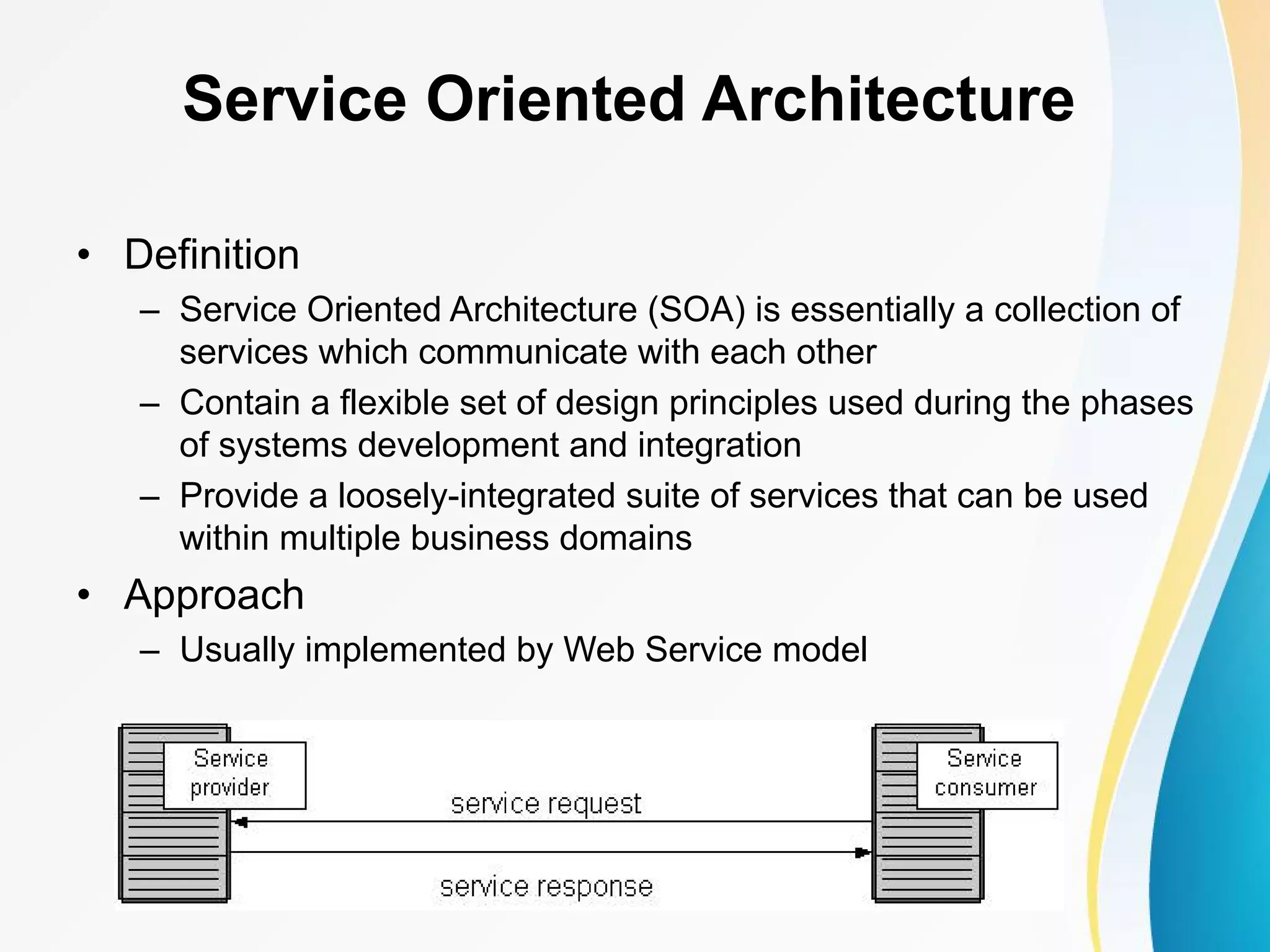
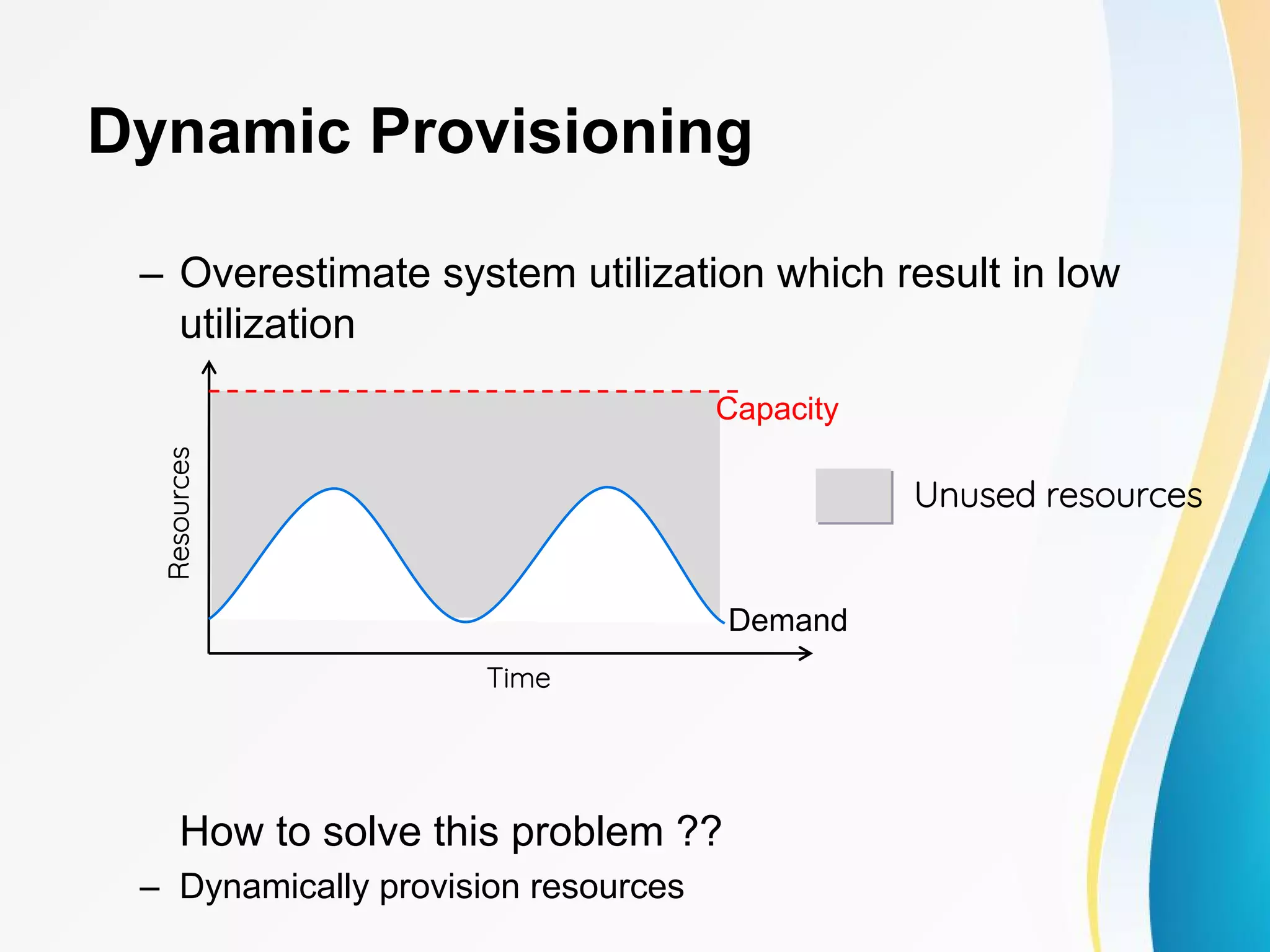
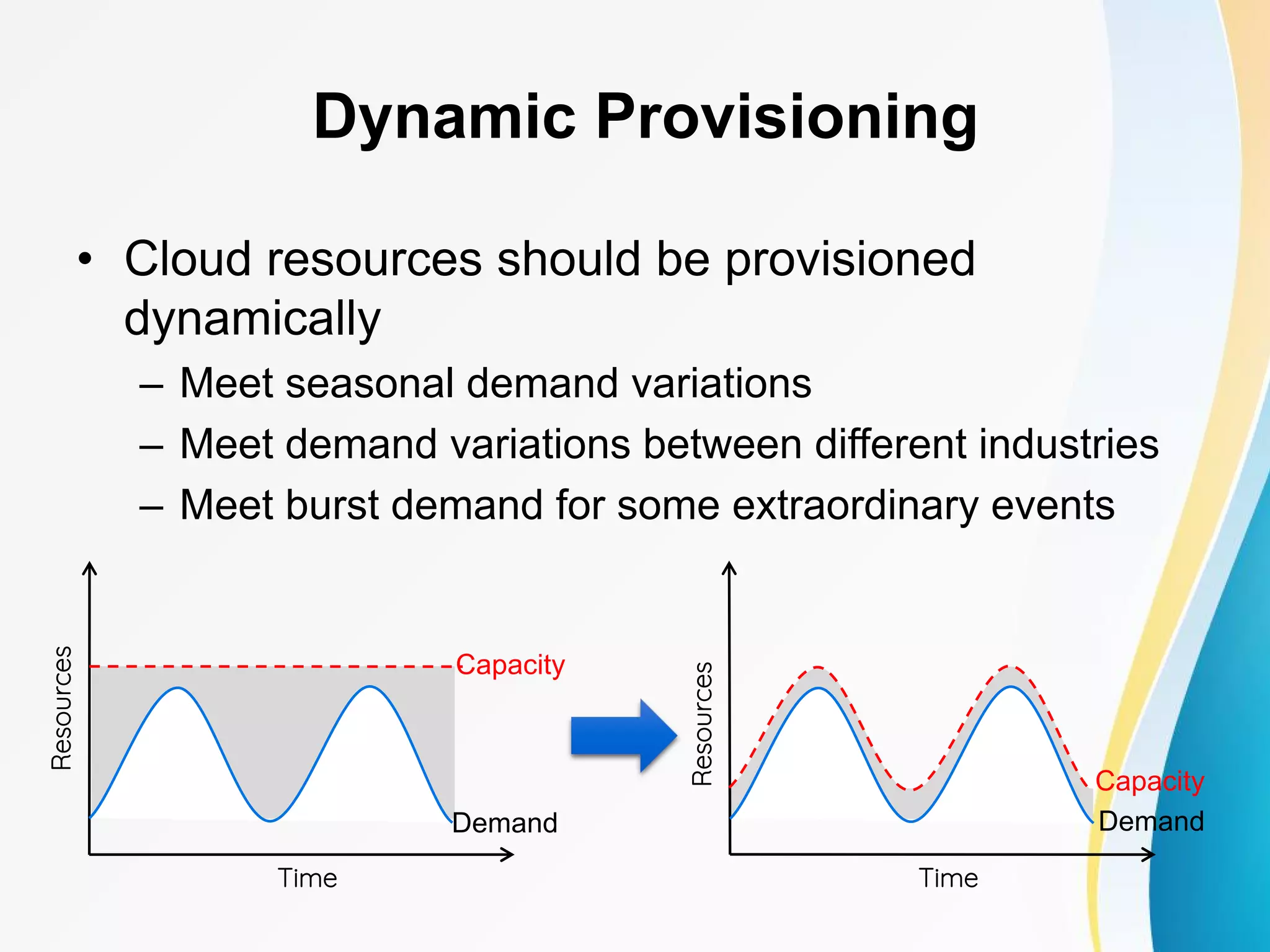
