0% found this document useful (0 votes)
203 views30 pagesUreter
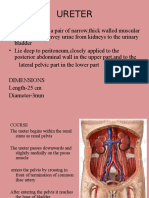
The ureters are narrow muscular tubes that convey urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Each ureter is approximately 25cm long and 3mm in diameter. The ureters have 3 layers - an outer fibrous coat, middle muscular coat, and inner mucous membrane. They course from the renal pelvis down through the abdomen and pelvis, with various anatomical relations along the way. The ureters have sphincter-like contractions at several points to aid in urine transport. They are supplied by blood vessels and nerves and develop from the intermediate mesoderm. Abnormalities can include double pelvises or bifid ureters. Ureteric stones commonly cause renal colic
Uploaded by
Puneet SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
203 views30 pagesUreter
The ureters are narrow muscular tubes that convey urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Each ureter is approximately 25cm long and 3mm in diameter. The ureters have 3 layers - an outer fibrous coat, middle muscular coat, and inner mucous membrane. They course from the renal pelvis down through the abdomen and pelvis, with various anatomical relations along the way. The ureters have sphincter-like contractions at several points to aid in urine transport. They are supplied by blood vessels and nerves and develop from the intermediate mesoderm. Abnormalities can include double pelvises or bifid ureters. Ureteric stones commonly cause renal colic
Uploaded by
Puneet SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd