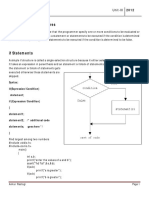
Conditionals, Loops, and
Other Kinds of Statements
CS-2301, System Programming
for Non-Majors
(Slides include materials from The C Programming Language, 2nd edition, by Kernighan and Ritchie and
from C: How to Program, 5th and 6th editions, by Deitel and Deitel)
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 1
Other Statements
Reading Assignment
• Chapter 3 of Kernighan and Ritchie
• Helpful to follow along in class
• Note on §3.8 :– we do not allow goto
statements in this course
• There is rarely, if any, situation at WPI
where a goto in C would be the right thing
• There is rarely a situation in any program
where a goto is the right thing!
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 2
Other Statements
Review
• Expression – a sequence of operators and
operands that return a value
• Assignment – expression with the side effect
of changing the value of the left operand
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 3
Other Statements
Definition – Side Effect
• The changing of the value of some data in the
course of evaluating or executing something else
• Sometimes unrelated data!
• Examples:–
– Explicit assignments
• x = y + 3; i++; --j;
– printf()
• Writes to internal buffer; flushes buffer to screen on '\n'
– scanf() – returns values from input
• Explicit – assigns data to arguments
• Implicit – keeps track of where it is in internal buffer
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 4
Other Statements
Definition – Statement
• Instruction to “do” something
• Specifies order of execution & evaluation
• §A.9 – a statement in C may be any of:–
• labeled-statement
• expression-statement
• compound-statement
• selection-statement
• iteration-statement
• jump-statement
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 5
Other Statements
Expression Statement
• expressionoptional ;
• Note: semicolon is terminator
• Exists primarily for its side effects
• E.g.,
• x = y + 3; i++; --j;
• printf(“string”, arg1, arg2, arg3);
• The following is perfectly legal in C:–
• y + 3;
• Evaluates the expression, then throws the result away!
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 6
Other Statements
Compound Statement
• A sequence of statements surrounded by {}
• Example:–
{
x = 0;
i++;
printf("The value of x is %d\n", x);
}
• Reason:– so that we can group together
statements in loops, if-else, functions, etc.
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 7
Other Statements
Compound Statement (continued)
• Compound statements may be nested
{
...;
{ x = 0;
i++;
} /* no semicolon needed here*/
printf("The value of x is %d\n", x);
...;
}
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 8
Other Statements
Compound Statement (continued)
• Compound statements may include declarations
inside
{
double angle;
angle = atan2(y, x) * 360/(2*pi);
printf("Angle is %f degrees\n", angle);
}
• Declarations inside of {} are not known outside of
{}
• Book says declarations must be at beginning of {}
• Later versions of C relax this rule
• Declaration must always precede first use of declared identifier
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 9
Other Statements
Questions?
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 10
Other Statements
If-else Statements
if (expr)
statement1 /*do this if expr is non-zero*/
else
statement2 /*do this if expr is zero*/
• The else clause is optional!
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 11
Other Statements
If-else Examples
if (j > limit)
return j; /* note semicolon*/
else
j += stepValue; /* note semicolon*/
...
if (++k >= 4)
k = 0; /* increment k mod 4*/
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 12
Other Statements
If-else Examples (continued)
if (n < maxInput) {
scanf("string", &arg1, &arg2, …);
n++;
printf("string2", arg3, arg4, …);
} else { /* note NO semicolon*/
printf("Summary\n", arg5, …);
return n;
}
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 13
Other Statements
Concatenated If-else Statements
if (expr1)
statement1 /*do this if expr1 is non-zero*/
else if (expr2)
statement2 /*i.e., expr1 == 0, expr2 != 0*/
else if (expr3)
statement3 /expr1 and expr2 are zero, expr3 != 0*/
else if (expr4)
statement4 /expr1, expr2 , expr3 all zero, expr4 != 0*/
else
statement5 /*i.e., all expr are zero*/
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 14
Other Statements
Concatenated If-else Statements
• Last else is always attached to last if
• If it should be attached to any other if, use
{} to control the flow of execution.
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 15
Other Statements
Switch Statement
• Somewhat like a concatenated if-else
• Occasionally easier to read
• Each arm is called a case
• Evaluate switch expression, select the
appropriate case (if any)
– default case is optional
• Difference from concatenated if-else
• Need break statement to exit switch after a case
• Otherwise, control falls through to next case
• See §3.4 and p. 59
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 16
Other Statements
Switch Statement Example
int month, daysInMonth, leapYear;
…
switch (month) {
case 0: printf("January\n");
daysInMonth = 31;
break;
case 1: printf("February\n");
daysInMonth = leapYear ? 29 : 28;
break;
case 2: printf("March\n");
daysInMonth = 31;
break;
case 3: printf("April\n");
daysInMonth = 30;
break;
…
} // switch
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 17
Other Statements
Switch Statement Example
int month, daysInMonth, leapYear;
…
switch (month) {
case 0: printf("January\n");
daysInMonth = 31;
break;
case 1: printf("February\n");
daysInMonth = leapYear ? 29 : 28;
break;
case 2: printf("March\n");
daysInMonth = 31;
break;
case 3: printf("April\n");
daysInMonth = 30;
break;
…
} // switch
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 18
Other Statements
Questions?
