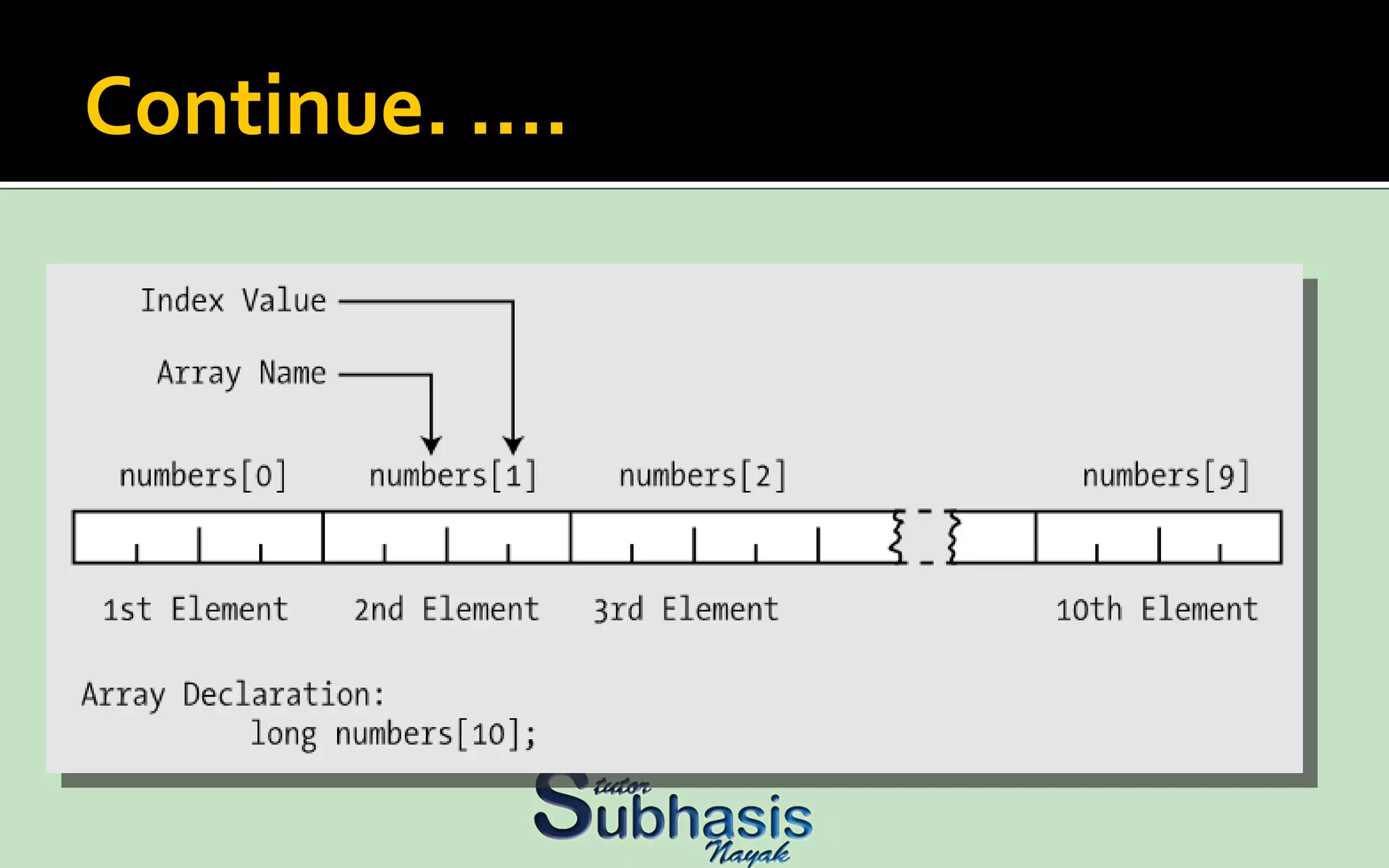
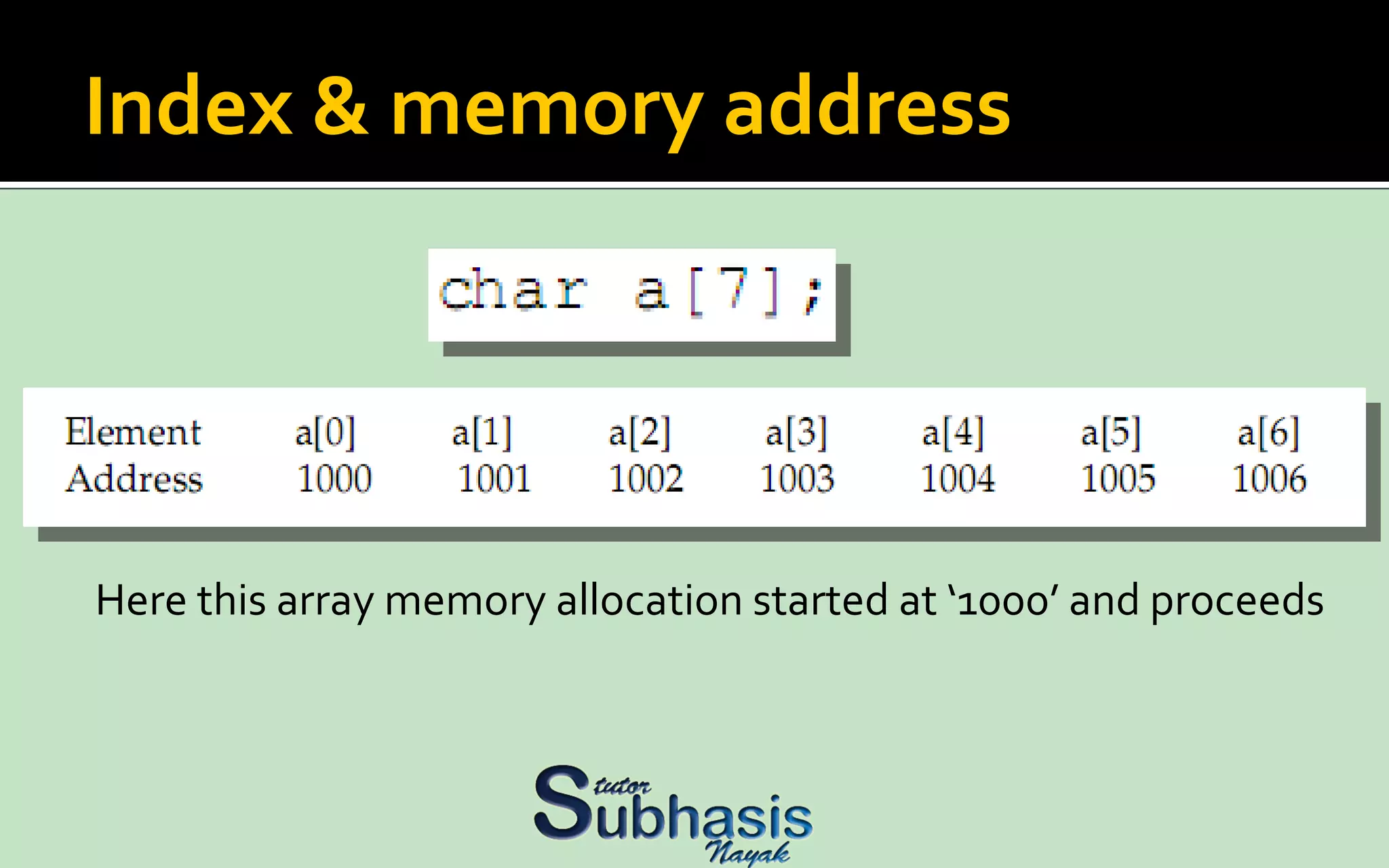
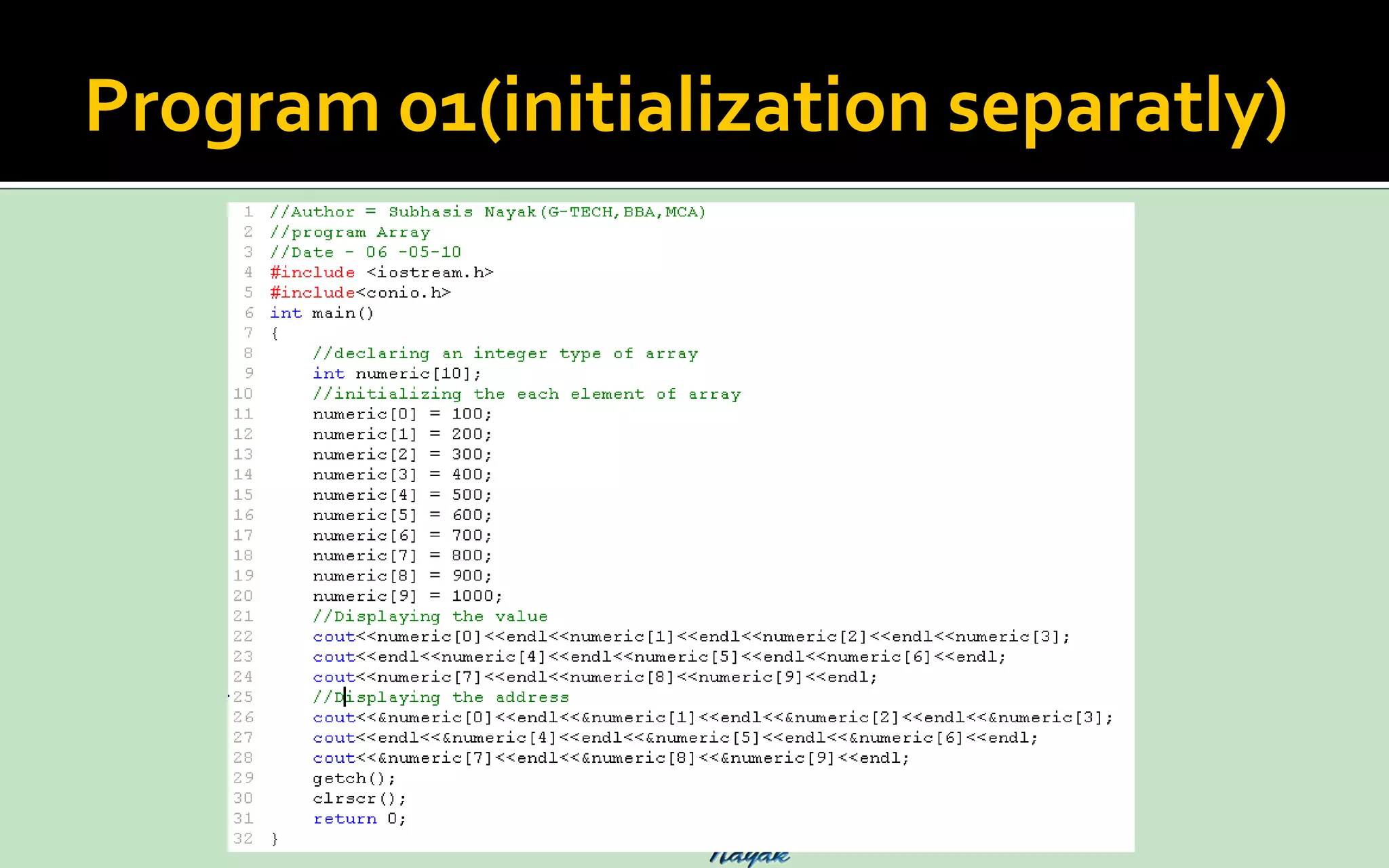
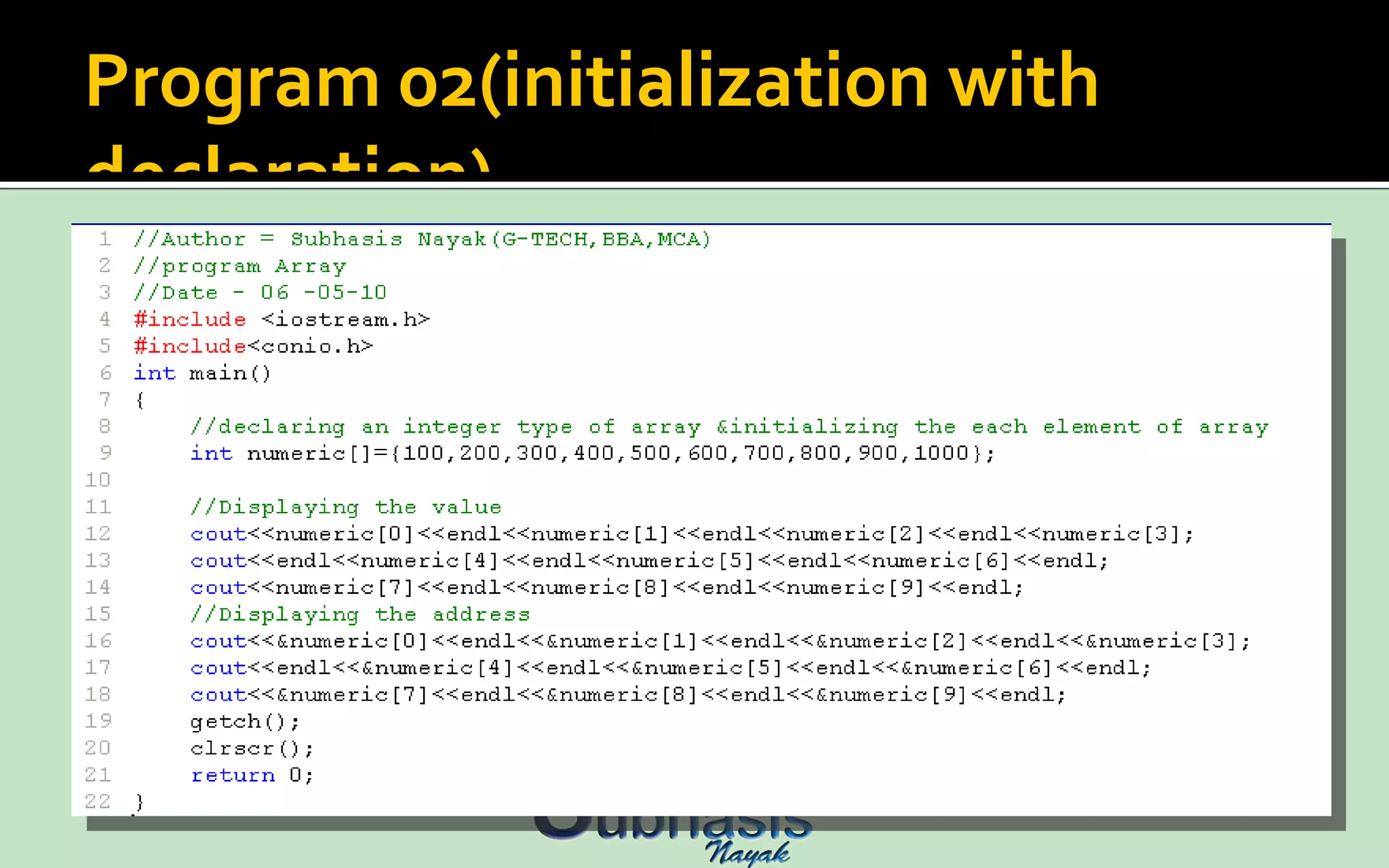
An array is a sequential collection of data storage locations of the same type. Each storage location is called an element of the array. Arrays are collections of variables of the same type that are referred to through a common name, with each variable possessing a unique number called a subscript. Individual members of an array are called elements of the array. An array is declared by specifying the type followed by the array name and the number of elements in square brackets.



![Declaring an array You declare an array by writing the certain type It will followed by the array name (array identifier) and subscript. Next, the subscript is the number of elements in the array. Subscript surrounded by the square brackets ‘ [] ’. Number of elements will be in square brackets.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carrayspart1-100512073918-phpapp01/75/C-arrays-part1-5-2048.jpg)
![Let’s declare an array. If I want to declare an array of integer type having name numeric & it has 10 elements. I will write like this int numeric[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carrayspart1-100512073918-phpapp01/75/C-arrays-part1-6-2048.jpg)