Special Thanks
Nakib Hayat Chowdhury
Lesson 1 -
Introduction
Md. Muktar Hossain
Lecturer
Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering
Varendra University
In this Class
Structured Programming Language
Why C is Structured Programming
Language
Importance of C
Features of C
How to develop a program
Algorithm
Flow Chart
History of Programming Language
Translator
Structured Programming Language
Structured programming, or modular programming, is a
programming paradigm that facilitates the creation of
programs with readable code and reusable components.
Structured programming is a programming paradigm
aimed at improving the clarity, quality, and development
time of a computer program by making extensive use of
structured control flow constructs like sequences, loops,
and conditionals. This paradigm emphasizes the use of
modular design and clear, understandable code.
“C is a Structured Programming
Language”
Modularity: C allows programmers to break down a
program into smaller, manageable pieces called
functions. Each function performs a specific task, and
these functions can be reused throughout the
program. This promotes code reuse and makes the
program easier to understand and maintain.
Structured Control Flow: C provides constructs for
structured control flow, such as loops (like for, while,
and do-while loops) and conditionals (like if-else
statements). These constructs enable programmers to
control the flow of execution in a clear and structured
manner.
“C is Structured Programming Language”
Clear Syntax: C has a simple and concise syntax that
promotes readability and maintainability. Its syntax closely
resembles the logical structure of algorithms, making it easier
for programmers to express their ideas in code.
Procedural Approach: C follows a procedural programming
paradigm, where the program is organized as a series of
procedures (functions) that operate on data. This approach
emphasizes step-by-step procedure execution, making it easier
to understand and debug programs.
Overall, C's support for modularity, structured control flow, clear
syntax, and procedural approach align it closely with the
principles of structured programming, making it an ideal language
for writing structured, maintainable, and efficient code.
Why C?
Operating System (OS)
Embedded System (ES)
Microcontroller based programming (Robotics)
System Programming
Programming Language Development
Game Engine
Programming Contest
Features of C Language
How to Develop a Program
Step 1: Analyze the program to identify inputs, outputs and
processing requirements.
Step 2: Identify various processing steps needed to solve the
problem.
Step 3: Refine Step 2
Step 4: Add the syntax of the programming language
Step 5: Run the program and check it with different types of
input to verify its correctness.
Algorithm
It is a complete step by step representation of the
solution of the problem, represented in English like
language.
An algorithm can be quite abstract or quite detailed.
Algorithm
1. Start
2. Read n1.
3. Read n2.
4. Calculate Sum = n1 +
n2.
5. Write the sum.
6. Stop.
Flow Chart
Very popular method to represent the
steps of the solution.
Uses many graphical symbols and thus,
is more understandable.
The symbols used for various different
types of statements/steps.
Flow Chart Start
Very popular method to represent the
Read n1
steps of the solution. Read n2
Uses many graphical symbols and thus,
is more understandable.
The symbols used for various different Sum = n1 + n2
types of statements/steps.
Print Sum
Stop
Flowchart Symbols
Beginning or end
oval START
of program
Read n
Parallelogra or
m Input or Output
Print n
Direction of logic
flow
Flowchart Symbols
Rectangular
Processing Sum = a+b
Diamond Decision If x>10 ?
Connector
Write a program to add two numbers
Start
Read n1
Algorithm Read n2
1. Start
2. Read n1.
3. Read n2. Sum = n1 + n2
4. Calculate Sum = n1 +
n2.
5. Write the sum.
Print Sum
6. Stop.
Stop
Write a program to find bigger one between two
numbers
Start
Read n1
Algorithm Read n2
1. Start
2. Read n1. Yes No
if
3. Read n2. n1 >
4. If n1>n2. n2
print n1 is ?
bigger Print n1 Print n2
5. else
print n2 is
bigger
6. Stop. Stop
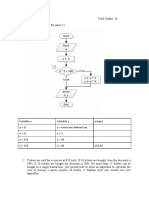
Write a program to Find Sum of first n
numbers Start
Read n
Algorithm i=1
1. Read n. Sum = 0
2. Initialize i=1.
3. Initialize sum, Sum=0. Sum = Sum + i
4. Calculate, Sum = Sum+i. i = i+1
5. Calculate, i = i+1. No
6. If i>n, then goto step 7 else goto step 4. If i >
7. Write the sum Sum. n?
8. Stop. Yes
Print sum
Stop
History of Programming Language
Computer Programming
Computer programming is the process of designing,
writing, testing, debugging and maintaining the source
code of computer programs.
This source code is written in one or more programming
languages (such as C++, C#, Java, Python, Smalltalk, etc.).
Type of Programming Language
• Machine languages
• Assembly languages
• Higher-level languages
Machine Languages
• Machine languages (first-generation languages) are the most basic type of
computer languages, consisting of strings of numbers the computer's hardware
can use.
• Different types of hardware use different machine code. For example, IBM
computers use different machine language than Apple computers
Machine Languages : 83+(-2)
Machine Languages : 83+(-2)
Assembly Languages
• Assembly languages (second-generation languages) are only somewhat easier to
work with than machine languages.
• To create programs in assembly language, developers use cryptic English-like
phrases to represent strings of numbers.
• The code is then translated into object code, using a translator called an
assembler.
Assembly Languages : 83+(-2)
Assembly Languages : 83+(-2)
Assembly
code
Assembler
Object code
Higher-Level Languages
Higher-level languages are more powerful than assembly language and allow
the programmer to work in a more English-like environment.
Higher-level programming languages are divided into three "generations," each
more powerful than the last:
• Third-generation languages
• Fourth-generation languages
• Fifth-generation languages
High Level Language : 83+(-2)
Translator
Translators are just computer programs which
accept a program written in high level or low
level language and produce an equivalent
machine level program as output. Translators
are of three types:
Assembler
Compiler
Interpreter
Assembler
Assembler is used for converting the code of low level
language (assembly language) into machine level
language.
Compiler
The compiler is one kind of system software
that translates the programs written in high
level language to machine language.
Interpreter
The interpreter is a system software which use
to convert high level language programs to
machine language. But it convert one line at a
time and execute it then it convert next line
and so on.
Compiler vs Interpreter
A complier converts the high level instruction into machine
language while an interpreter converts the high level instruction
into an intermediate form.
The compiler executes the entire program at a time, but the
interpreter executes each and every line individually.
List of errors is created by the compiler after the compilation
process while an interpreter stops translating after the first error.
Autonomous executable file is generated by the compiler while
interpreter is compulsory for an interpreter program.
Interpreter is smaller and simpler than compiler
Interpreter is slower than compiler.
Thank You