0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views8 pagesAccess Specifiers
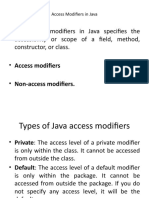
The document explains access specifiers in Java, which are essential for encapsulation in object-oriented programming. It outlines four access specifiers: public, protected, default (package-private), and private, detailing their accessibility levels and use cases. Each specifier defines the visibility of classes, methods, and variables, influencing how they can be accessed within and outside their defining classes.
Uploaded by
amazinganish11Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views8 pagesAccess Specifiers
The document explains access specifiers in Java, which are essential for encapsulation in object-oriented programming. It outlines four access specifiers: public, protected, default (package-private), and private, detailing their accessibility levels and use cases. Each specifier defines the visibility of classes, methods, and variables, influencing how they can be accessed within and outside their defining classes.
Uploaded by
amazinganish11Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8