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 19
Other Statements
Iterative Statement
• while loop
• for loop
• do-while loop
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 20
Other Statements
while loops
while (expression)
statement Often a compound statement
• Evaluate expression
• If true, execute statement and then repeat
• Repeat until expression becomes false
• statement may be executed zero or more
times!
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 21
Other Statements
while loop example
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
int input;
while (scanf("%d", &input) != EOF){
sum += input;
count++;
printf("Input value of %f recorded.\n", input);
...
}
if (count > 0)
printf("Average is %f\n", (double)sum/count);
else
printf("No inputs recorded\n");
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 22
Other Statements
while loop examples (continued)
• Study example on p. 59 (§3.4)
• A program to count digits, white space
characters, and other characters.
• Includes a while loop with a switch
statement inside
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 23
Other Statements
do-while loop
• do
statement
while (expression);
• Similar to while loop, but guaranteed to
execute statement at least once
• See §3.6
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 24
Other Statements
Breaking out of a Loop
• When it becomes necessary to terminate a
loop prematurely
– break; /*exits smallest containing
switch or loop*/
• When it becomes necessary to terminate the
current iteration and start the next one
– continue; /*terminates this iteration
only*/
• See p. 65, §3.7
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 25
Other Statements
Questions?
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 26
Other Statements
for loop
• A counting loop
for (expr1; expr2; expr3)
statement
• Evaluate expr1 to initialize
• Evaluate expr2 to test
• If true, execute statement
• If not true, exit for loop
• Evaluate expr3 to prepare for next iteration
• Repeat expr2 to test
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 27
Other Statements
for loops and while loops
• The for loop
for (expr1; expr2; expr3)
statement
• is exactly equivalent to the following
expr1;
while (expr2) {
statement
expr3;
}
• See p. 60
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 28
Other Statements
The most common kind of for-loop
int i;
for (i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
...;
/* do something with ith entity */
...;
}
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 29
Other Statements
The most common kind of for-loop
int i;
for (i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
...;
/* do something with ith entity */
...;
}
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 30
Other Statements
The most common kind of for-loop
int i;
for (i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
...;
/* do something with ith entity */
...;
}
• This loop iterates limit times.
– Iterations are numbered i = 0, 1, 2, …, limit-1
• Reason:– arrays are indexed this way!
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 31
Other Statements
Nested for-loops
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
...; /*prepare subgroup i*/
for (j=0; j < limit2; j++) {
...;
/* do something with item j of
subgroup i*/
...;
}
...;
}
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 32
Other Statements
An Extension in Modern C Compilers
• The following construct (not in book) is legal in C99:–
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++){
expression involving i;
...;
printf(“Iteration %d completed.\n”, i);
...;
}
• The loop counter i is declared in for loop
• Not visible outside of loop!
• Common practice
• Good programming style
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 33
Other Statements
Notes on Loop Style
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
...; /*prepare for subgroup i*/
for (int j=0; j < limit2; j++) {
...;
/* do something with item j of
subgroup i*/
...;
} /* end of loop j */
...;
} /* end of loop i */
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 34
Other Statements
Notes on Loop Style
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++) {
...; /*prepare for subgroup i*/
for (int j=0; j < limit2; j++) {
...;
/* do something with item j of
subgroup i*/
...;
} /* end of loop j */
...;
} /* end of loop i */
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 35
Other Statements
Questions?
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 36
Other Statements
Simple Example
• Read a series of numbers
• Add up the numbers and also the squares of
those numbers “on-the-fly”
• After all numbers are input, print out:–
– The mean
– The standard deviation
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 37
Other Statements
Simple Example (continued)
#include <stdio.h> for (n = 0; ; n++) {
#include <math.h> int rc;
double input;
int main(int argc, char
*argv[]) { rc = scanf("%lf", &input);
unsigned int n;
double mean; if (rc == EOF)
double sum = 0; break;
double sumOfSquares = 0; else if (rc == 0)
continue;
printf("Enter sequence“
" of numbers:- "); sum += input;
sumOfSquares += input *
input;
} //for (n = 0 ...
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 38
Other Statements
Simple Example (concluded)
printf("The total number of input entries“
" was %u.\n", n);
if (n > 0 ) {
printf("The mean is %g.\n", mean = sum/n);
printf("The standard deviation is %g.\n",
sqrt(sumOfSquares/n - pow(mean, 2)));
} // if (i > 0)
return 0;
} //main
Example can be found here
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 39
Other Statements
Questions?
CS-2301, B-Term 2009 Conditionals, Loops, and 40
Other Statements