Lab Assignment 2:
MIPS single-cycle
implementation
Electrical and Computer
Engineering
University of Cyprus
Lab Tutorial Assignment
ISE Tool setup
Any Questions?
A solution/tutorial will be uploaded
once all assignments have been
submitted
The Five Classic Components of
a Computer
Processor
Input
Control
Memory
Datapath
Output
Datapath: The processor elements that operate on and/or
store data
Control: The processor element that decides how and when
parts of the datapath are executed FSM
INTRODUCTION
The MIPS processor, designed in 1984 by
researchers at Stanford University.
Is a RISC (Reduced Instruction Set
Computer) processor. Compared with
their CISC (Complex Instruction Set
Computer) counterparts (such as the
Intel Pentium processors), RISC
processors typically support fewer and
much simpler instructions.
A RISC processor can be made much
faster than a CISC processor because of
its simpler design.
INTRODUCTION ()
RISC processors typically have a
load-store architecture.
Two instructions for accessing
memory:
a load (l) instruction to load data from
memory,
a store (s) instruction to write data to
memory.
None of the other instructions can
access memory directly.
5-Stage MIPS
Stage 5
PC
Instruction
Memory
(Imem)
Stage 1
Registers
Stage 2
ALU
Stage 3
IFtch Dcd Exec Mem WB
Reg
ALU
IM
DM
Reg
Data
Memory
(Dmem)
Stage 4
STAGES OF EXECUTION IN MIPS
5 stage instruction pipeline
1) I-fetch: Fetch Instruction, Increment
PC
2) Decode: Instruction, Read Registers
3) Execute:
Mem-reference: Calculate Address
R-format: Perform ALU Operation
4) Memory:
Load: Read Data from Data
Memory
Store: Write Data to Data Memory
Block Diagram of MIPS single-cycle
processor
Datapath elements
Instruction memory
PC register, adder increment PC by 4
Register file
ALU
Data memory
Data
PC
Address
Instruction
memory
Instruction
Register #
Registers
ALU
Address
Register #
Data
memory
Register #
Data
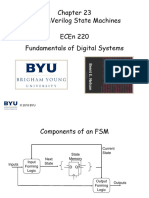
Edge Triggered Methodology
Unclocked vs. Clocked
Clocks used in synchronous logic
when should an element that contains state
be updated?
wouldn't want to read a signal at the same
time it was being written
falling edge
cycle time
rising edge
Edge Triggered Methodology
Register file
A clocking methodology defines
when signals can be read and written
State
element
1
Combinational logic
State
element
2
Write Data to Memory
Clock cycle
Instruction Read From Memory Value Written to Register File
Read Register
Values
The MIPS instructions
format
Single-cycle Implementation
All operations take the same amount
of time - a single cycle
long cycle time
Instructions same size
Source registers always in same place
Immediates same size, location
Operations always on
registers/immediates
LAB2
You will become familiar with the
MIPS instruction set by implementing
a single-cycle core in VHDL
The example code will be uploaded to
the website
You have two weeks for this project
dont wait until the night before to
tackle
LAB2
You will be given the design skeleton
of a single-cycle MIPS processor that
is capable of performing some
instructions.
Complete the design of the singlecycle implementation in order to
support the required MIPS instruction
set.
MIPS 32 Instruction Set
- We're ready to look at an
implementation of the MIPS
- Simplified to contain only:
- memory-reference
instructions: lw, sw
- arithmetic-logical
instructions: add, sub,
and, or, slt
- control flow instructions:
beq
- Generic Implementation:
- use the program counter
(PC) to supply instruction
address
- get the instruction from
memory
- read registers
- use the instruction to
decide exactly what to do
MIPS
MIPS
IFETCH
IFETCH
CONTROL
CONTROL
EXECUTE
EXECUTE
DMEMORY
DMEMORY
IFETCH
IFETCH
IFETCH
IFETCH
IDECODE
IDECODE
DEMO
You'll want to build a suite of test
programs to test the new capabilities
of your implementation as you add
them.
Test Programs
IFETCH.vhd file
are
Stored
in
the
You will be expected to run a number
of supplied programs.
REPORT
Objective of this lab and intro.
Your implementation
Your test programs and results
(simulations)
Your conclusion
Attach your VHDL source code
(email)
Important Announcements!
Lab material (Tutorials, VHDL Files) will
be uploaded in the website!
Deadline for Lab 2 is on: 1/10/2014
No Lab Lecture next week, but we can
be at the lab if there are questions
Adding Instructions to MIPS
(Tutorial)
Branch not Equal (Bne)
Load Upper Immediate (Lui)
Branch Not Equal (Ben)
Load Upper Immediate (Lui)