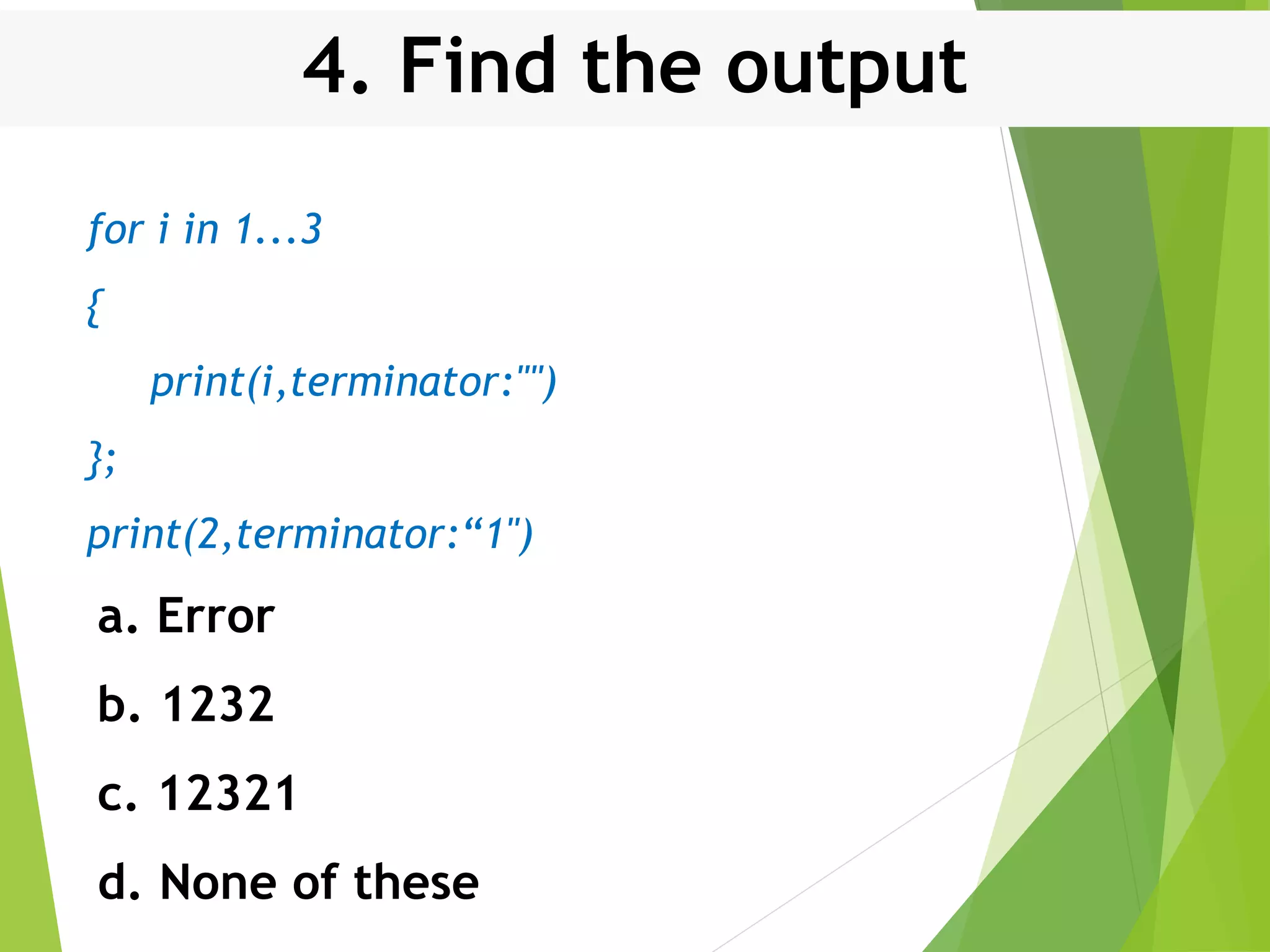
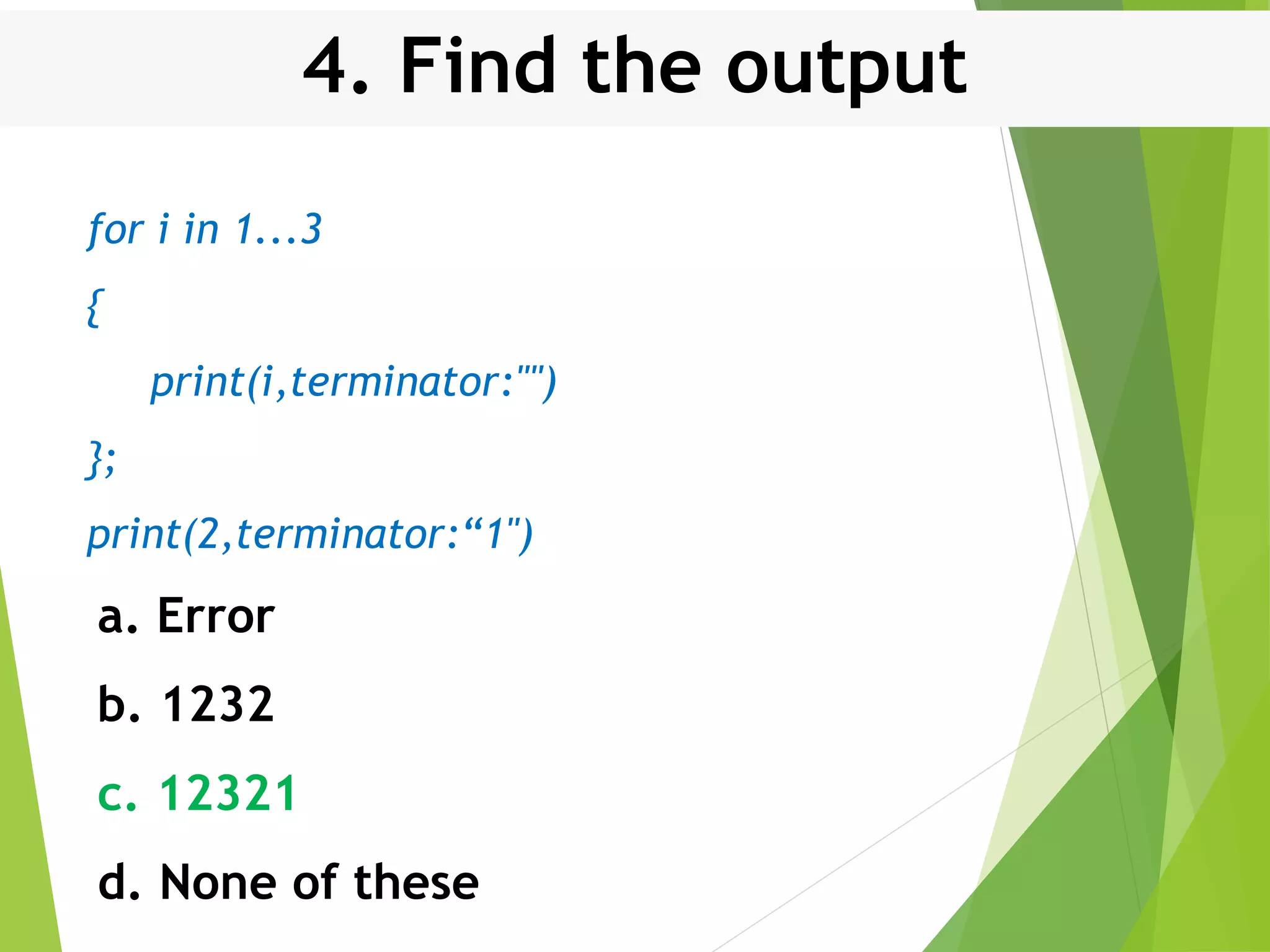
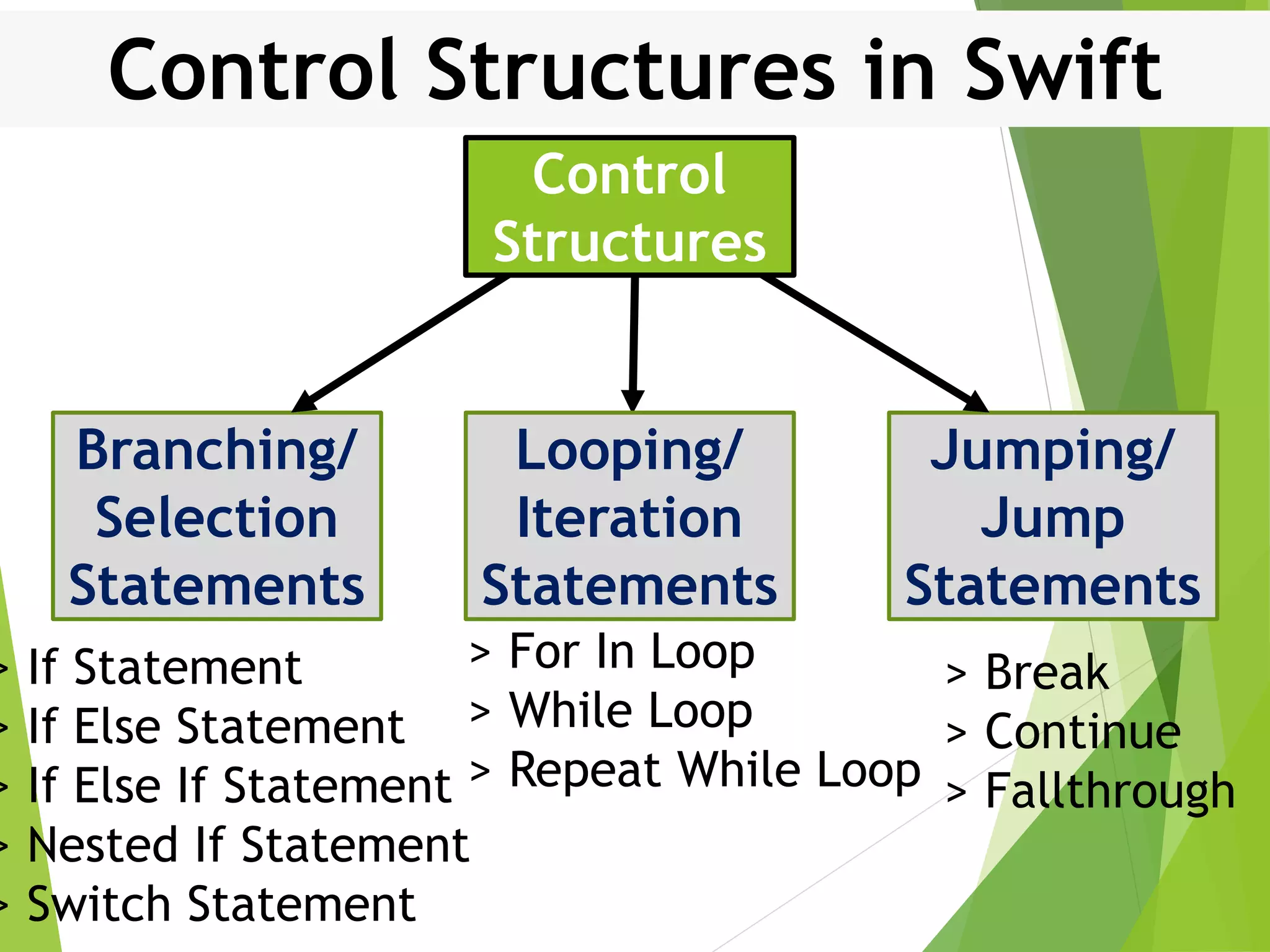
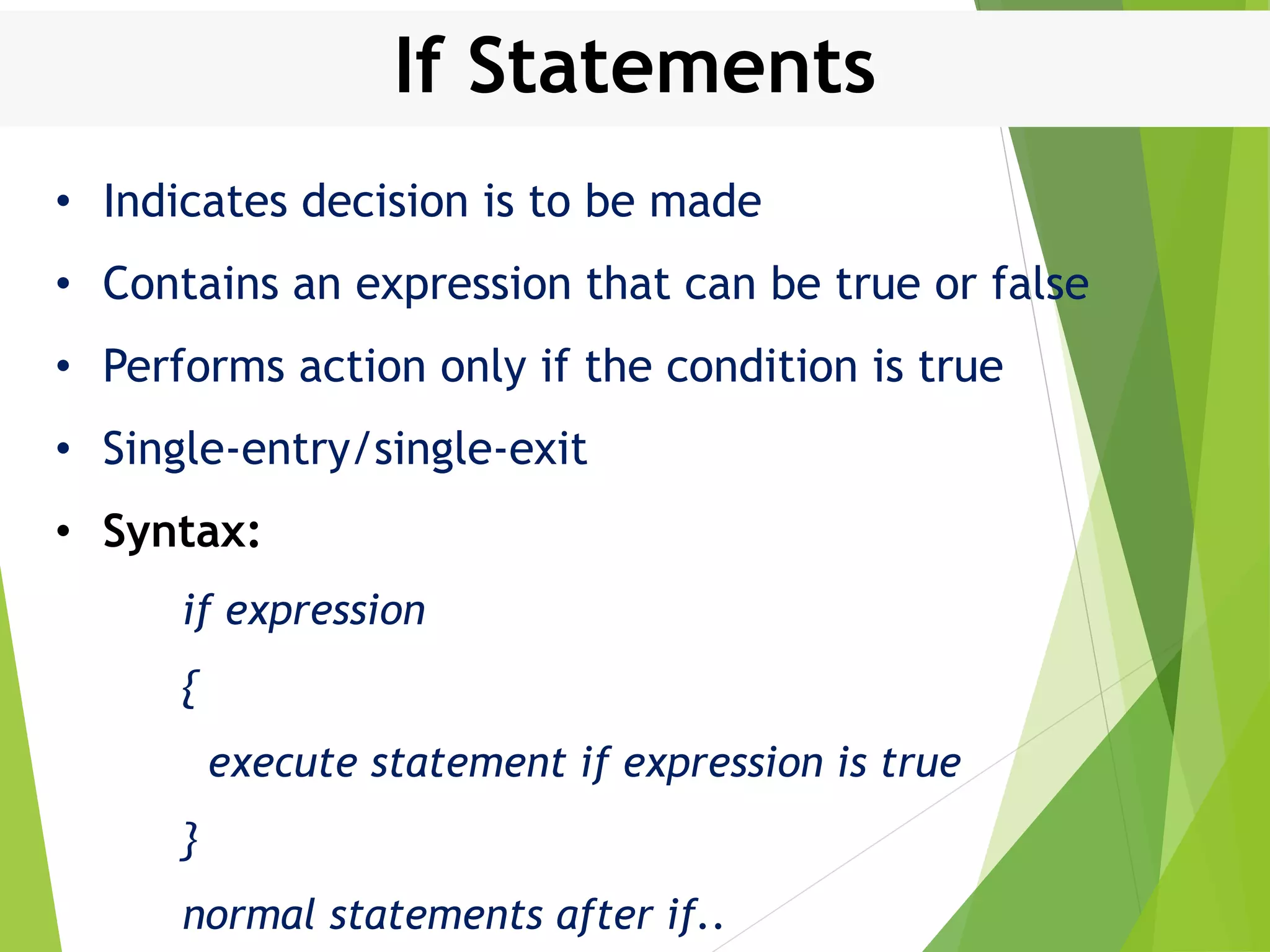
