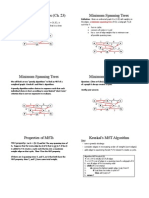
Minimum Spanning Trees
Minimum Spanning Tree
• A town has a set of houses and a set of roads
• A road connects 2 and only 2 houses
• A road connecting houses u and v has a repair cost w(u, v)
• Goal: Repair enough (and no more) roads such that
» everyone stays connected: can reach every house from all other houses, and
» total repair cost is minimum
Minimum Spanning Tree
• Model as a graph:
» Undirected graph G = (V, E)
» Weight w(u, v) on each edge (u, v) ∈ E
» Find T ⊆ E such that
• T connects all vertices
• (T is a spanning tree)
• w(T ) = ∑ w(u, v) is minimized ( u ,v )∈T
Minimum Spanning Tree
• A spanning tree whose weight is minimum over all spanning trees is called
a
Minimum Spanning Tree, or MST
• Example:
• In this example, there is more than one MST
• Replace edge (b,c) by (a,h)
• Get a different spanning tree with the same weight
Minimum Spanning Tree
•Which edges form the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) of the below
graph?
A
6 4
5 9
H B C
14 2
10
15
G E D
3 8
F
Minimum Spanning Tree
• MSTs satisfy the optimal substructure
property: an optimal tree is composed of
optimal subtrees
» Let T be an MST of G with an edge (u,v) in the
middle
» Removing (u,v) partitions T into two trees T1 and
T2
» Claim: T1 is an MST of G1 = (V1,E1), and T2 is an MST of G2 =
(V2,E2) ( Do V1 and V2 share vertices? Why? )
» Proof: w(T) = w(u,v) + w(T1) + w(T2)
(There can’t be a better tree than T1 or T2, or T would be suboptimal)
Some definitions
• A cut (S, V – S) of an undirected graph G =(V,E) is a partition of V
• We say that an edge (u,v) ϵ E crosses the (S, V – S) if one of its
endpoints is in S and the other is in V - S.
Some definitions
• We say that a cut respects a set A of edges if no edge in A crosses the
cut.
• An edge is a light edge crossing a cut if its weight is the minimum of any
edge crossing the cut.
• Note that there can be more than one light edge crossing a cut in the
case of ties.
• More generally, we say that an edge is a light edge satisfying a given
property if its weight is the minimum of any edge satisfying the property
• Theorem 23.1
Let G = (V,E) be a connected, undirected graph with a real-valued
weight function w defined on E. Let A be a subset of E that is
included in some minimum spanning tree for G, let (S, V – S) be any cut
of G that respects A, and let (u, v) be a light edge crossing (S, V – S).
Then, edge (u, v) is safe for A.
Proof of theorem
Except for the dashed edge (u, v), all edges
shown are in T. A is some subset of
the edges of T, but A cannot contain any
edges that cross the cut (S, V − S), since
this cut respects A. Shaded edges are the
path p.
Proof of theorem (1)
Since the cut respects A, edge (x, y) is not in A.
To form T‘ from T :
• Remove (x, y). Breaks T into two components.
• Add (u, v). Reconnects.
So T‘ = T − {(x, y)} ∪ {(u, v)}.
T’ is a spanning tree.
w(T’ ) = w(T ) − w(x, y) + w(u, v)
≤ w(T) ,
since w(u, v) ≤ w(x, y). Since T is a spanning tree, w(T’) ≤ w(T ), and T is an
MST, then T’ must be an MST.
Need to show that (u, v) is safe for A:
• A ⊆ T and (x, y) ∉ A ⇒ A ⊆ T’.
• A ∪ {(u, v)} ⊆ T’ .
• Since T’ is an MST, (u, v) is safe for A.
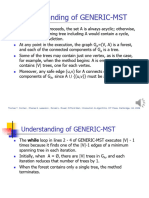
Generic-MST
So, in GENERIC-MST:
• A is a forest containing connected components. Initially, each
component is a single vertex.
• Any safe edge merges two of these components into one. Each
component is a tree.
• Since an MST has exactly |V| − 1 edges, the for loop iterates |V| − 1
times. Equivalently, after adding |V|−1 safe edges, we.re down to just
one component.
Corollary
If C = (VC, EC) is a connected component in the forest GA = (V, A) and
(u, v) is a light edge connecting C to some other component in GA (i.e.,
(u, v) is a light edge crossing the cut (VC, V − VC)), then (u, v) is safe for
A.
Proof Set S = VC in the theorem.
Growing An MST
• Some properties of an MST:
It has |V| -1 edges
It has no cycles
It might not be unique
• Building up the solution
» We will build a set A of
edges
» Initially, A has no edges
» As we add edges to A,
maintain a loop invariant:
• Loop invariant: A is a
subset of some MST
» Add only edges that
maintain the invariant
If A is a subset of some
MST, an edge (u, v) is
safe for A
Growing An MST
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1?
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2? 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5?
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8? 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9?
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13? 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14? 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17?
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19?
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21? 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25?
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Run the algorithm:
Kruskal() 2 19
{ 9
14 17
T = ∅; 8 25
5
for each v ∈
V MakeSet(v); 21 13 1
sort E by increasing edge weight w
for each (u,v) ∈ E (in order)
sorted if FindSet(u) ≠
T = T U {{u,v}};
FindSet(v)
Union(FindSet(u), FindSet(v));
}
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Spring 2006 Algorithm Networking Laboratory 11-37/62
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Kruskal() What will affect the running time?
{ 1 Sort
O(V) MakeSet()
T = ∅; calls O(E) FindSet()
for each v ∈ calls
V MakeSet(v); O(V) Union() calls
sort E by increasing (Exactly how many
edge weight w Union()s?)
for each (u,v) ∈ E sorted order)
(inif FindSet(u) ≠
FindSet(v) T = T U
{{u,v}};
Union(FindSet(u),
FindSet(v));
}
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞;
14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL;
while (Q not
empty) 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q); Run on example graph
for each v ∈ < key[v])
Adj[u]
if (v ∈ Q and
w(u,v)
П[v] = u;
key[v] =
w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
• MST-Prim(G, w, 6 ∞ 4
5 9
r) Q = V[G]; ∞ ∞ ∞
• for each u ∈ Q
14 2
• key[u] = ∞; 10
• key[r] = 0; 15
∞ ∞ ∞
• П[r] = NULL;
3 ∞ 8
• while (Q not
empty) Run on example graph
•u = ExtractMin(Q); key[v])
for each v ∈ Adj[u]
• if (v ∈ Q and
w(u,v) <
• П[v] = u;
• key[v] =
w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
• MST-Prim(G, w, 6 ∞ 4
5 9
r) Q = V[G]; ∞ ∞ ∞
• for each u ∈ Q
14 2
• key[u] = ∞; 10
• key[r] = 0; 15
r 0 ∞ ∞
• П[r] = NULL;
3 ∞ 8
• while (Q not
empty) Pick a start vertex r
•u = ExtractMin(Q); key[v])
for each v ∈ Adj[u]
• if (v ∈ Q and
w(u,v) <
• П[v] = u;
• key[v] =
w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 ∞ 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
for each u ∈ Q
∞ ∞ ∞
key[u] = ∞; 14
10 2
key[r] = 0;
15
П[r] = NULL; u 0 ∞ ∞
while (Q not empty)
3 ∞ 8
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v ∈ Black vertices have been removed from Q
Adj[u]
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v) <
key[v])
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
• MST-Prim(G, w, 6 ∞ 4
5 9
r) Q = V[G]; ∞ ∞ ∞
• for each u ∈ Q
14 2
• key[u] = ∞; 10
• key[r] = 0; 15
u 0 ∞ ∞
• П[r] = NULL;
3 3 8
• while (Q not
empty) Black arrows indicate parent
•u = ExtractMin(Q); pointers
for each v ∈ Adj[u] key[v])
• if (v ∈ Q and
w(u,v) <
• П[v] = u;
• key[v] =
w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 ∞ 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
14 ∞ ∞
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14
10 2
key[r] = 0;
15
П[r] = NULL; u 0 ∞ ∞
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v ∈ Adj[u]
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v) key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 ∞ 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
14 ∞ ∞
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14
10 2
key[r] = 0;
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 ∞ ∞
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q); u
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 ∞ 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
14 ∞ ∞
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 ∞
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q); u
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 ∞ 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
10 ∞ ∞
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 ∞
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q); u
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 ∞ 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
10 ∞ ∞
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 ∞
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q); u
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 ∞ 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
10 2 ∞
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 ∞
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q); u
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 ∞ 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
10 2 ∞
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 15
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q); u
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) ∞ u
6 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
10 2 ∞
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 15
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) ∞ u
6 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
10 2 9
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 15
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 4 u
6 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
10 2 9
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 15
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 4 u
6 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
5 2 9
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 15
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 4 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
5 2 9
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 15
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) u 4
6 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
5 2 9
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 15
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
u
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 4 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
5 2 9
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 15
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
MST-Prim(G, w, r) 6 4 4
Q = V[G]; 5 9
5 2 9
for each u ∈ Q
key[u] = ∞; 14 u
2
key[r] = 0; 10
15
П[r] = NULL; 0 8 15
while (Q not empty)
3 3 8
u = ExtractMin(Q);
for each v ∈
if (v ∈ Q and w(u,v)
Adj[u] key[v])
<
П[v] = u;
key[v] = w(u,v);
Prim’s Algorithm
Spring 2006 Algorithm
Networking Laboratory 11-61/62
Prim’s Algorithm
Spring 2006 Algorithm
Networking Laboratory 11-62/62