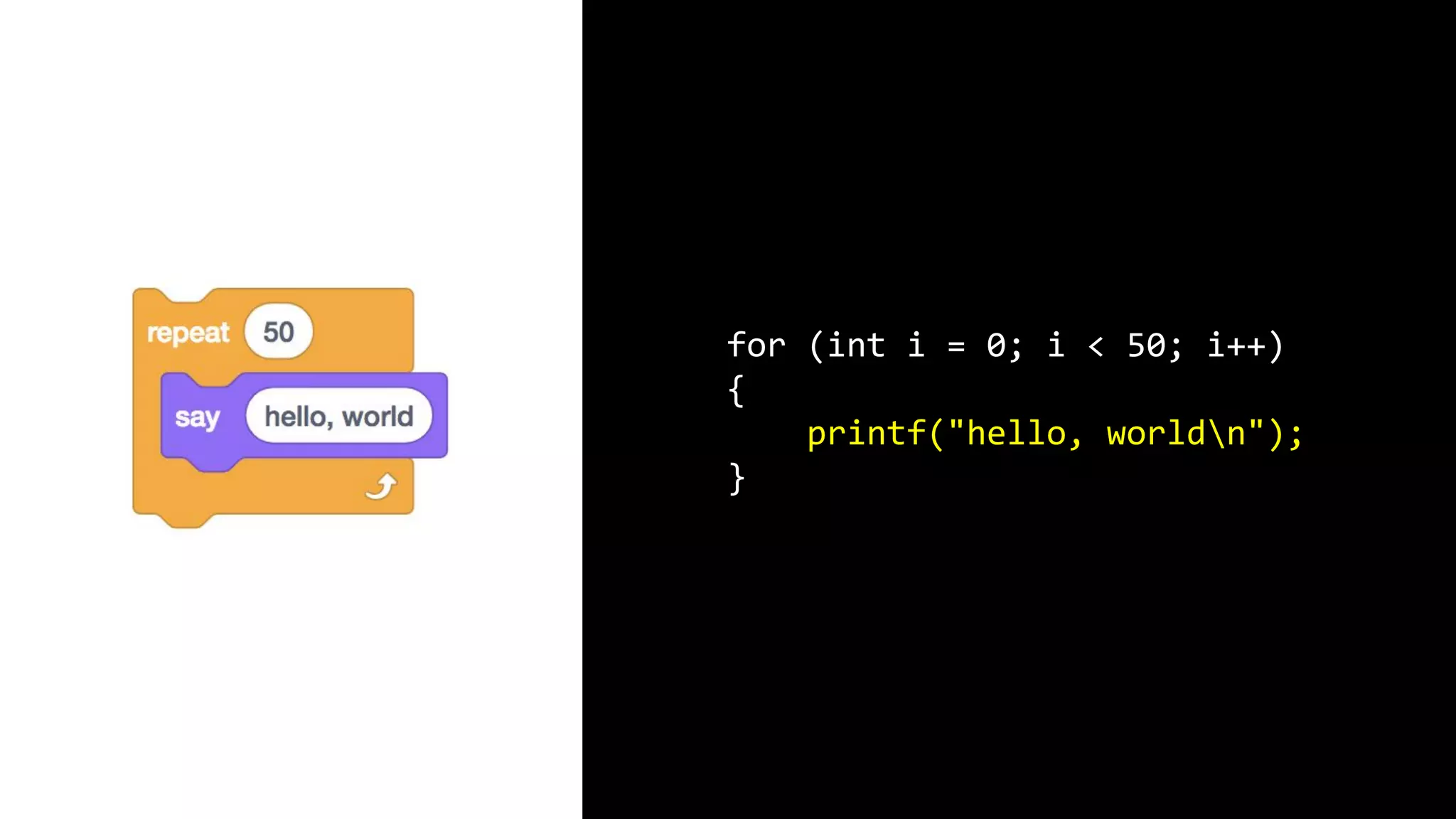
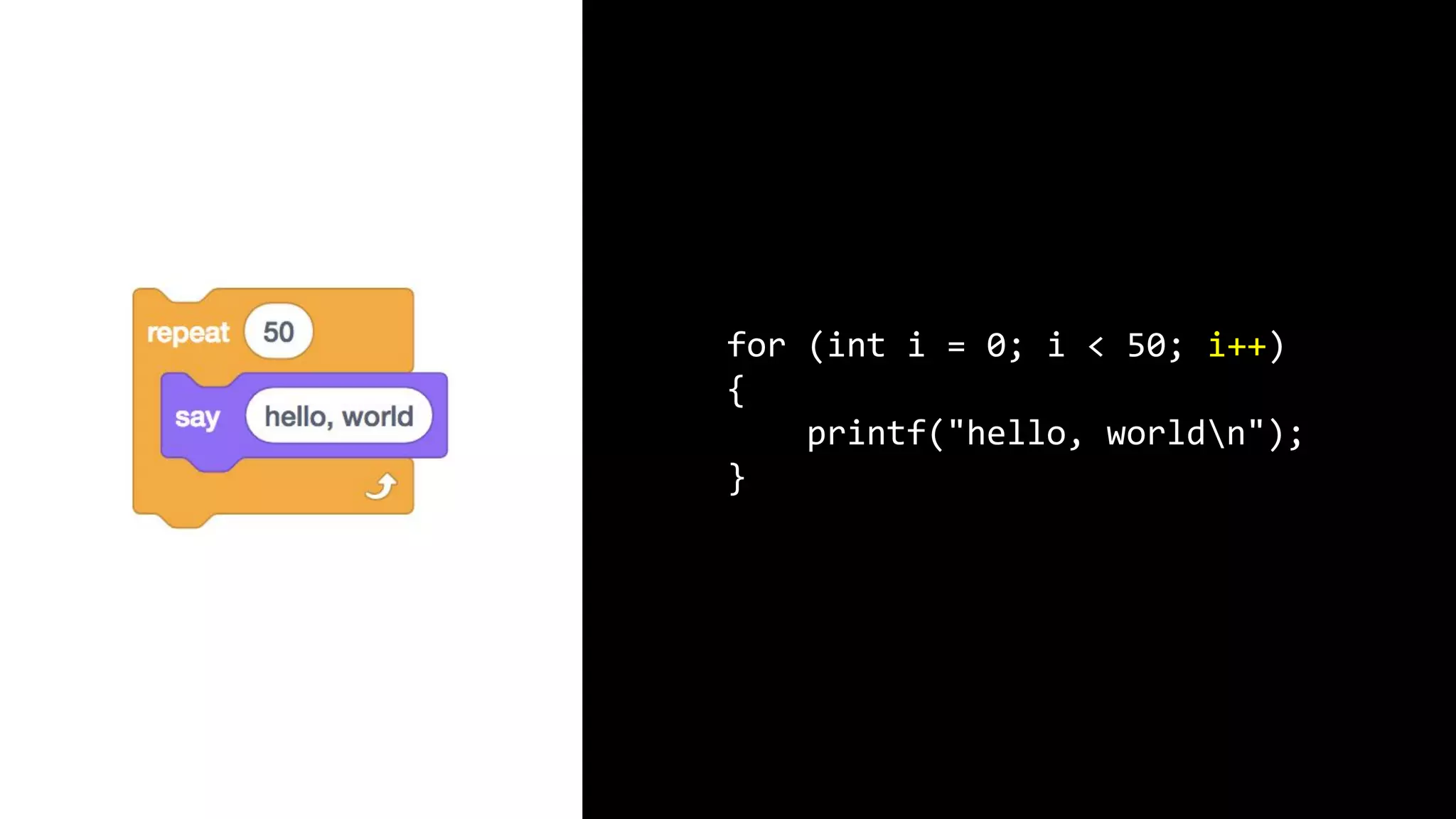
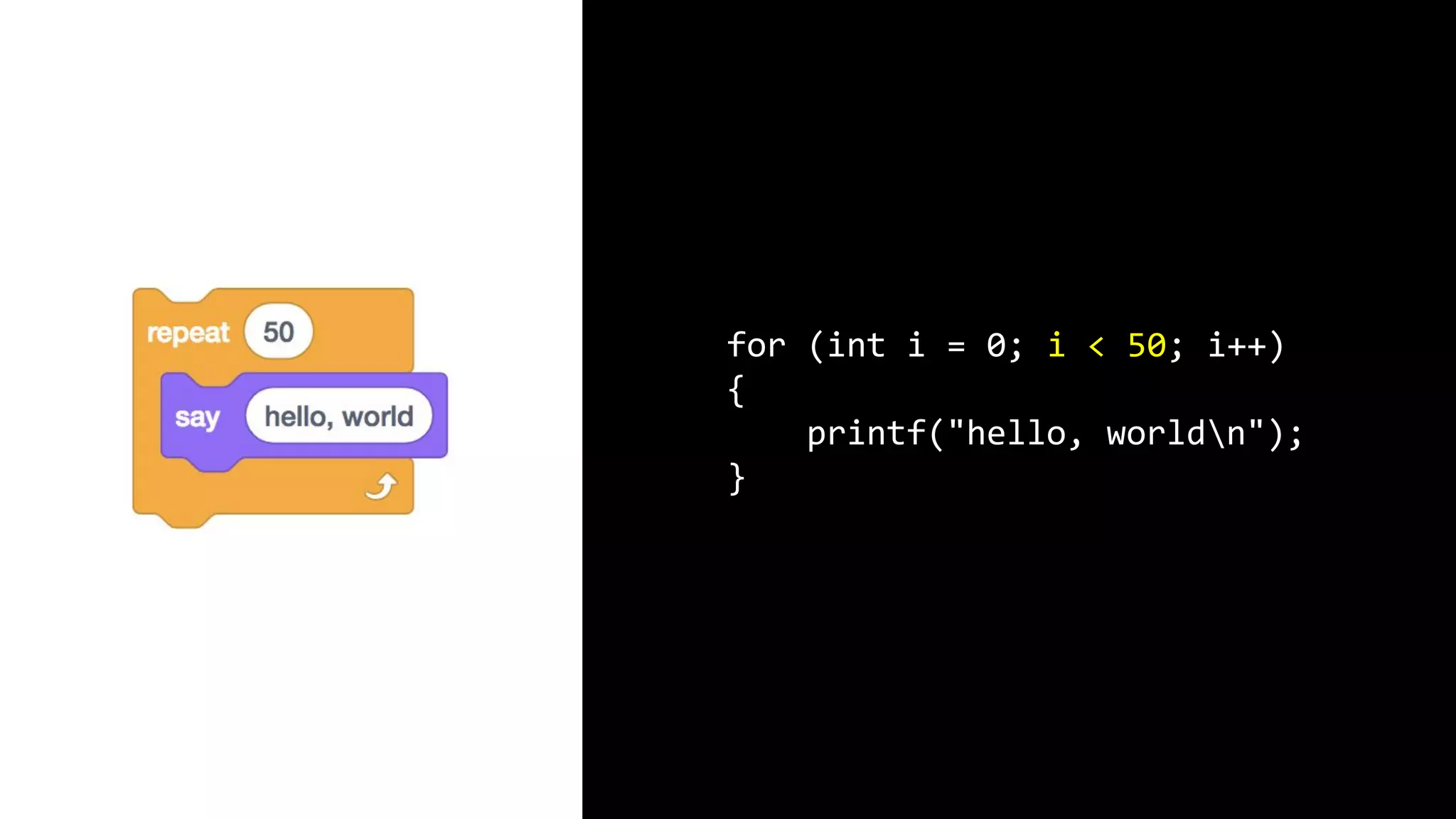
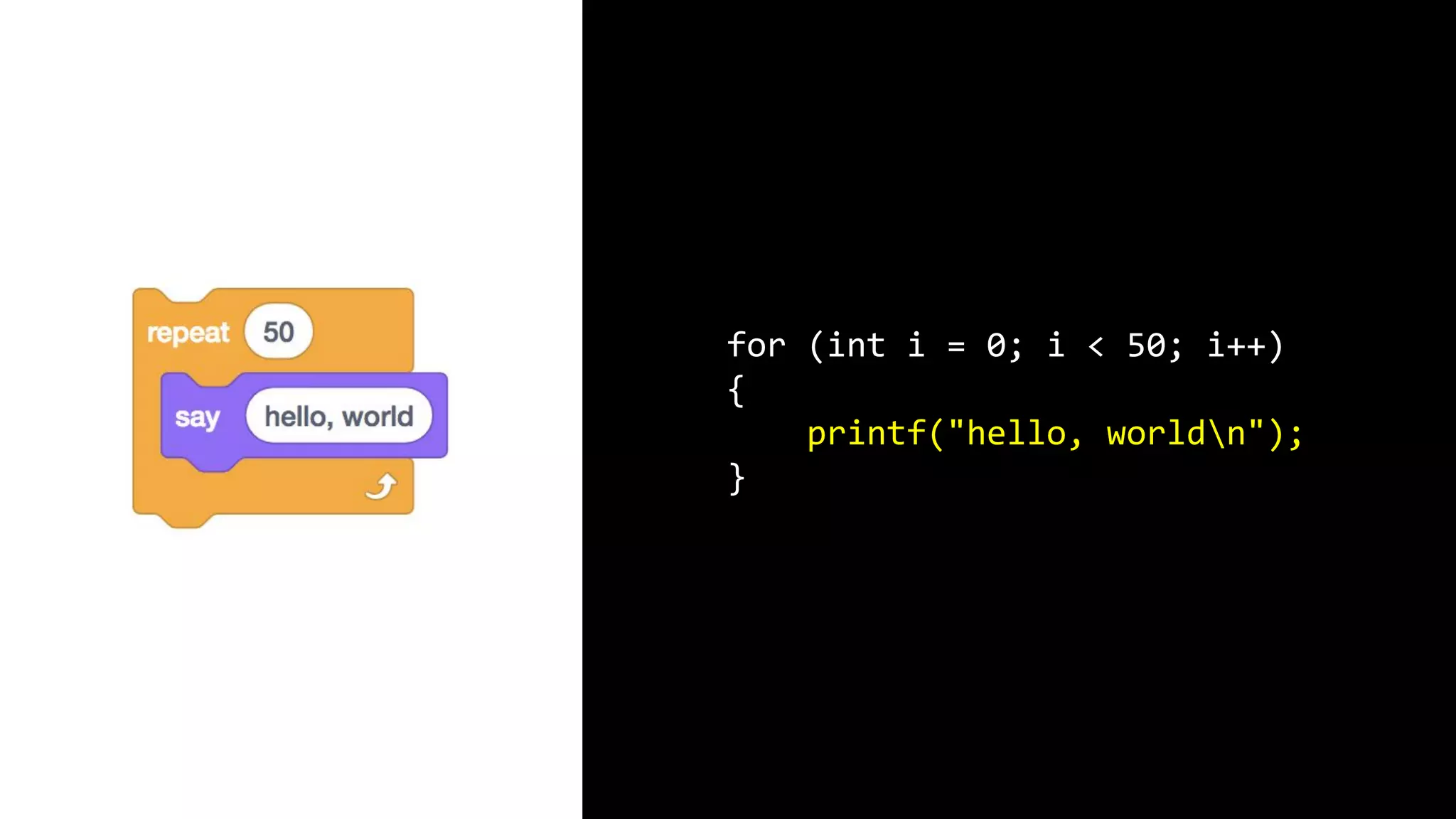
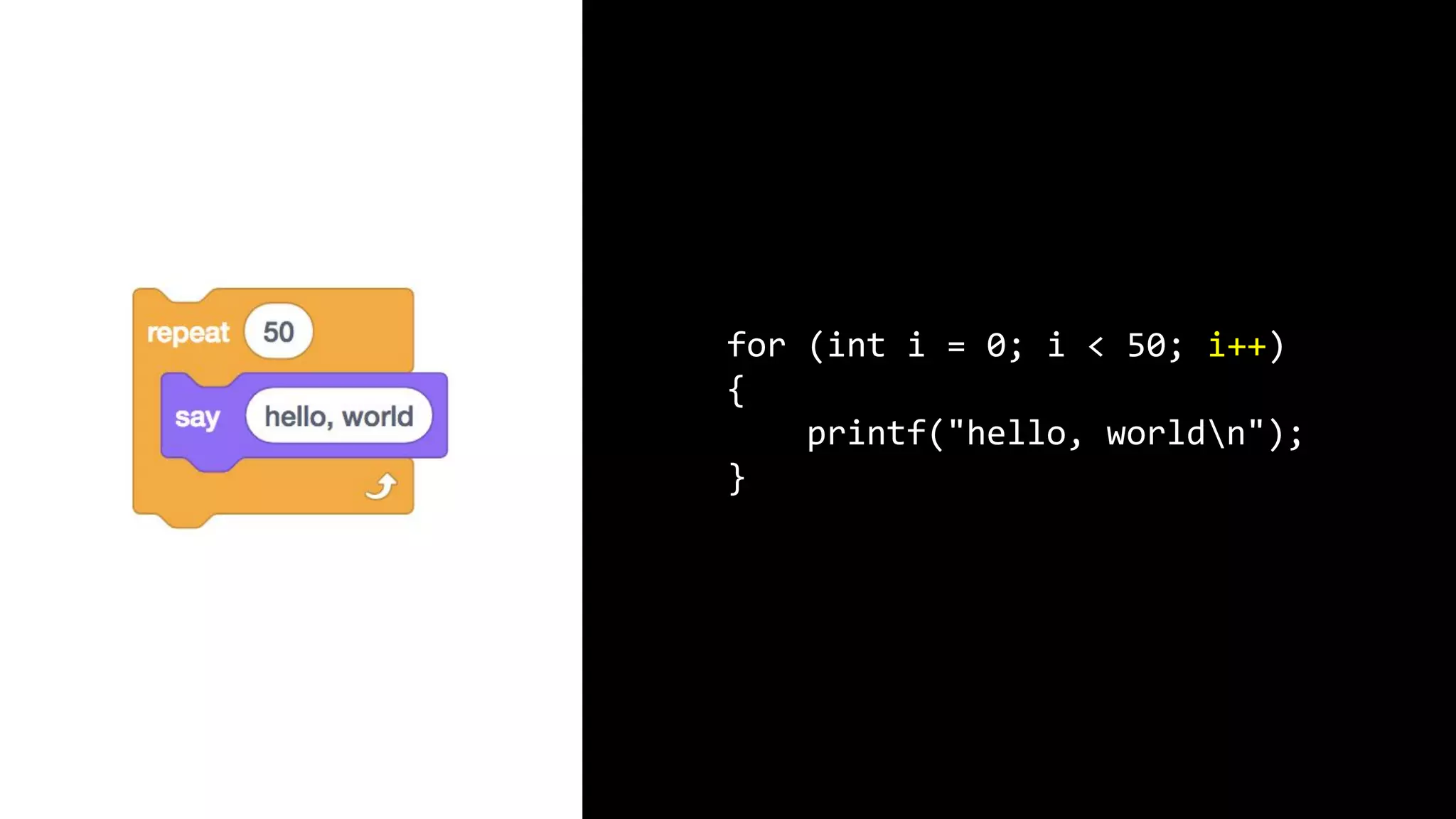
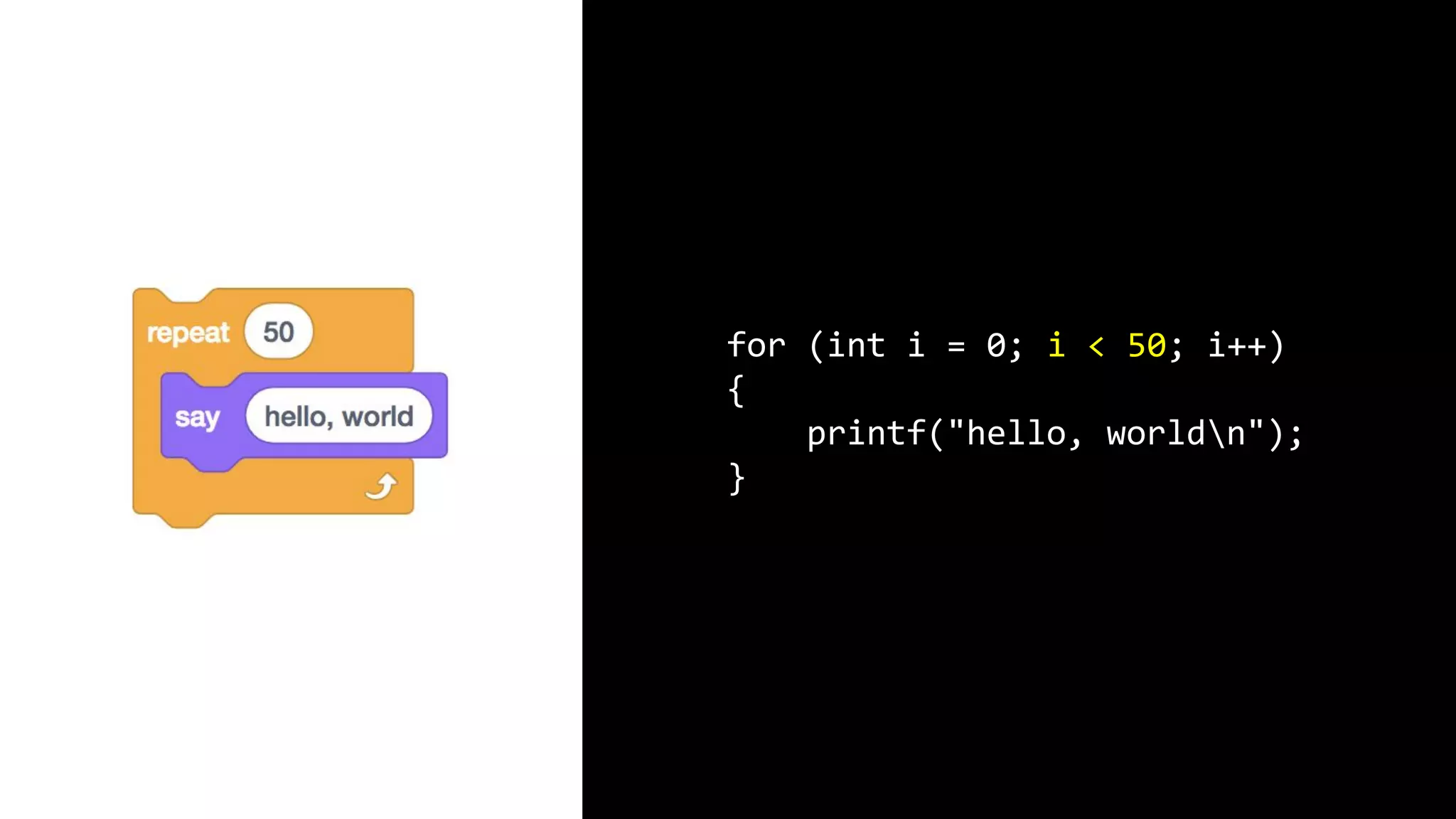
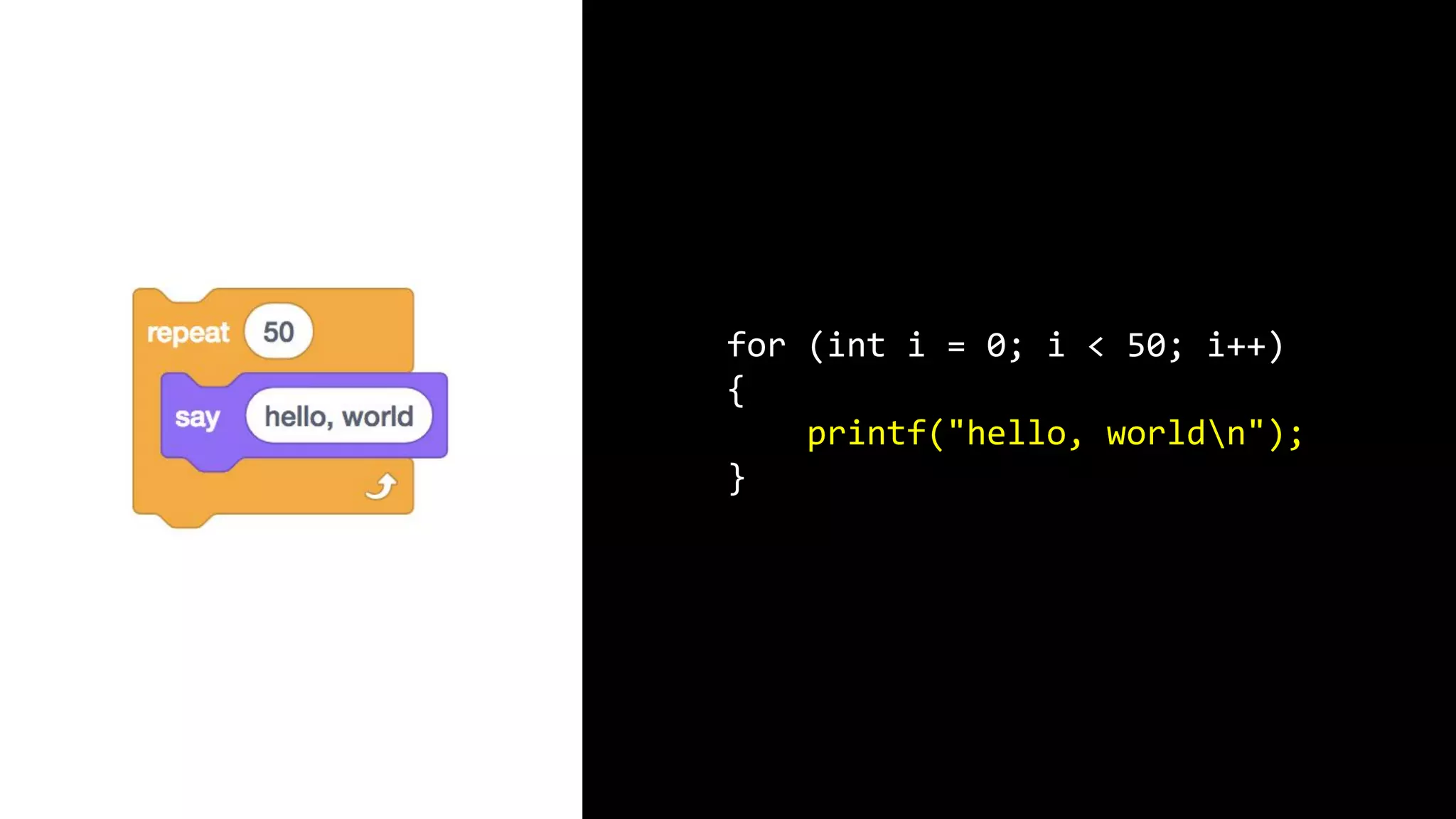
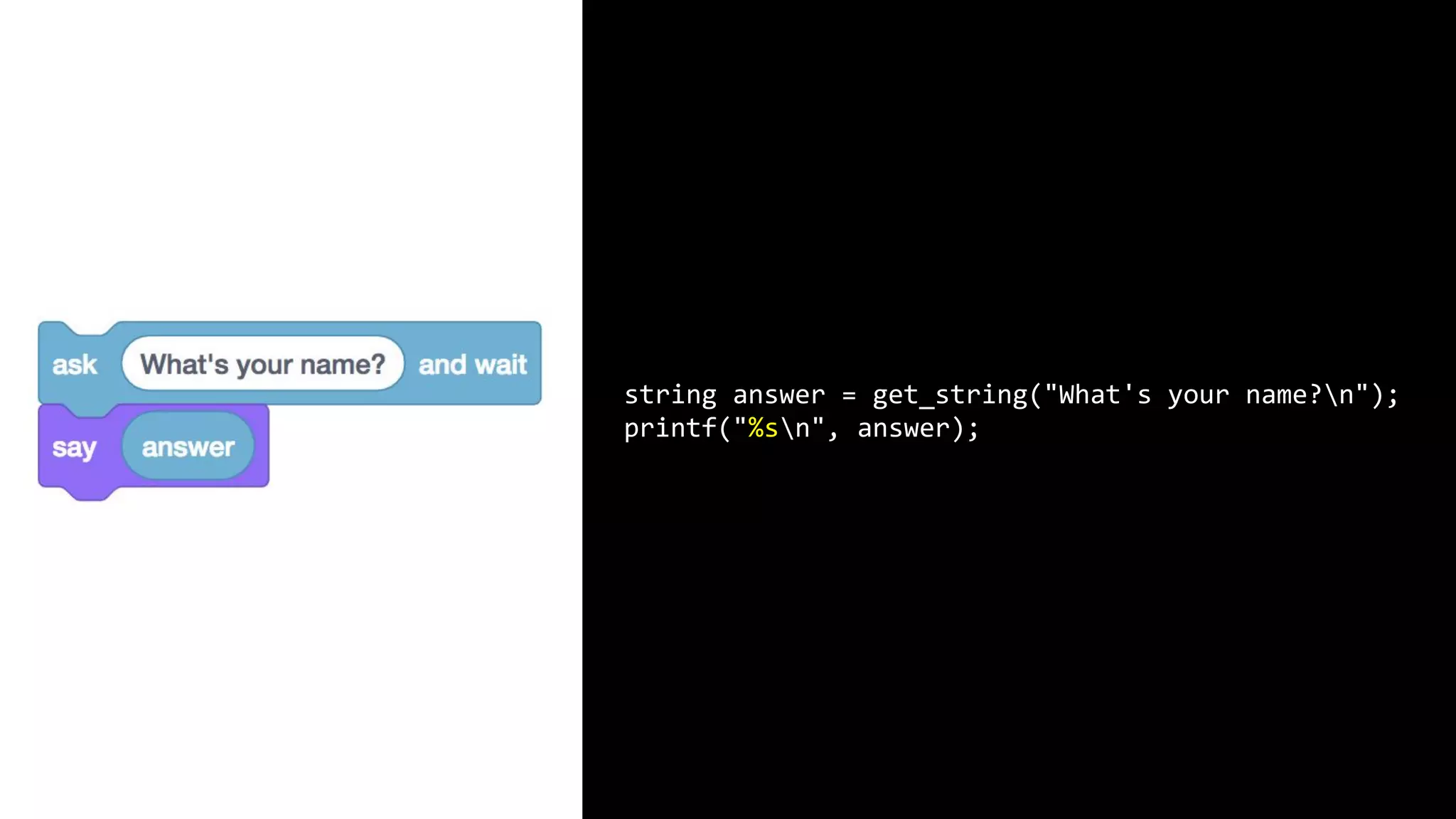
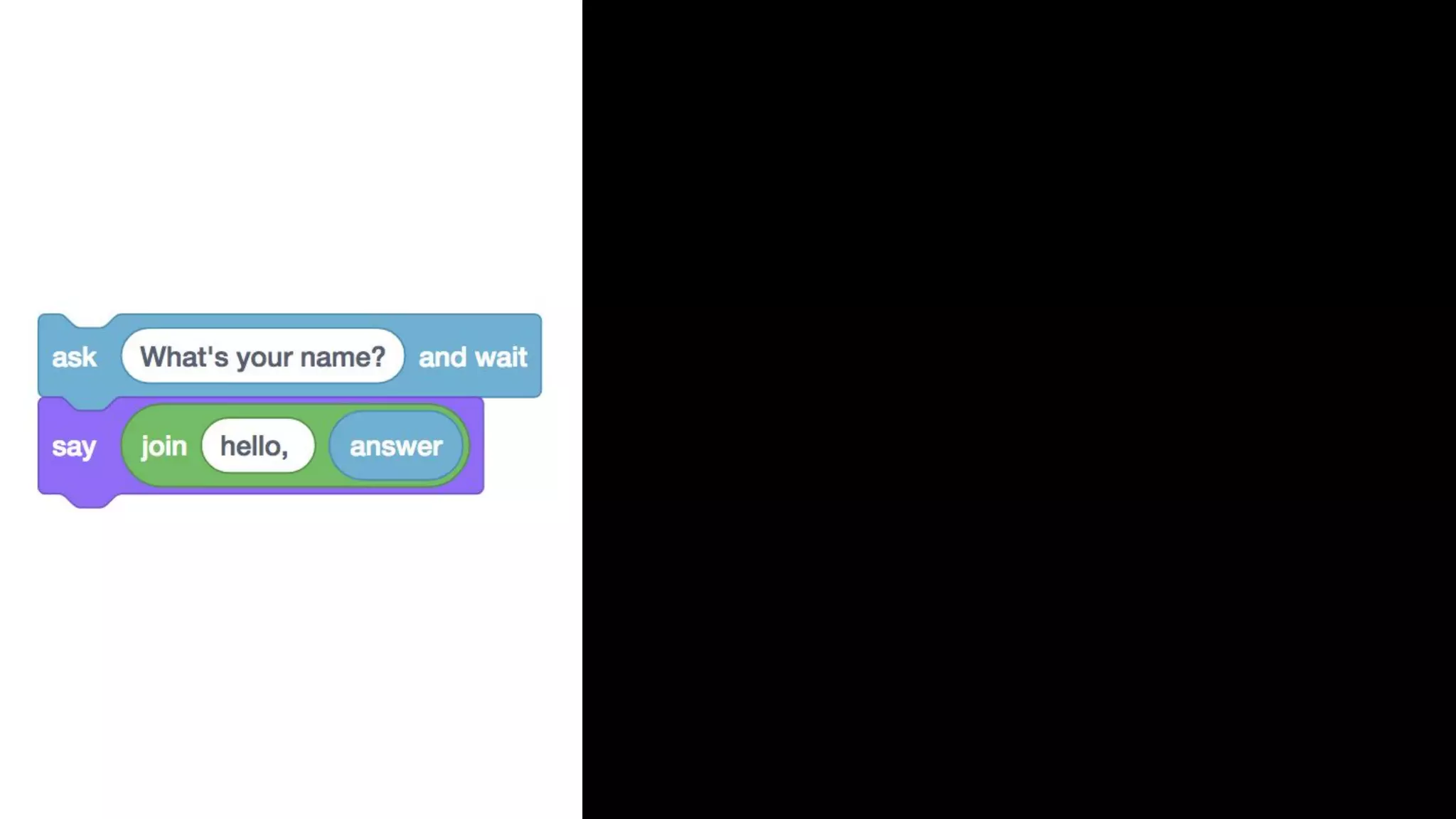
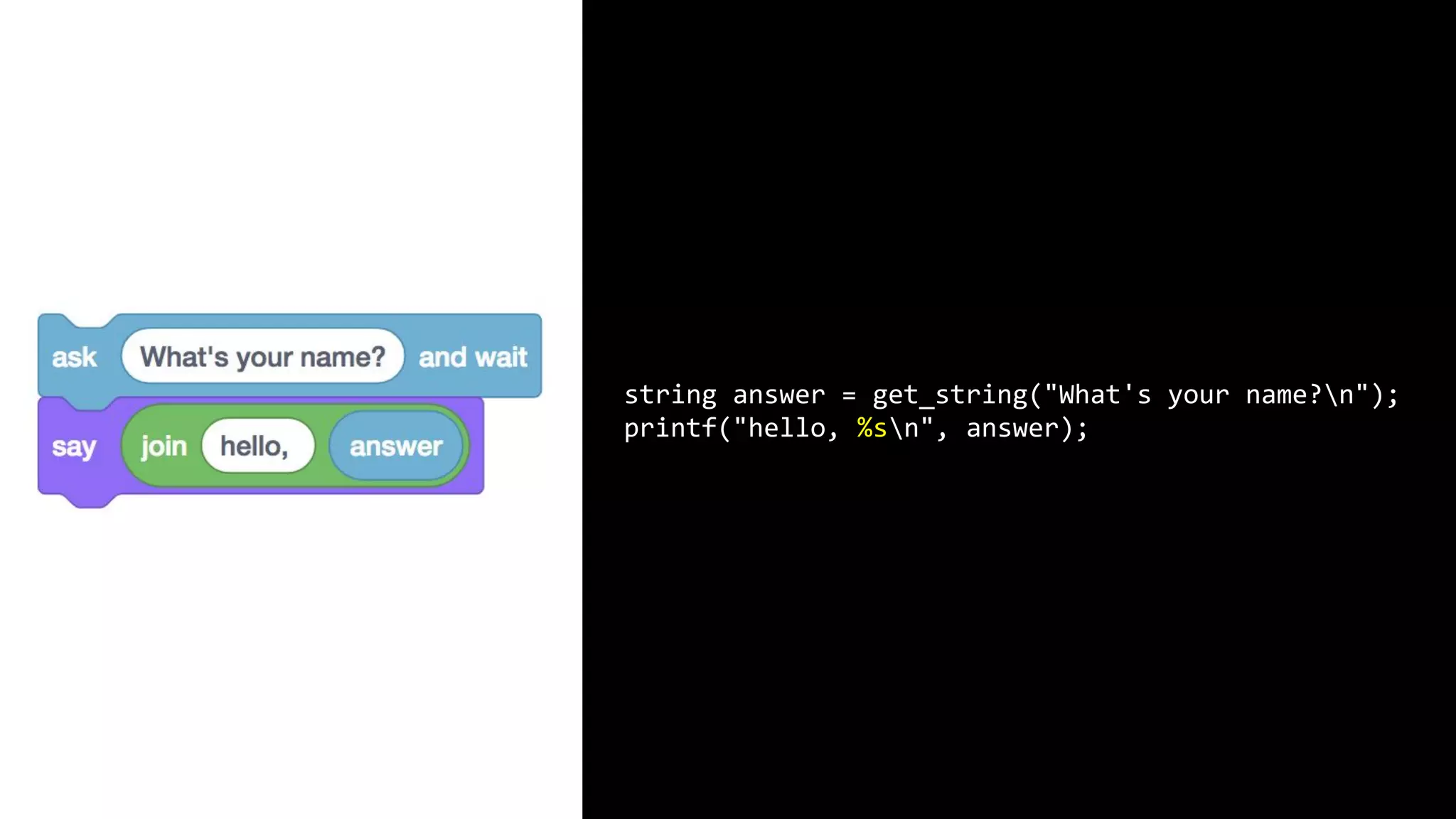
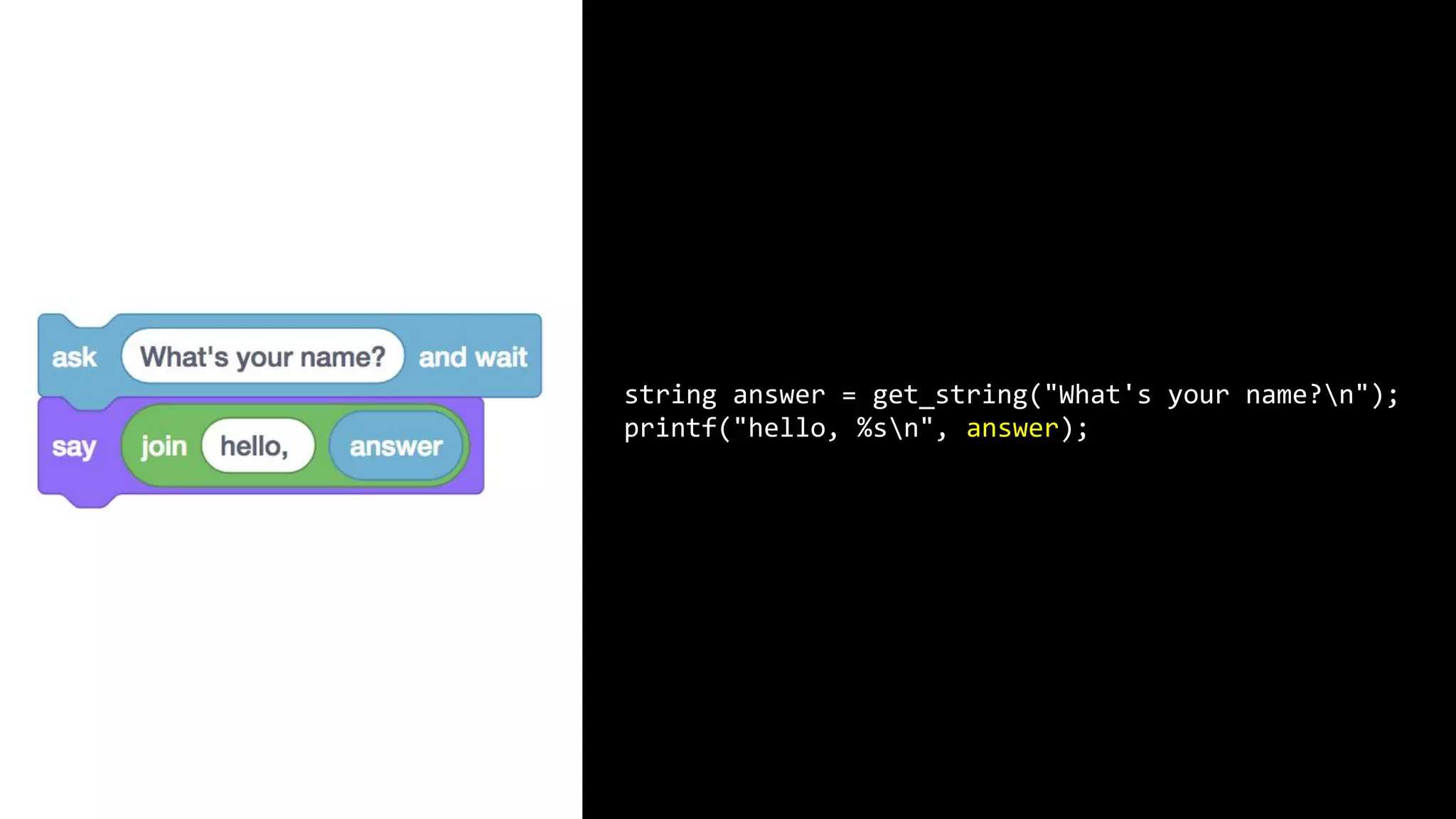