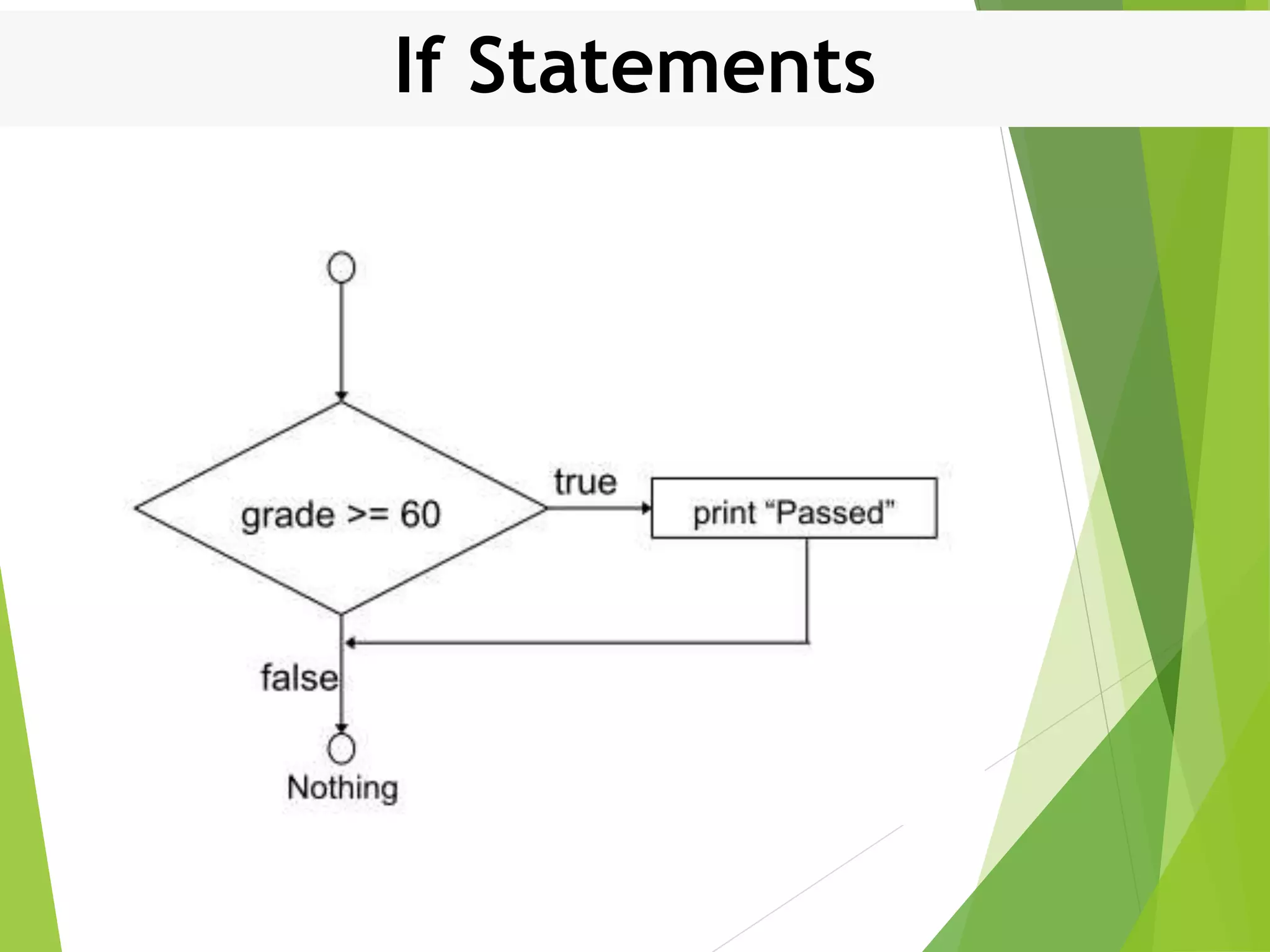
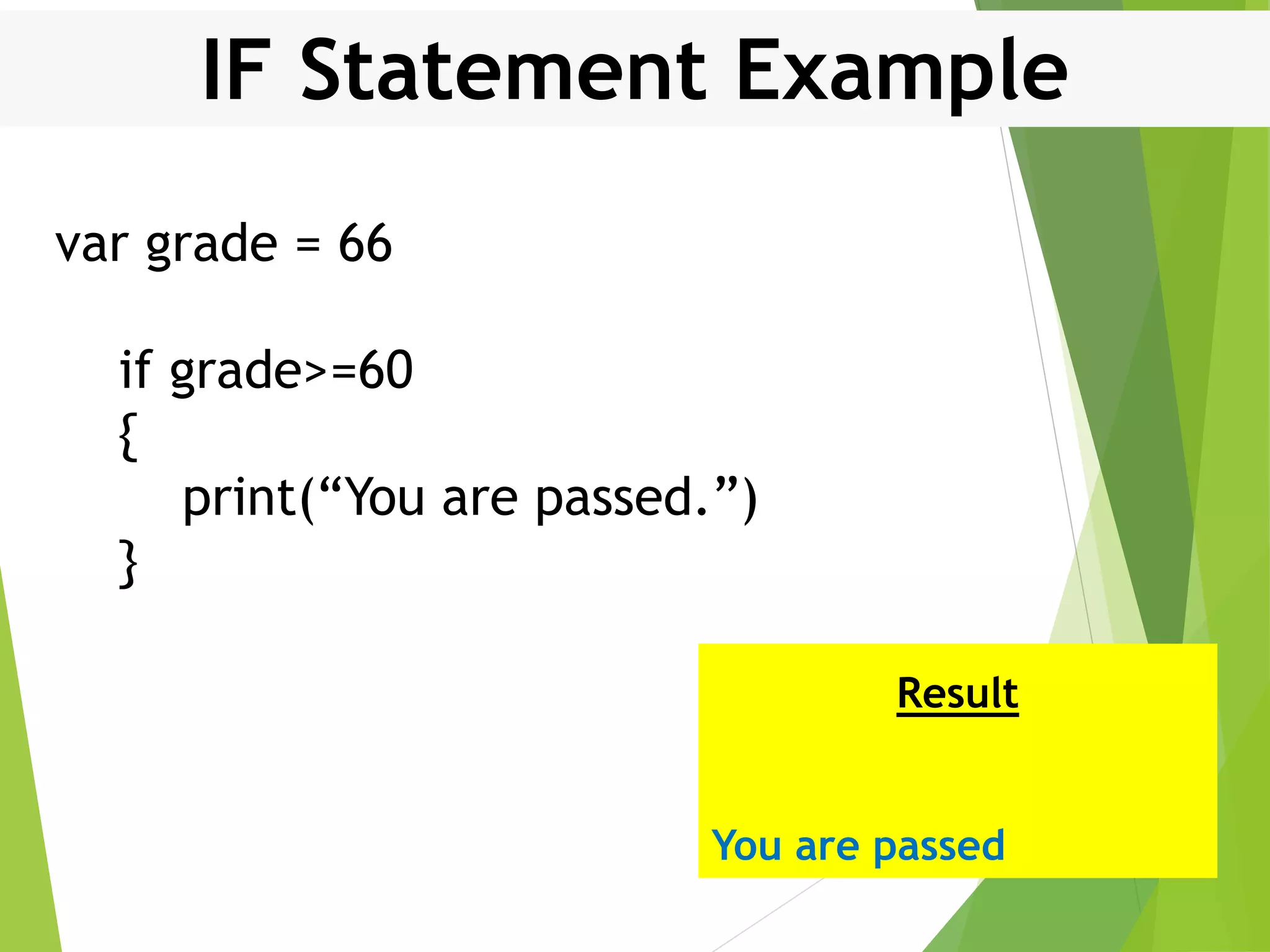
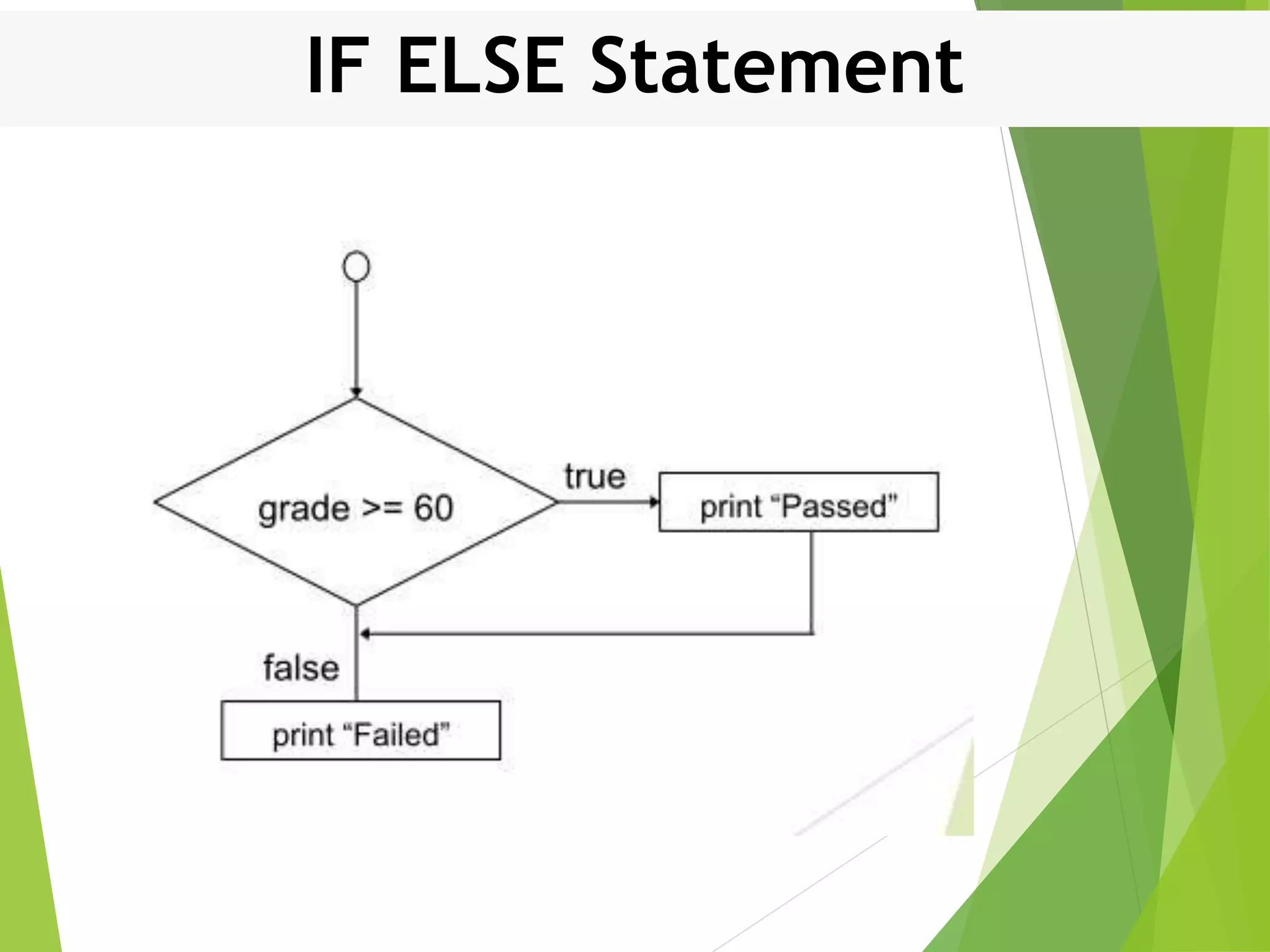
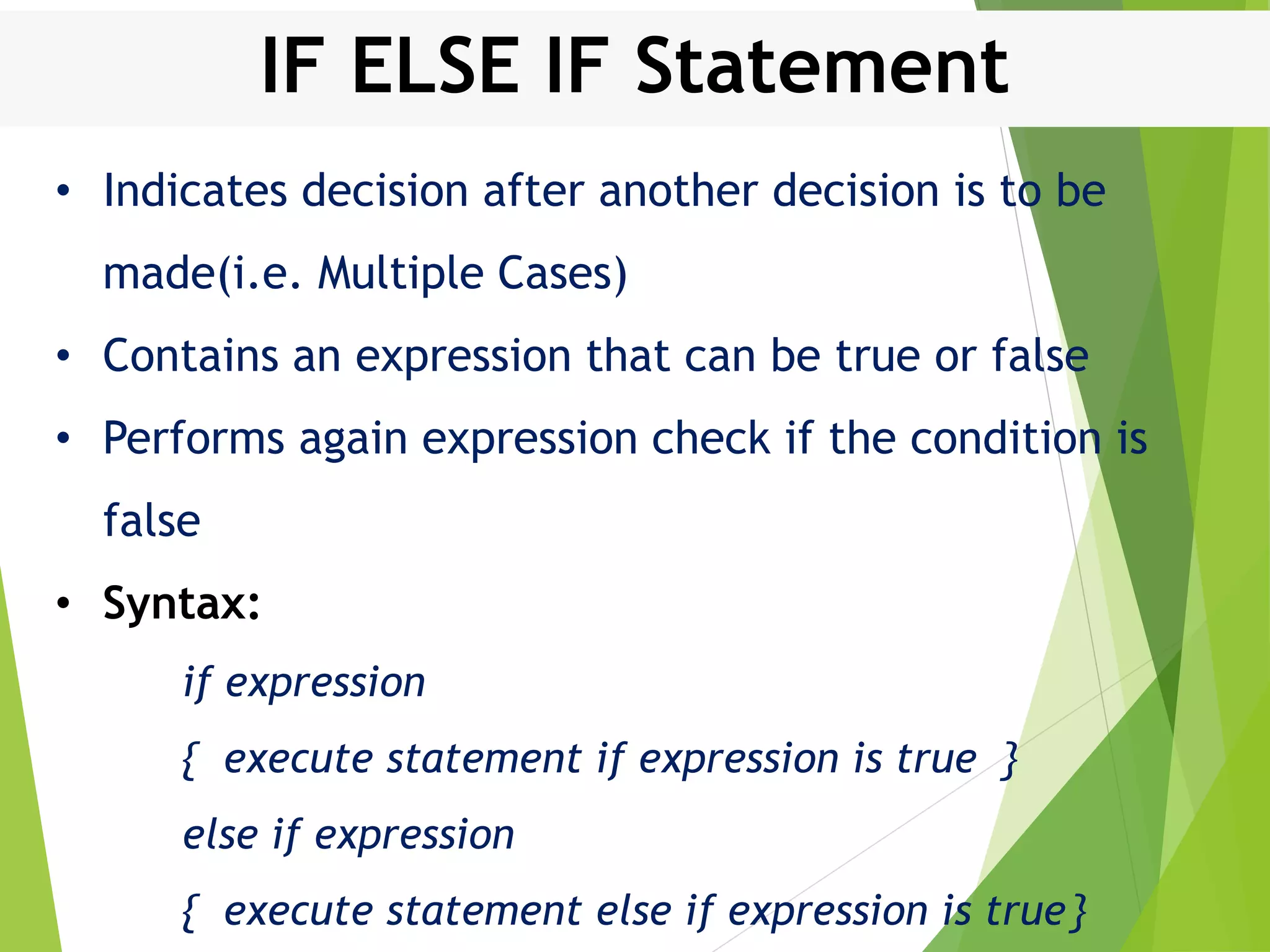
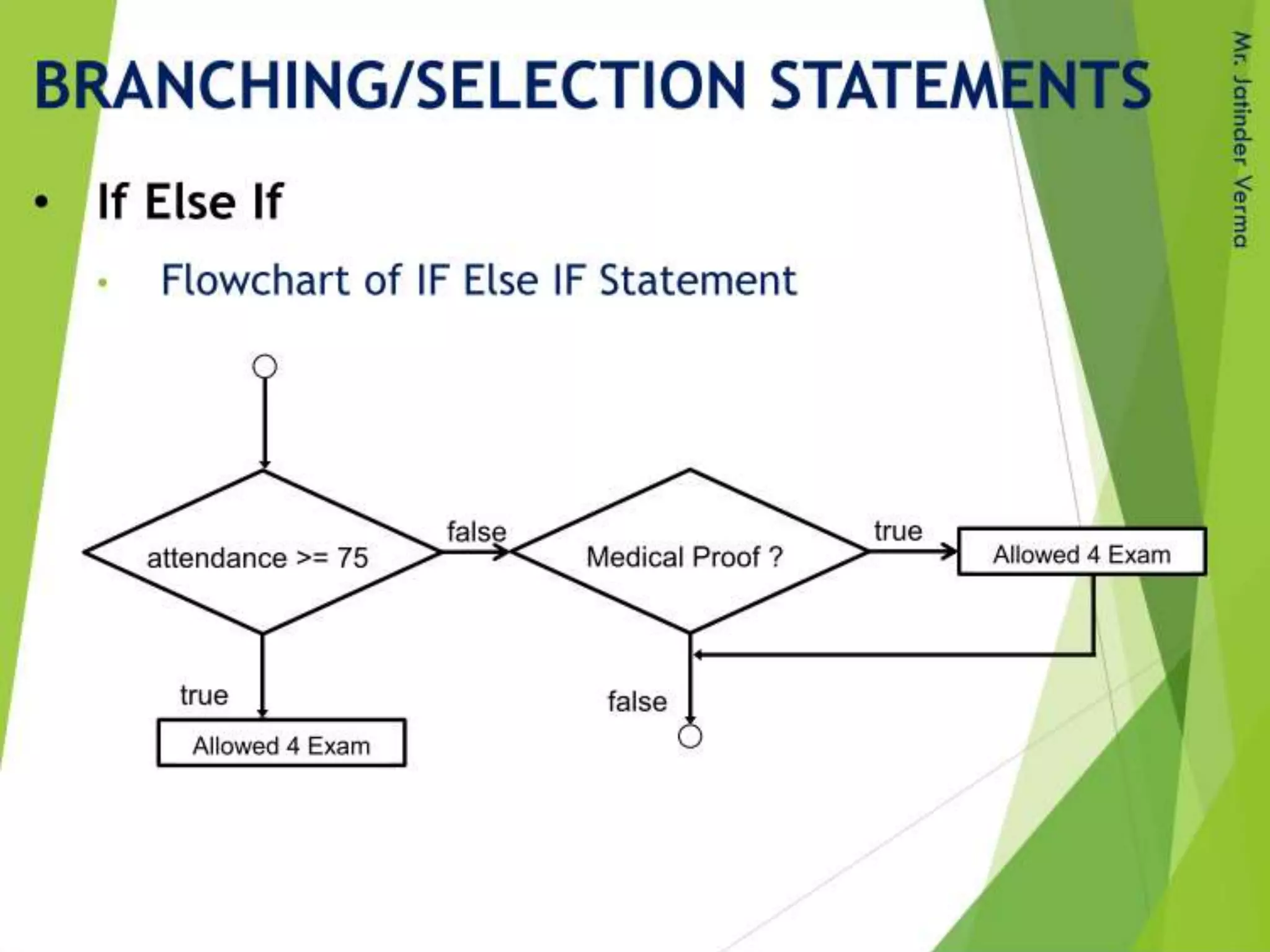
