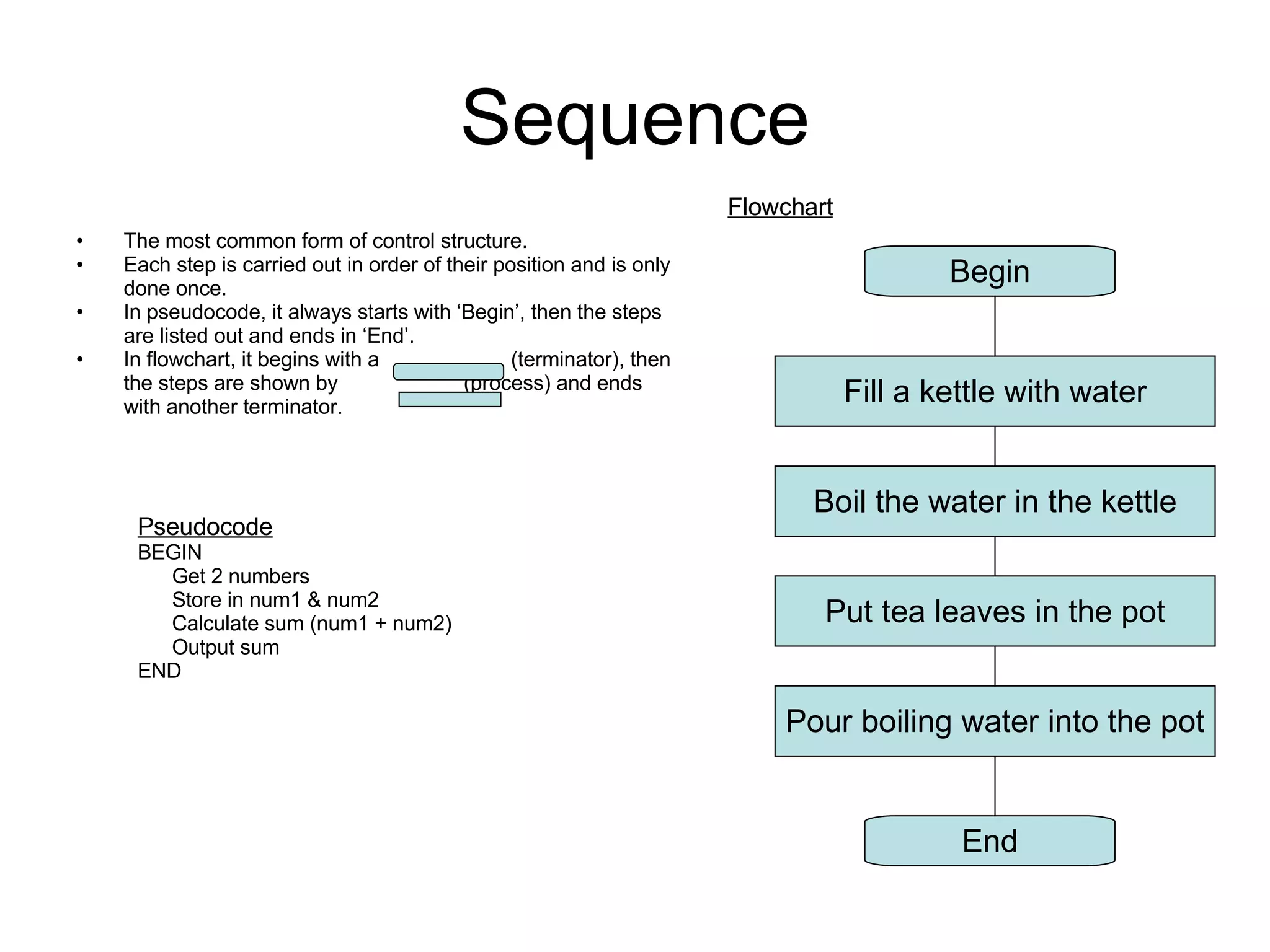
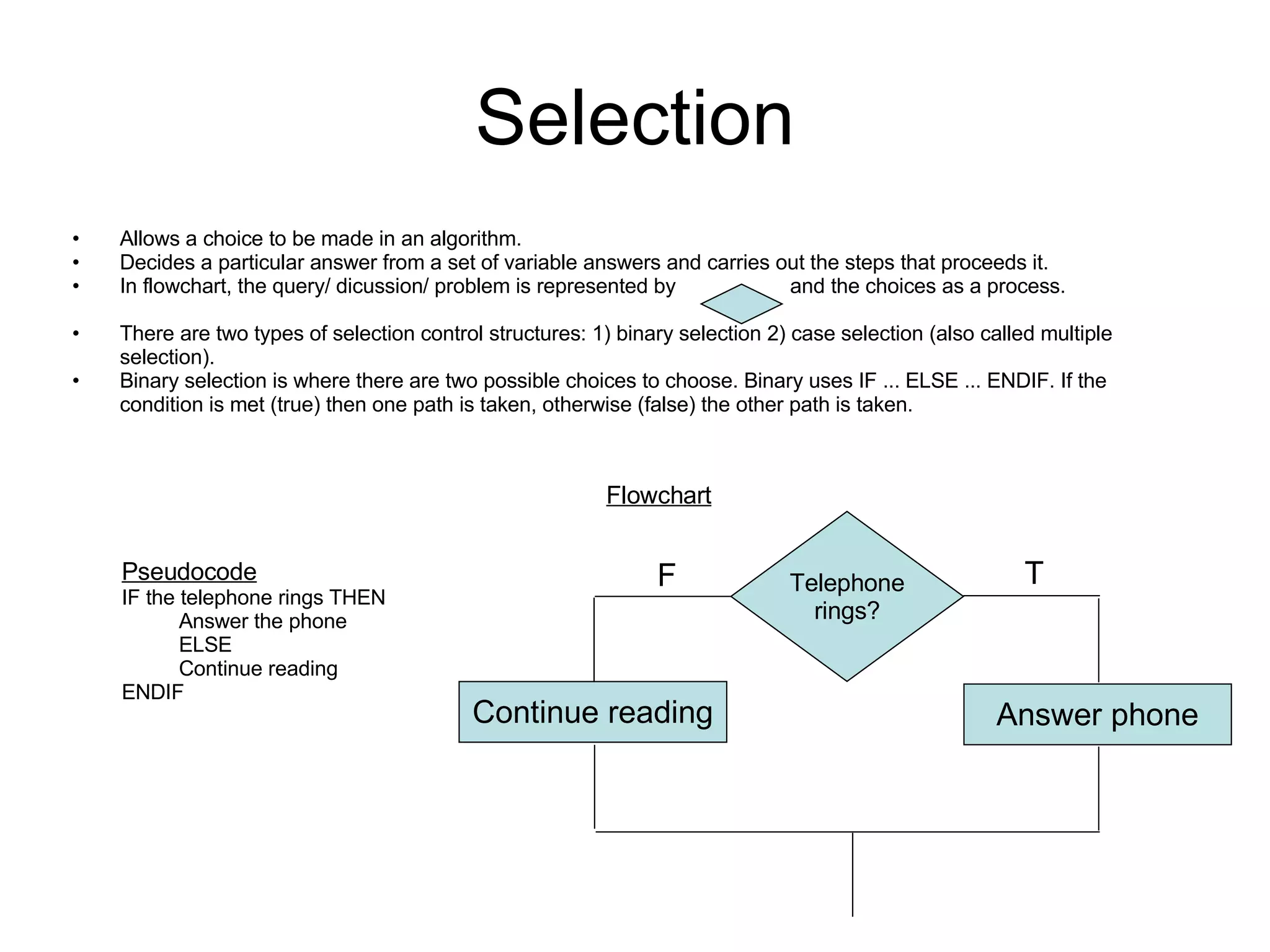
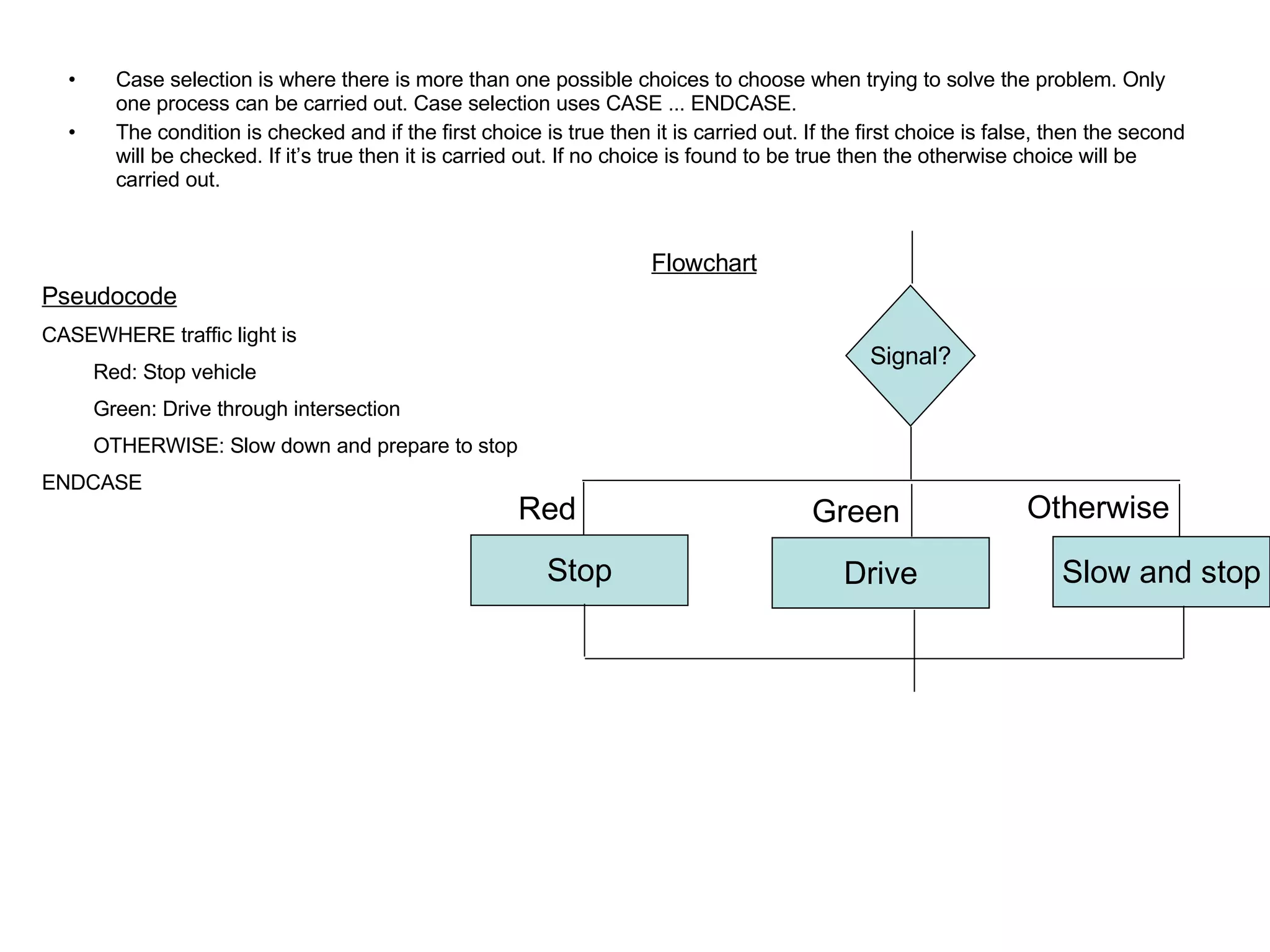
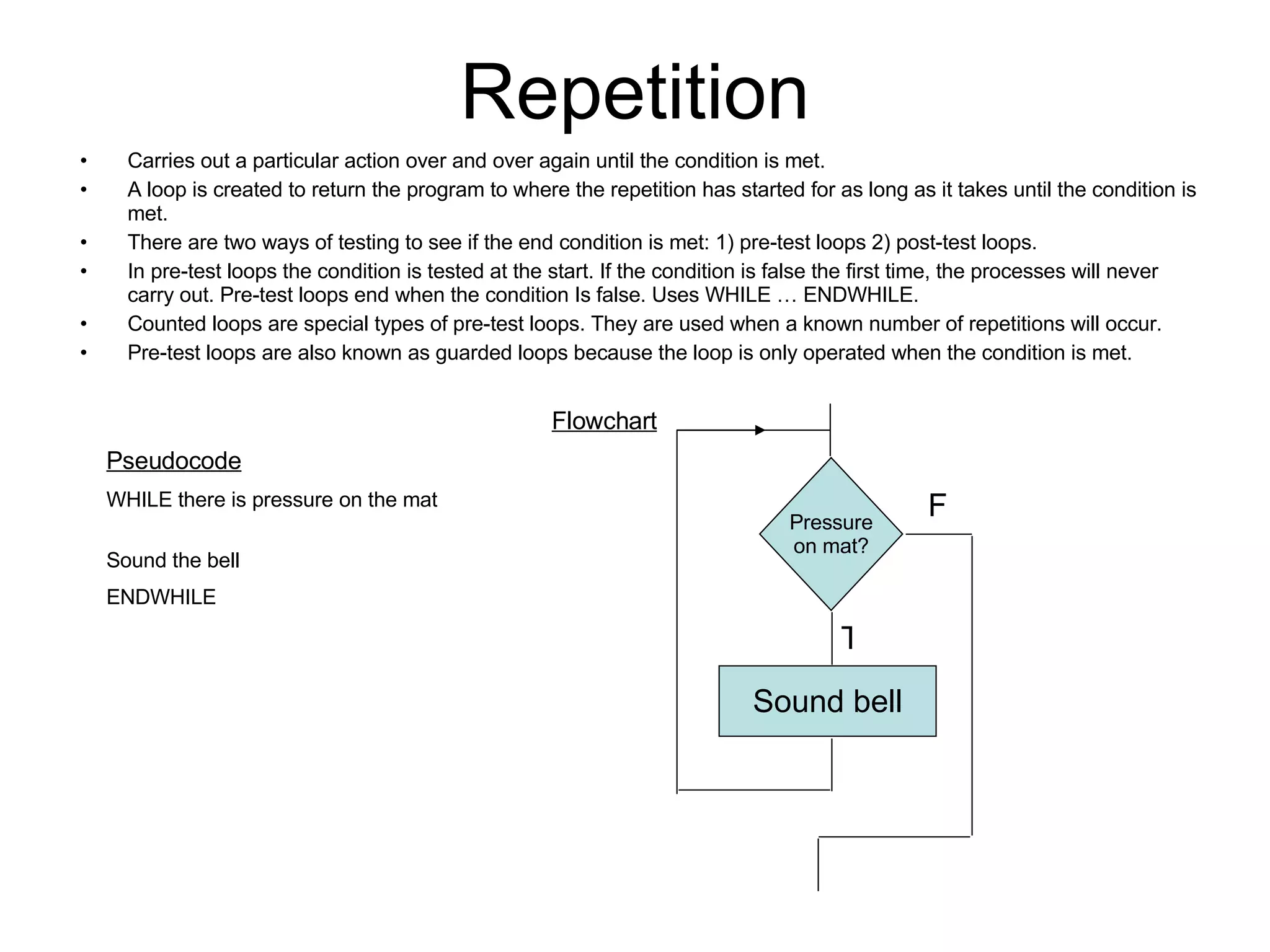
There are three main types of control structures in algorithms: sequence, selection, and repetition. Sequence structures run steps in order, selection structures allow for choices with conditions like IF/ELSE, and repetition structures repeat steps until a condition is met, using loops like WHILE. Control structures are represented differently in pseudocode and flowcharts.