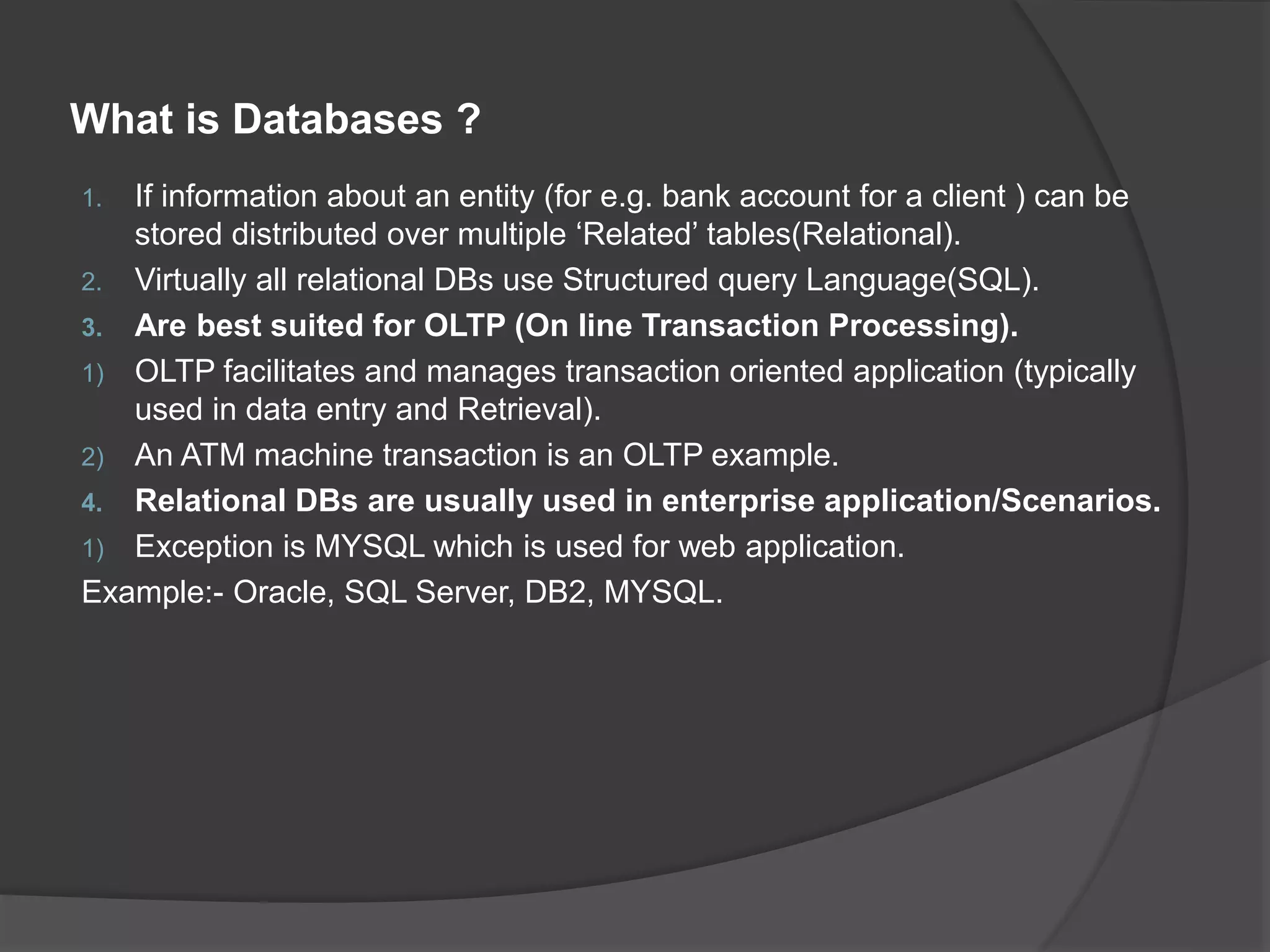
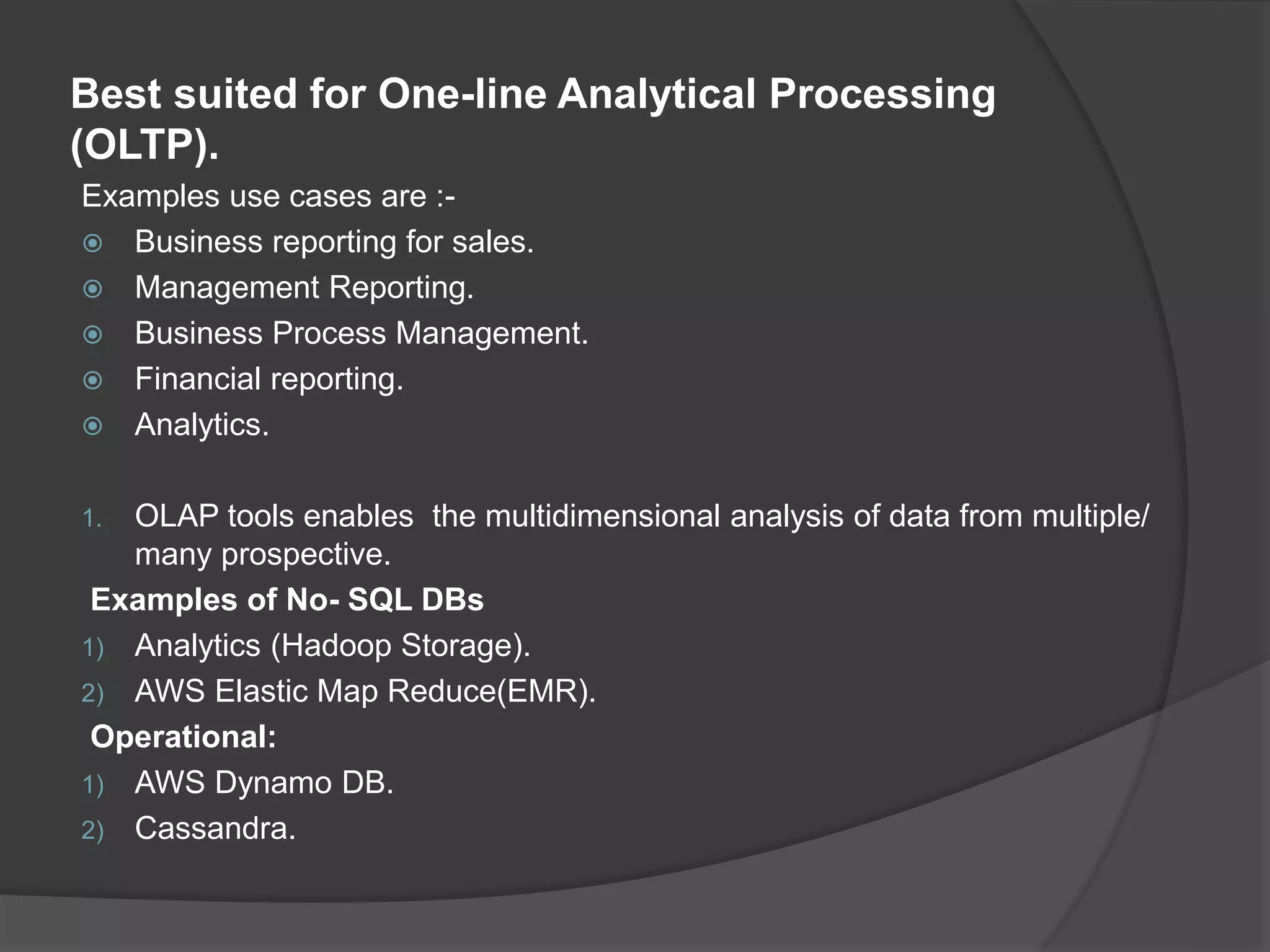
A database is a structured store for datasets that allows for repeated access, safeguards against errors, and enables multi-user read access, particularly in relational databases using SQL for transaction processing. Non-relational databases, which store unstructured data, offer flexibility, scalability, and performance advantages suited for modern applications such as social media and analytics. AWS RDS provides managed relational database services including automated backups and performance tuning, supporting various engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle.
![By- Nitin Kr. Kashyap B.Tech [CTIS] TCA1650021 i -Nurture,TMU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databases-200707052615/75/AWS-Databases-1-2048.jpg)