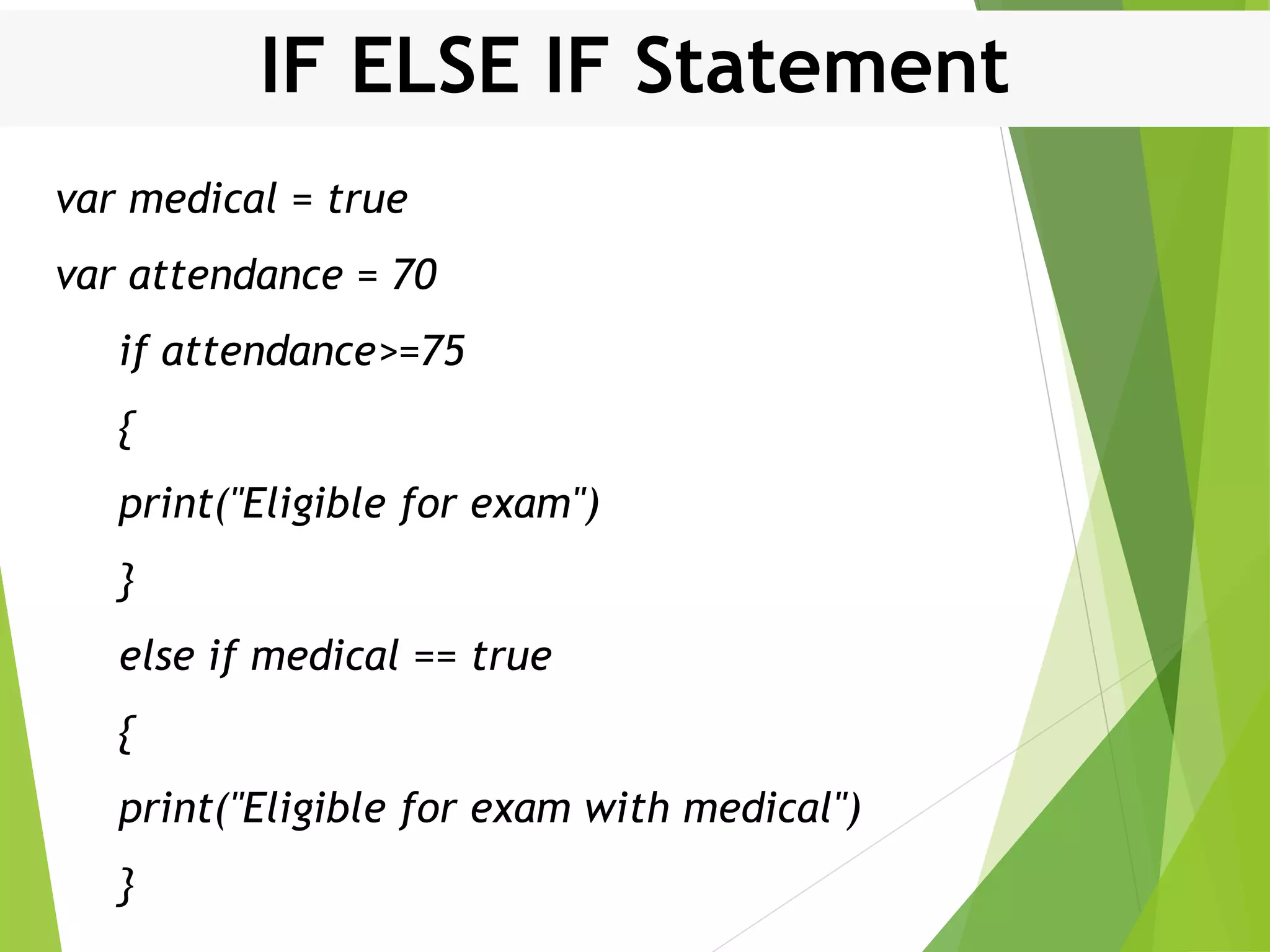
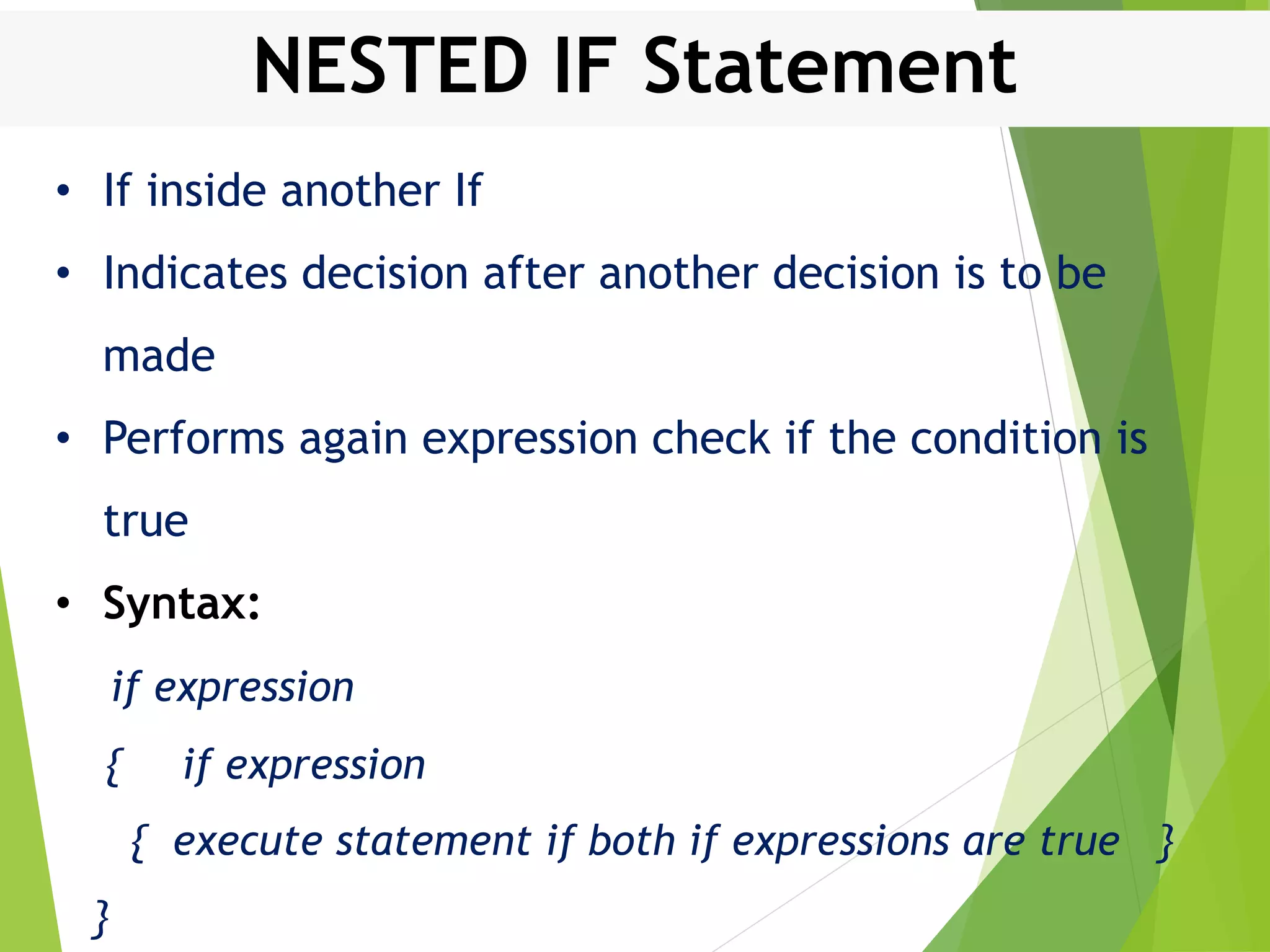
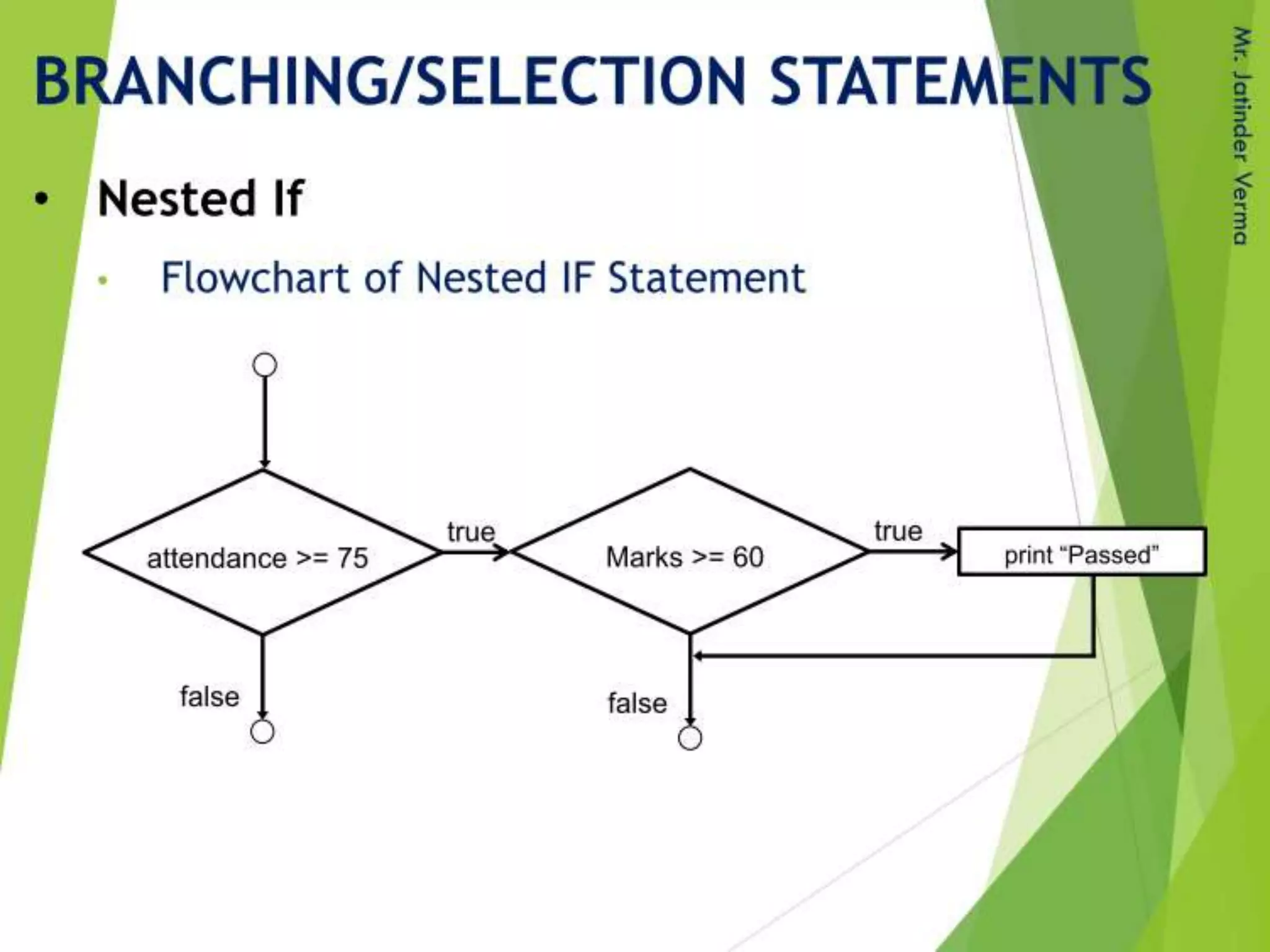
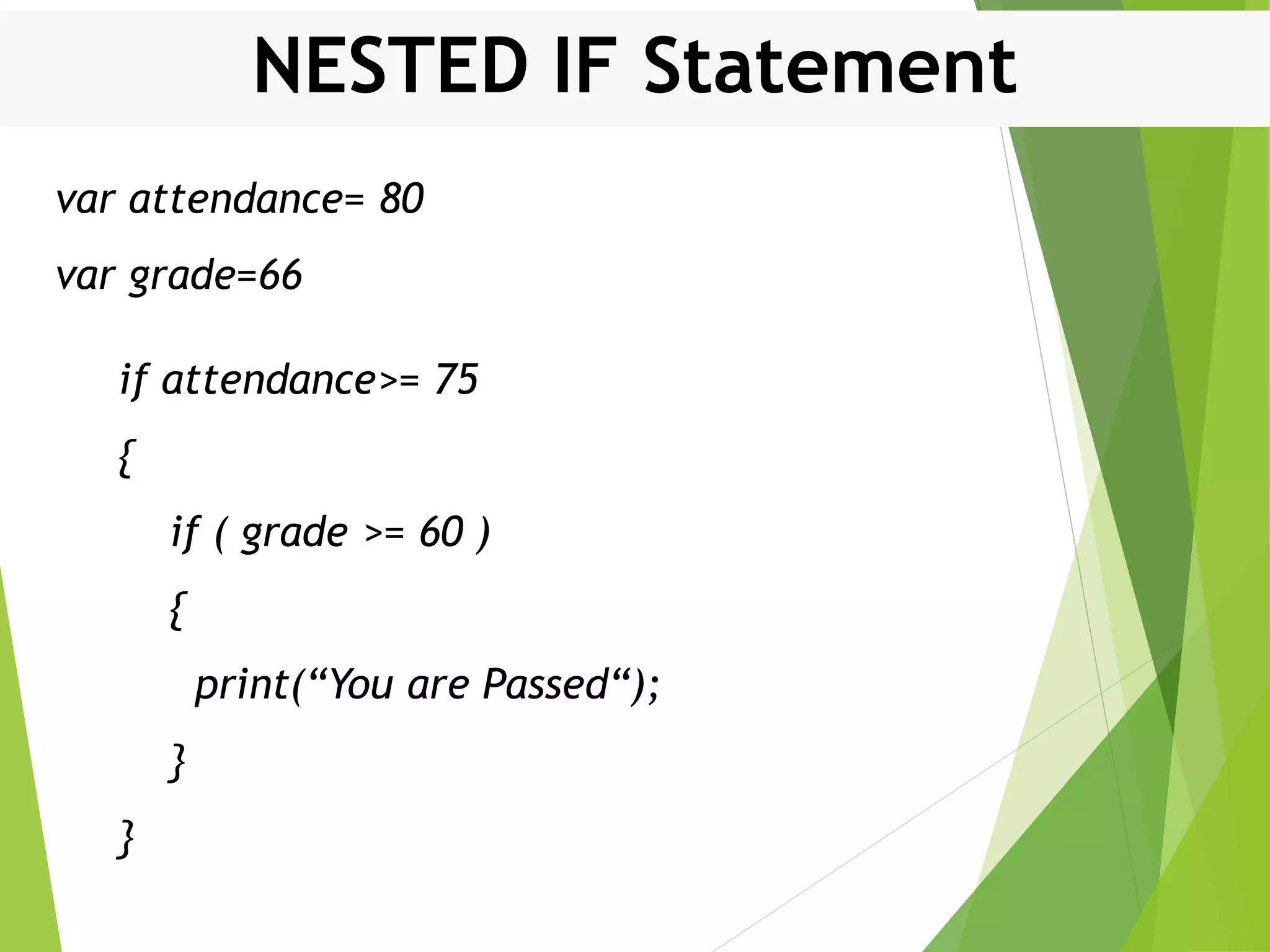
