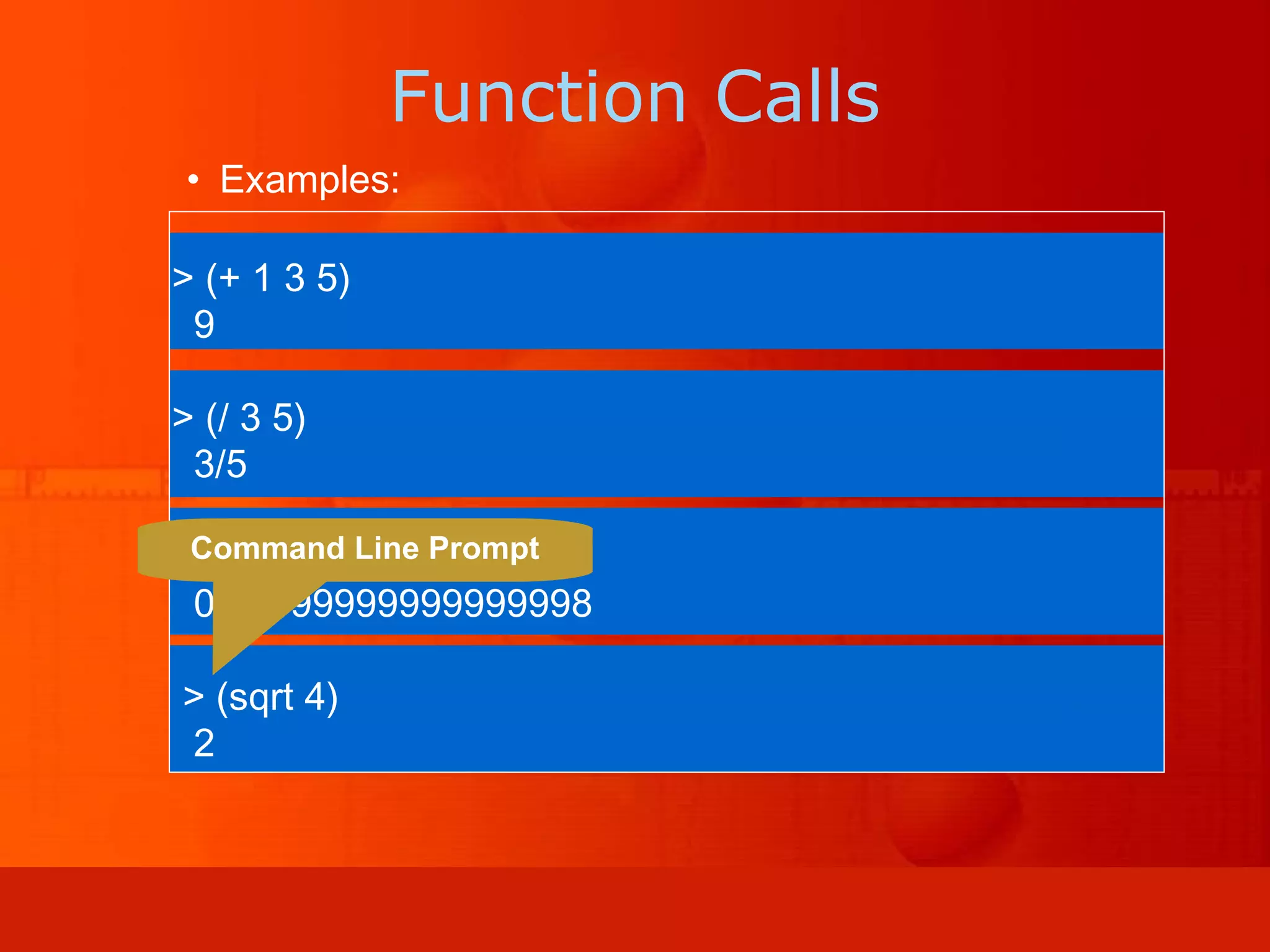
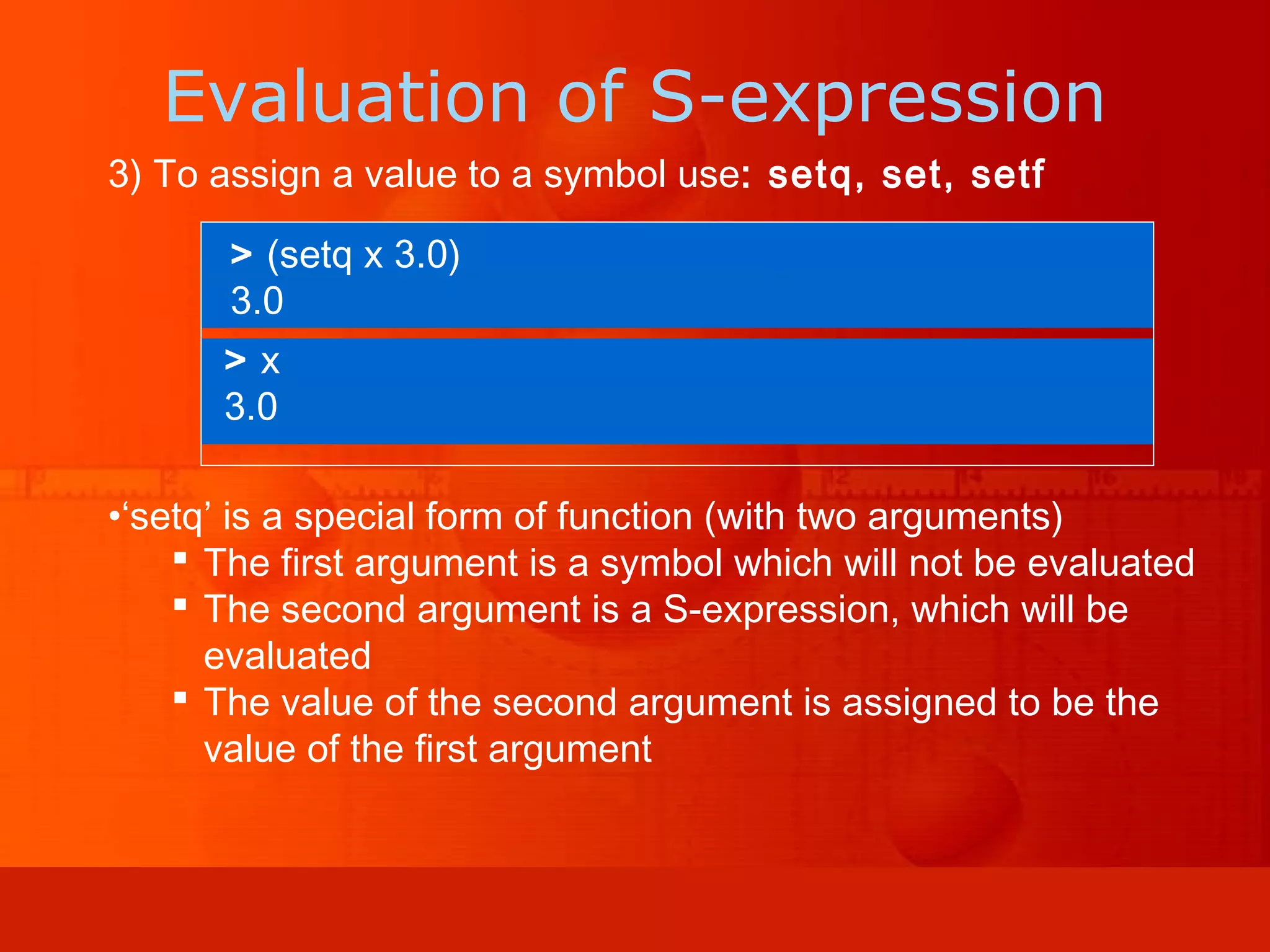
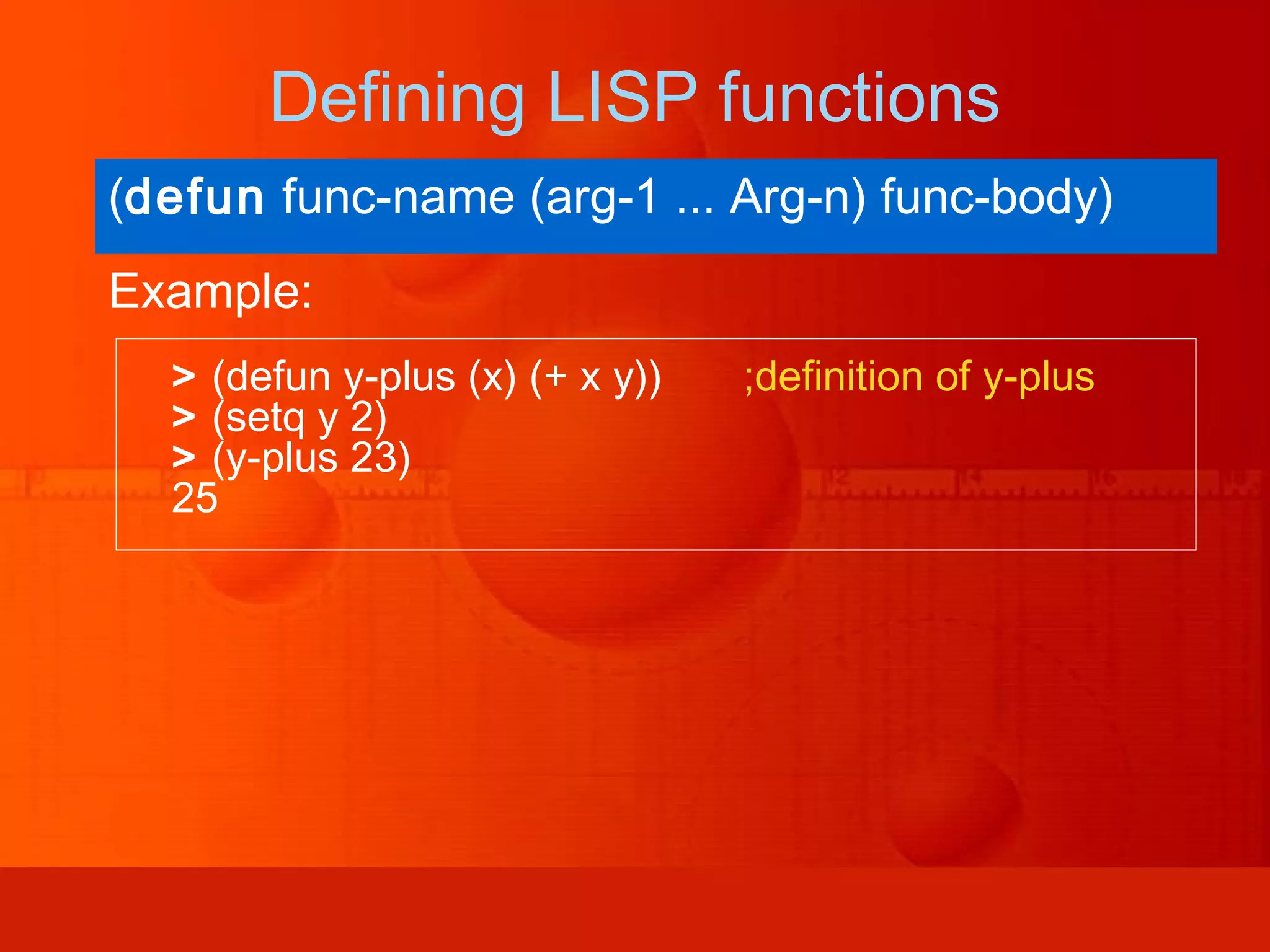
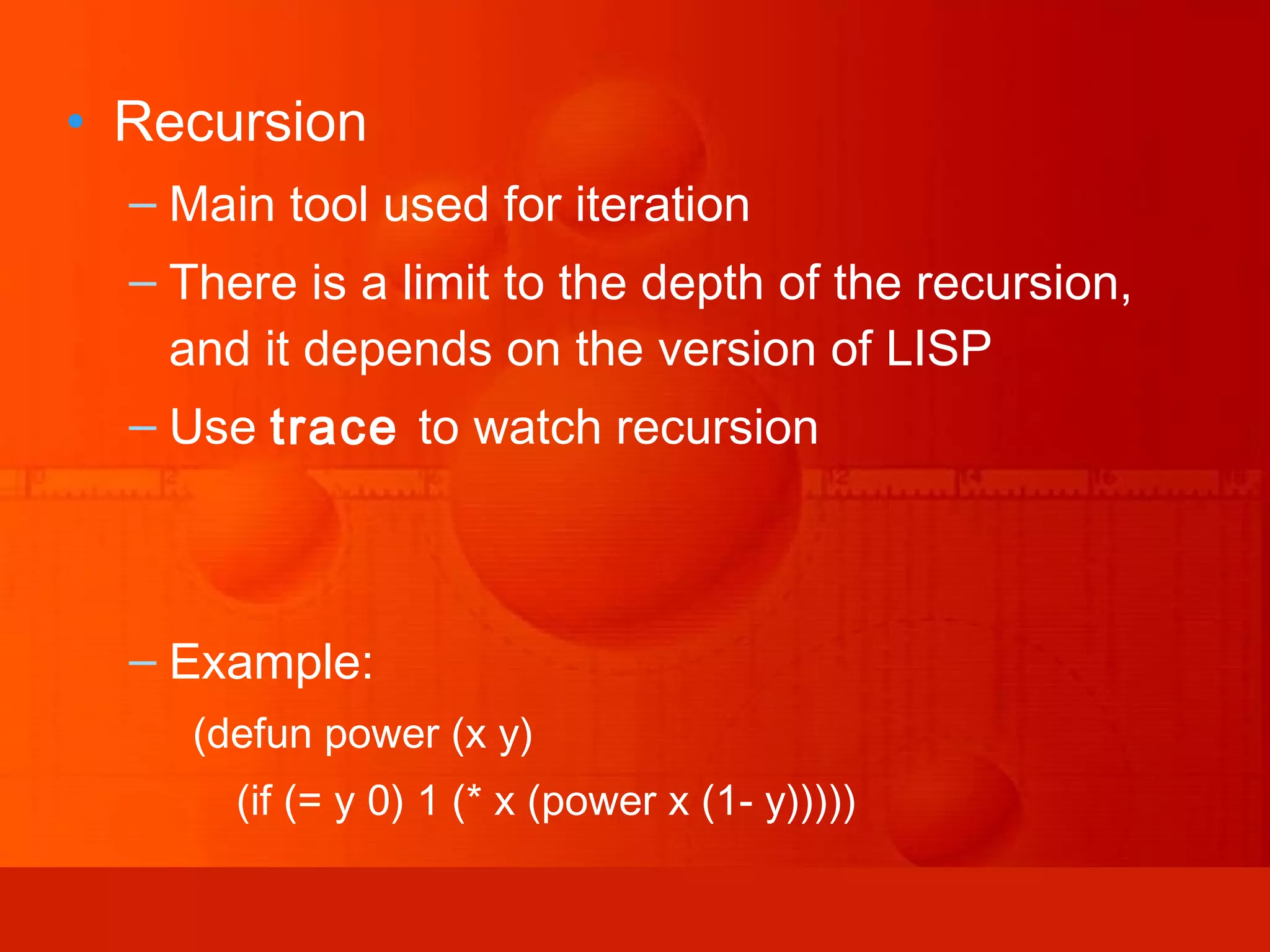
LISP is a programming language invented in 1958 that uses two simple data structures - atoms and lists. It heavily relies on recursion and functional programming. LISP defines all data as lists and represents programs as nested function calls, allowing for dynamic typing and easy abstraction. It introduced many concepts still used in modern languages, including conditionals, recursion, dynamic typing, garbage collection, and representing programs as mathematical expressions.
![Artificial Intelligence [LISP] Presented by:-A.RAVINDRA KUMAR RAO (B.TECH (C.E)) Madanapalle Institute Of Technology & Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-lisp-160915130339/75/Ai-lisp-1-2048.jpg)