Wireshark
Networking
intro
⟩ Wireshar
k
HUB’s
Connects all device on the network
only connection status: connected yes or no…
Replicates all packets on all ports
less throughput
Risks…???
⟩ Wireshar
k
Switches
Learn where all devices are on the network
Only sends data to the port where needed
⟩ Wireshar
k
Data Flow of the Internet Protocol Suite
⟩ Wireshar
k
Data Flow of the Internet Protocol Suite
⟩ Wireshar
k
HEADERS VOOR IP & TCP
⟩ Wireshar
k
HEADERS VOOR IP & TCP
⟩ Wireshar
k
Wireshark
intro
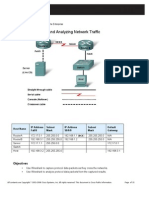
Wireshark: Locating Wireshark
You can monitor:
LAN port
WAN port
server or router port
any other device
connected to the network.
Some LAN switch vendors:
Monitoring a whole VLAN: We can monitor a server's VLAN, Telephony
VLAN, and so on. In this case you will see all the traffic on a specific VLAN.
Monitoring several ports to a single analyzer: We can monitor traffic
on servers S1 and S2 together.
Filtering: Filtering means choosing and accordingly configuring whether
to monitor incoming traffic, outgoing traffic, or both.
11
⟩ Wireshark: How to do
it?
12
⟩ Wireshark:
Where?
Monitoring a server:
most common
either configuring the port monitor to the server
(numbered as 1 in the preceding diagram)
either installing Wireshark on the server itself
Monitoring a router:
A LAN port
(numbered as 2 and 6 in the
preceding diagram),
A WAN port
connect a switch between the router port and the
Service Provider (SP) network, and configure the port
monitor on this switch
13
⟩ Wireshark: where?
others
TAPs: Test Access Point (TAP)
simple three-port device
same role as that of the switch.
Advantages:
simplicity and price.
forward errors that can be monitored on Wireshark, (a LAN switch drops
them)
Disadvantages:
Switches are much more expensive, take a few minutes to configure, but
provide you with additional monitoring capabilities, for example, Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
When you troubleshoot a network, it is better to have an available
managed LAN switch, even a simple one.
Hubs:
connect a hub in parallel to the link you want to monitor,
Disadvantage: the hub itself slows the traffic, and it therefore influences the
test. 14
⟩ Wireshark:
VLAN’s (1)
For monitoring all traffic on a VLAN, you have to connect to
a switch on which all traffic of the VLAN goes through, and
this is usually the central switch.
15
⟩ Wireshark: VLAN’s
(2)
Monitoring a VLAN: you might see duplicate packets.
For example, S4 sends a packet to S2,
and you configure the port mirror to
VLAN30, you will see the packet once
when sent from S4 passing through
the switch and entering the VLAN30,
and then when leaving VLAN30 and
coming to S2.
16
⟩ Wireshark: multiple interface
capturing
With multiple physical NICs, you can monitor the port on
two different servers, two ports of a router, or other
multiple ports at the same time.
17
Hands
on !!!
⟩ Setup test
environment(1)
Virtualbox: capturing traffic in VM from 2 VM’s
• Delete all Win10_HackTheBox VM’s.
• Reimport 1 and rename to Win10_Client
• Install Guest additions (Virtualbox Extensions)
• Clone 2 others:
• Reset MAC addresses.
• Linked clone. (preserve storage space)
• Rename to Win10_Server and Win10_Wireshark
• Install Filezilla Server on Win10_Server
• Install Wireshark (version 3.x) on Win10_Wireshark
• Create Internal network (see next slide)
⟩ Create internal network on
Virtualbox
• Create internal network in the 3 VM’s:
• Enter command in command line:
• vboxmanage dhcpserver add --network=hacknet --server-ip=
192.168.99.1 --lower-ip=192.168.99.100 --upper-ip=
192.168.99.120 --netmask=255.255.255.0 --enable
• Location of VBoxManage.exe:
• C:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox
• Tips:
• vboxmanage list vms
• vboxmanage list intnets
• vboxmanage kali --intnet1 hacknet (cmd-line to add VM to internal network)
• vboxmanage list dhcpservers
• vboxmanage dhcpserver restart --network=hacknet
• vboxmanage dhcpserver remove --network=hacknet
• vboxmanage showvminfo Win10_Client | grep hacknet
⟩ Capture
FTP
• Ping from client to server (firewall???)
• Ftp from client to server (Filezilla Server, put Transfer
Settings to Active)
• Put network card from VM10_Wireshark to Promiscuous
mode to Allow all.
• Capture packets
• Discover what you can see on the network:
• …
• …
⟩ Capture
SFTP
• Setup secure FTP (TLS)
• ???
• SecureFtp from client to server
• Capture packets
• Discover what you can see on the network:
⟩ Setup test
environment(2)
Virtualbox: capturing on Host from virtual interface
VBoxManage modifyvm ”Win10_Client" --nictrace1 on –
nic-trace-file1 c:\users\xxx\netlog.pcap
Open the netlog.pcap file with Wireshark
Wireshark
tools
Using Basic Statistics Tools
Statistics: Overview
Using the Summary tool from the Statistics menu
Using the Protocol Hierarchy tool from the Statistics
menu
Using the Conversations tool from the Statistics menu
Using the Endpoints tool from the Statistics menu
Using the HTTP tool from the Statistics menu
Configuring Flow Graph for viewing TCP flows
Creating IP-based statistics
26
Statistics: Summary
Using the Summary tool from the Statistics menu
27
Statistics: Summary
28
Statistics: Protocol Hierarchy
Using the Protocol Hierarchy tool from the Statistics
menu
29
Statistics: Conversations (1)
Using the Conversations tool from the Statistics menu
You can use these statistics tools:
On layer 2 (Ethernet): To find and isolate broadcast
storms:
Large amount of broadcasts: you might be viewing a
broadcast storm (a minor one. In a major one, you might
not see anything.)