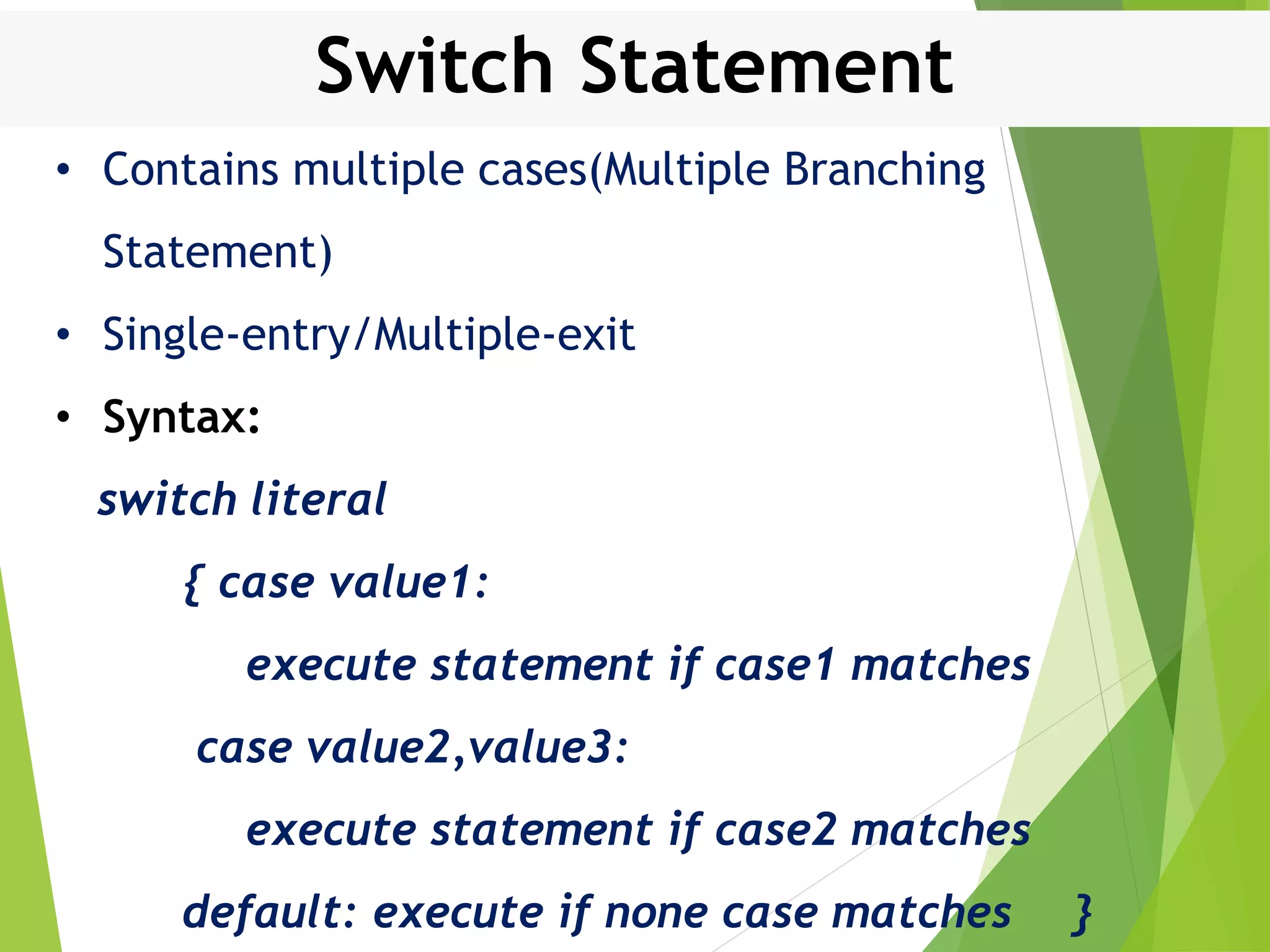
This document discusses control structures in Swift, including branching/selection statements like if, else if, switch statements; looping/iteration statements like for-in, while, repeat-while loops; and jumping statements like break, continue. It provides examples of how to use each statement type and explains their syntax and usage. Key control structures covered are if/else, switch, for-in, while and repeat-while loops, and the break, continue, and fallthrough statements.


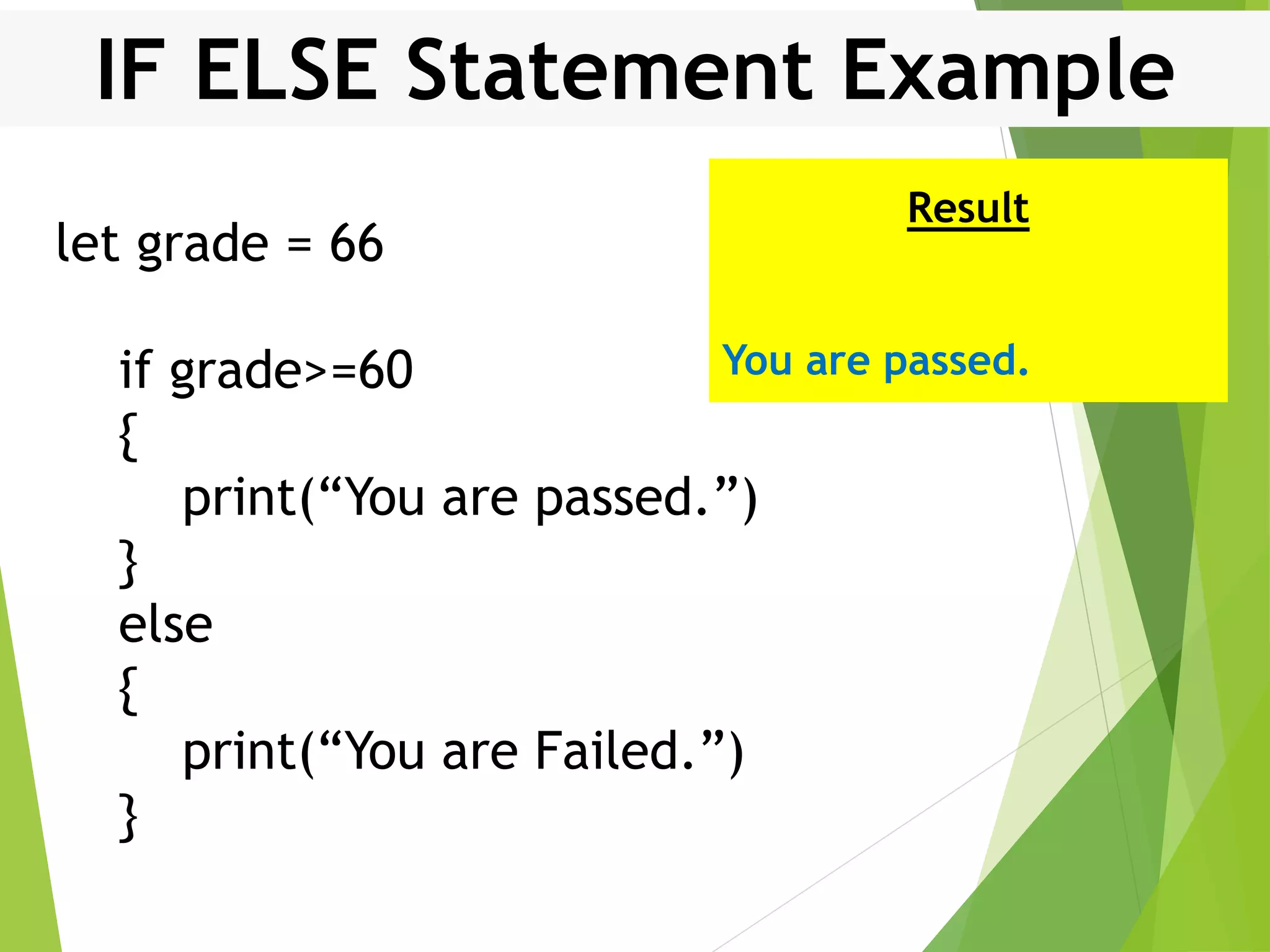
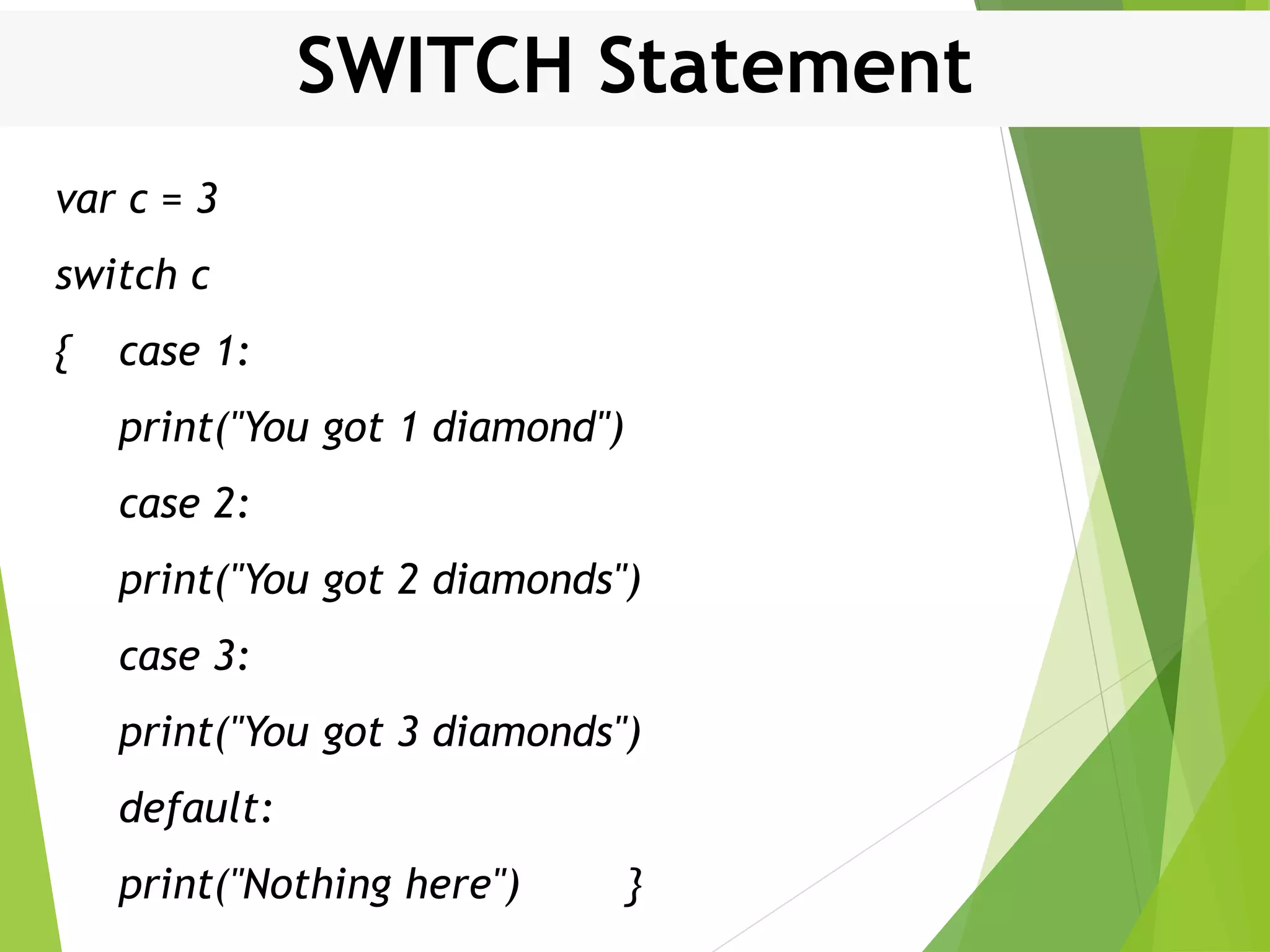
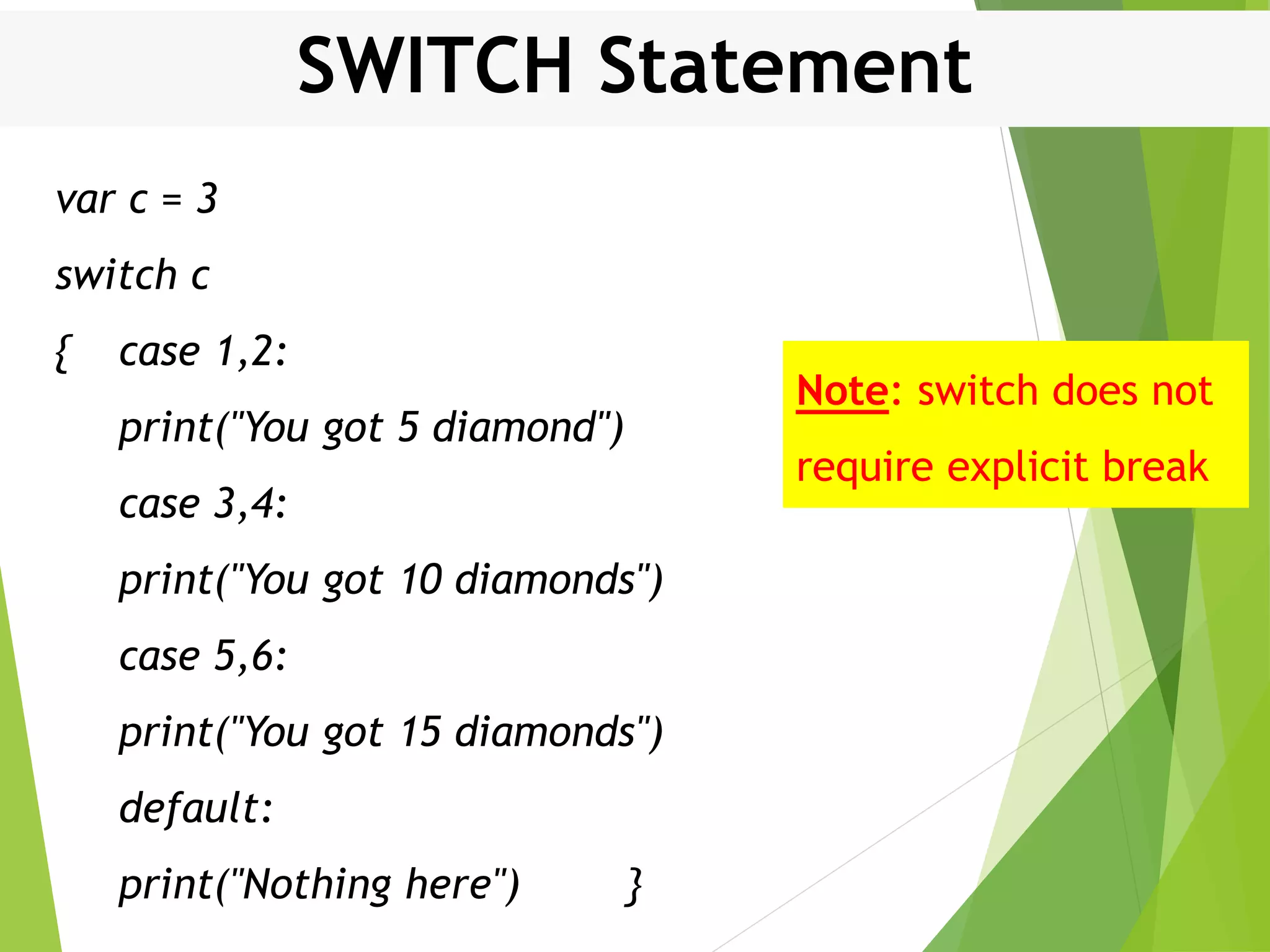
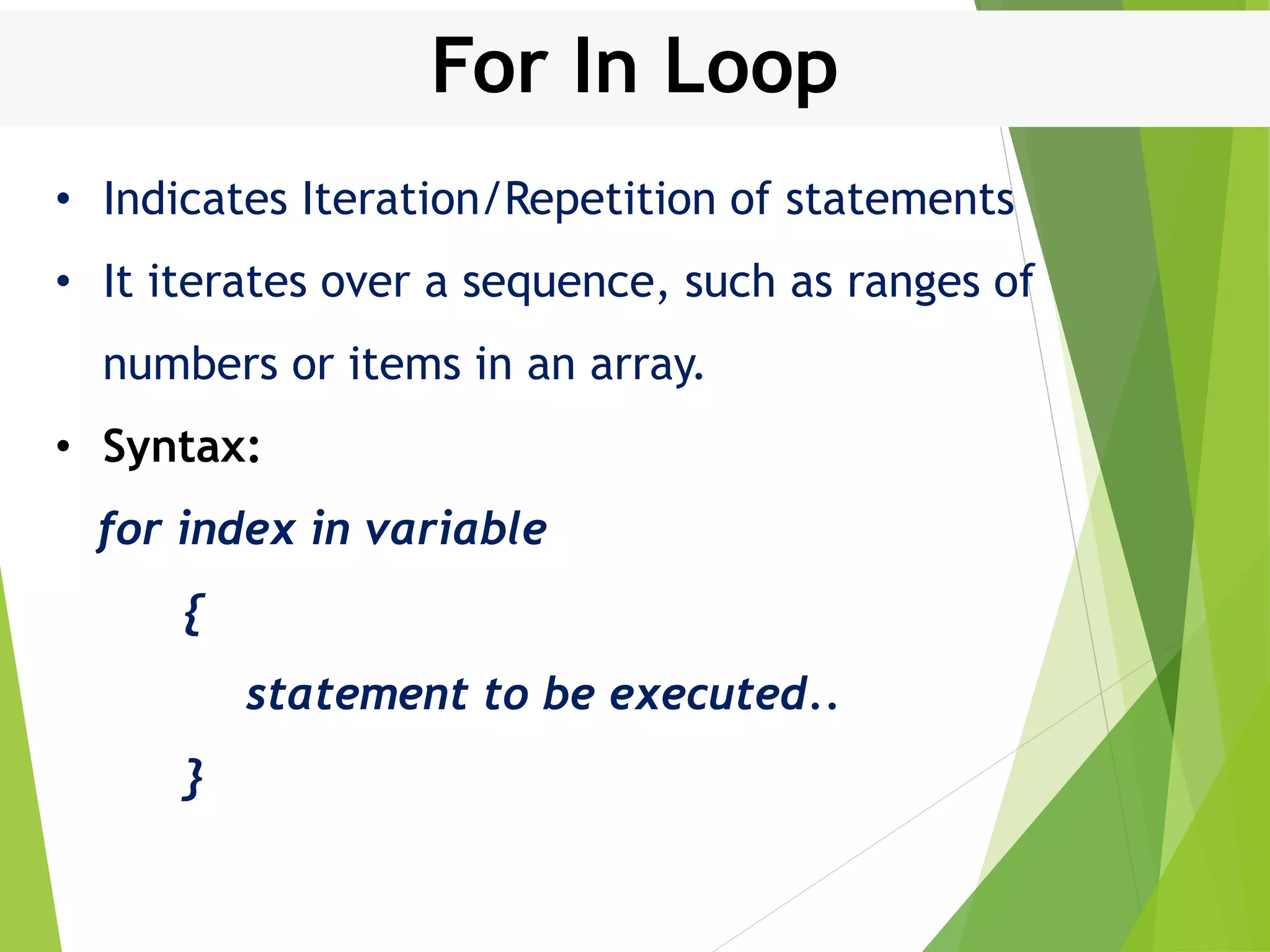
![For In Loop Example var arr:[Int] = [10, 20, 30, 40] for i in arr { print("Value of i is (i)") } Result Value of i is 10 Value of i is 20 Value of i is 30 Value of i is 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlstructures-200515133813/75/Control-structures-IN-SWIFT-21-2048.jpg)