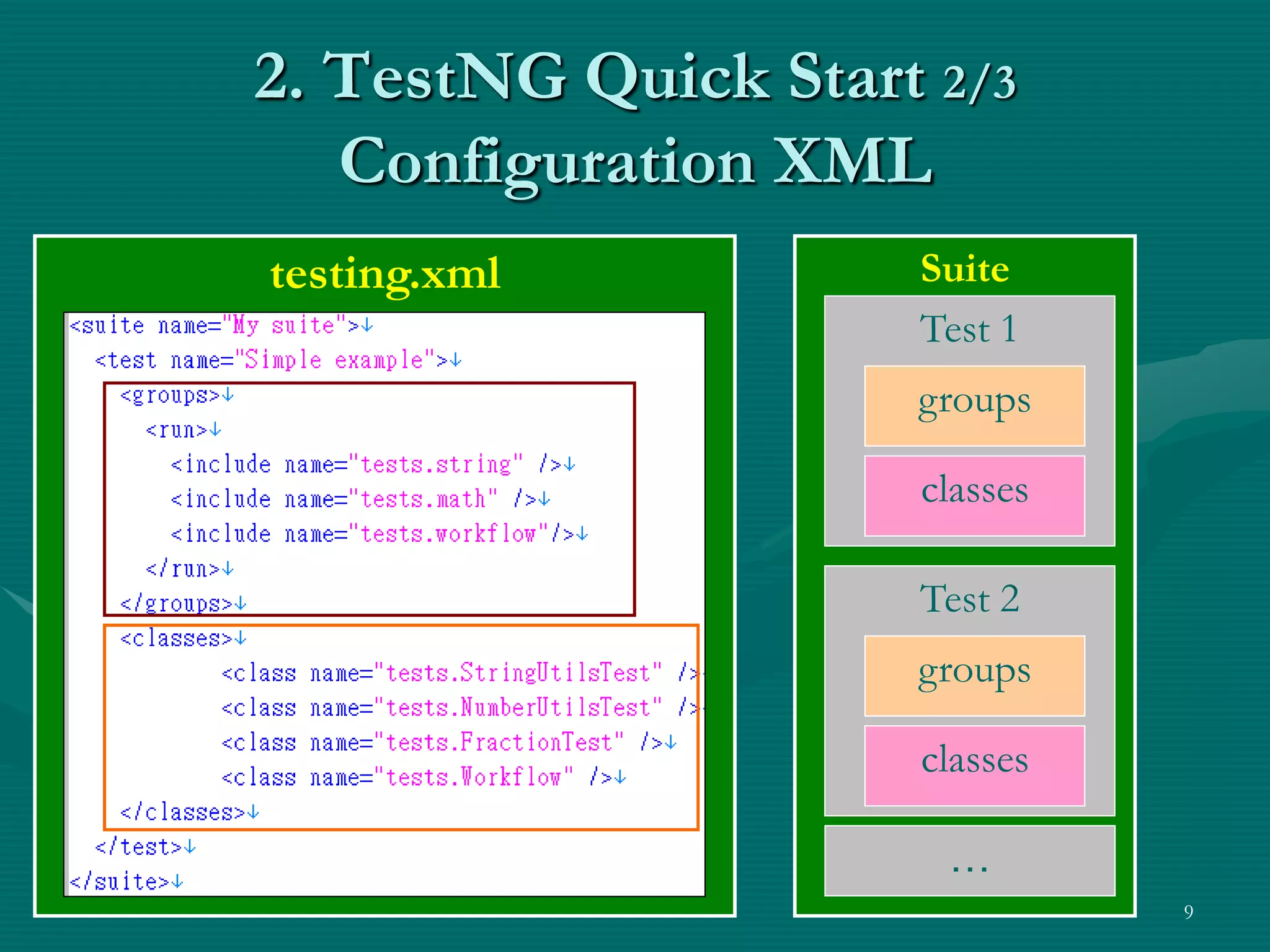
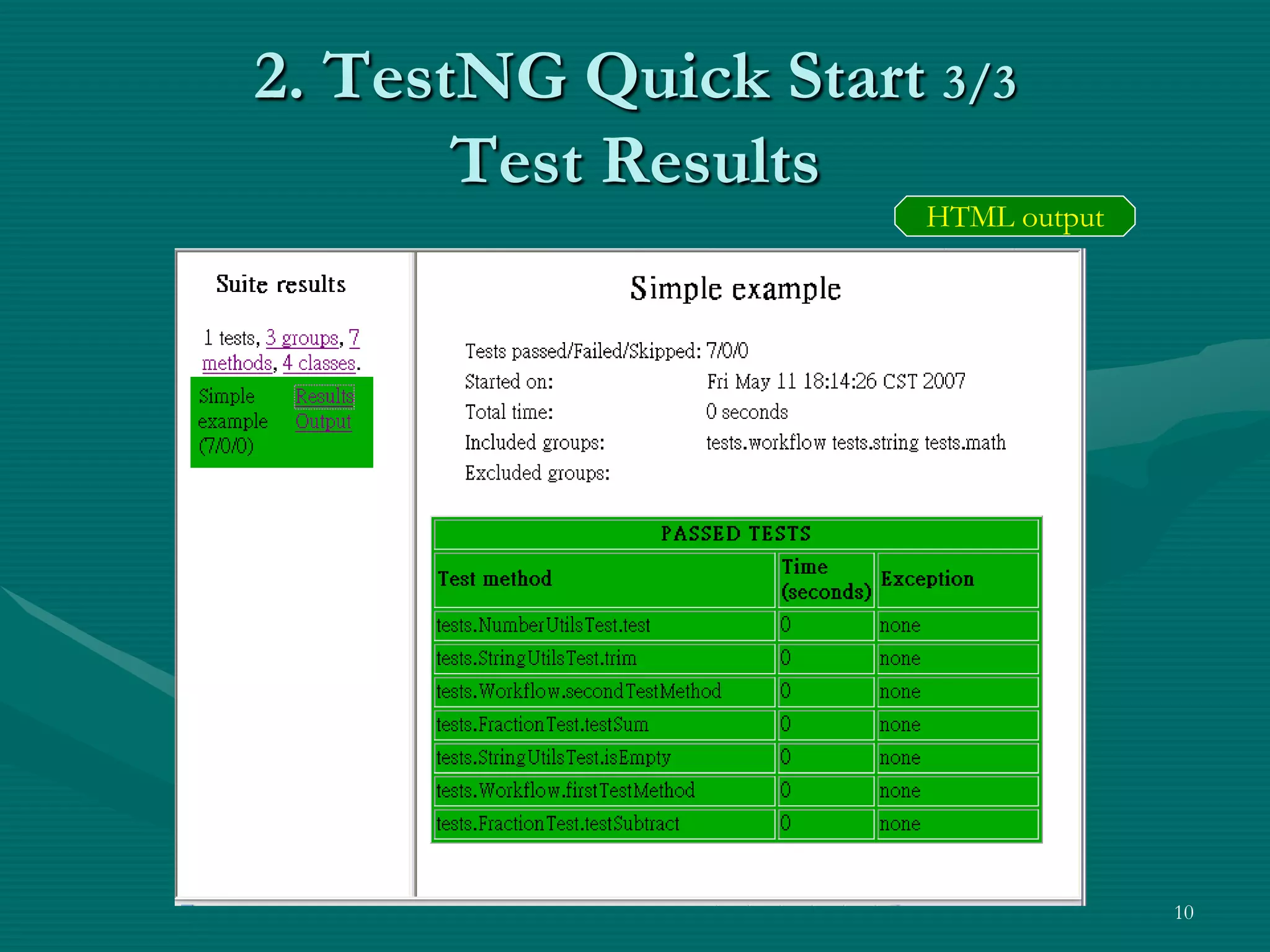
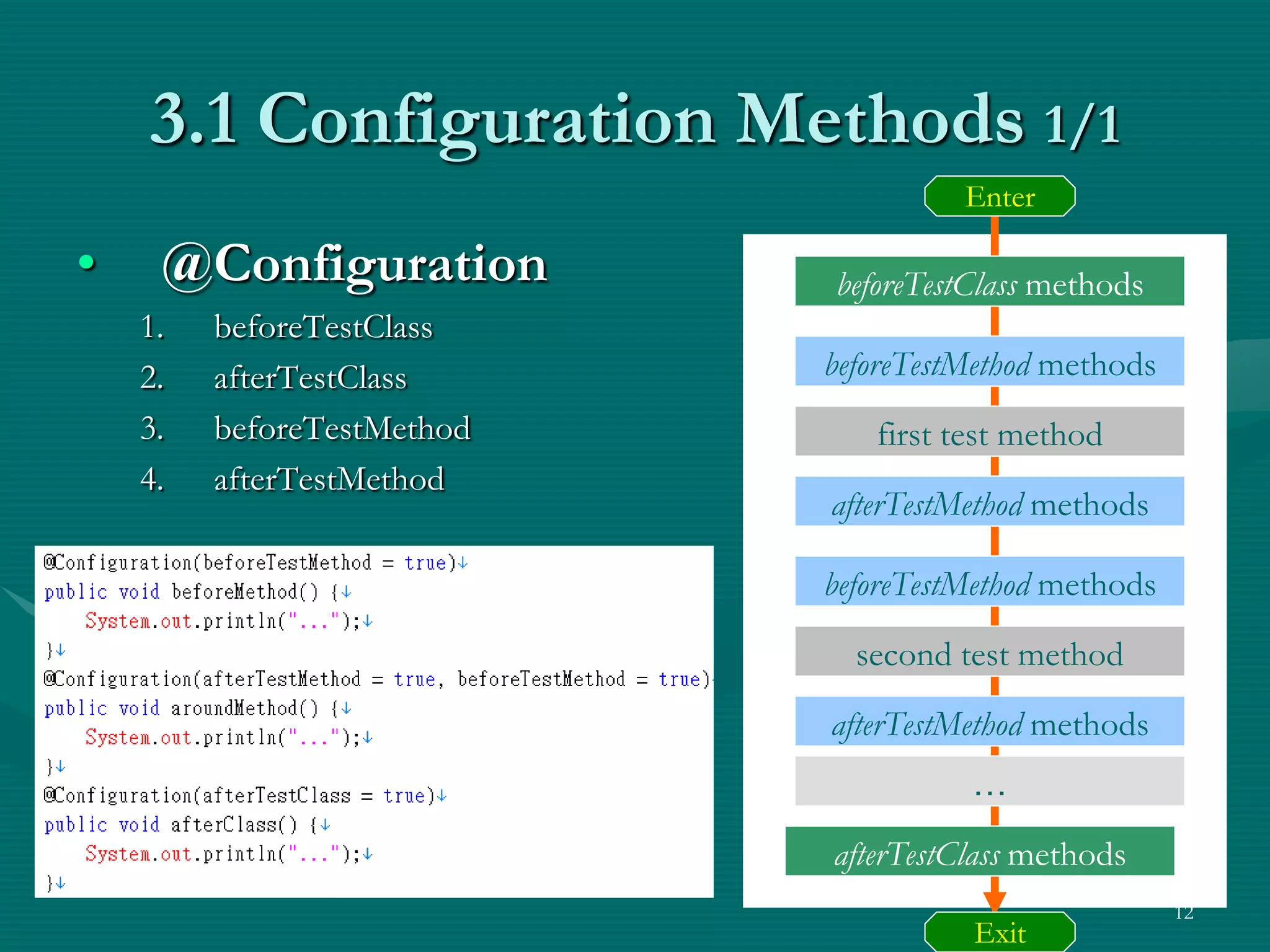
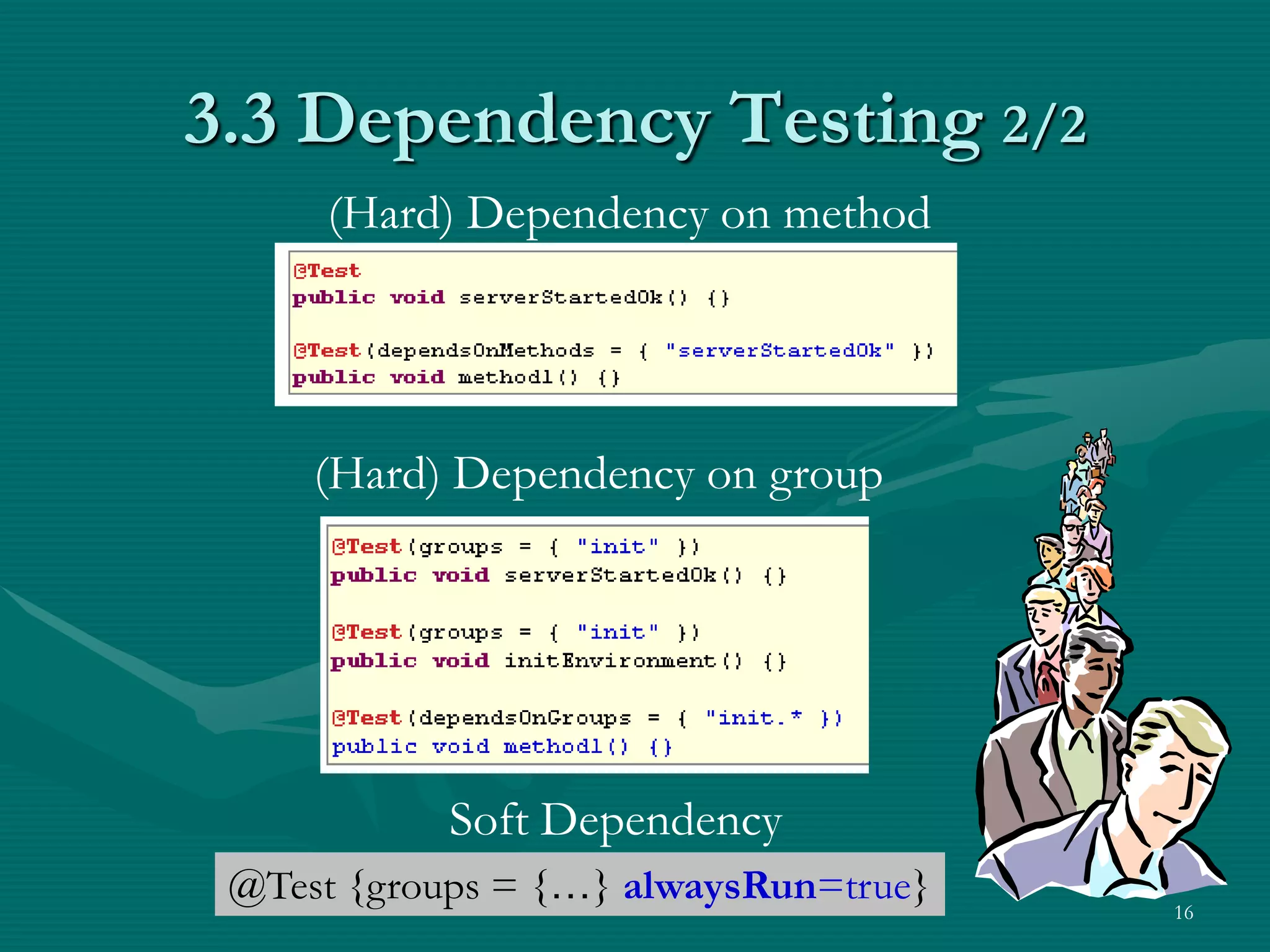
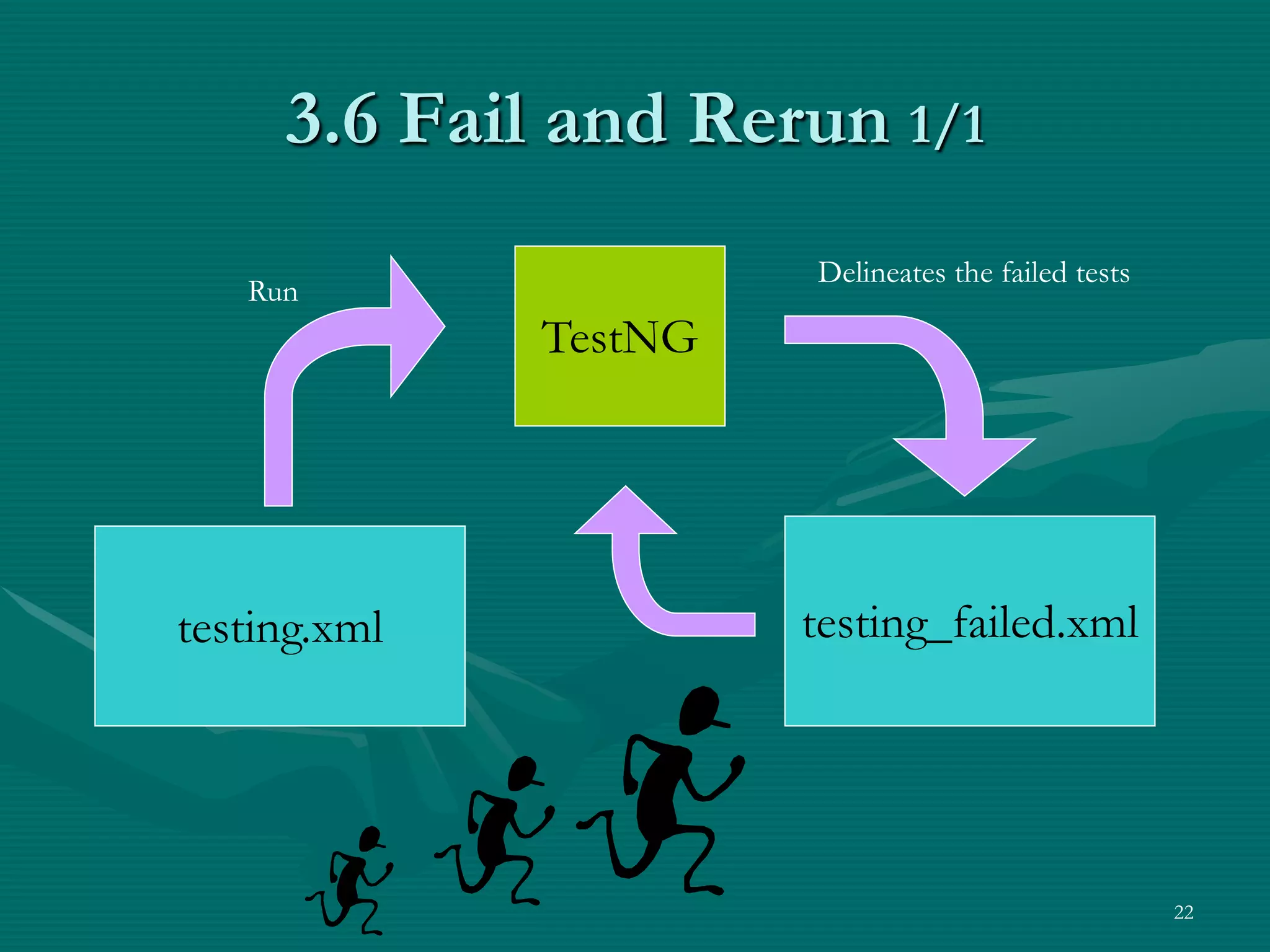
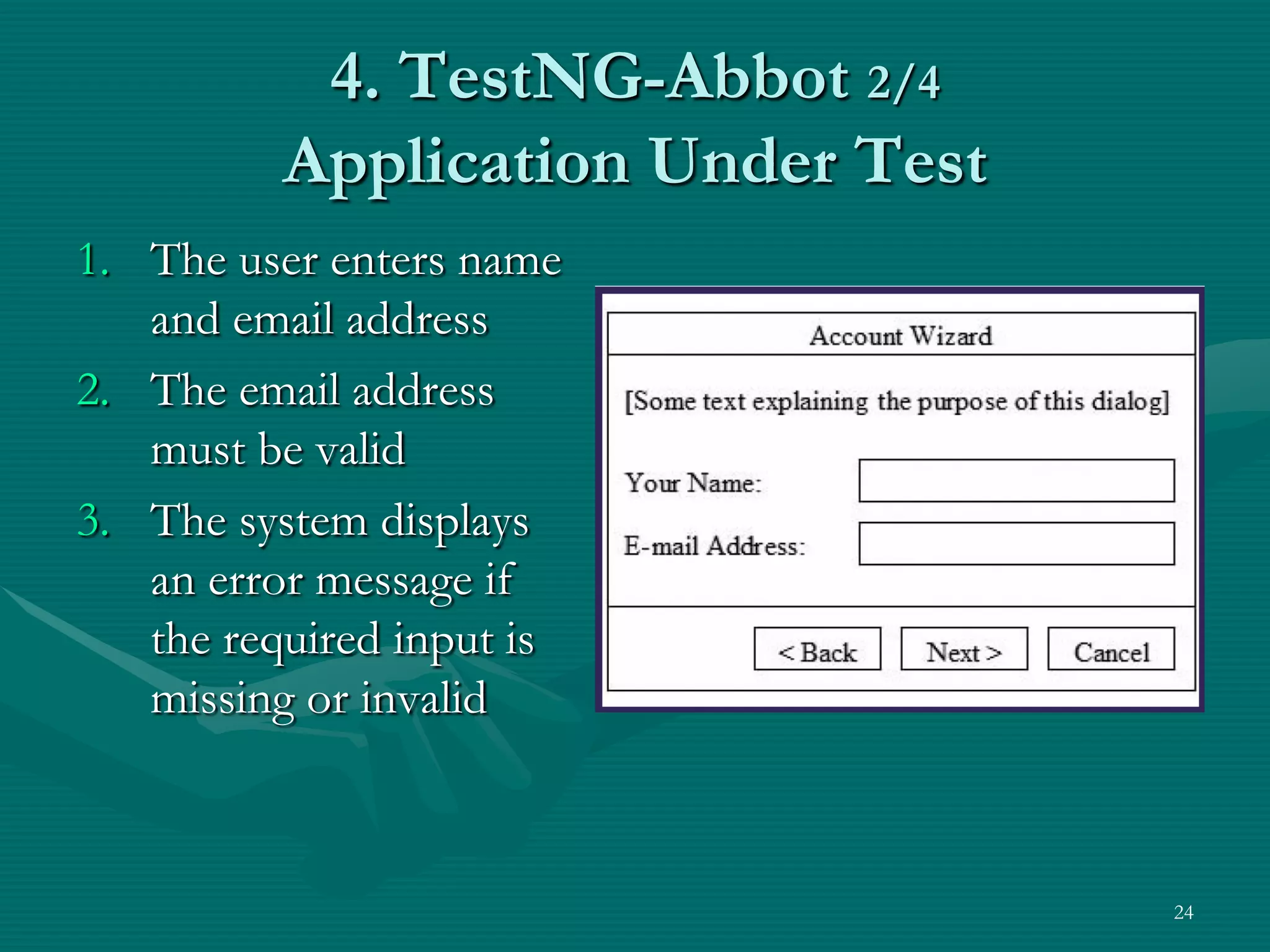
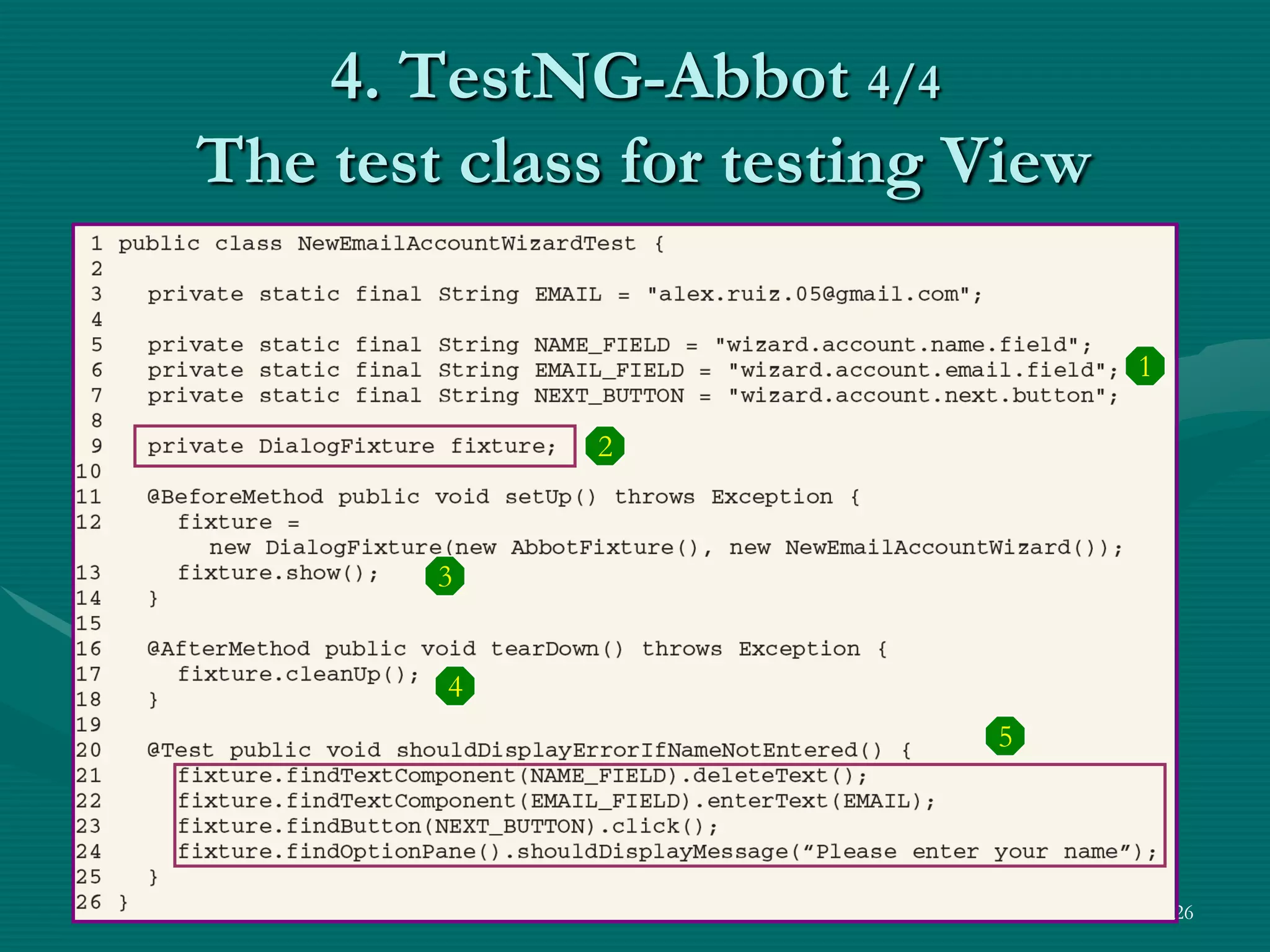
TestNG is a testing framework that uses annotations to make testing more simple and flexible. It allows choosing different testing strategies like unit testing, integration testing, and GUI testing. The document introduces TestNG and its features like configuration methods, test grouping, dependency testing, and parametric testing. It also describes using TestNG-Abbot for test-driven GUI development, with an example of testing an email registration form by separating tests for the model and view.