Programming Language
Lecture 3
Dastan Faruq Ismail
dastan. faruq 1995@gmail .com
1
In this tutorial, we will create a simple
calculator using Visual Basic .NET.
• Steps include:
• Designing the form in Windows Forms
• Writing event-driven code for button clicks
• Performing arithmetic operations
• Displaying results in a TextBox
Step 1: Create a New Windows Forms App
1. Open Visual Studio.
2. Click Create a new project.
3. Select Windows Forms App (.NET Framework).
4. Click Next, name the project (e.g., CalculatorApp), and click
Create.
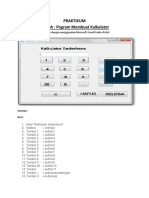
Step 2: Design the Calculator UI
1. Add Controls from the Toolbox
One TextBox → To display numbers (txtDisplay).
Ten Buttons (0–9) → For numeric input.
*Four Buttons (+, -,* , /) → For operations.
One "=" Button → To calculate the result.
One "C" Button → To clear the display.
2
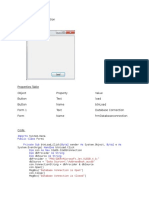
2. Arrange the Controls
Control Name Text Property
Property
TextBox txtDisplay (Empty)
Button btn1 1
Button btn2 2
Button btn3 3
Button btn4 4
Button btn5 5
Button btn6 6
Button btn7 7
Button btn8 8
Button btn9 9
Button btn0 0
Button btnAdd +
Button btnSubtract -
Button btnMultiply *
Button btnDivide /
Button btnEquals =
Button btnClear C
3
Step 3: Write the Code
Public Class Form1
Dim num1, num2 As Double
Dim operation As String
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
MyBase.Load
End Sub
Private Sub btn1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btn1.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "1"
End Sub
Private Sub btn2_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btn2.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "2"
End Sub
Private Sub btn3_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btn3.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "3"
End Sub
Private Sub btn4_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btn4.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "4"
4
End Sub
Private Sub btn5_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btn5.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "5"
End Sub
Private Sub btn6_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btn6.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "6"
End Sub
Private Sub btn7_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btn7.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "7"
End Sub
Private Sub btn8_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btn8.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "8"
End Sub
Private Sub btn9_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btn9.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "9"
End Sub
Private Sub btn0_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btn0.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "0"
End Sub
Private Sub btndot_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btndot.Click
txtdisply.Text &= "."
End Sub
Private Sub btnadd_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btnadd.Click
num1 = Val(txtdisply.Text)
operation = "+"
txtdisply.Clear()
End Sub
Private Sub btnsub_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btnsub.Click
num1 = Val(txtdisply.Text)
operation = "-"
txtdisply.Clear()
End Sub
Private Sub btnmultiply_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btnmultiply.Click
num1 = Val(txtdisply.Text)
operation = "*"
txtdisply.Clear()
End Sub
Private Sub btndivide_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btndivide.Click
num1 = Val(txtdisply.Text)
5
operation = "/"
txtdisply.Clear()
End Sub
Private Sub btnequle_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btnequle.Click
num2 = Val(txtdisply.Text)
Select Case operation
Case "+"
txtdisply.Text = (num1 + num2).ToString
Case "-"
txtdisply.Text = (num1 - num2).ToString
Case "*"
txtdisply.Text = (num1 * num2).ToString
Case "/"
txtdisply.Text = (num1 / num2).ToString
End Select
End Sub
Private Sub btnclear_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles
btnclear.Click
txtdisply.Clear()
num1 = 0
num2 = 0
End Sub
End Class