If you see a lot of traffic coming from a specific MAC
address, look at the first part of the conversation; this is
the vendor ID that will give you a hint about the
troublemaker.
30
Statistics: Conversations (2)
IP conversations statistics :
Look for IP addresses with a lot of traffic going in or out of
them.
If it is a server you know (and probably you remember the
server's address or address range), then it is OK;
but it might also be that someone scanned the network, or
just a PC that generated too much traffic.
Look for scanning patterns
It can be a good scan, such as an SNMP software that sends
a ping to discover the network
but usually the scans in the network are not good.
31
Statistics: Conversations (3)
TCP/UDP conversations statistics:
Look for devices with too many open TCP connections.
‐ 10 to 20 connections per PC are reasonable,
‐ hundreds are not.
Look and try to find unrecognized port numbers. It
might be OK, but it can mean trouble. In the following
screenshot, you can see a typical TCP scan:
32
Statistics: Endpoints
Using the Endpoints tool from the Statistics menu
Few Ethernet endpoints (these are MAC addresses) with many IP
end nodes (these are IP addresses):
This will be the case where, for example, we have a router
that sends/receives packets from many remote devices, and
what we will see is the MAC address of the router and many IP
addresses coming/going through it.
Few IP end nodes with many TCP end nodes:
this will be the case for many TCP connections per host. It can
be a regular operation of a server with many connections, and
it can also be a kind of attack that comes through the network
(for example, an SYN attack).
33
Statistics: HTTP
Using the HTTP tool from the Statistics menu
Packet Counter: This provides us with the number of
packets to each website. This will help us to identify how
many requests and responses we have had.
Requests: This is used to see request distribution to
websites.
Load Distribution: This is used to see load distribution
between websites.
34
Statistics: Flow Graph
Configuring Flow Graph for viewing TCP flows
35
Statistics: IP-based statistics (1)
Navigate to Statistics | IP Addresses.
In the window that comes up, select the filter
ip.addr==10.0.0.2 will show you only IP packets sent to
or from this address.
36
Statistics: IP-based statistics (2)
This is one of the tools that brings up suspected issues; for
example, when you see a suspected port with too many
packets sent to it, start looking for a reason.
37
Using advanced Statistics Tools
Advanced Statistics
Configuring IO Graphs with filters for measuring network
performance issues
Throughput measurements with IO Graph
Getting information through TCP stream graphs
the Time-Sequence (Stevens) window
the Time-Sequence (tcp-trace) window
the Throughput Graph window
39
Configuring IO Graphs with filters
Graph window
40
Throughput measurements
Measuring throughput between end devices
NAS: 192.168.50.10 Laptop: 192.168.50.124
41
Time-Sequence (Stevens) window
Click on the packet of the stream you want to monitor.
Tip :The TCP Stream shows a directional graph, so when
you click on a packet, it should be in the direction you
want to view the statistics on. If, for example, you
download a file and want to view the download statistics,
click on a packet in the download direction.
Statistics menu navigate to
TCP StreamGraph |
Time-Sequence Graph (Stevens).
42
Time-Sequence (tcp-trace) window
43
Throughput Graph
Here the throughput is stable
44
Well-known issues
Advanced Statistics
Discovering broadcast and error storms
Analyzing VLANs and VLAN tagging issues
Finding fragmentation problems
Analyzing routing problems
Finding duplicate IPs
46
Advanced Statistics: Discovering broadcast and error storms
47
Advanced Statistics: Fixed pattern broadcasts
48
Advanced Statistics: VLAN’s
Analyzing VLANs and VLAN tagging issues
#monitor session 1 source vlan 100
#monitor session 1 destination interface fastethernet 0/6
In case you don’t see TAGs in Wireshark:
Configure the adapter with Priority & VLAN Disabled. This will move the tags
for the WinPcap driver to Wireshark.
49
Advanced Statistics: Finding fragmentation
https://wiki.wireshark.org/SampleCaptures?action=AttachFil
e&do=get&target=teardrop.cap
50
Advanced Statistics: Analyzing routing problems
Time To Live (TTL) messages:
A TTL value of 0 is in most cases is a loop.
Filter: ip.ttl == 0
The following ICMP message should indicate a configuration problem
in a router or in several routers:
ICMP Destination network unreachable: It usually indicates a
missing route in one of the network routers.
ICMP Destination host unreachable: It usually indicates a device
(for example, a PC) on the destination network that is not connected
to the network or a default gateway is not configured on it.
Packets with source IP address to the destination, back to the source,
back to the destination, and so on, while TTL is reducing by 1 to 0.
51
Advanced Statistics: Finding duplicate IP’s (1)
Ping the IP address.
Use arp –a : If you get two lines for the IP address you've
pinged with different MAC addresses, this is a duplicate.
Try to find out the vendor of the MAC addresses.
Try to find the port location on a managed switch connected
to.
Start Wireshark and port mirror the network VLANs.
Wireshark will show you a duplicate address error with the
relevant details:
Use the filter: arp.duplicate-address-frame
52
Advanced Statistics: Finding duplicate IP’s (2)
53
End