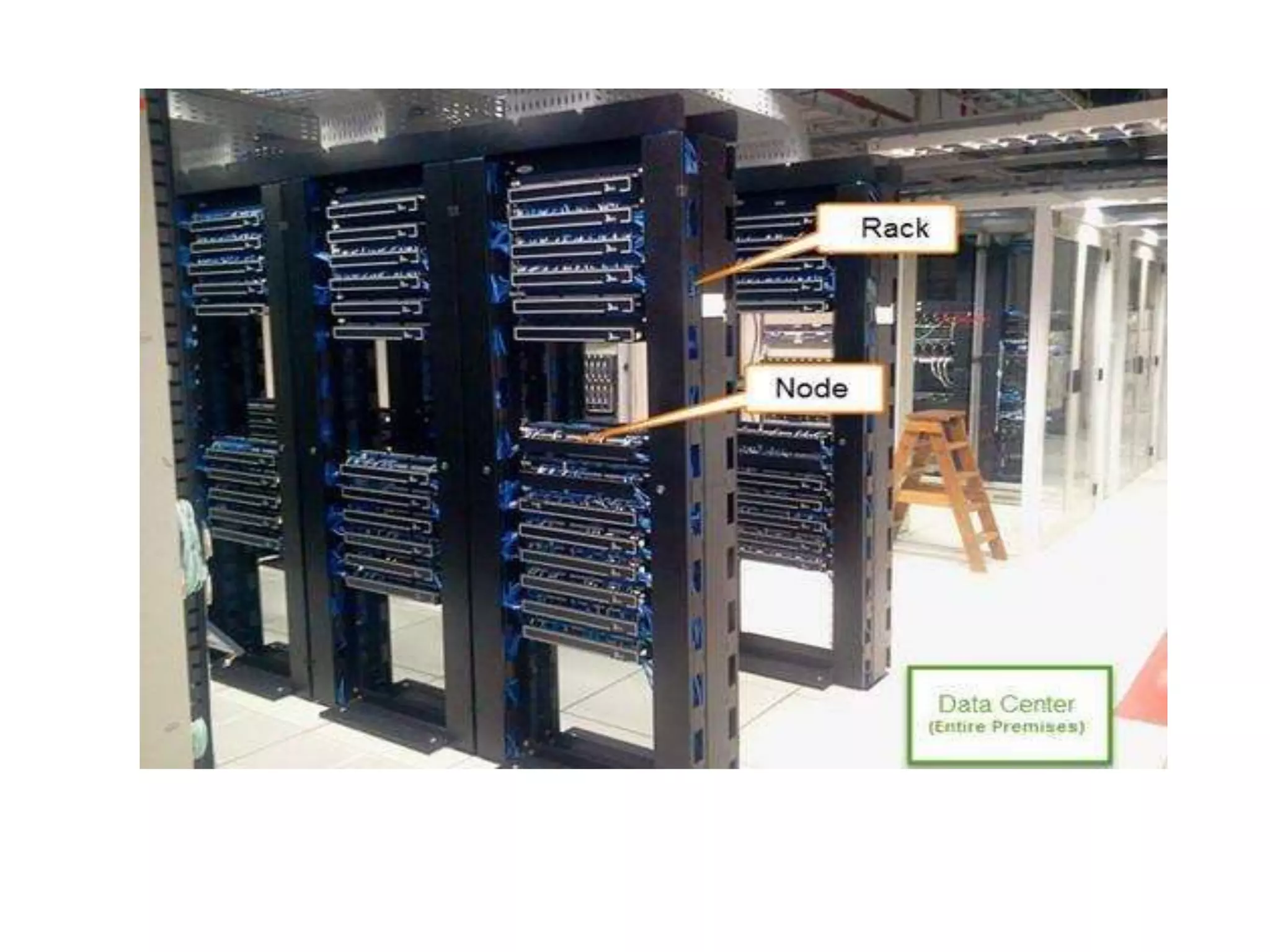
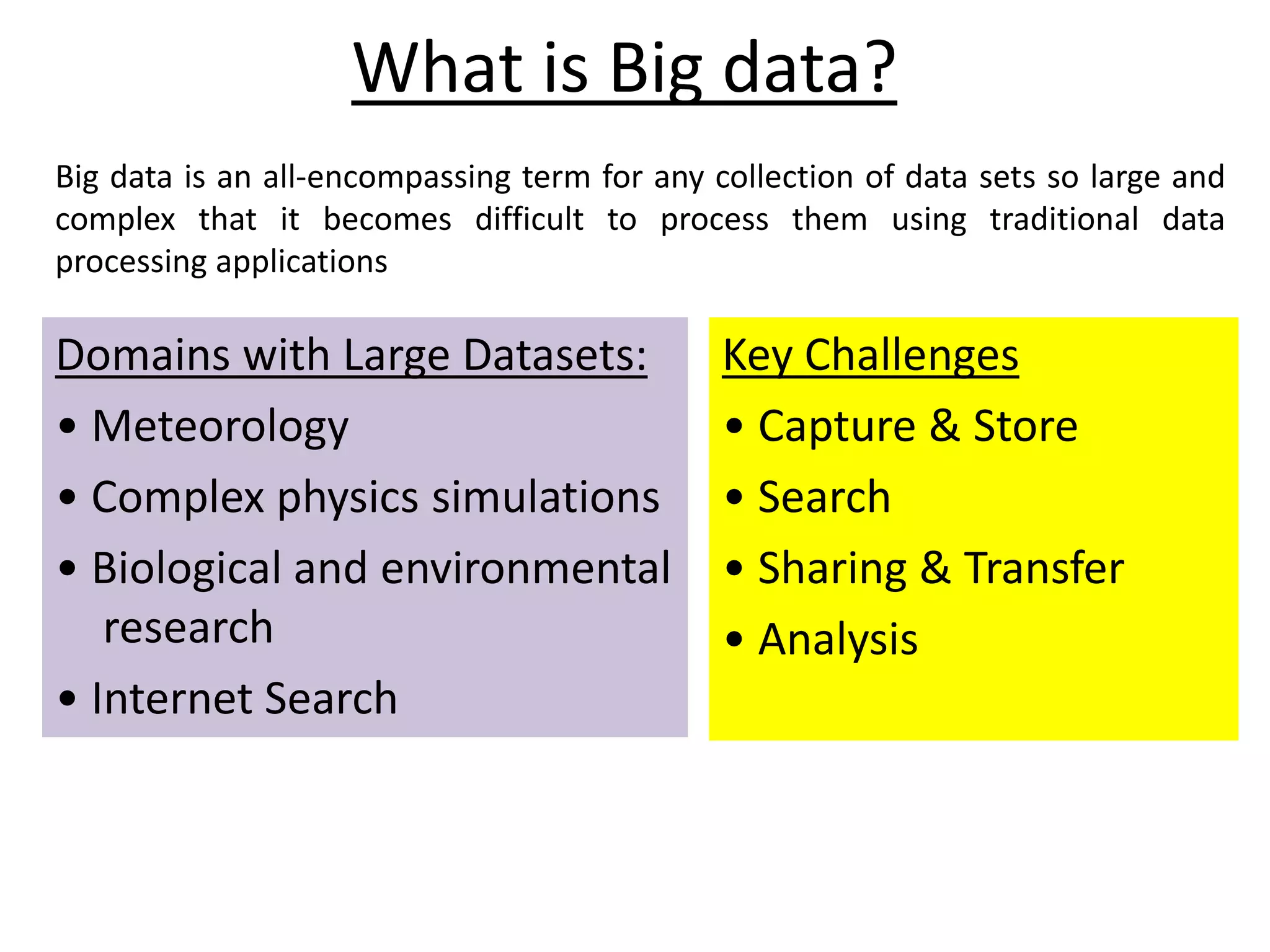
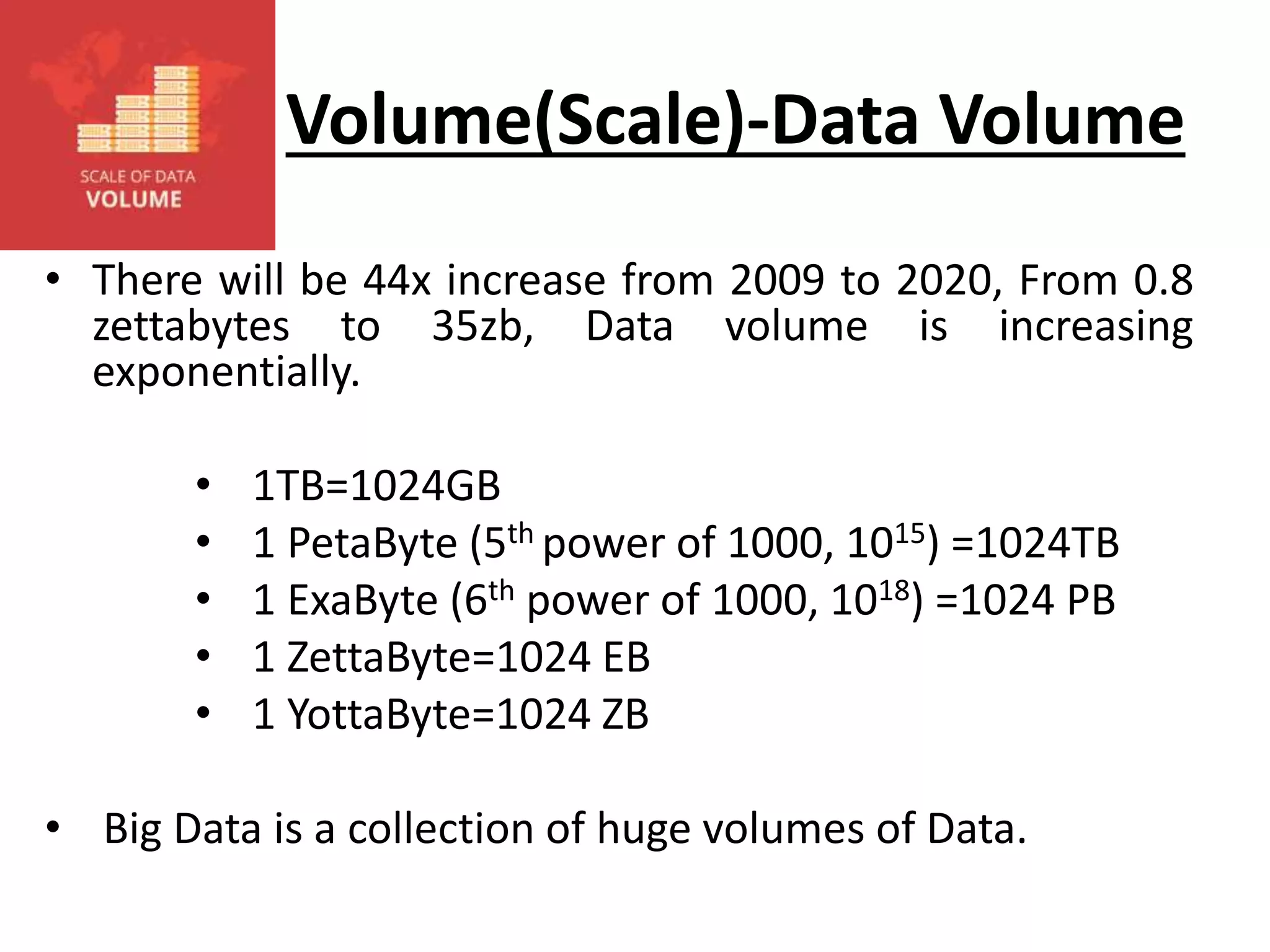
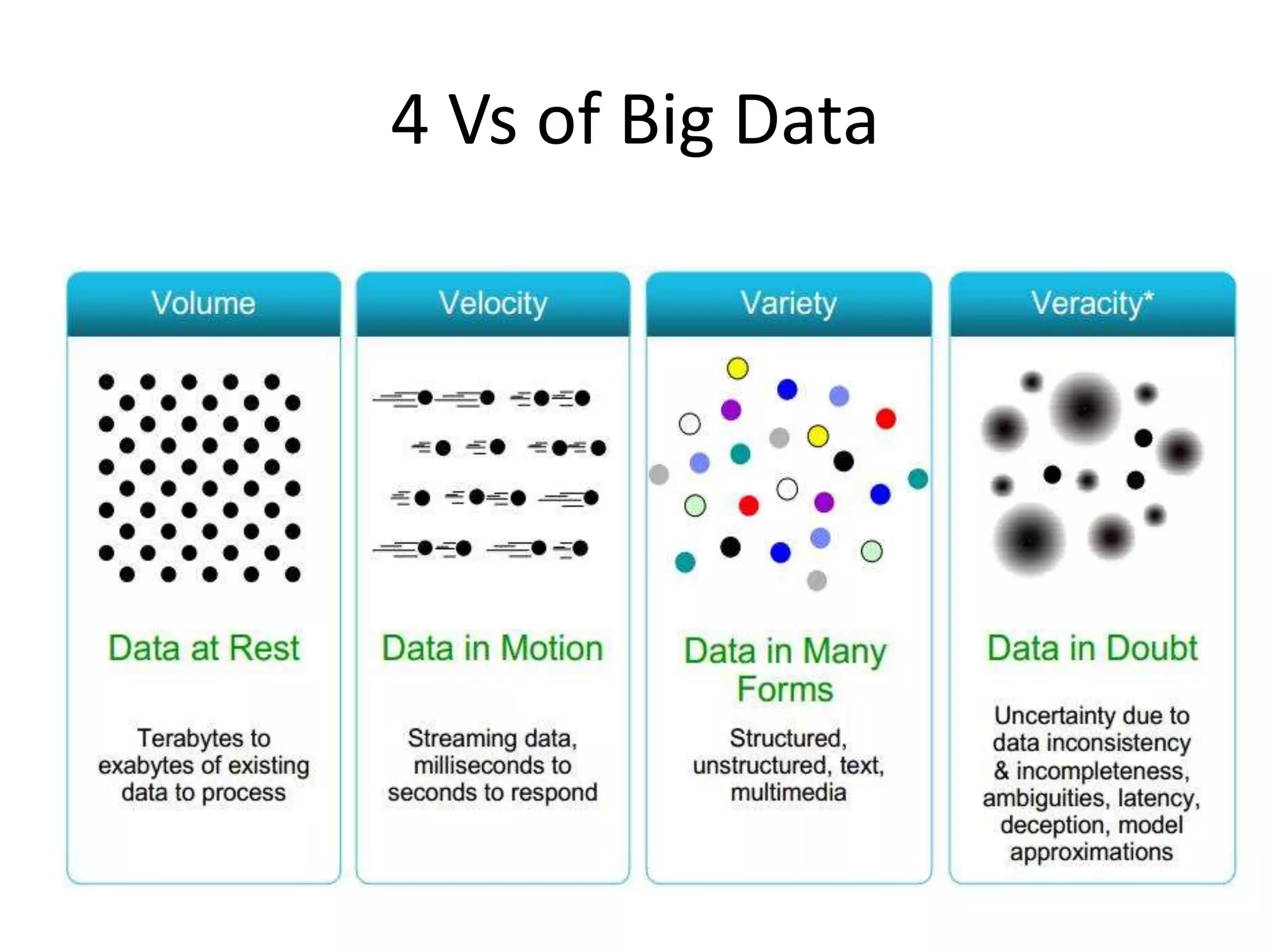
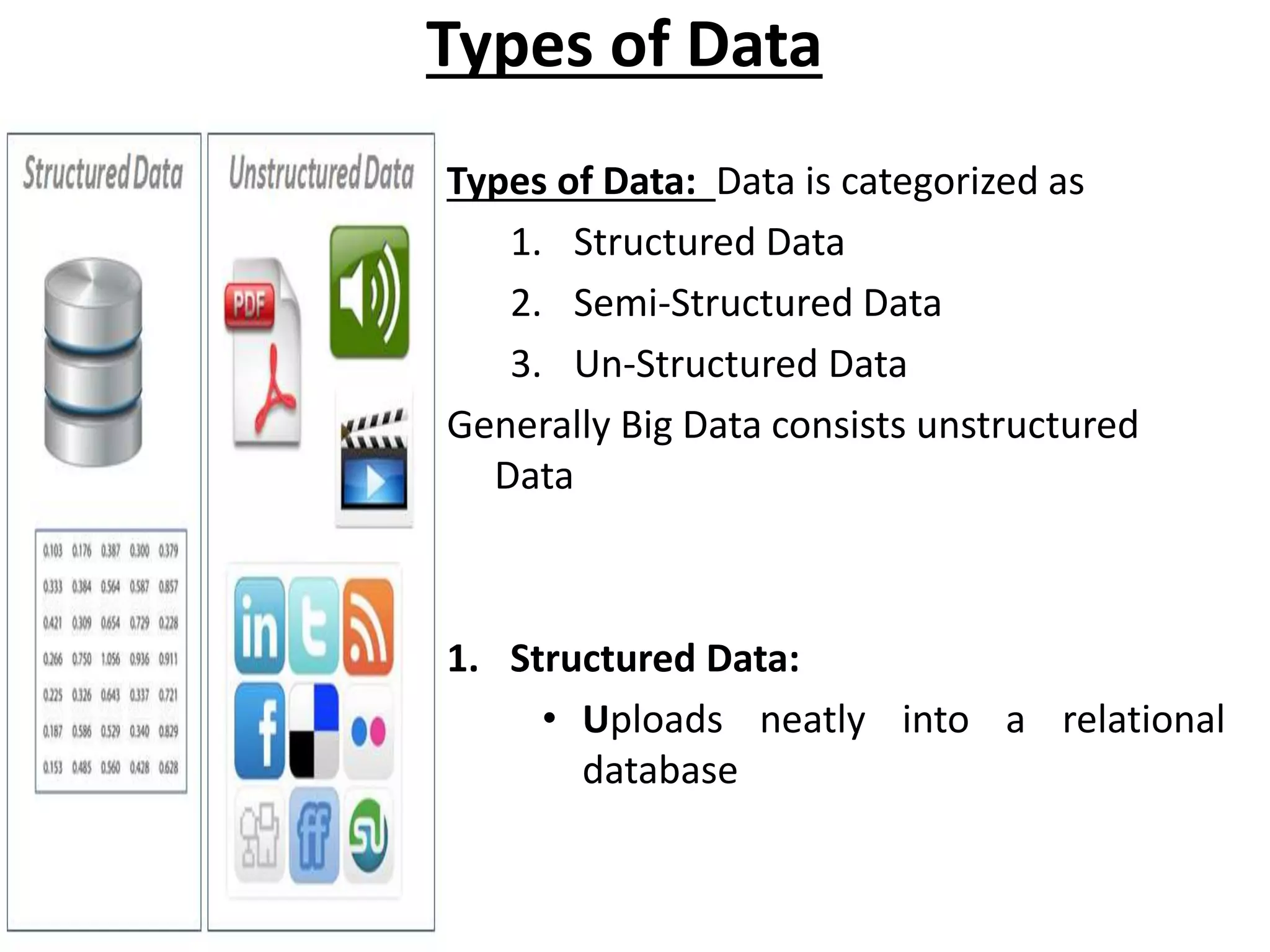
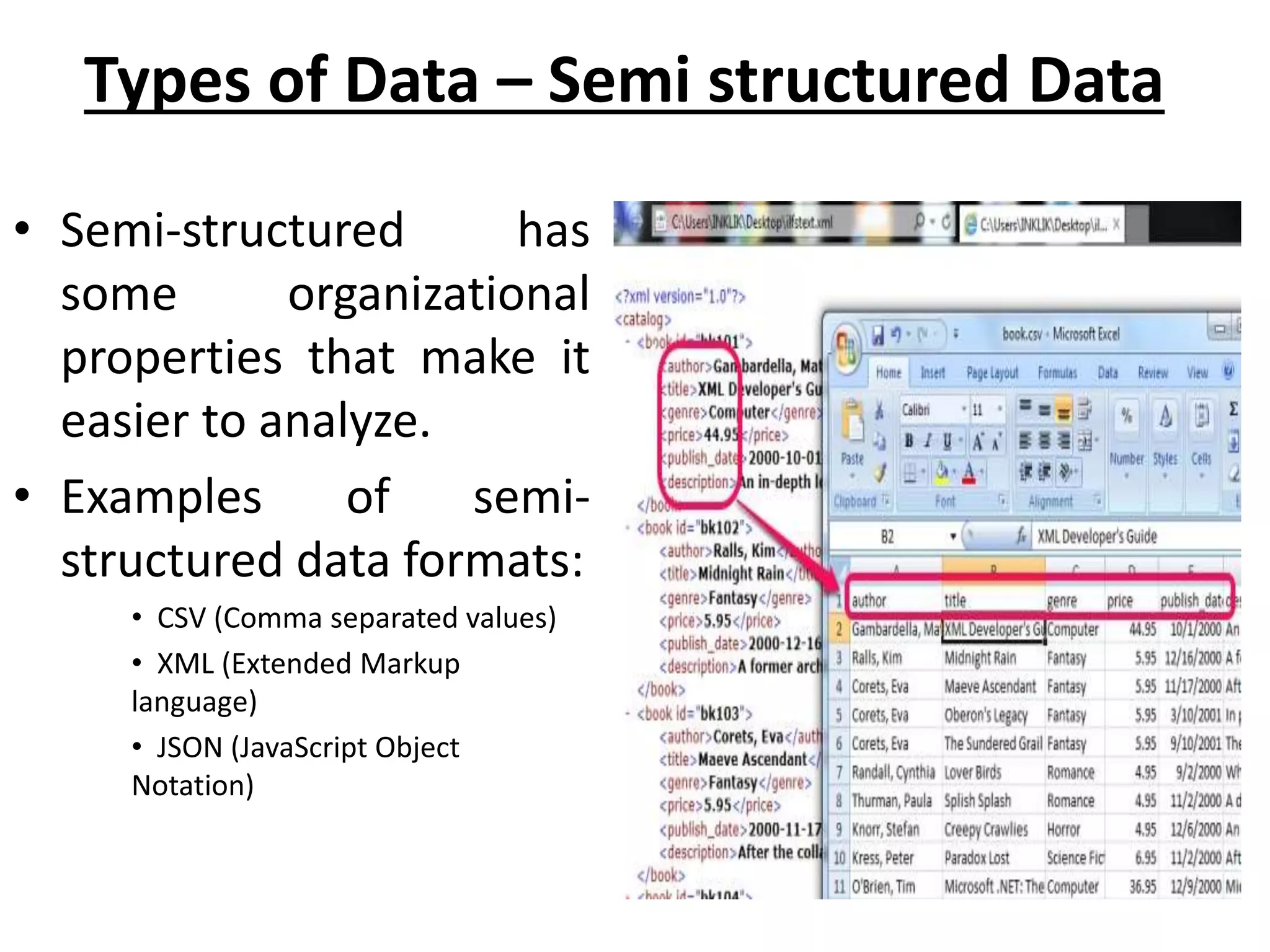
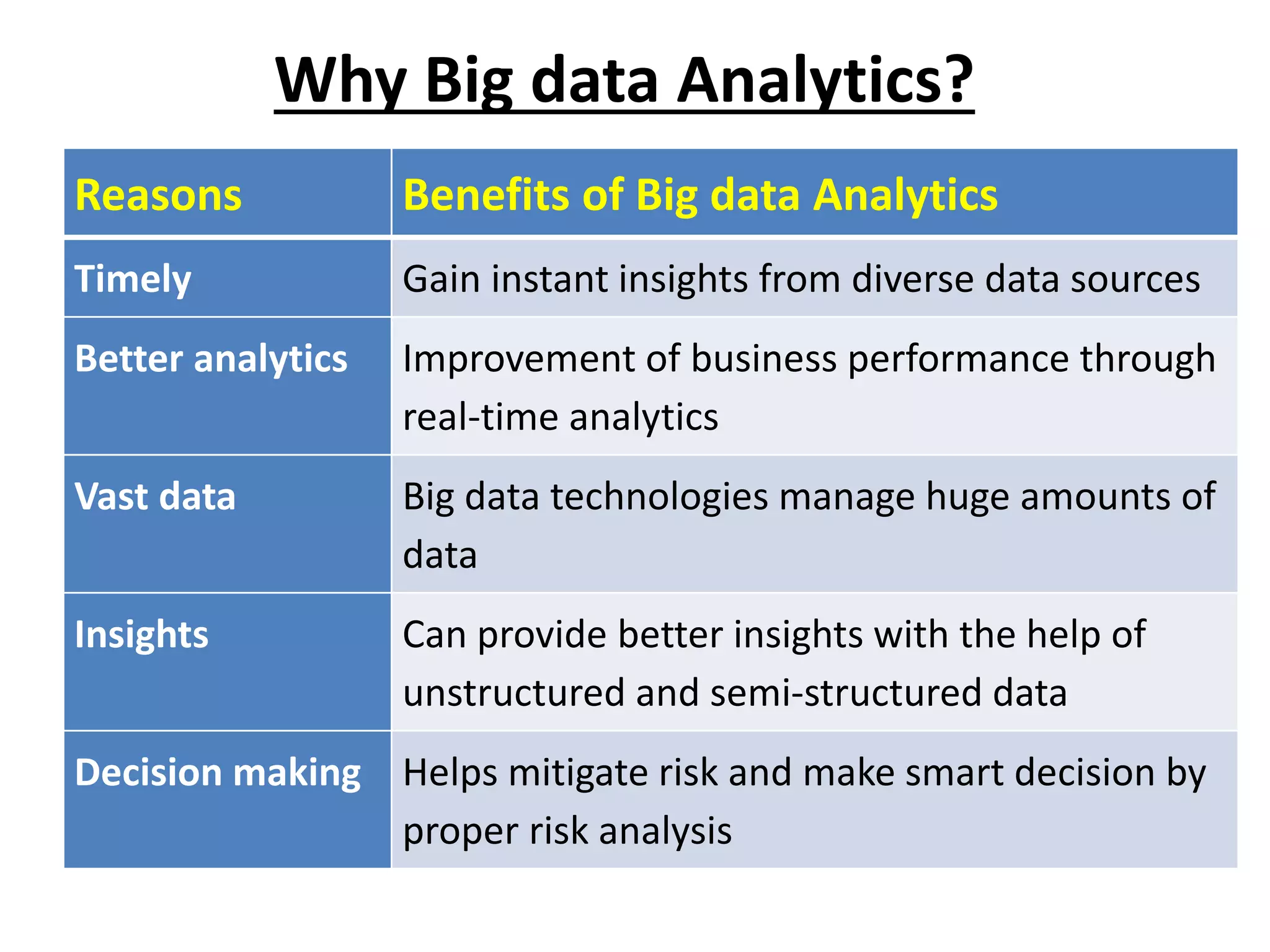
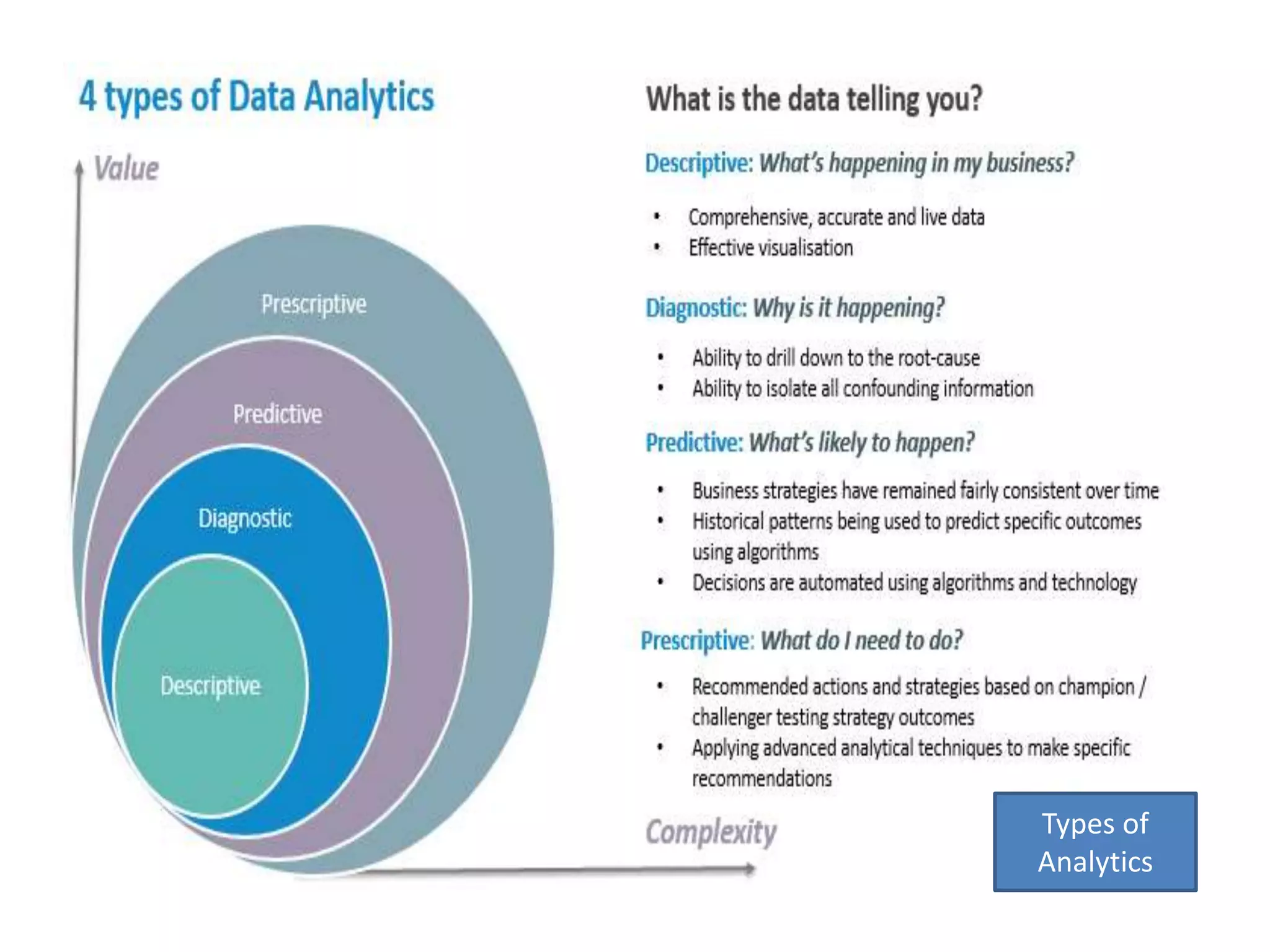
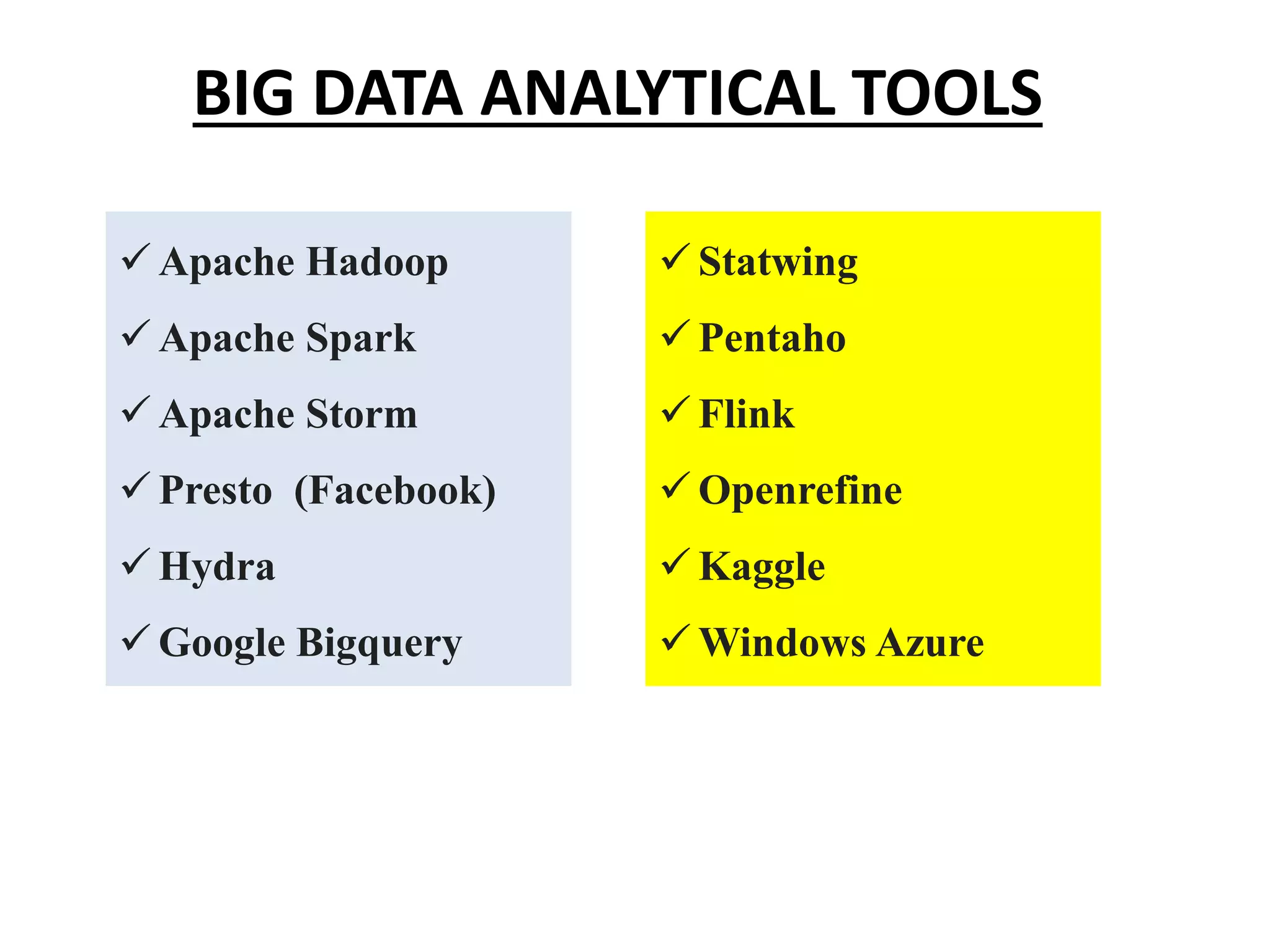
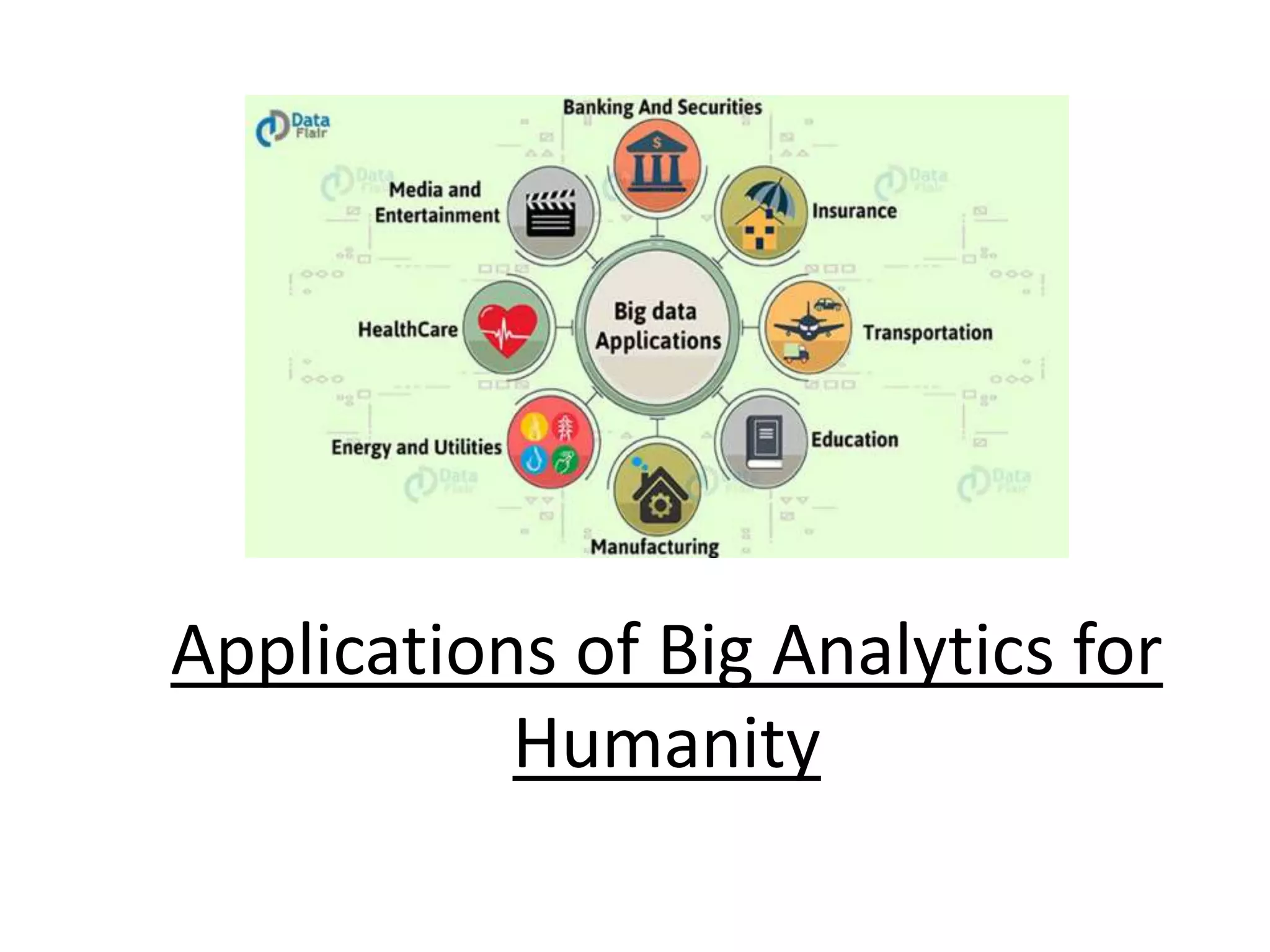
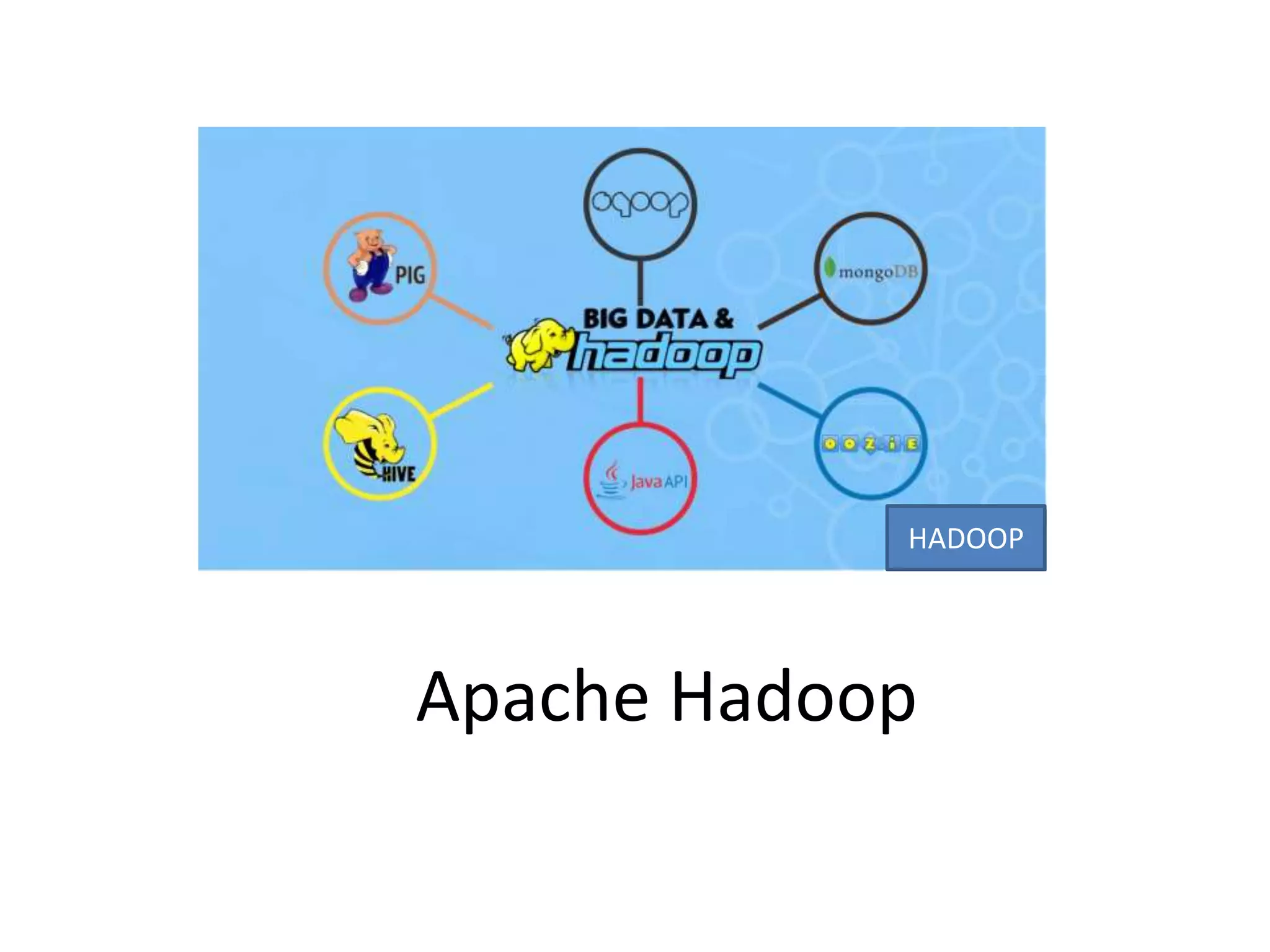
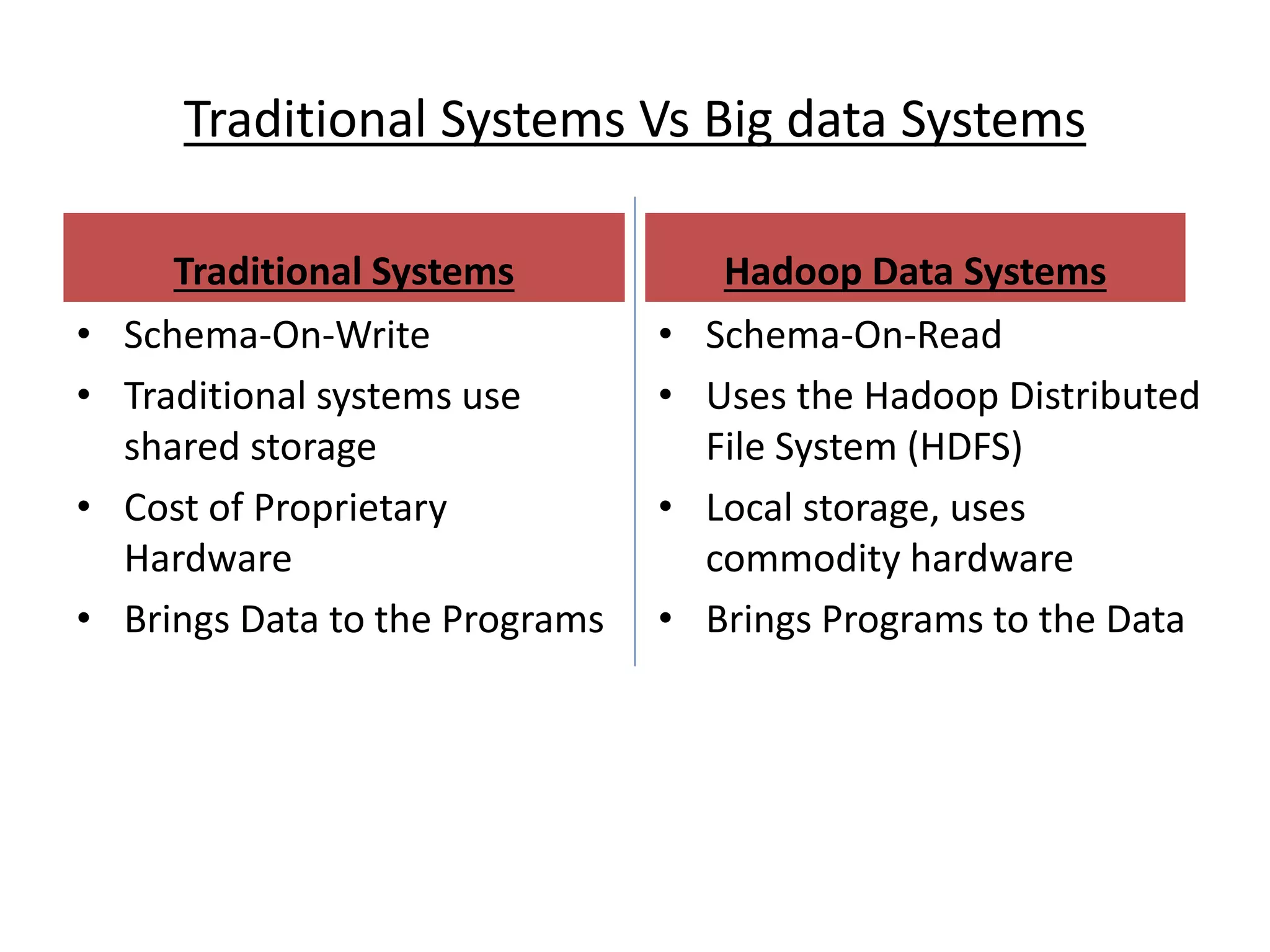
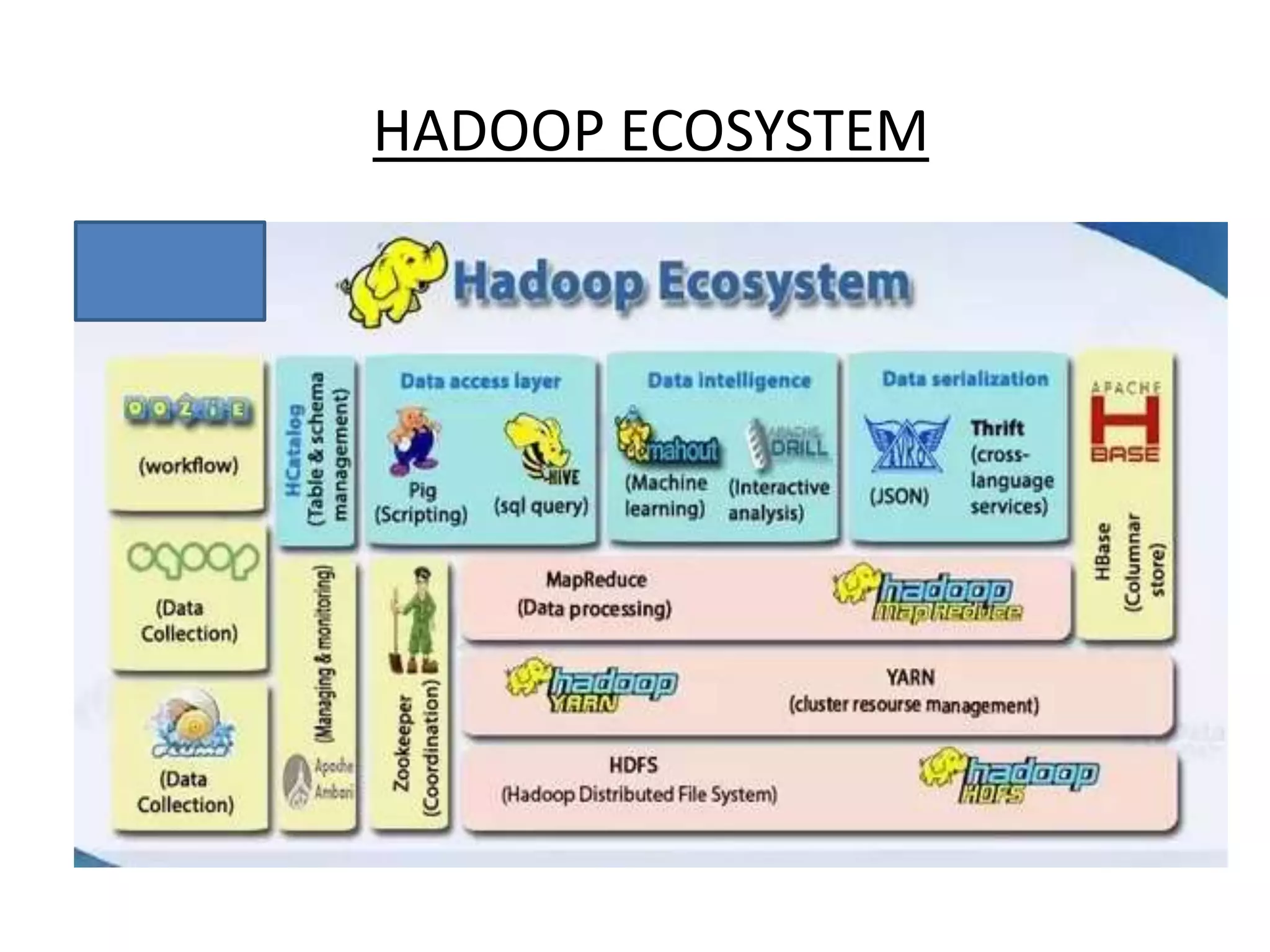
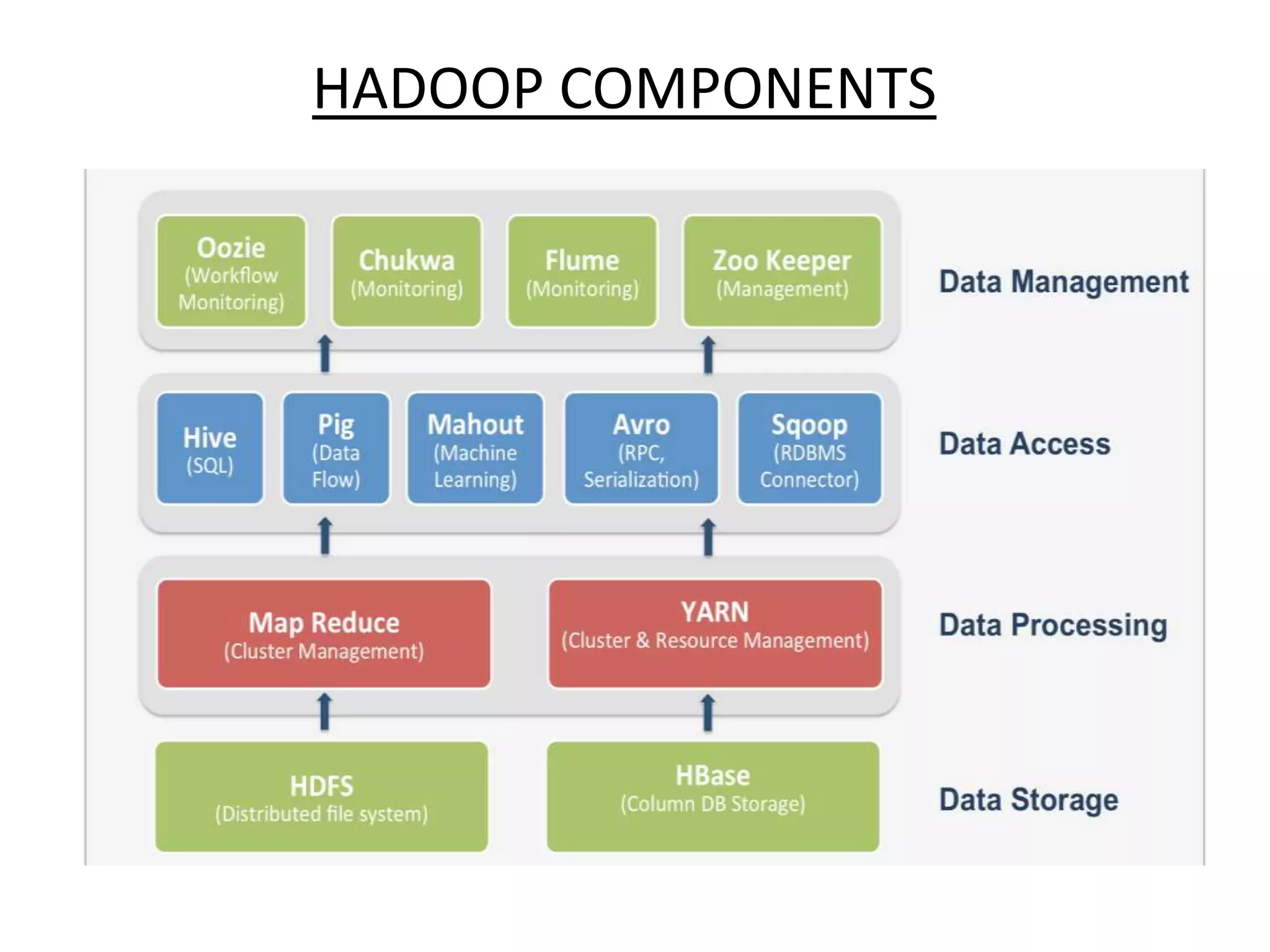
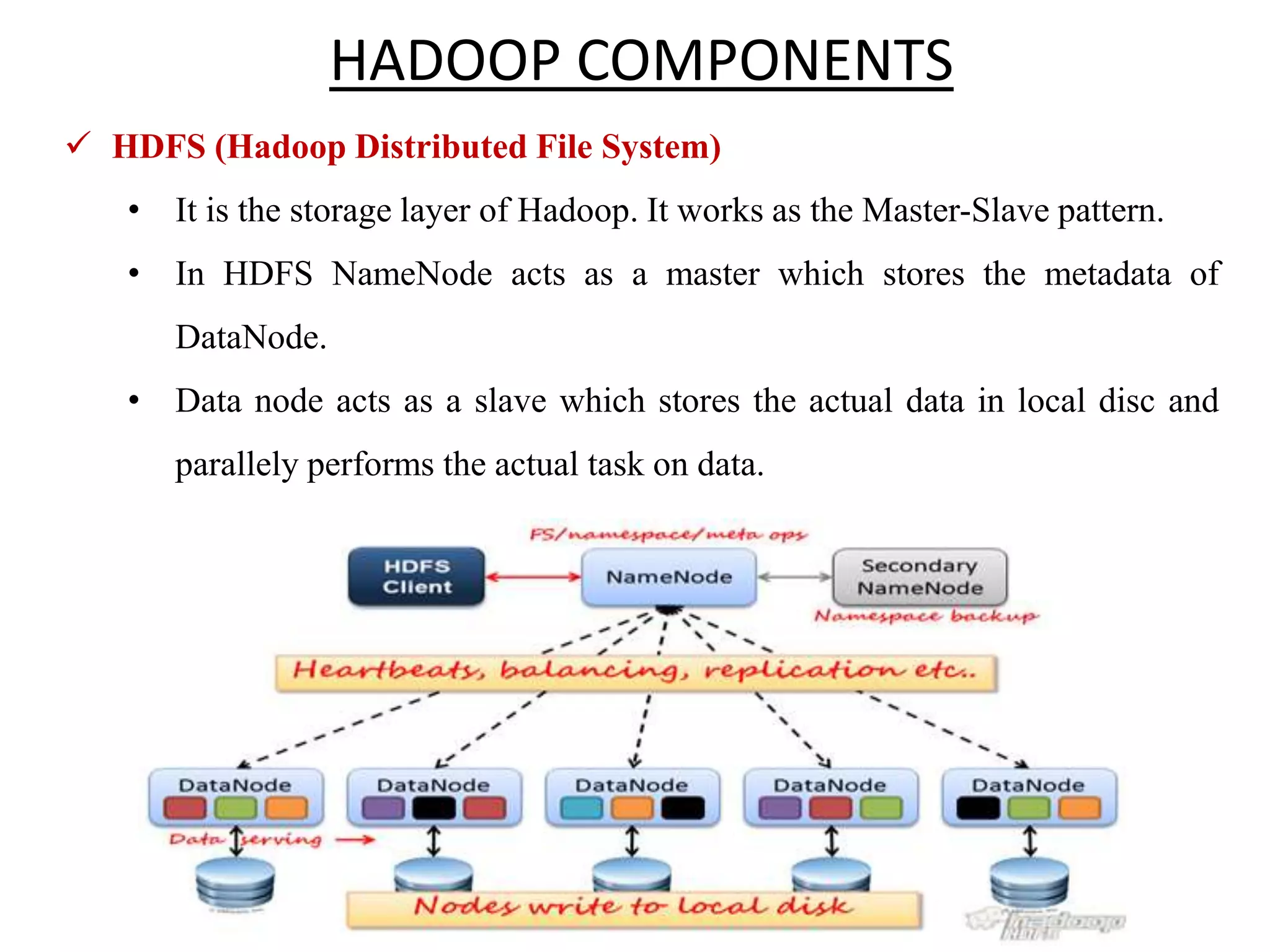
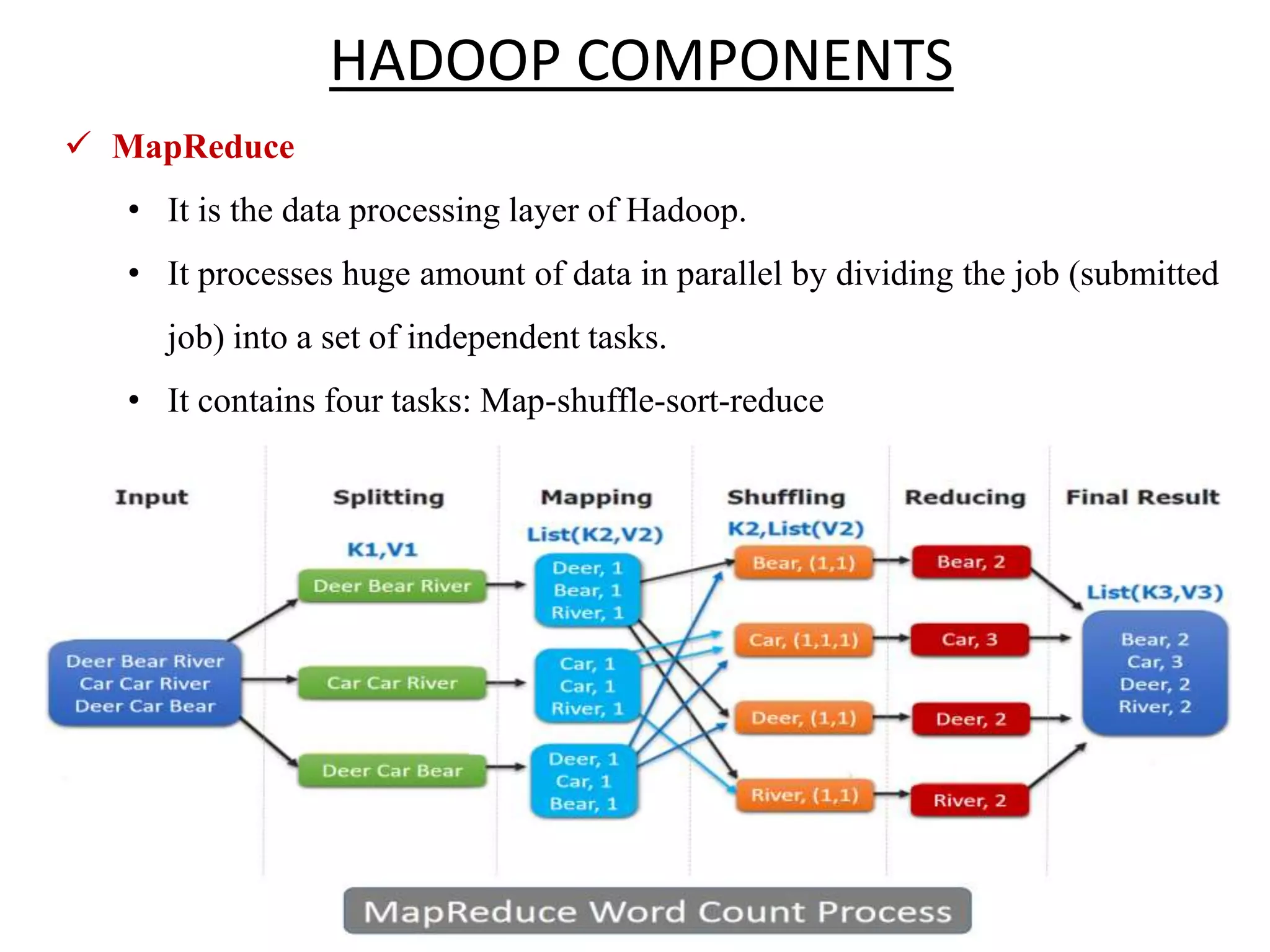
Big Data Analytics and Hadoop is presented. Key points include: - Big data is large and complex data that is difficult to process using traditional methods. Domains that produce large datasets include meteorology, physics simulations, and internet search. - The four V's of big data are volume, velocity, variety, and veracity. Hadoop is an open-source framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets across clusters of computers. Its core components are HDFS for storage and MapReduce for processing. - Apache Hadoop has gained popularity for big data analytics due to its ability to process large amounts of data in parallel using commodity hardware, its scalability, and automatic failover. A Hadoop ecosystem of