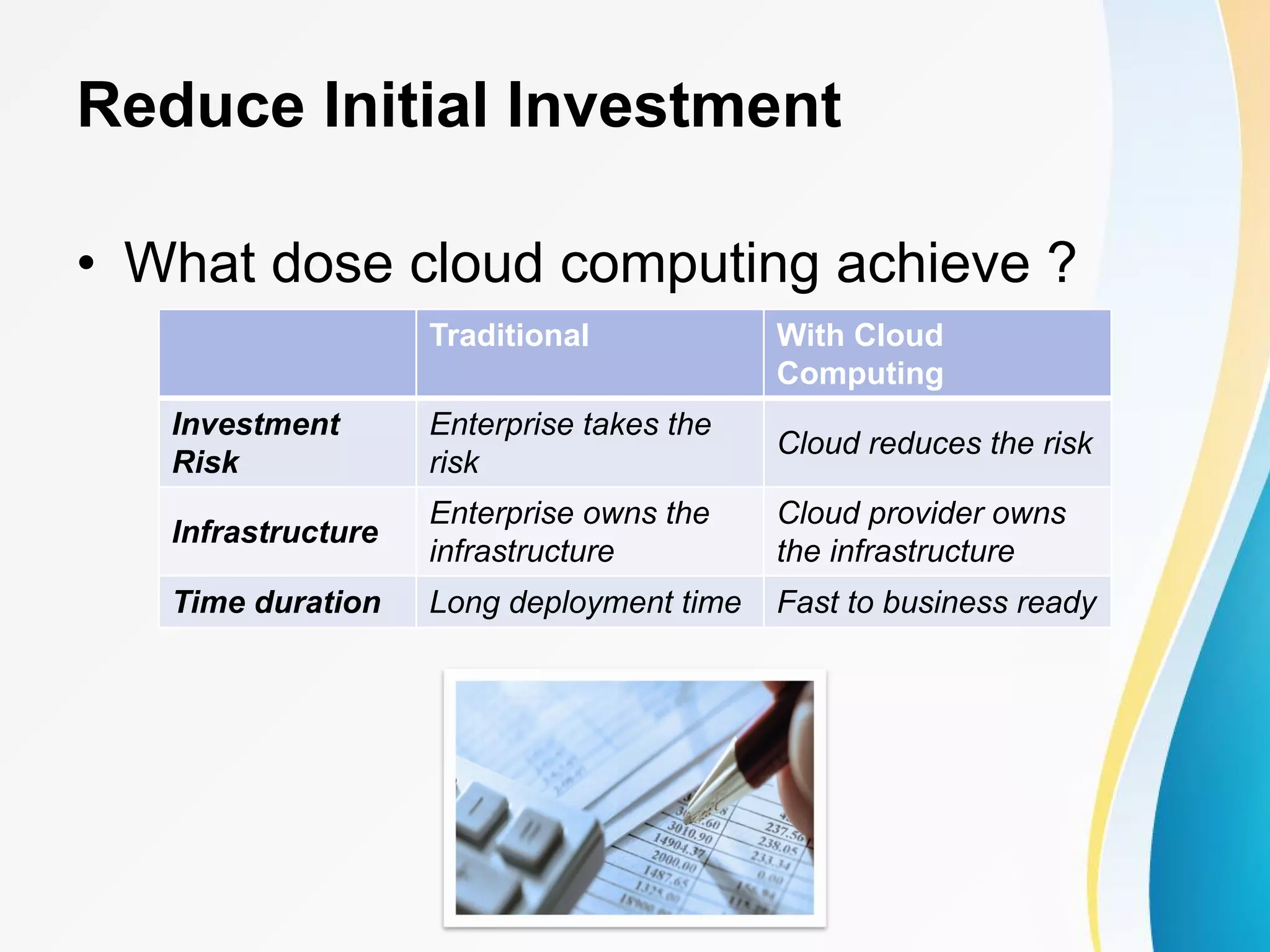
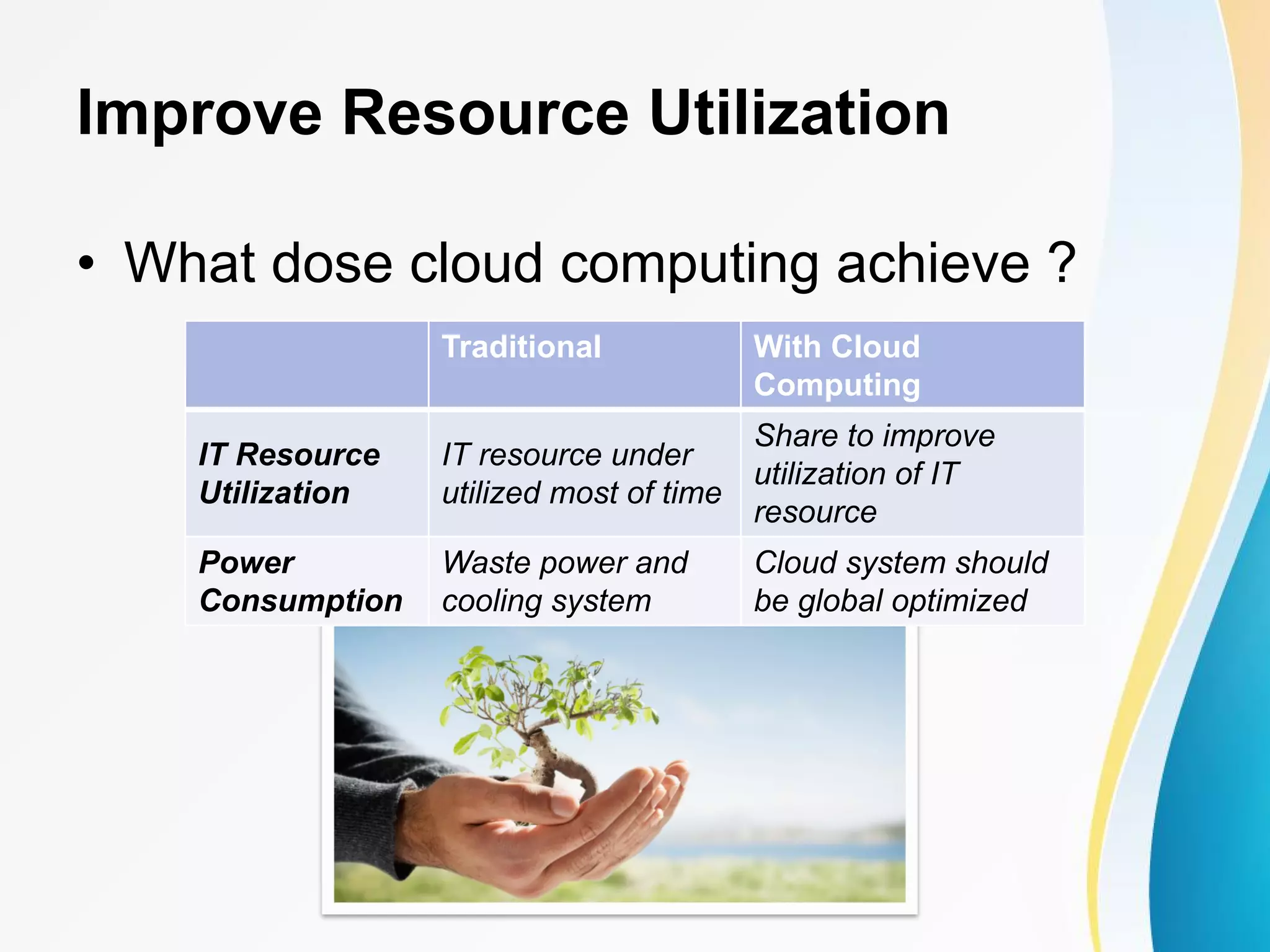
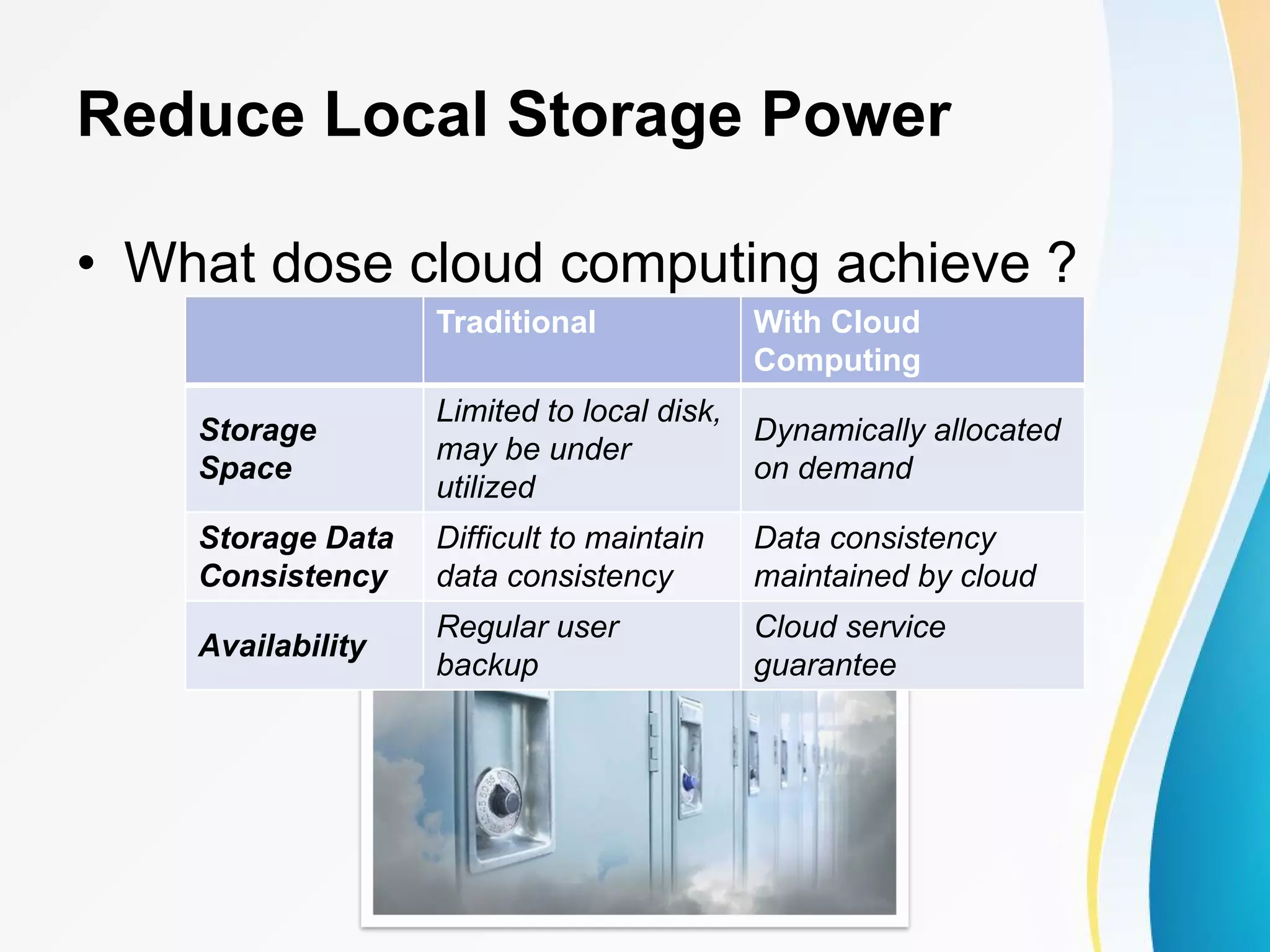
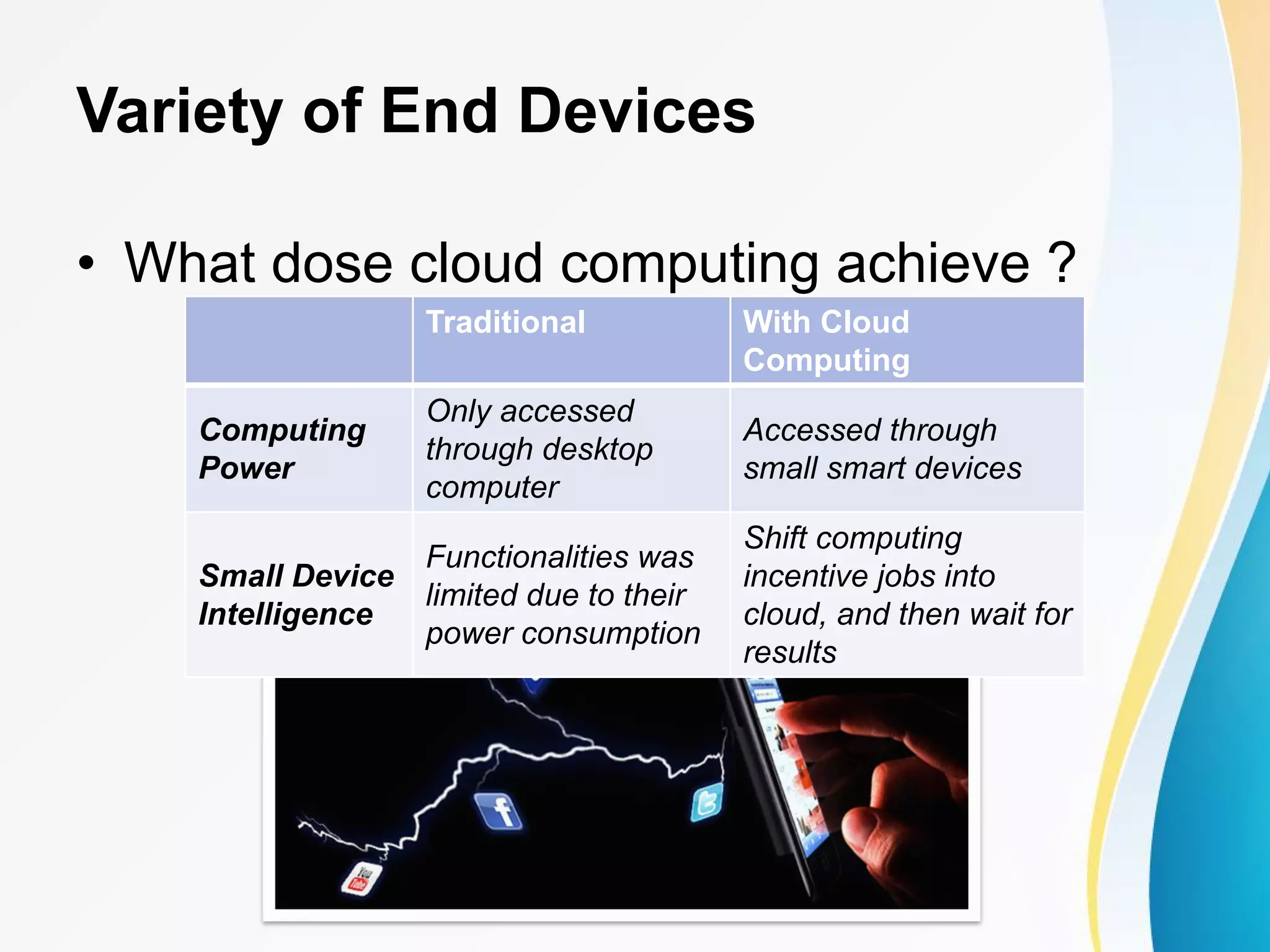
The document discusses cloud computing, including definitions from various sources, properties and characteristics of cloud computing, and service and deployment models. It defines cloud computing as on-demand access to shared configurable computing resources over the internet. The key properties discussed are high scalability, availability, reliability, manageability, interoperability, accessibility, and optimization through techniques like virtualization, parallel computing, and load balancing. It outlines service models of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS and deployment models of private, public, hybrid and community clouds.