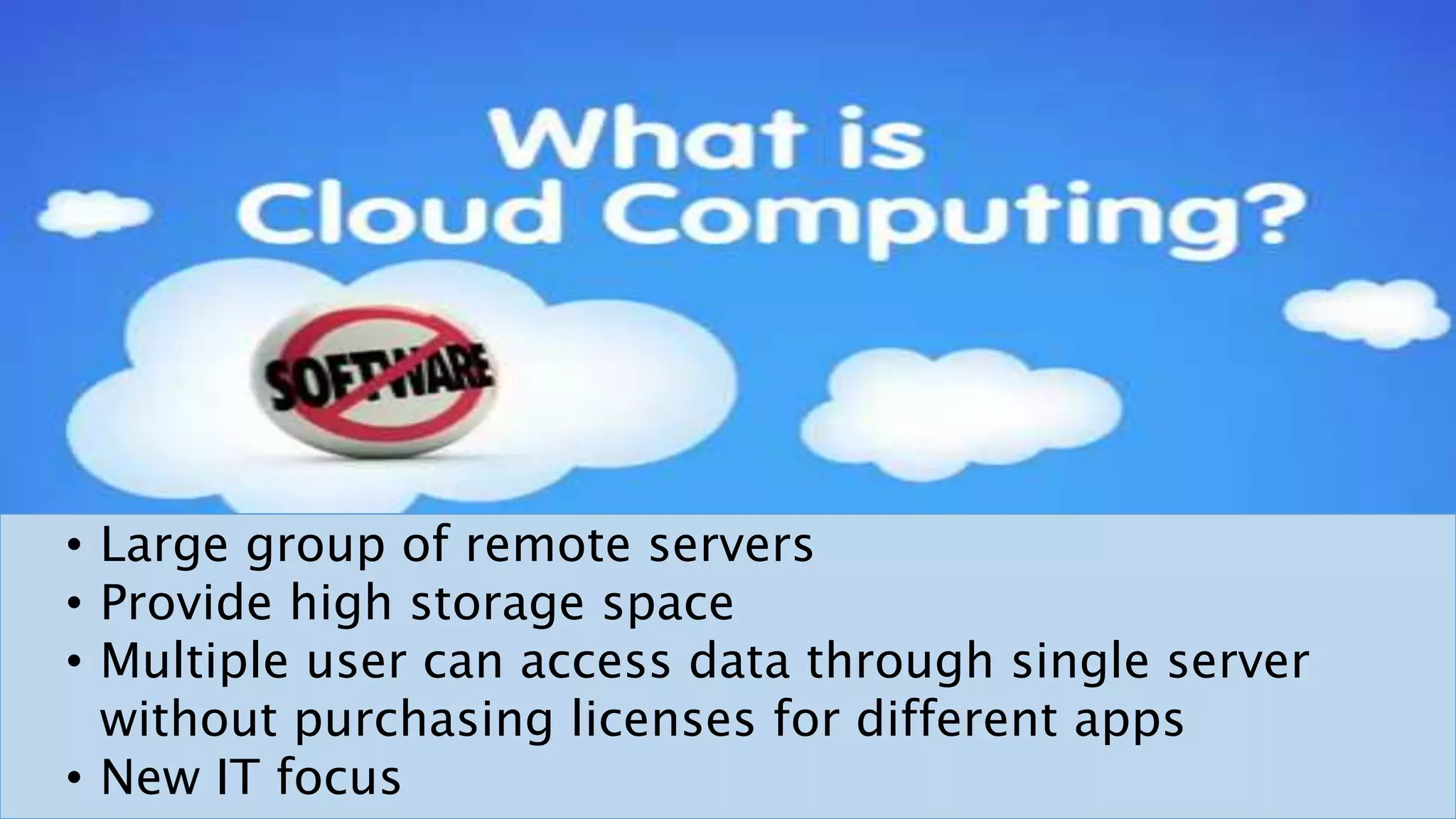
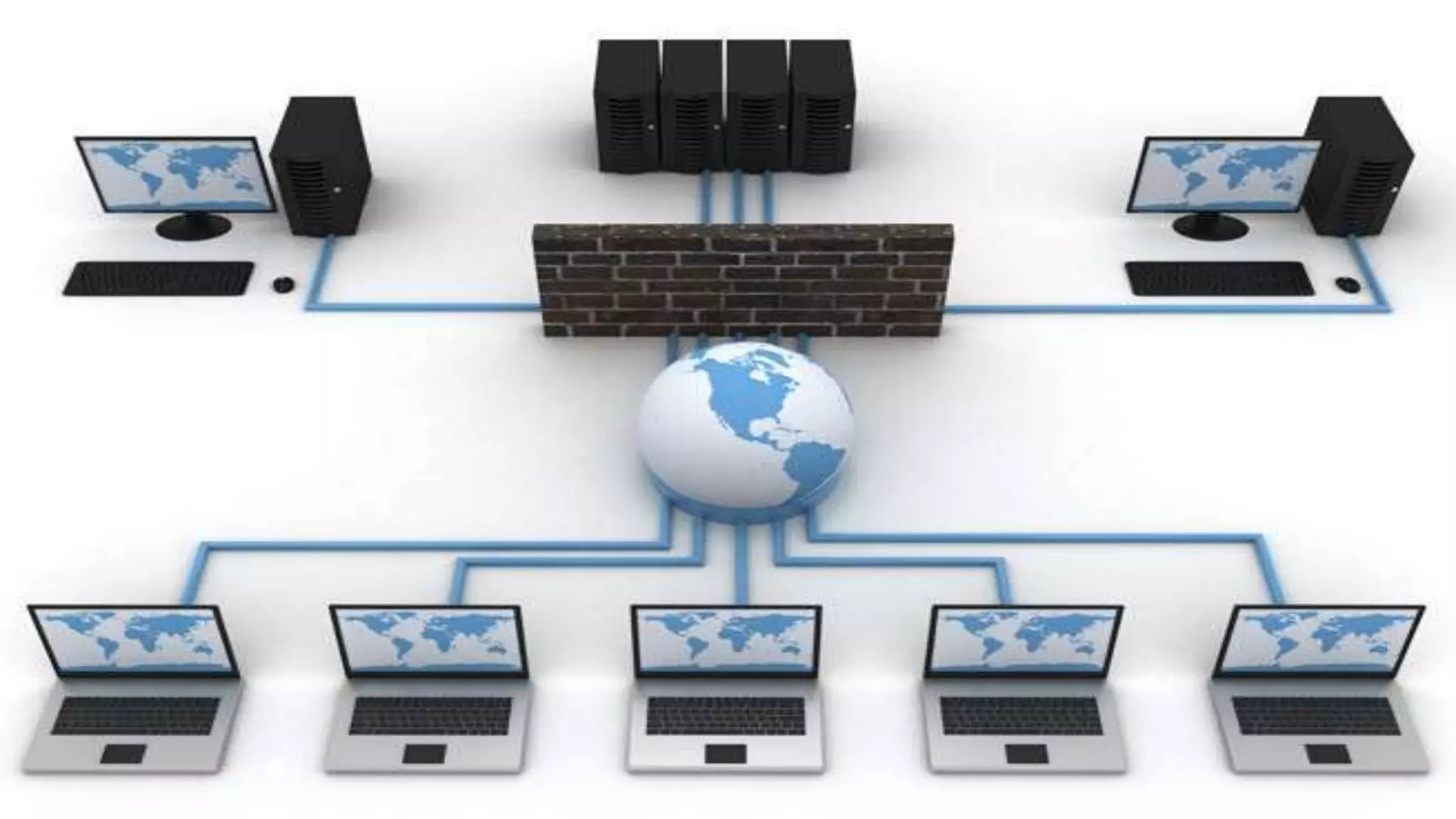
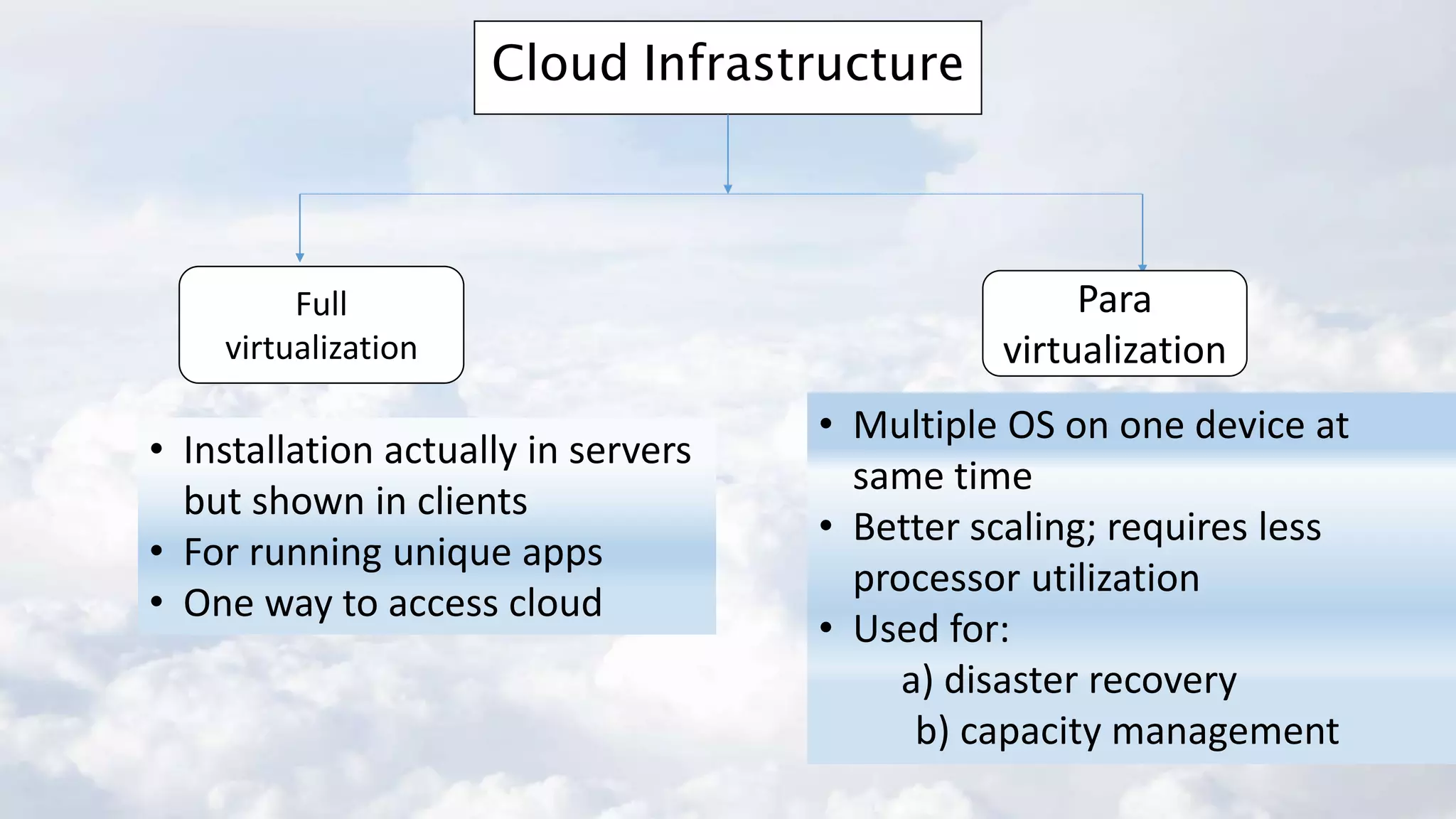
