Chapter 1
Basics of Computer Organization
Introduction to computer system
A computer is an electronic device, under the control of instructions stored in its memory that can
accept data (input), process the data according to specified rules(Program) on processor & produces
information (output), and store the information for future use.
Data vs Information
Data are raw numbers or other findings which, by themselves, are of limited value.
Information is data that has been converted into a meaningful and useful context.
Advantages of computer
• Speed
• Accuracy
• Huge storage
• Versatility
• Tirelessness
Disadvantages of computer
• Data security issue
• Computer crimes
• Health risk
• Bad impact on environment if not properly disposed off
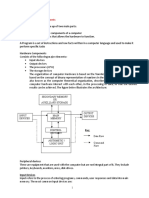
Any digital computer performs five functions in gross term.
1. Take data as input
2. Stores data/instructions
3. Process those stored data
4. Generate the output
5. Control all above steps
Computer Components
Any kind of computers consists of HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE.
Hardware: Computer hardware is the collection of physical elements/parts that constitutes a computer
system, such as the monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, hard drive disk (HDD), system
unit (graphic cards, sound cards, memory, motherboard and chips), etc. all of which are physical objects
& can be touched.
Software: Software is a generic term for organized collections of computer data and instructions, often
broken into two major categories: system software that provides the basic non task specific functions of
the computer, and application software which is used by users to accomplish specific tasks.
Hardware
Input/Output Units
Input Unit:
A device through which data and programs from the outside world enter the computer system.
Output unit:
A device through which results stored in the computer memory are made available outside the
computer system.
Central processing unit – Comprises three parts
1. Arithmetic/Logic Unit: Performs basic arithmetic operations such as addition and subtraction Performs
logical operations such as AND, OR, and NOT. Most modern ALUs have a small amount of special storage
units called registers that can be accessed faster than main memory.
2. Control unit: It organizes the computer to work computer as single unit & generates control signals for
various devices regarding read/write or execute operation
3. Memory Unit: A collection of cells, each with a unique physical address. Most computers are byte-
addressable.
Memory Types
*Primary Memory
Random Access Memory (RAM) - is a type of volatile memory that is stores information on an integrated
circuit which hold the data mainly when the program is being executed by the CPU. As it is volatile in
nature so it can't store data permanently.
Read Only Memory (ROM) - a non-volatile memory chip in which data are stored permanently, and
cannot be altered by the programmer.
Cache Memory - is the volatile computer memory which is very nearest to the CPU,so also called CPU
memory, and is between CPU and RAM all the Recent Instructions are Stored into the Cache Memory. It
is the fastest memory that provides high-speed data access to a computer microprocessor.
Types of ROM
MROM (Masked ROM)-The very first ROMs were hard-wired devices that contained a preprogrammed
set of data or instructions & are known as masked ROMs & are inexpensive.
PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory)- PROM is read-only. The user buys a blank PROM and enters
the desired contents using a PROM program. Inside the PROM chip, there are small fuses which are
burnt open during programming. It can be programmed only once and is not erasable.
EPROM (Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory)-EPROM can be erased by exposing it to ultra-
violet light for a duration of up to 40 minutes. Usually, an EPROM eraser achieves this function. During
programming, an electrical charge is trapped in an insulated gate region. The charge is retained for more
than 10 years because the charge has no leakage path.
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable and Programmable Read Only Memory)-EEPROM is programmed and
erased electrically. It can be erased and reprogrammed about ten thousand times. Both erasing and
programming take about 4 to 10 ms (millisecond). In EEPROM, any location can be selectively erased and
programmed.
*Secondary Memory: A storage, which supplements the main memory.
Secondary Storage Devices
Hard disk Fixed Head HDD / Movable head HDD
A hard disk is a set of stacked disks. Each disk has data recorded electromagnetically in concentric circles,
or tracks, on the disk Hard Drive Types
1. Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment (PATA)
2. Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
3. Small Computer System Interface (SCSI)
4. Solid State Drives (SSD)
Input Devices
Input devices can send data or information to a computer or another device. Examples of various input
devices are as:
Keyboard: It is an input device which sends data in to the computer. The data send depends on the key
pressed by the user.
Mouse: A mouse is a small handheld input device which controls a cursor in a graphical user interface. It
can move and select text, files, folders etc. on our computer according to the user input.
Scanner: Scanner optically reads and document, file or image and then changes it into digital signal and
sends to the computer. It converts hardcopy to softcopy.
OMR: Optical Mark Recognition/ Reader, is used to read marks on a document and send them to
computer.
OCR: OCR stands for Optical Character Recognition, is an input device which reads printed text and sends
that to computer.
MICR: Magnetic Ink Character Reader is an input device which generally finds application is banks to
process cheques.
Microphone: it receives audio generated by some input source and sends it to a computer. Webcam: it
sends the captured images to a computer.
Graphics Tablets: This input device is used to draw using hand.
Trackballs: An upside-down mouse, encased within a socket. Is a cursor control device.
Barcode reader: It is used to read the barcode of various items and feed the same to computer.
Gamepad: Also known as joy pad is the input controller for video games.
Joystick: these input devices are used to control video games.
Output Devices
A device that can receive data from computer or another device and create output with that data is
called output device. Examples of various output devices are as:
Monitor: A monitor is an output device that is responsible for receiving data from a computer and
displaying that information as text or images for users to see.
Speakers: Receives sound signal from a computer and then plays that sound signal and thus we hear
songs or music or any other audio.
Projector: Gets data from a computer and displays or projects the same information onto a screen or a
wall. Projector cannot directly accept data from a user and send that data to another device.
Printer: Device used to convert a softcopy to hardcopy, i.e., any files contents can be converted in a
printed page.
Both Input / Output Devices
An input/output device is capable of receiving data from users or other devices and also sending data to
another devices or computers. That means a device which can be used as both input device and output
device are called Input / Output (I/O) devices. Some examples of input/output devices are as:
USB drive: Also known as pen drive or flash stick works as both input device to computer and as an
output device. USB drives receive or save data from a computer as an input and it can also send data to a
computer or another device.
Facsimile: Facsimile or FAX machine has a scanner which is an input device and a small printer to provide
output.
Modems: It is used to transmit and receive data from one computer to another computer or other
devices using telephone lines
CD-RW drives and DVD-RW drives: Receives data from a computer as input to copy onto and save into
writable CD or DVD. We also use CDs or DVDs to transfer data to a computer.
Touch Screen: Touch screen is both input and output device. By touching the screen input is provided
and being a screen, it is used as an output device.
Headsets: Headset consists of speaker as an output device and microphone functions as an input device.
Software
Software is an organized instructions/code written by programmers using any of various special
computer languages for specific purpose. Types of software are as follows:
(1) System software: controls the basic functions of a computer & hides complexity of computer system
from user and application software. E.g. Operating System, Compiler, Interpret etc.
(2) Application software: It handles specialized/ common tasks a user wants to perform, such as
banking, hotel management, any data processing, word processing etc.
(3) Utility software: Which helps to manage, maintain and control computer resources. E.g. are antivirus
software, backup software and disk tools.
(1) System software
OPERATING SYSTEM
An Operating System (OS) is a system program that controls and manages the computer resources
(resource manager) so that application software can run on it. