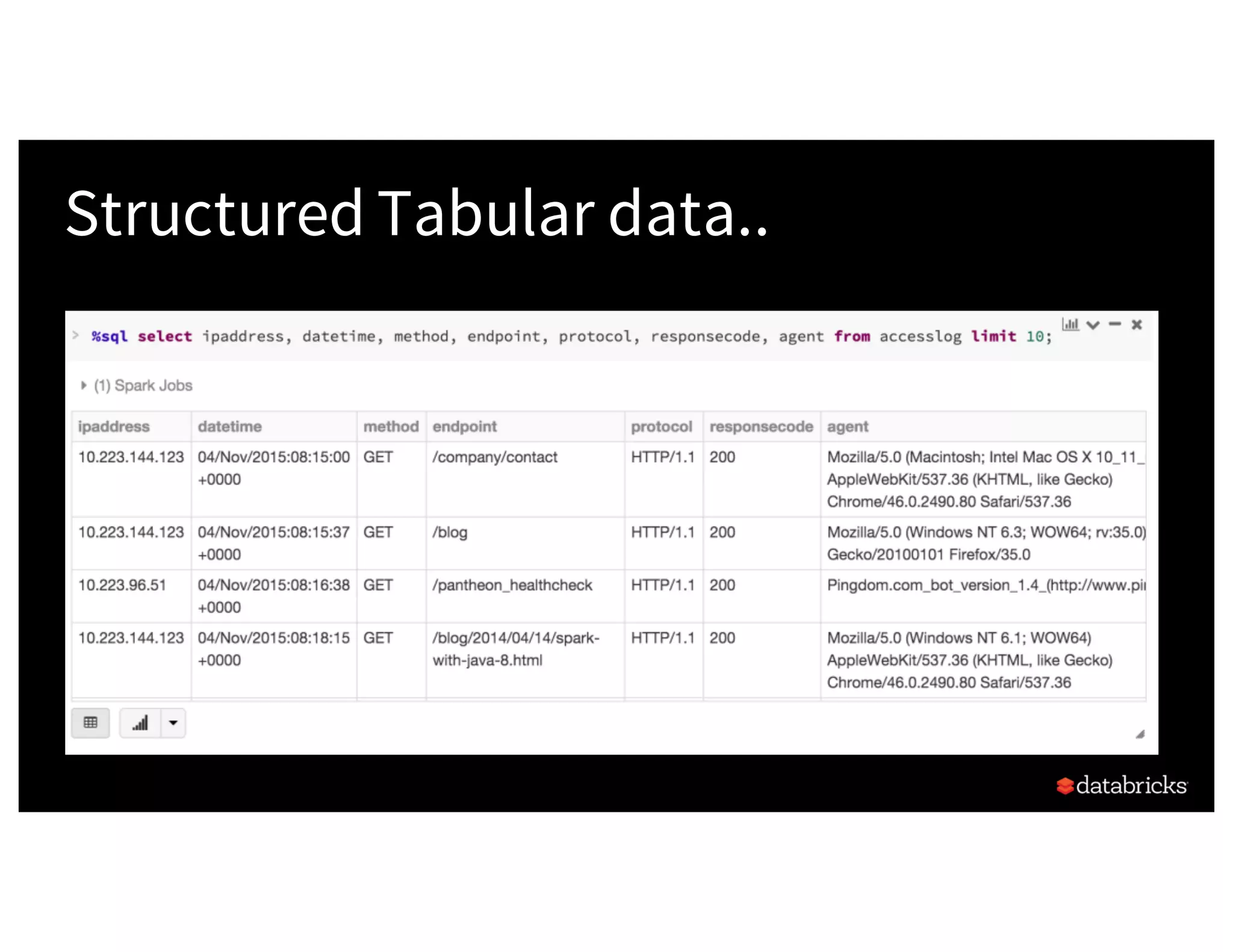
The document discusses the three Apache Spark APIs: RDDs, DataFrames, and Datasets, detailing their features, use cases, and performance characteristics. RDDs offer low-level control and flexibility for working with distributed data, while DataFrames and Datasets provide higher-level abstractions that optimize performance and ease of use. The presentation also highlights the evolution of these APIs and their integration within Spark for structured data processing.





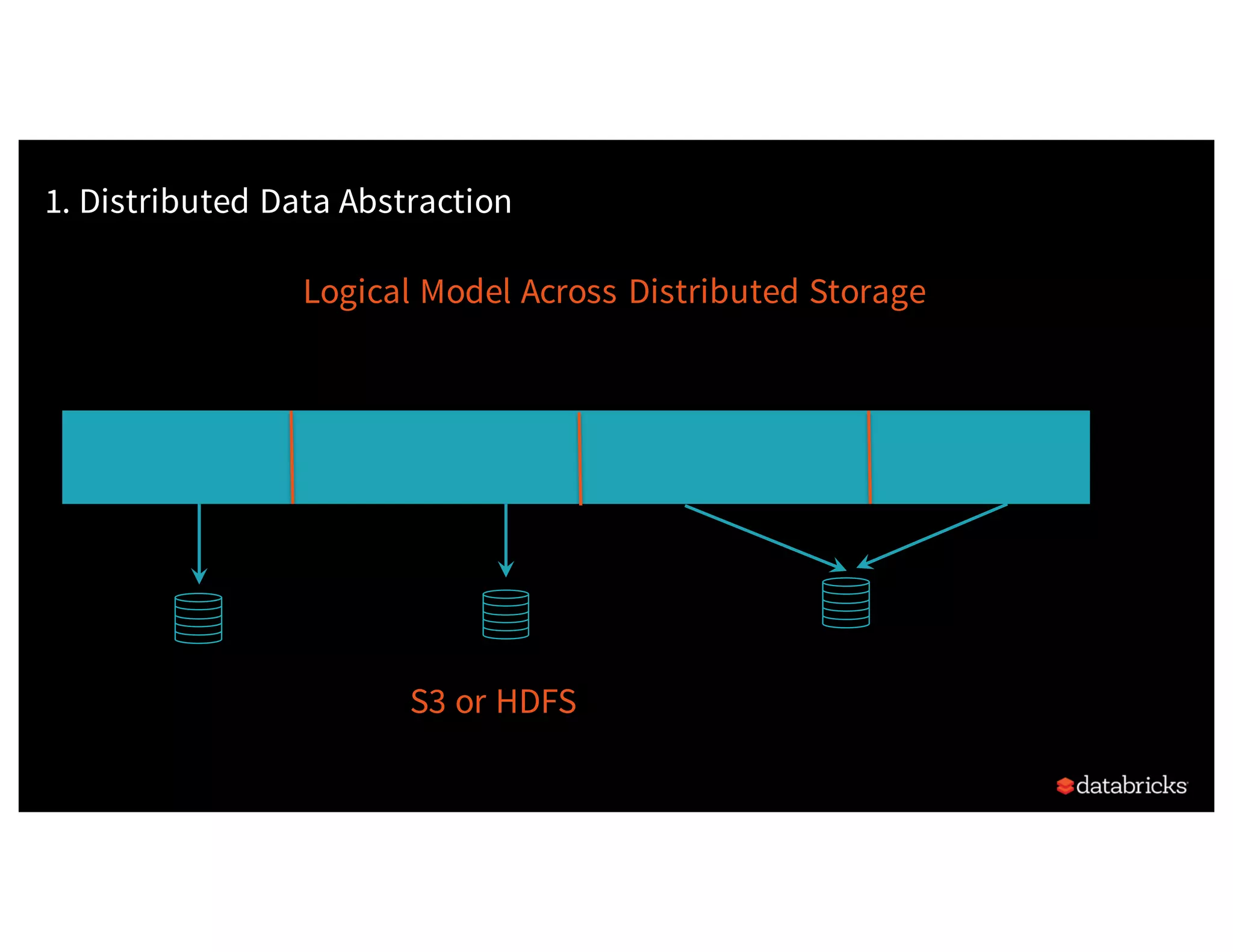
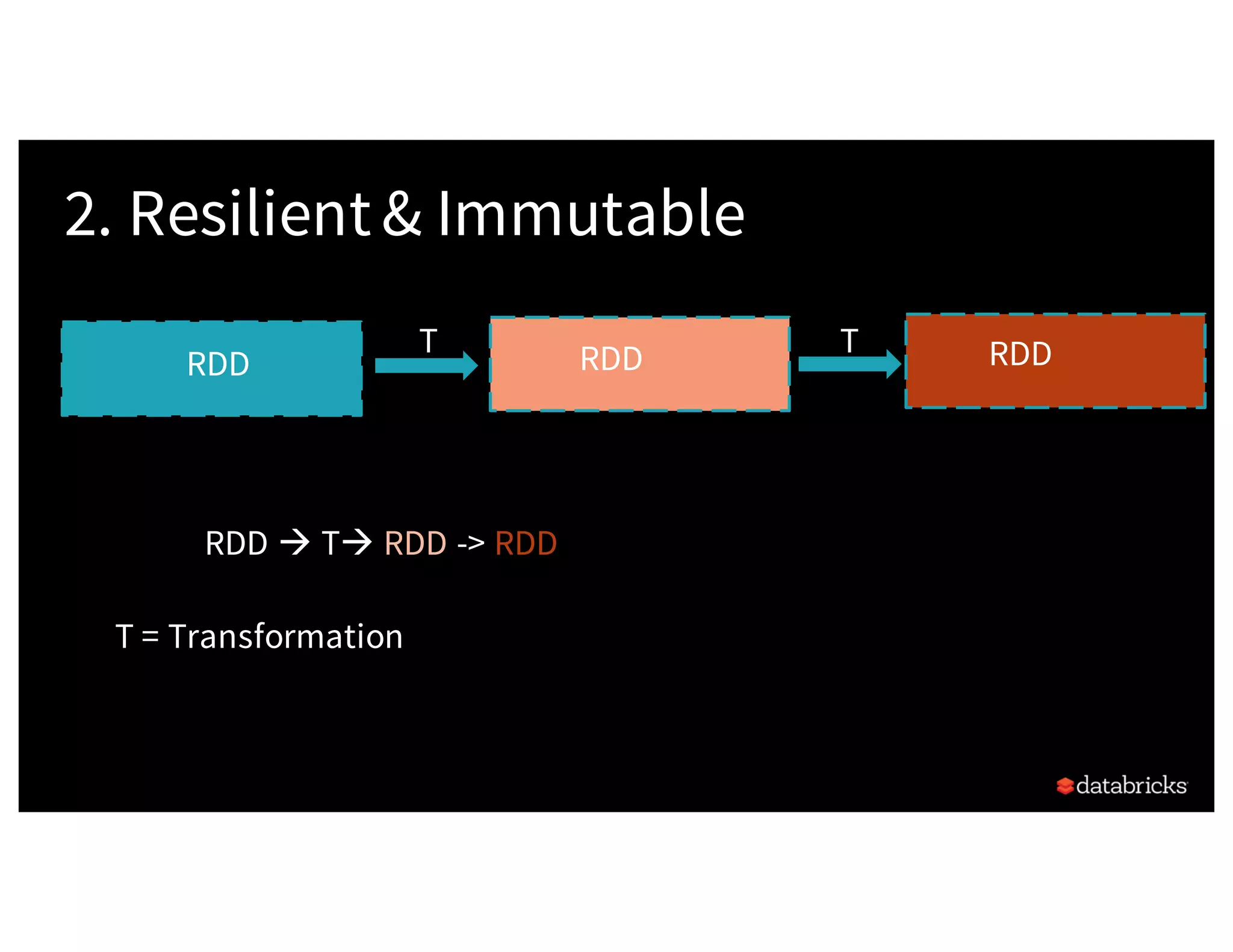
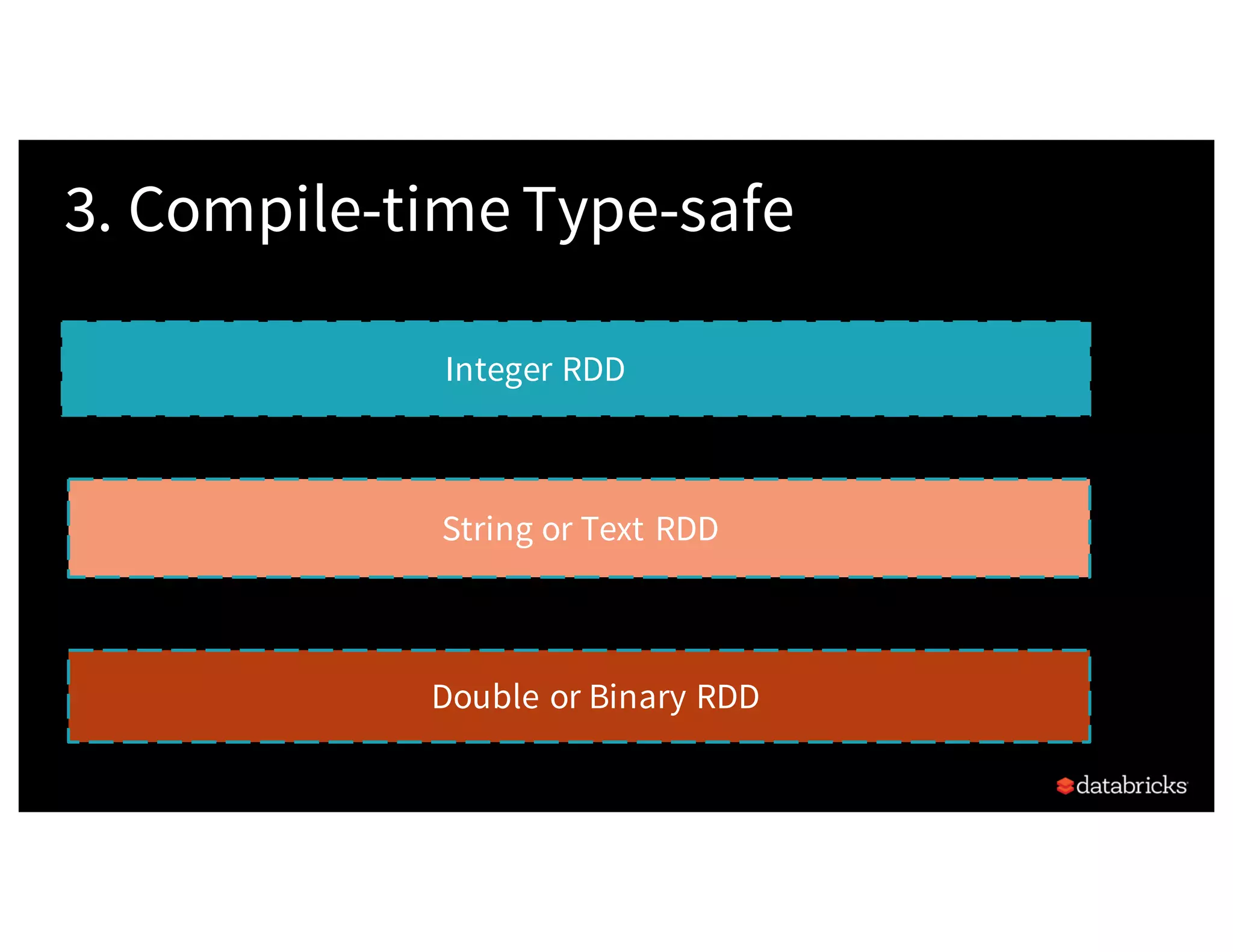
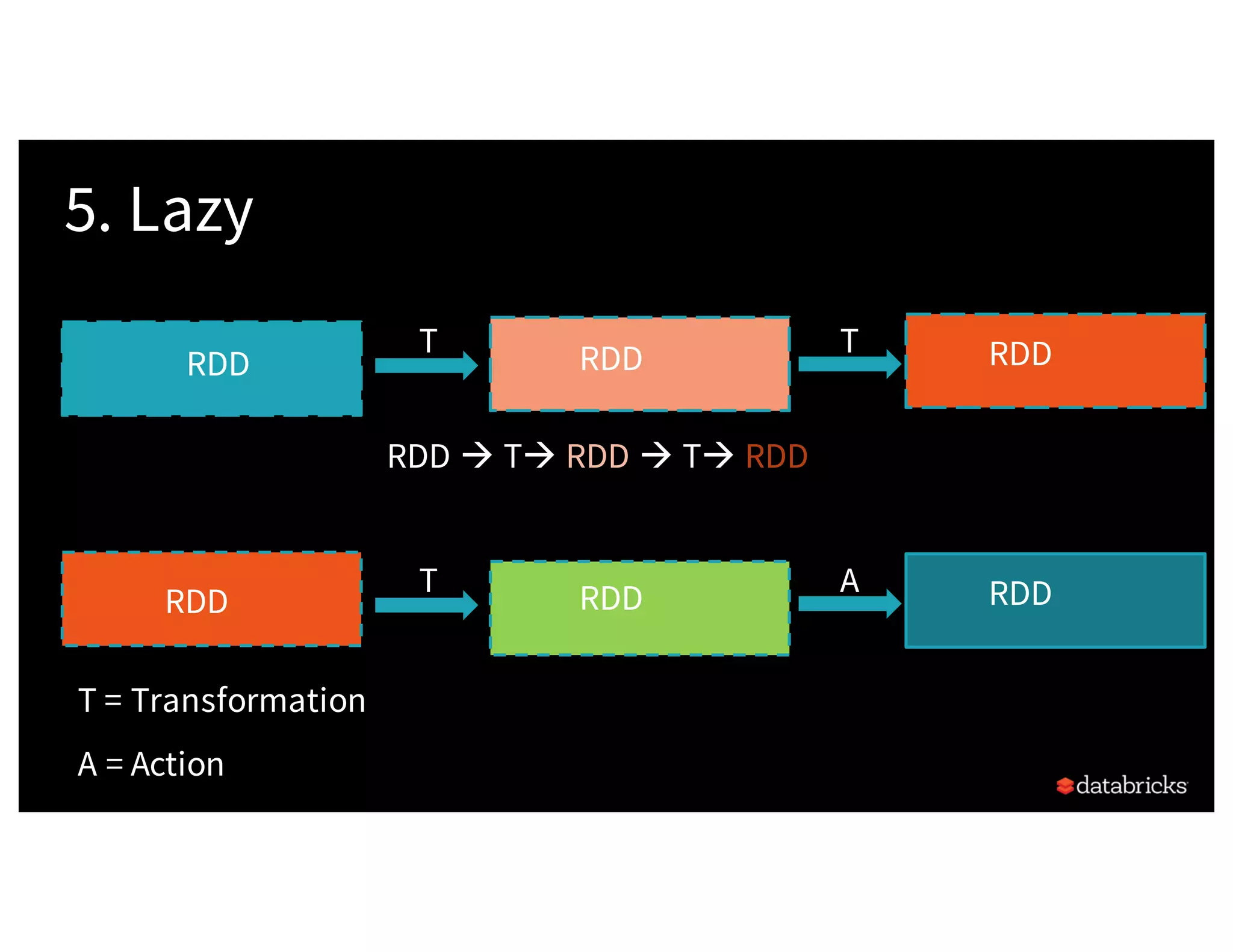
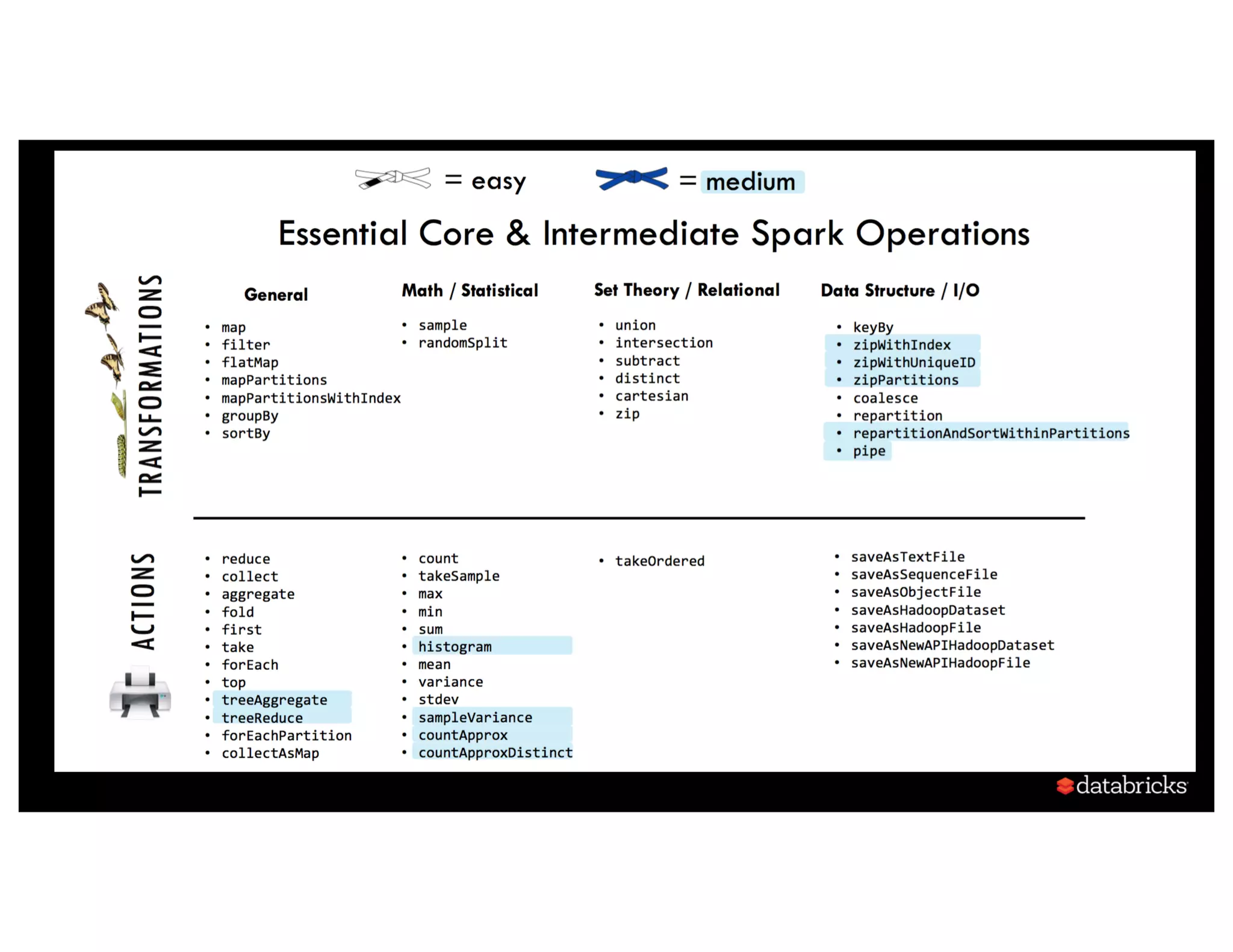






![Background:What is in an RDD? •Dependencies • Partitions (with optional localityinfo) • Compute function: Partition=>Iterator[T] Opaque Computation & Opaque Data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a3julesdamji-171031221012/75/A-Tale-of-Three-Apache-Spark-APIs-RDDs-DataFrames-and-Datasets-with-Jules-Damji-22-2048.jpg)
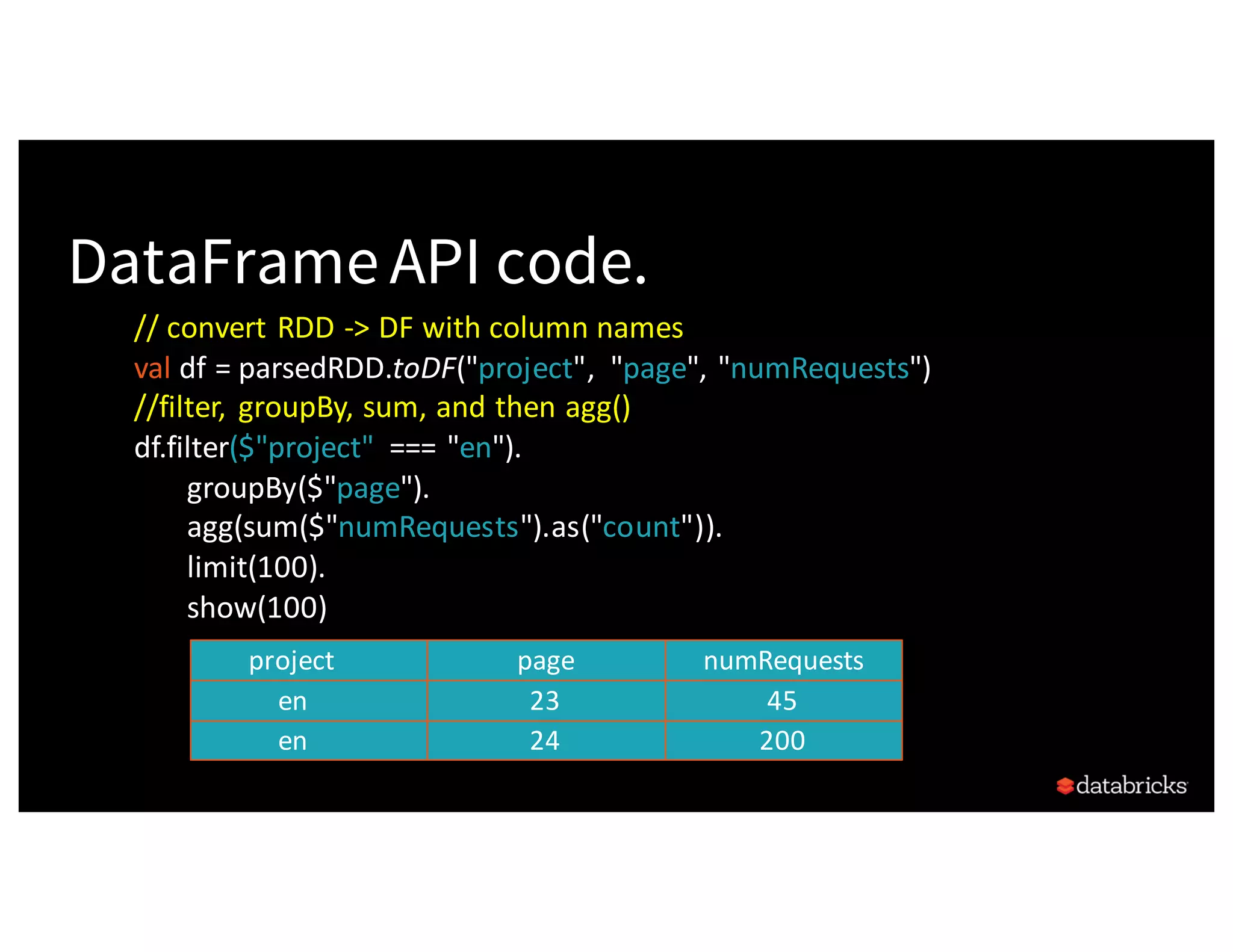
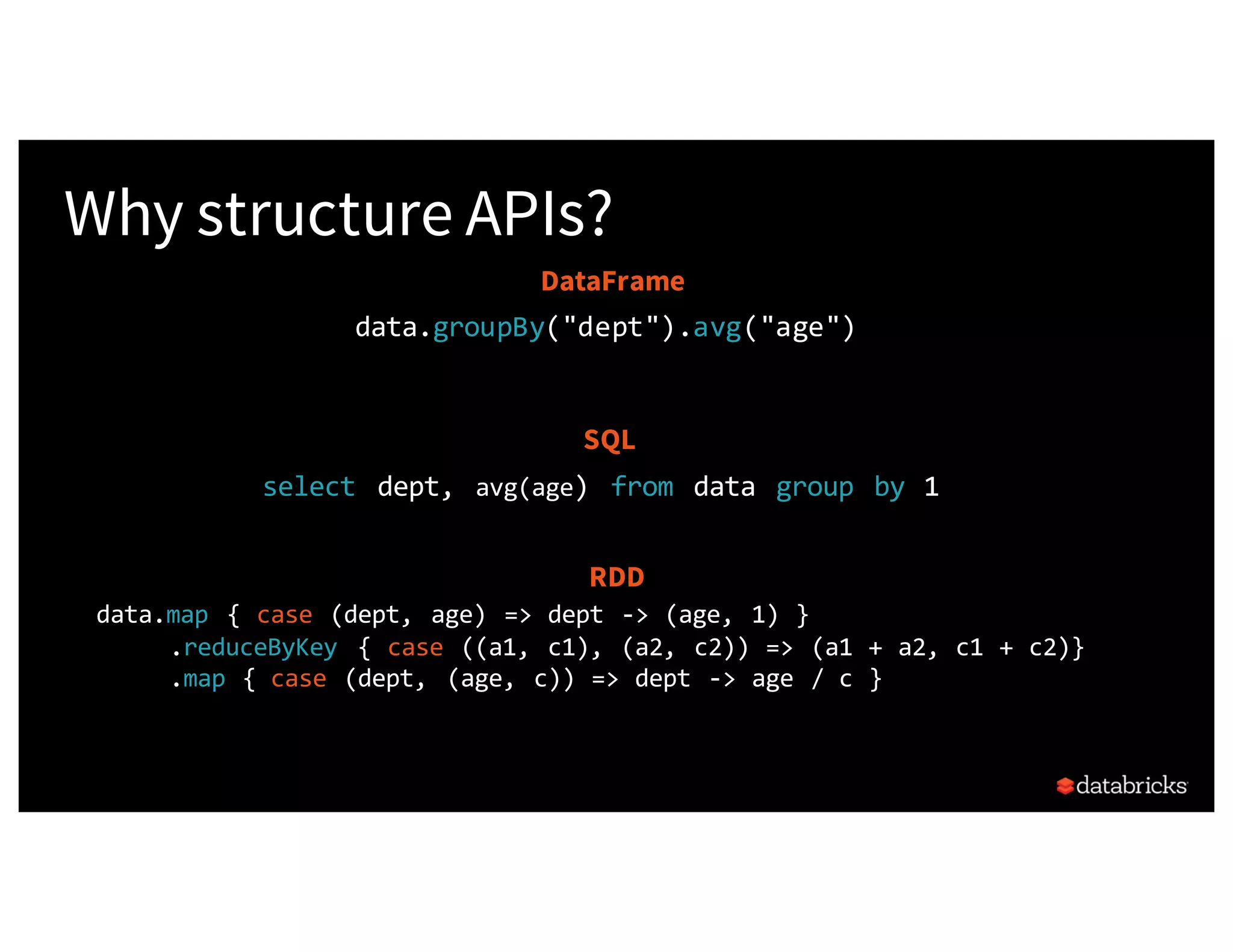
![Easy to write code... Believe it! from pyspark.sql.functions import avg dataRDD = sc.parallelize([("Jim", 20), ("Anne", 31), ("Jim", 30)]) dataDF = dataRDD.toDF(["name", "age"]) # Using RDD code to compute aggregate average (dataRDD.map(lambda (x,y): (x, (y,1))) .reduceByKey(lambda x,y: (x[0] +y[0], x[1] +y[1])) .map(lambda (x, (y, z)): (x, y / z))) # Using DataFrame dataDF.groupBy("name").agg(avg("age")) name age Jim 20 Ann 31 Jim 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a3julesdamji-171031221012/75/A-Tale-of-Three-Apache-Spark-APIs-RDDs-DataFrames-and-Datasets-with-Jules-Damji-27-2048.jpg)
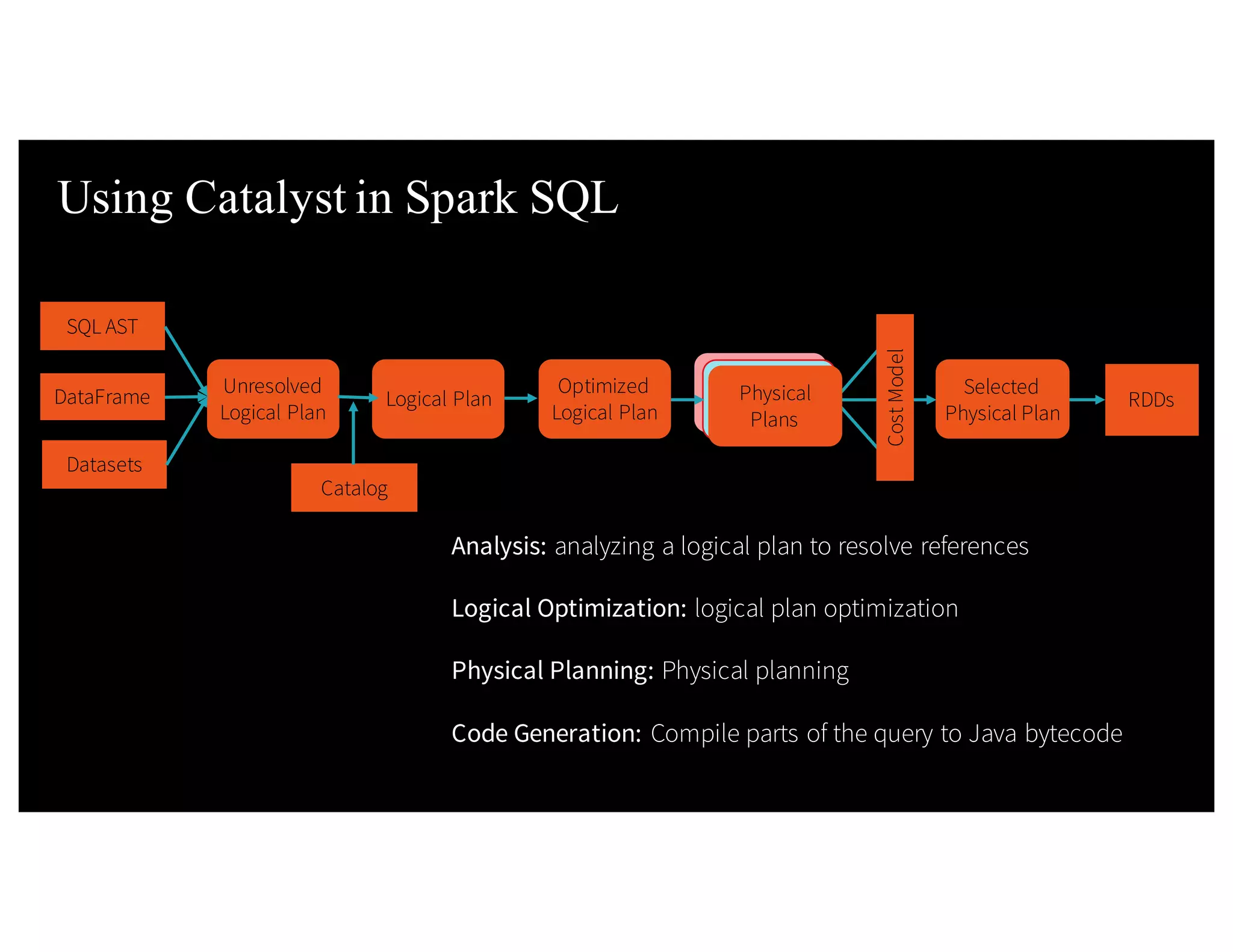