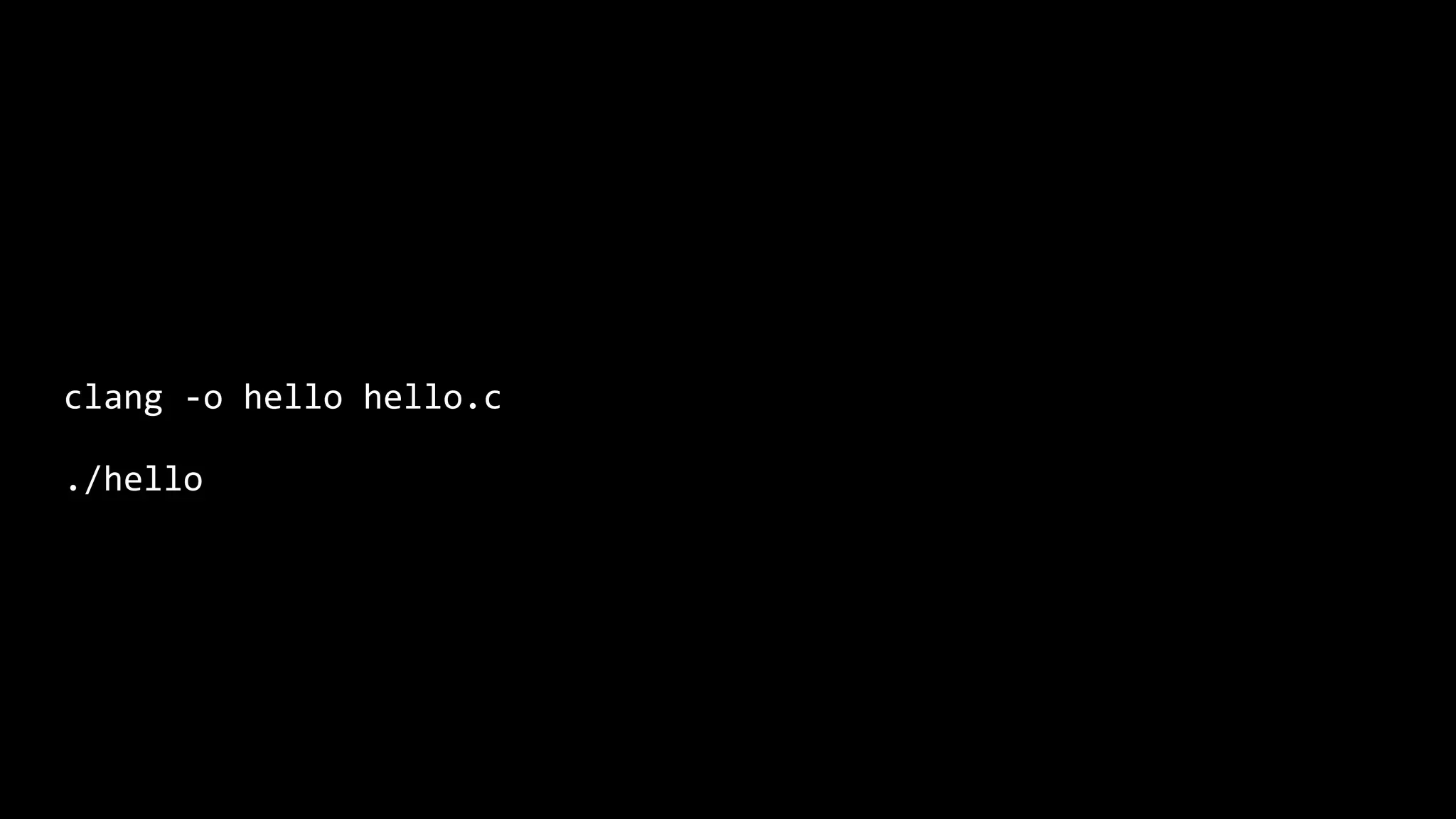
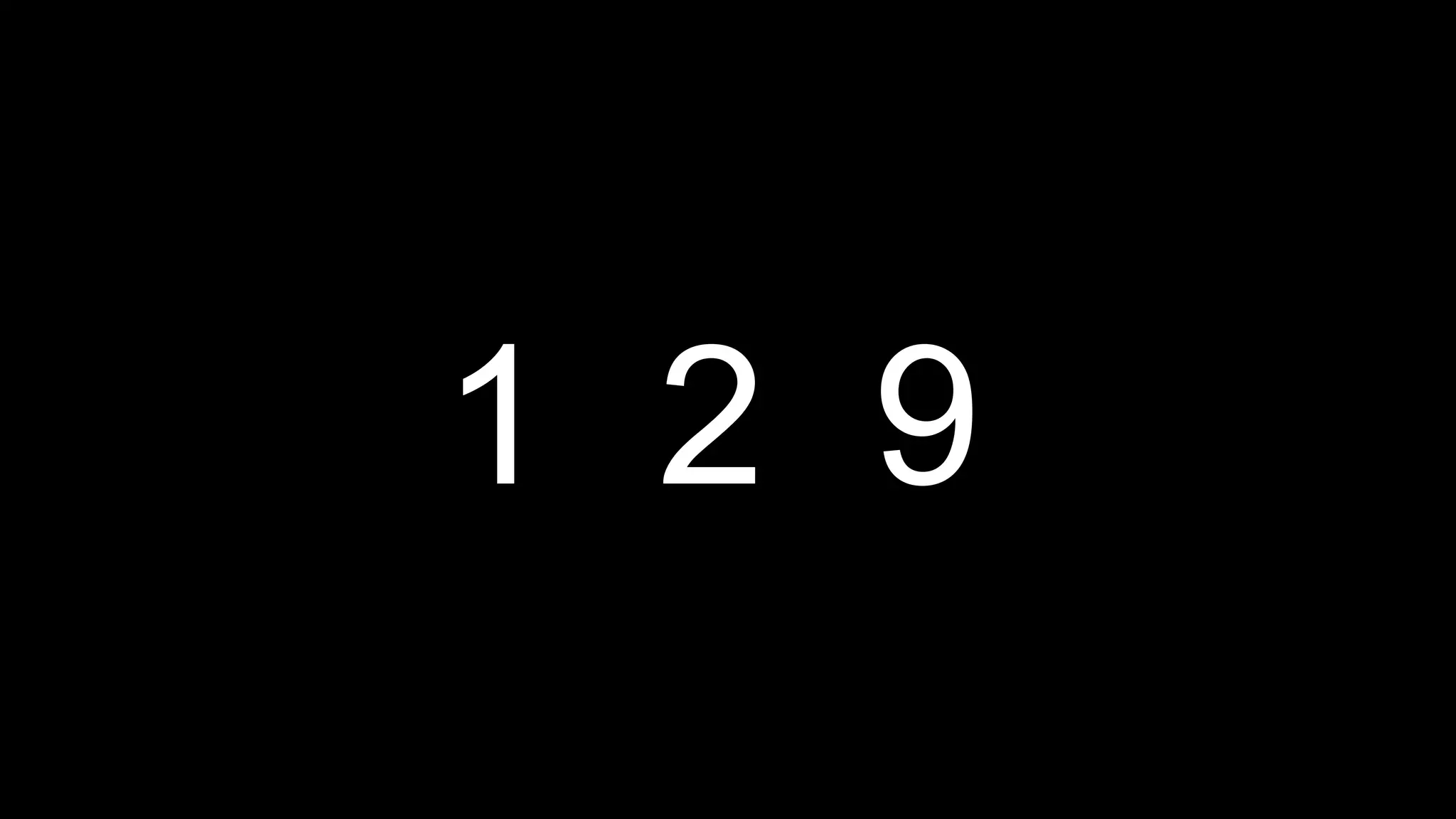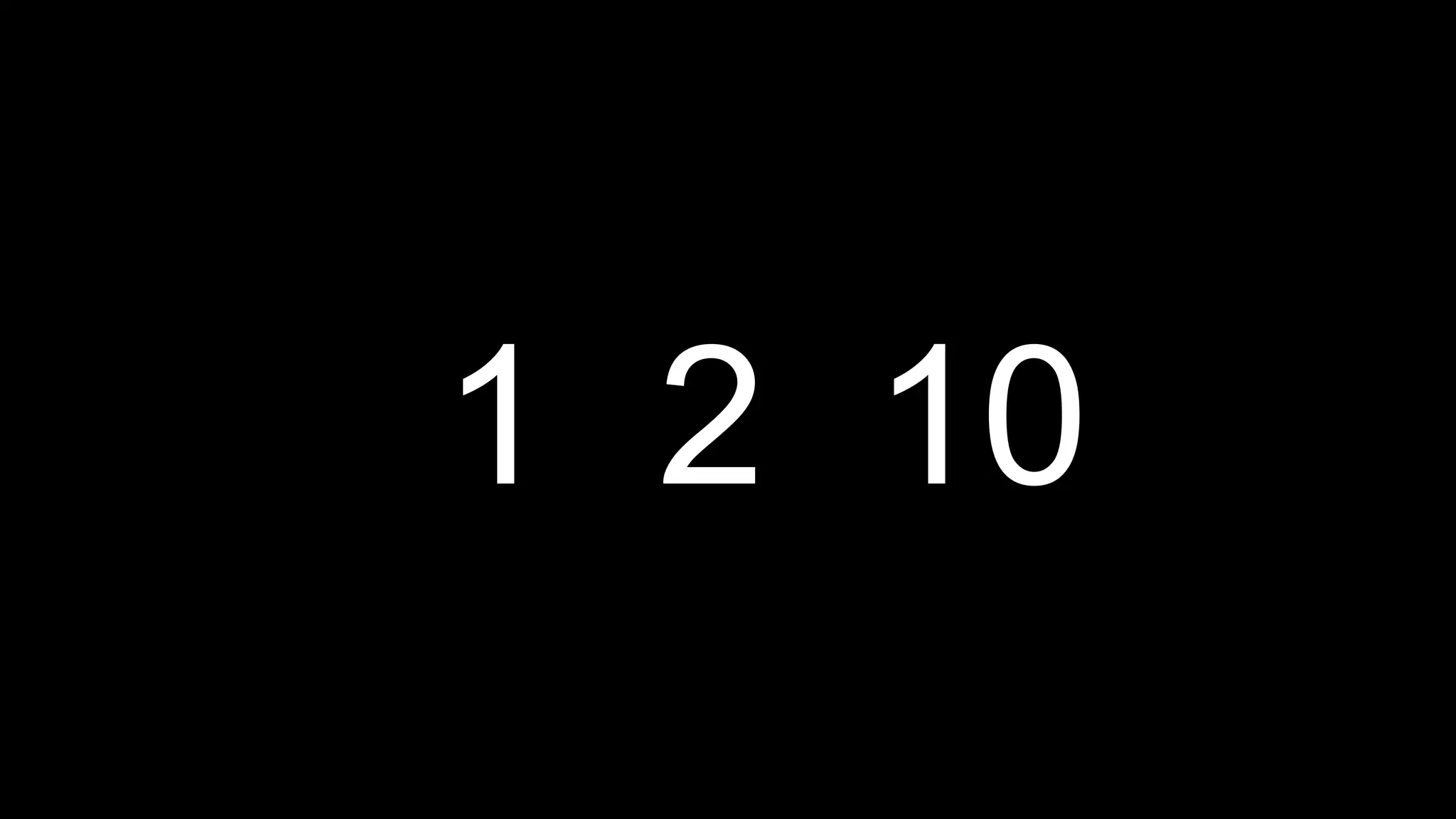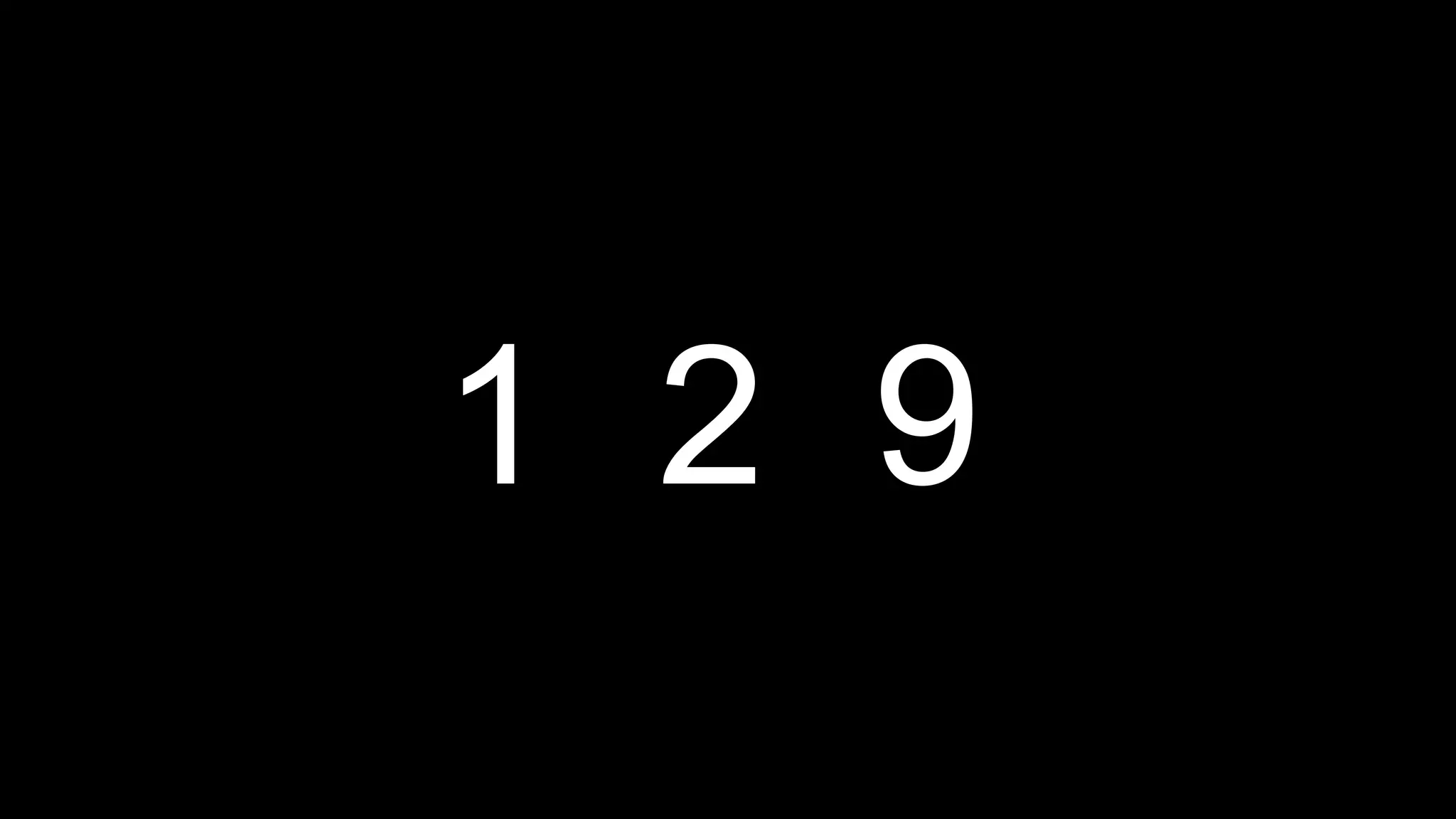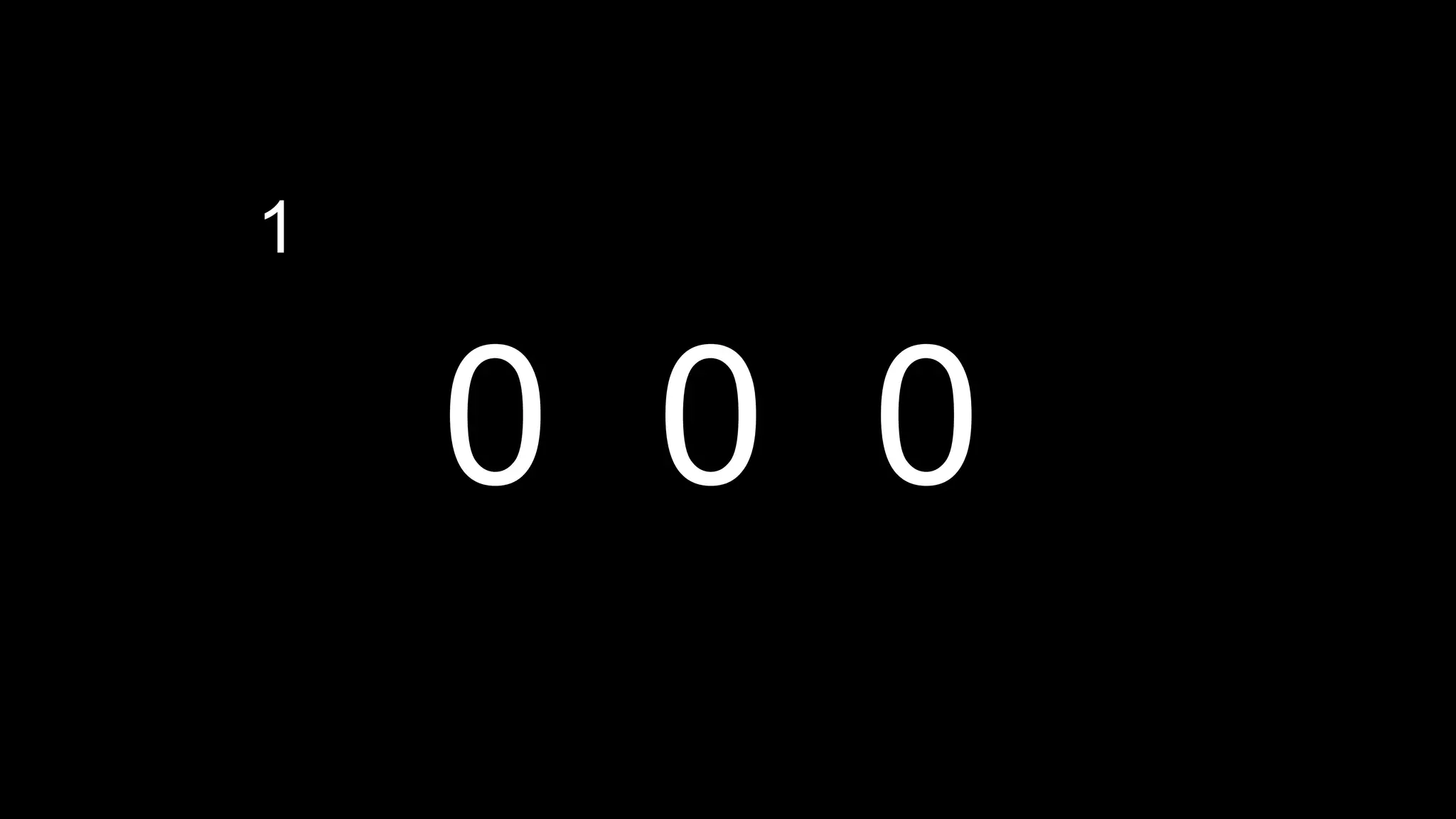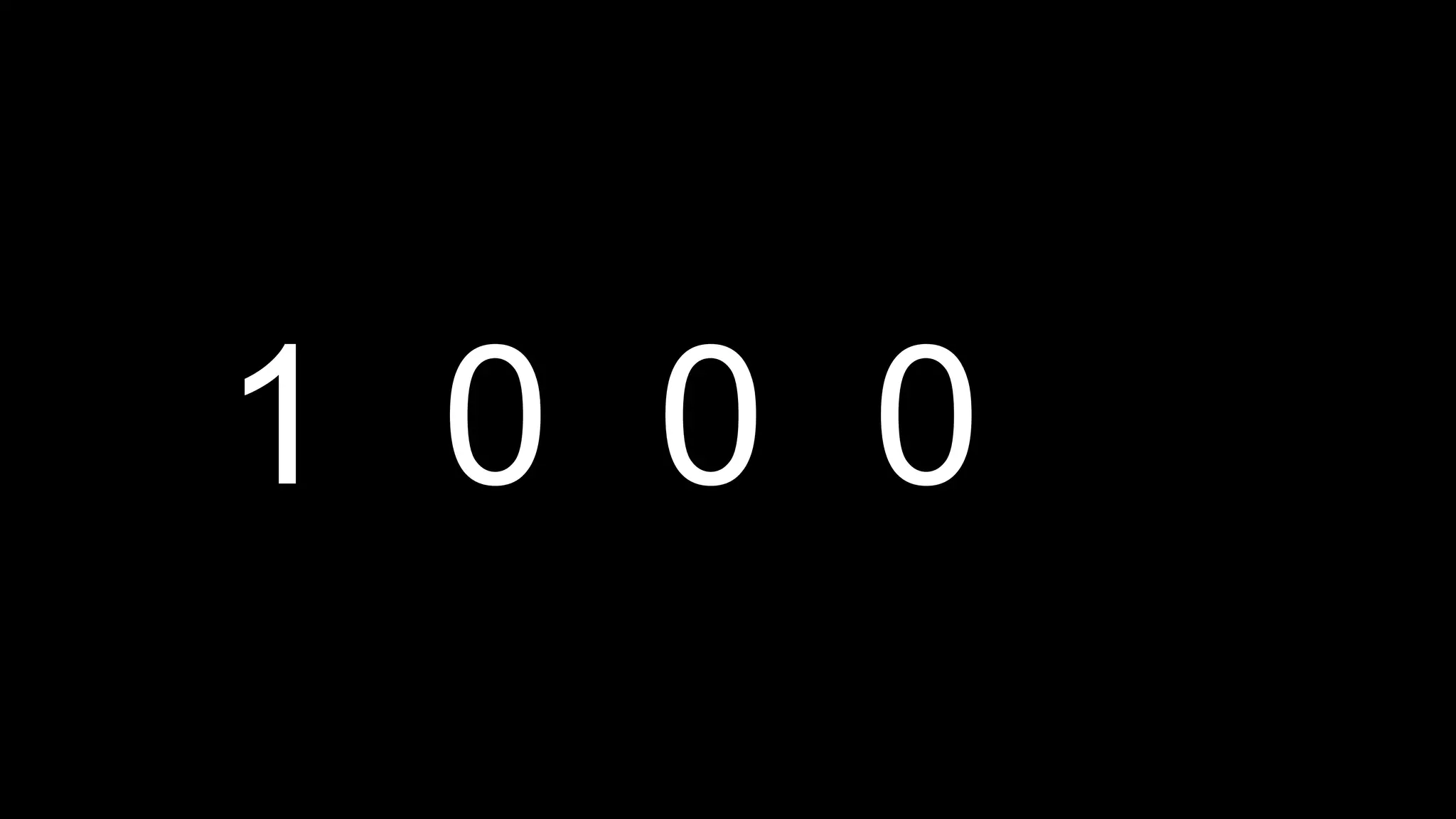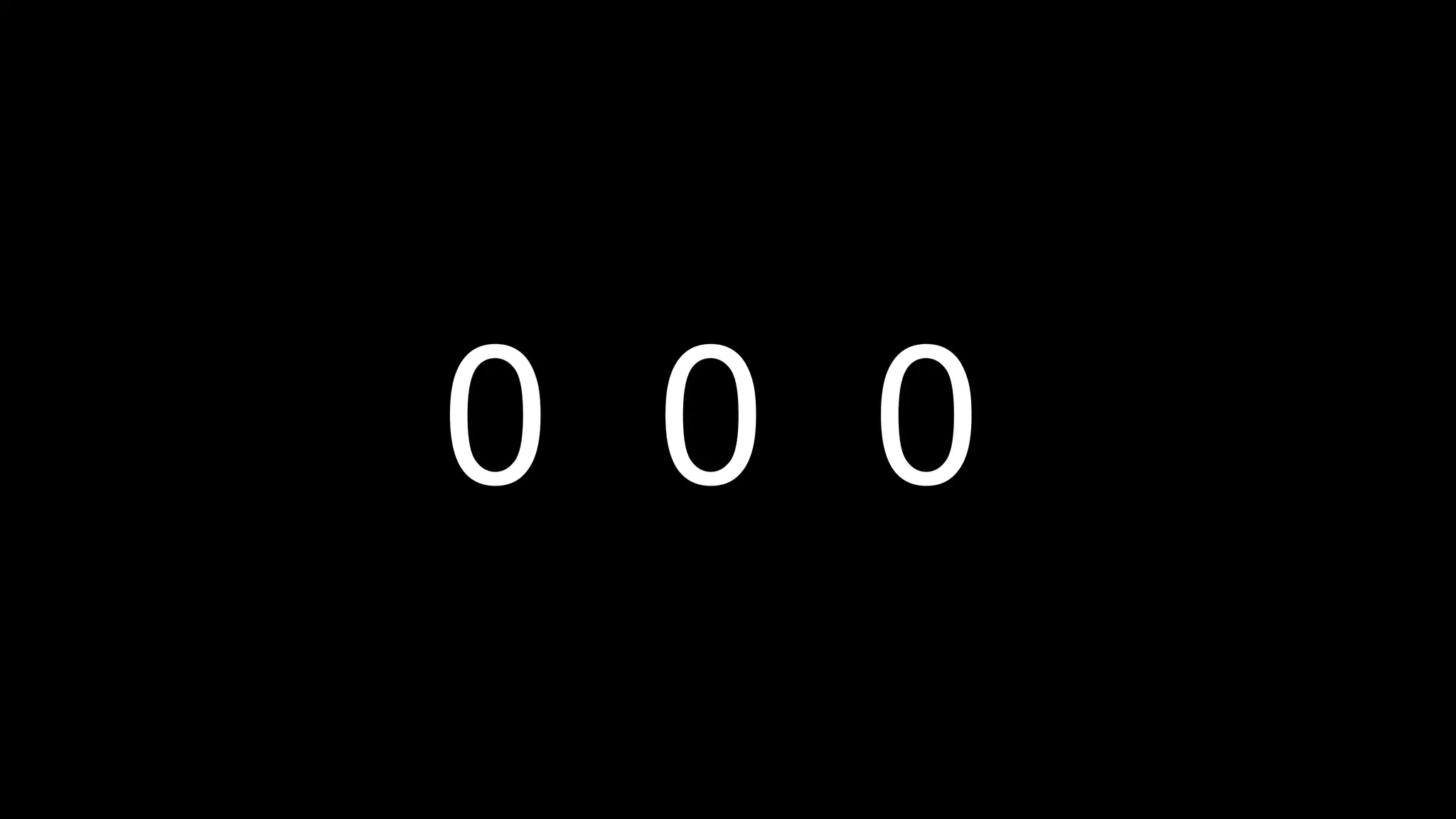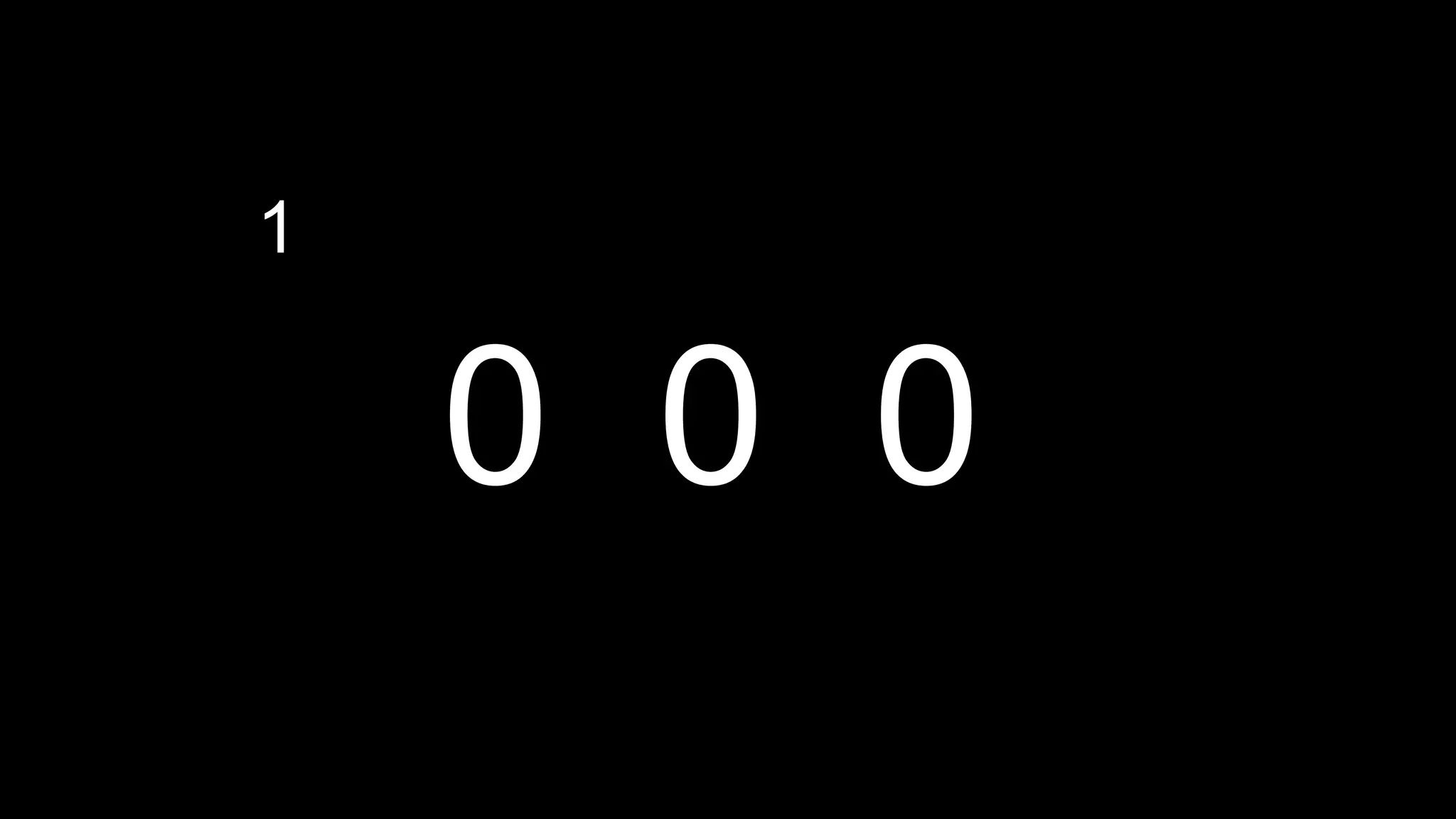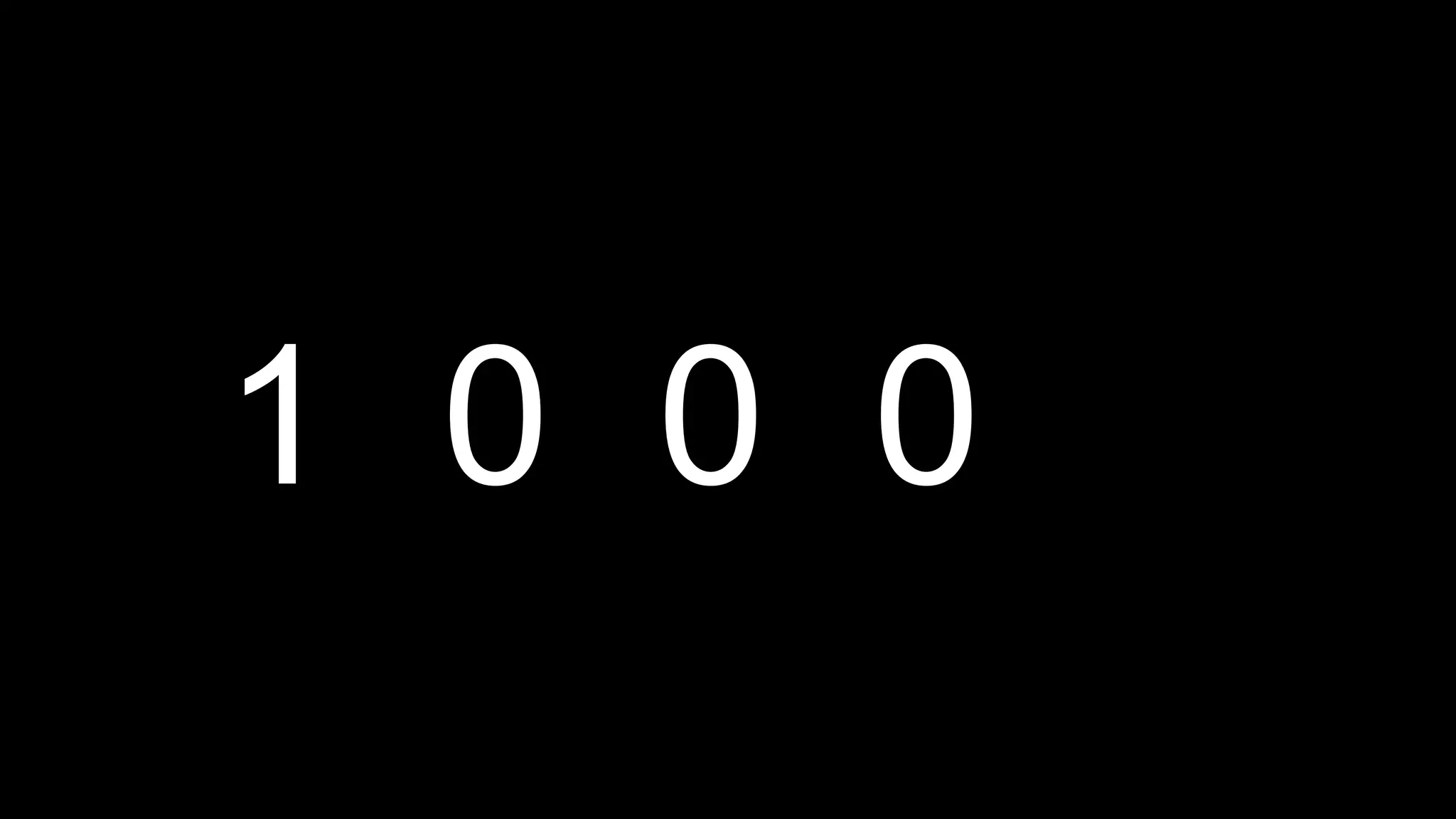This document appears to be a transcript of a CS50 course that covers various computing topics through examples and exercises in C programming language. It introduces concepts like input/output, representation of data in binary, algorithms, conditionals, loops, functions, and debugging techniques. Code snippets are provided throughout to demonstrate different programming constructs.