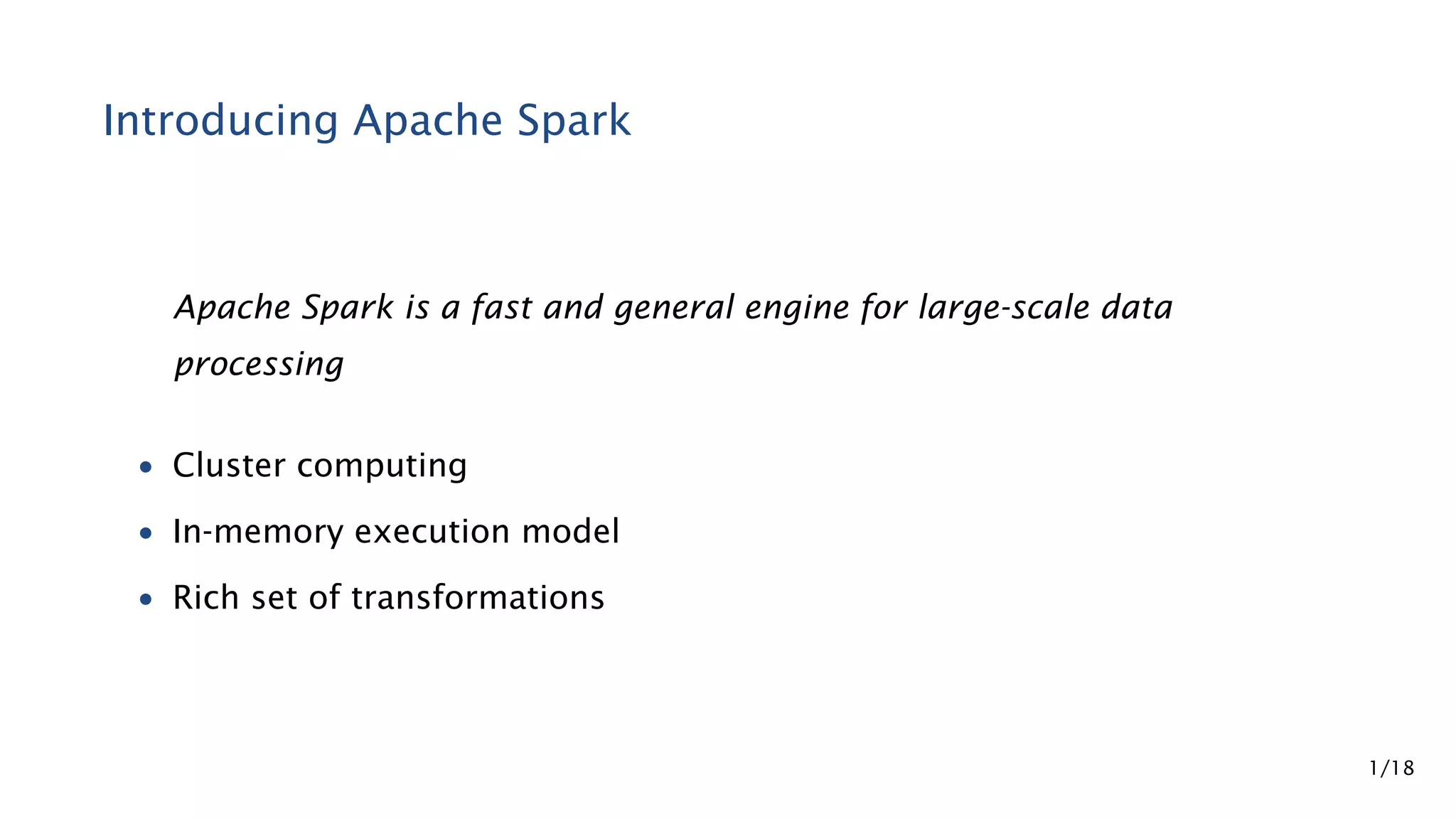
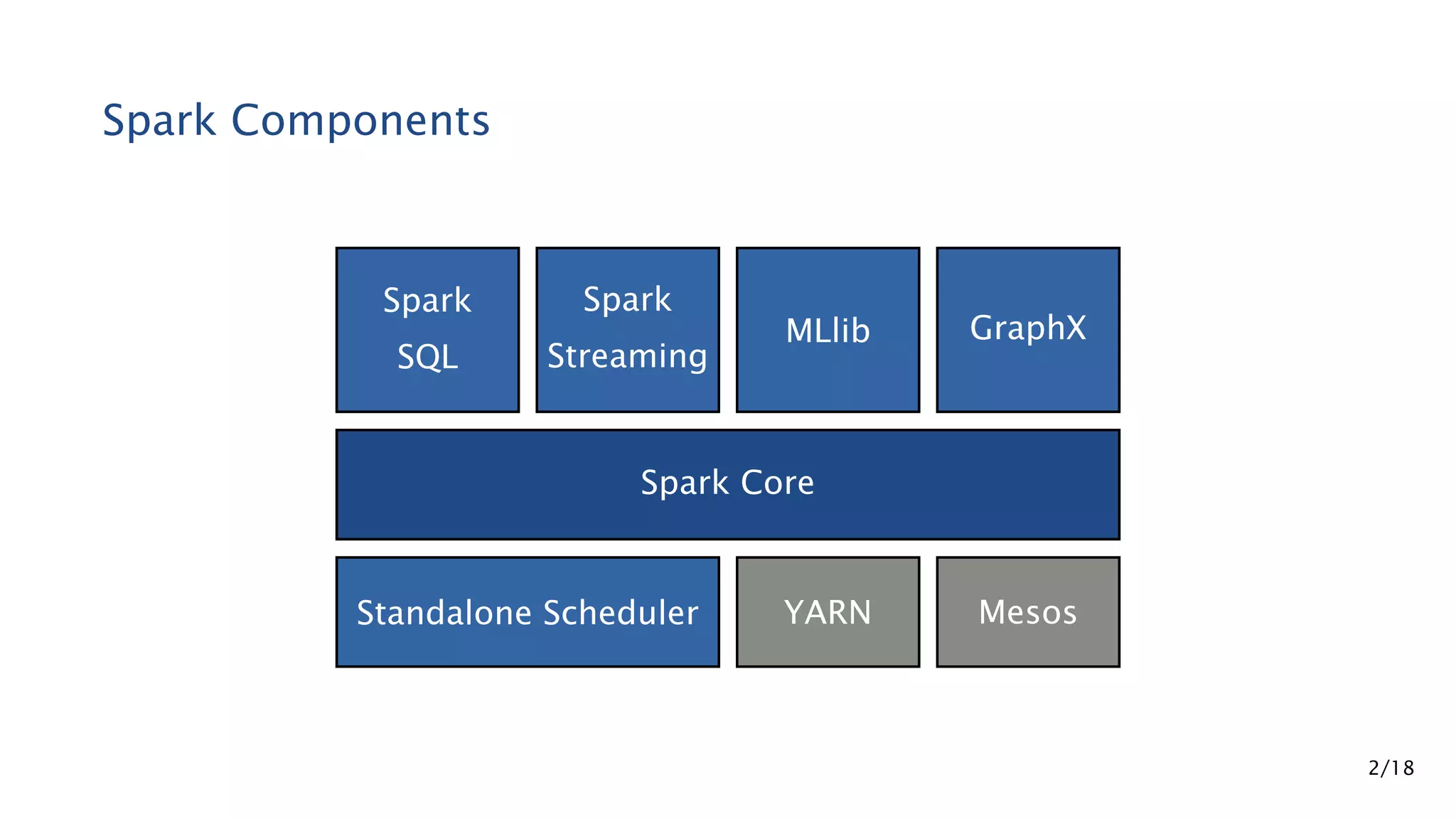
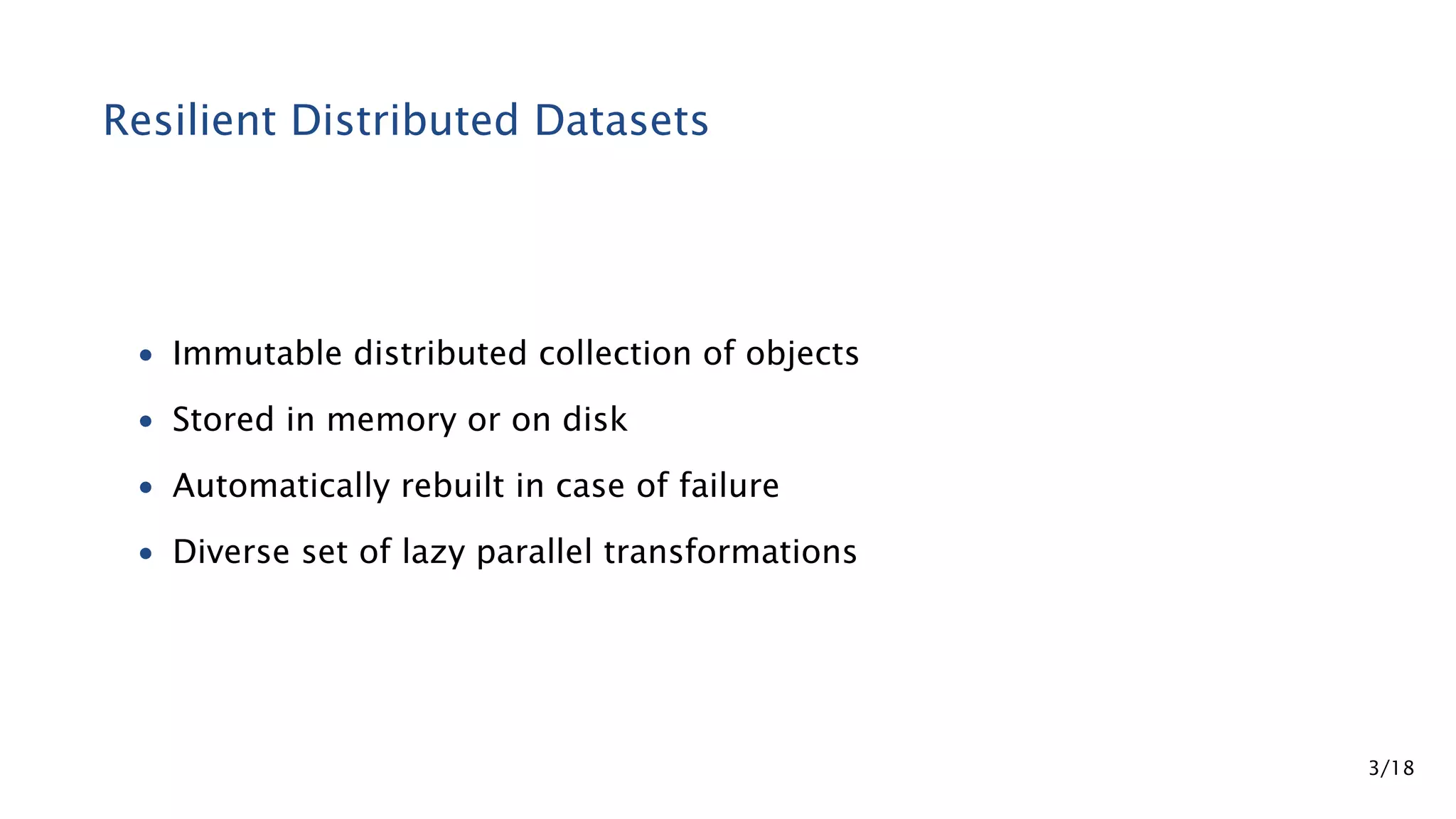
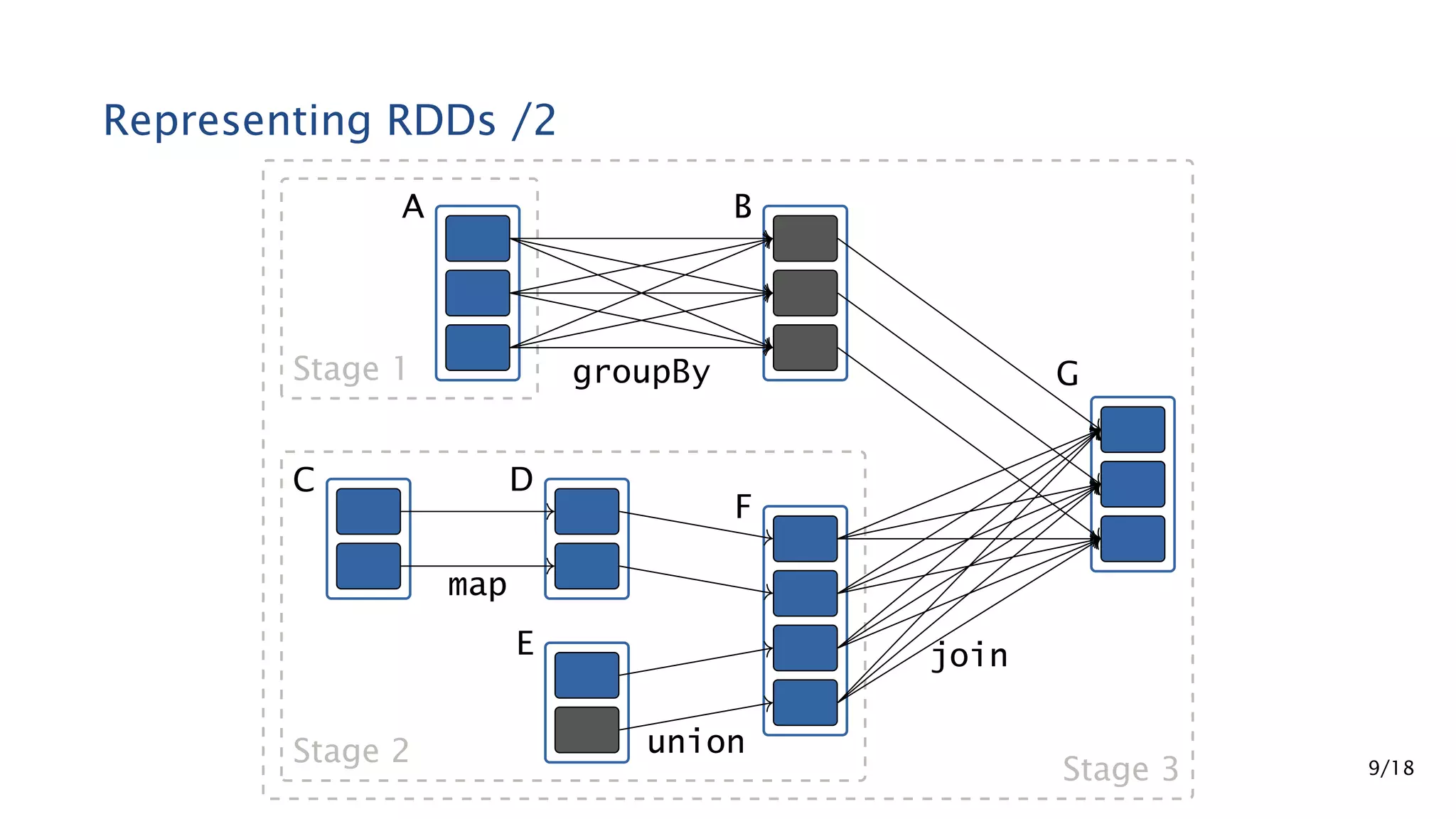
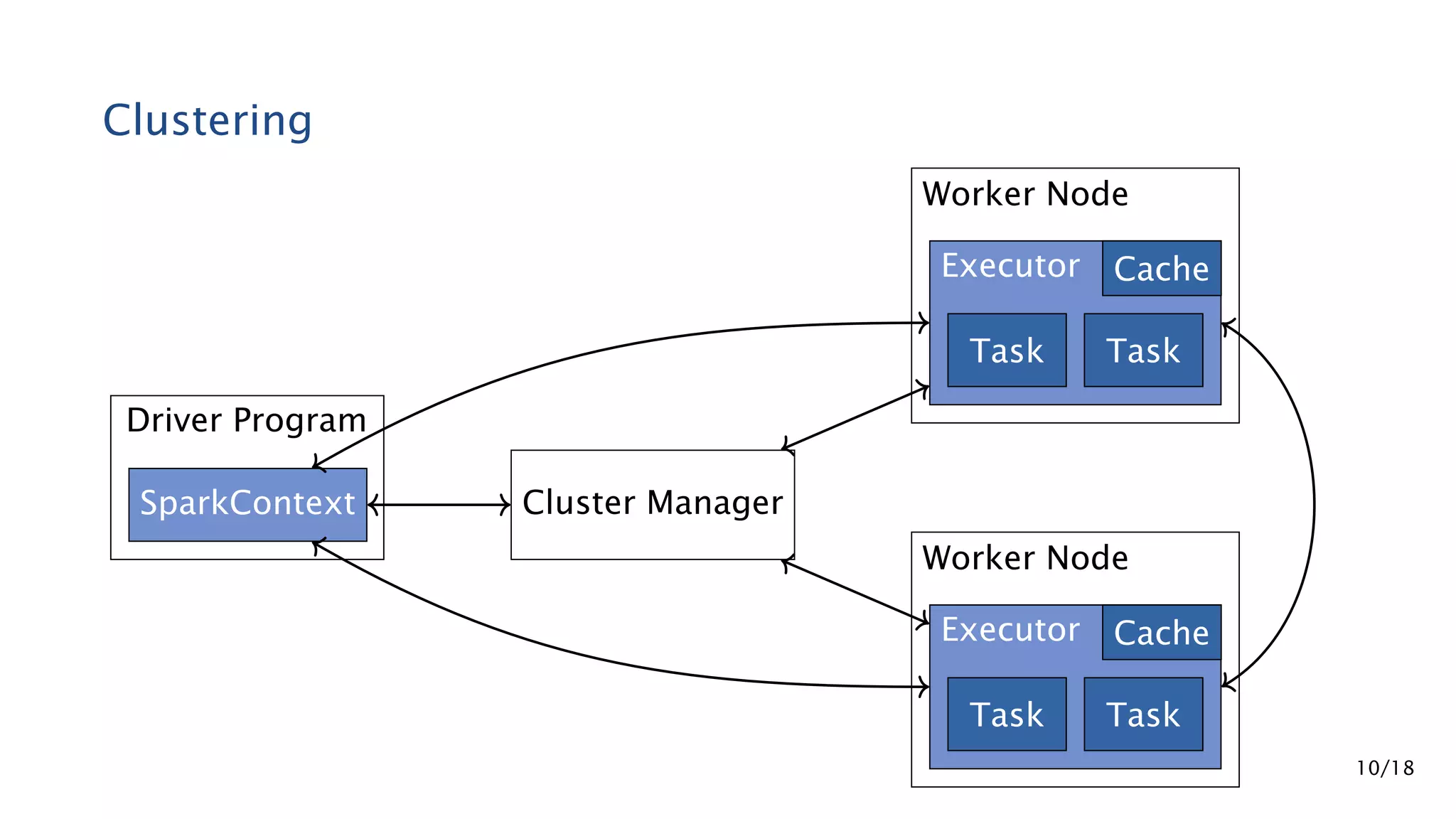
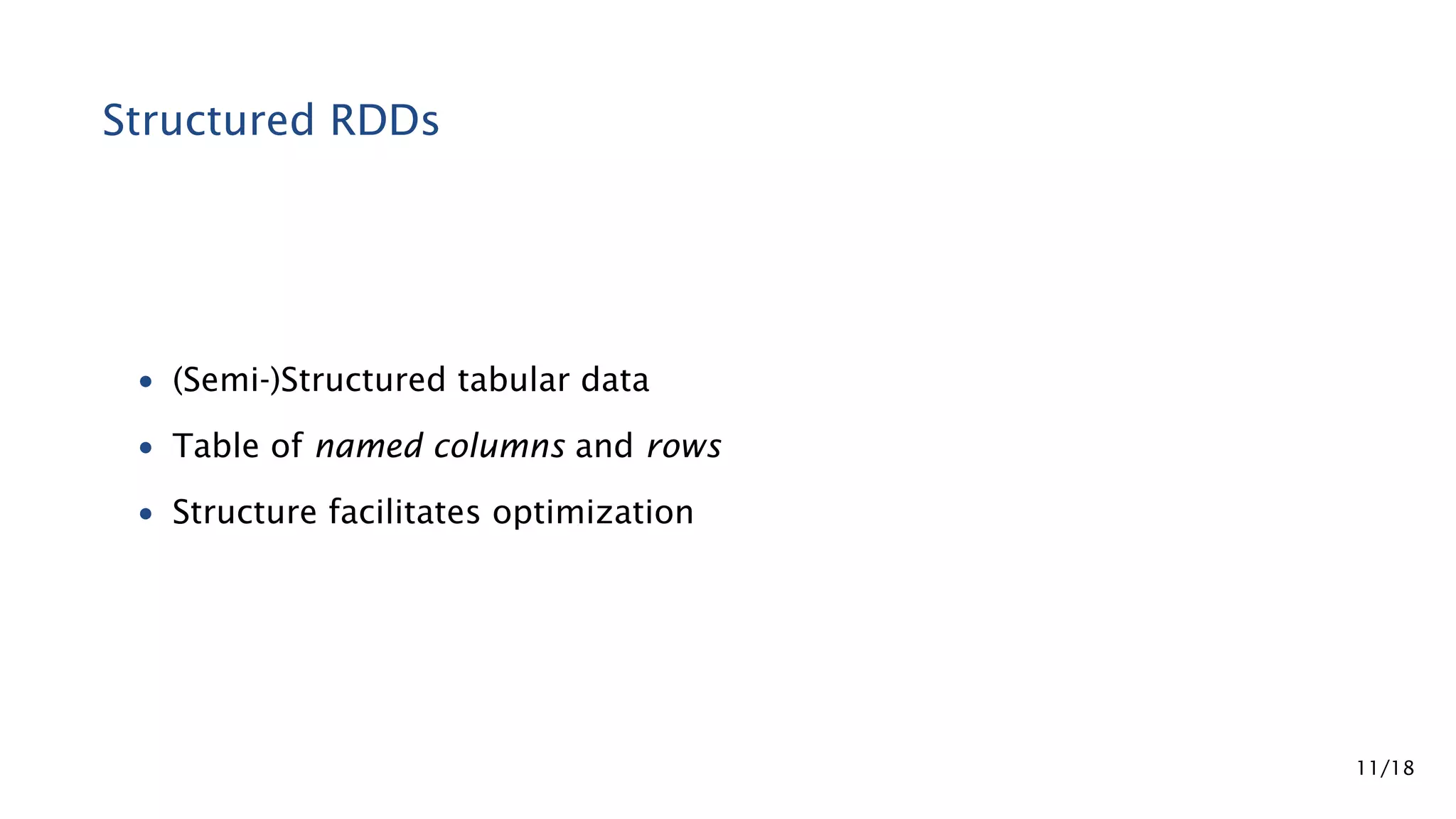
Apache Spark is a fast and general engine for large-scale data processing. It contains components for cluster computing with an in-memory execution model, SQL and streaming processing, and machine learning through MLlib. Spark uses Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) that can be operated on in parallel through transformations like map and reduce. RDDs can be used to represent both raw and structured data like DataFrames to facilitate optimization.


 => U): RDD[U] • flatMap[U](f: (T) => Seq[U]): RDD[U] • filter(f: (T) => Boolean): RDD[T] • union(other: RDD[T]): RDD[T] • intersection(other: RDD[T]): RDD[T] • distinct(other: RDD[T]): RDD[T] • groupBy[K](f: (T) => K): RDD[(K, Seq[T])] • keyBy[K](f: (T) => K): RDD[(K, T)] 5/18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/praesentation-170625151826/75/Apache-Spark-Fundamentals-and-MLlib-6-2048.jpg)
 => U): RDD[(K, U)] • flatMapValues[U](f: (V) => Seq[U]): RDD[(K, U)] • reduceByKey(f: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] • foldByKey(zeroValue: V)(f: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] • combineByKey[C](createCombiner: (V) => C, mergeValue: (C, V) => C, mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C): RDD[(K, C)] • groupByKey(): RDD[(K, Seq[V])] 6/18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/praesentation-170625151826/75/Apache-Spark-Fundamentals-and-MLlib-7-2048.jpg)
![Actions on RDDs • count(): Long • first(): T • take(num: Int): Array[T] • takeOrdered(num: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T]): Array[T] • collect(): Array[T] • reduce(f: (T, T) => T): T • aggregate[U](zeroValue: U)(seqOp: (U, T) => U, combOp: (U, U) => U): U • saveAsObjectFile(path: String): Unit 7/18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/praesentation-170625151826/75/Apache-Spark-Fundamentals-and-MLlib-8-2048.jpg)


![DataFrame and Dataset Transformations • select(cols: Column*): DataFrame • join(right: Dataset[_], usingColumns: Seq[String]): DataFrame • where(condition: Column): Dataset[T] • groupBy(cols: Column*): RelationalGroupedDataset • cube(cols: Column*): RelationalGroupedDataset • rollup(cols: Column*): RelationalGroupedDataset • drop(col: Column): DataFrame • withColumn(colName: String, col: Column): DataFrame 13/18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/praesentation-170625151826/75/Apache-Spark-Fundamentals-and-MLlib-14-2048.jpg)

![Actions on Datasets • count(): Long • first(): T • take(n: Int): Array[T] • takeOrdered(num: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T]): Array[T] • collect(): Array[T] • show(numRows: Int): Unit 15/18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/praesentation-170625151826/75/Apache-Spark-Fundamentals-and-MLlib-16-2048.jpg)