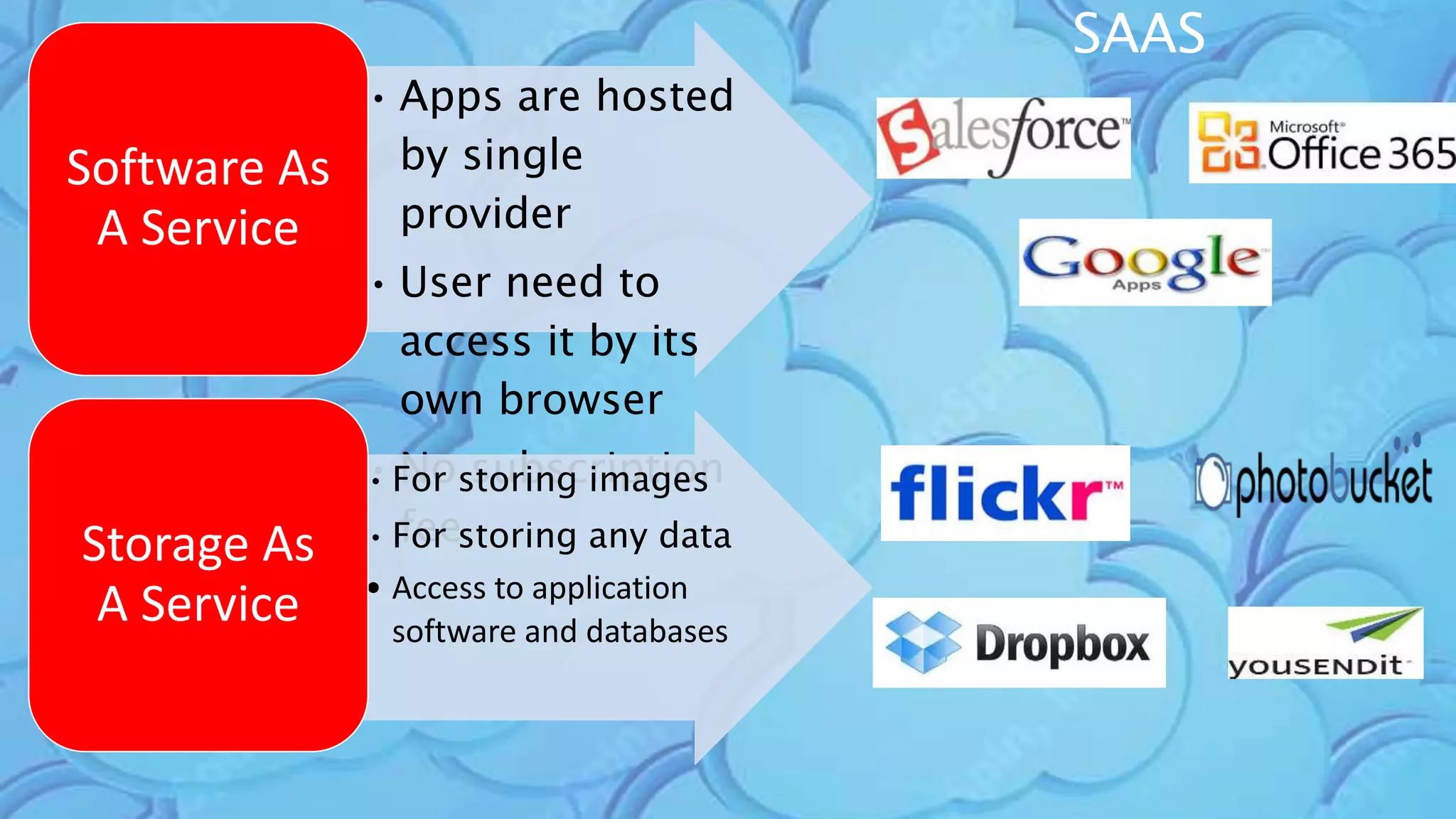
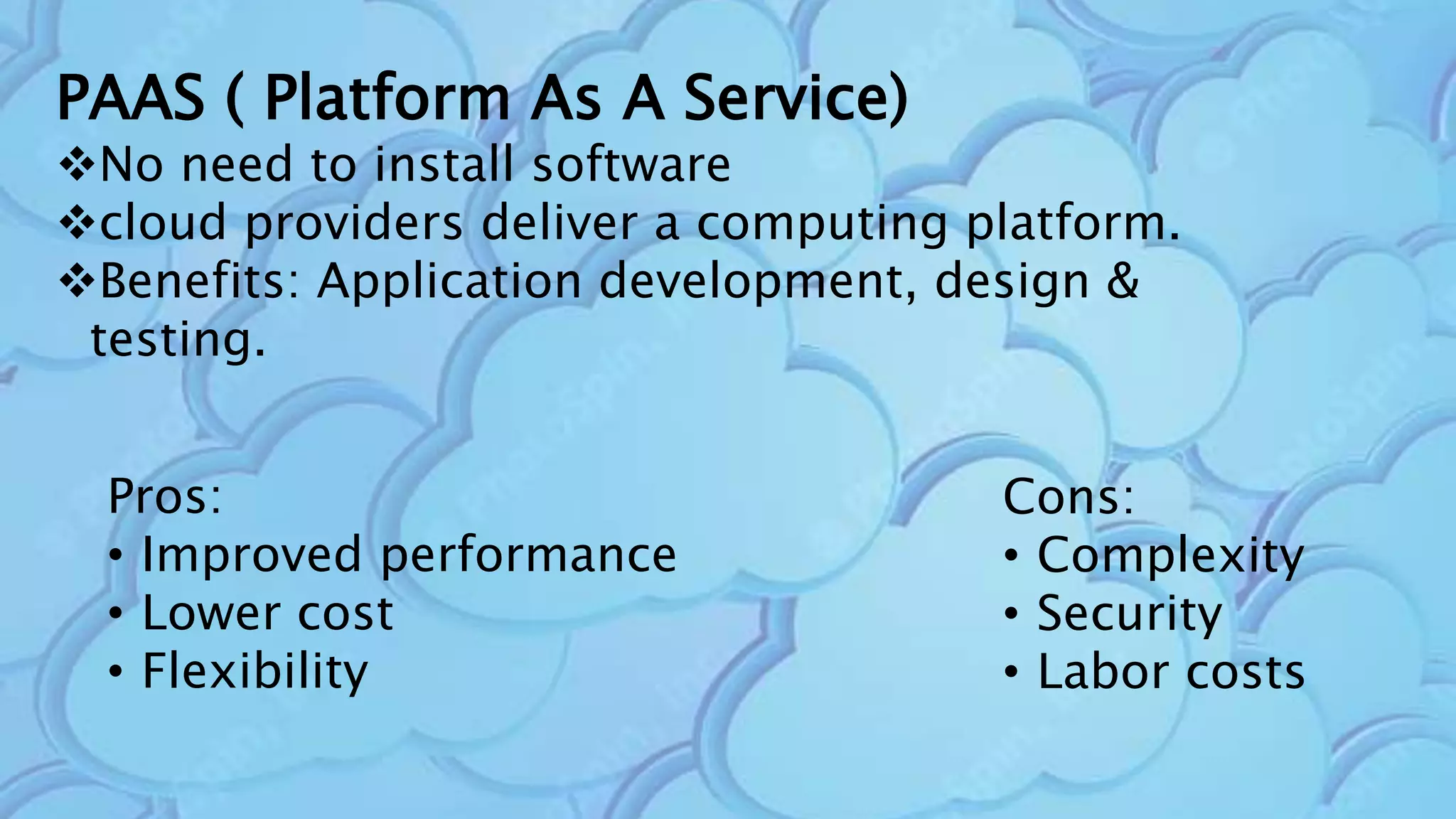
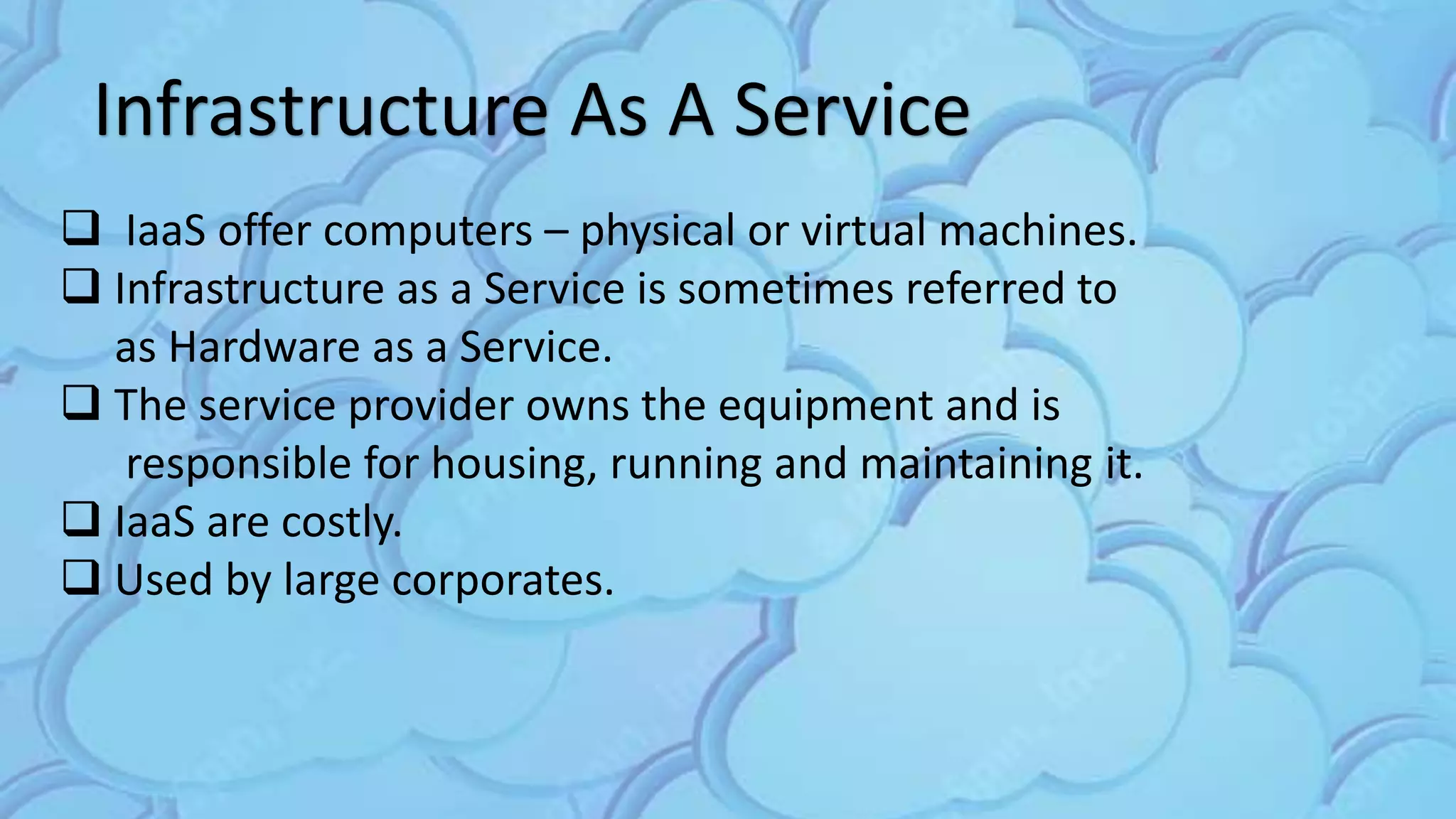
The document discusses cloud computing, highlighting its infrastructure, service models (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS), and benefits such as high storage capacity and cost reduction. It elaborates on the pros and cons of cloud services, including accessibility and flexibility versus concerns like internet outages and security. The piece also outlines economic and operational benefits of adopting cloud solutions for businesses.