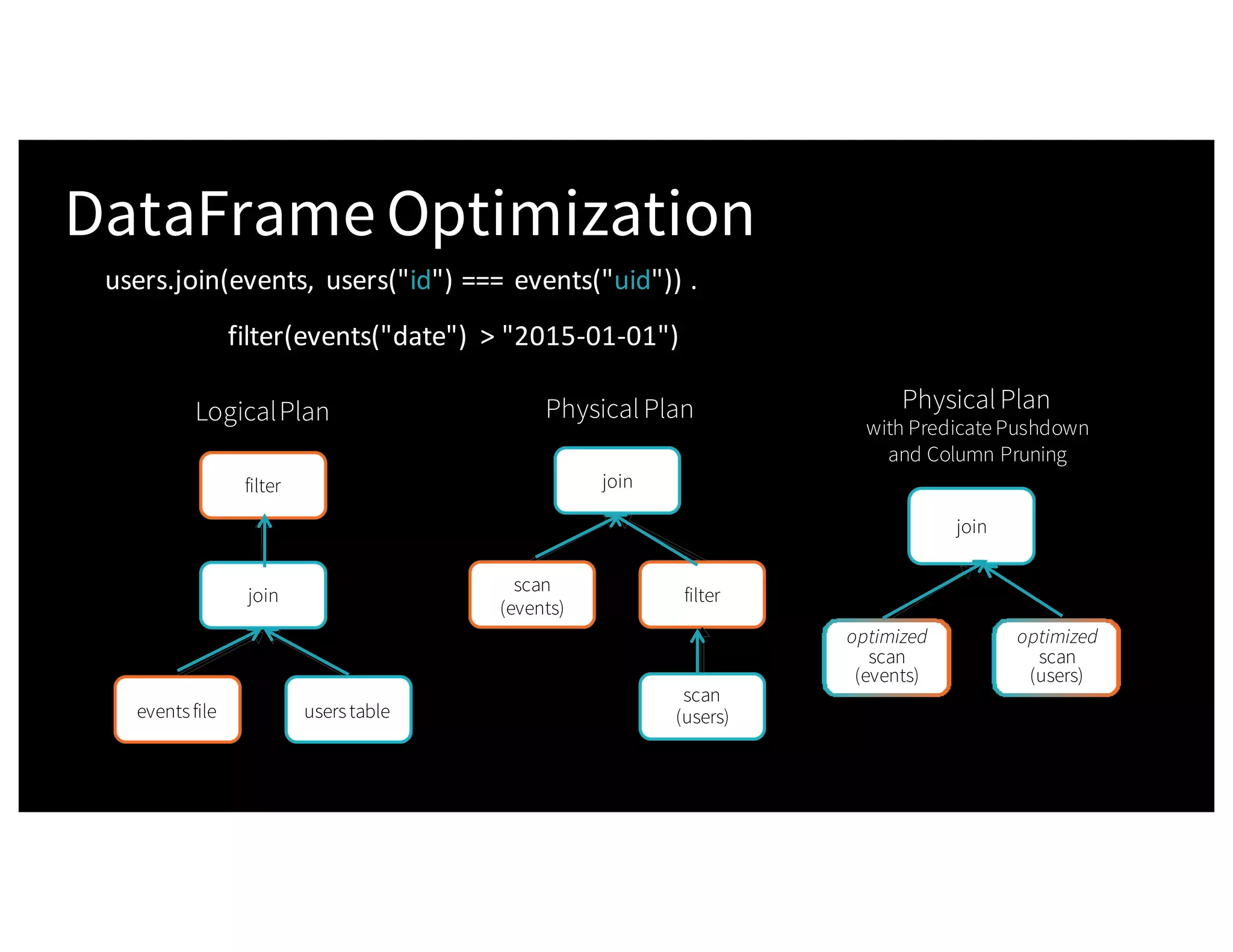
![Type-safe: operate on domain objects with compiled lambda functions 8 Dataset API in Spark 2.x val df = spark.read.json("people.json") / / Convert data to domain objects. case class Person(name: String, age: I nt ) val ds: Dataset[Person] = df.as[Person] val = filterDS = ds . f i l t er( p= >p. age > 3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a3julesdamji-171031221012/75/A-Tale-of-Three-Apache-Spark-APIs-RDDs-DataFrames-and-Datasets-with-Jules-Damji-31-2048.jpg)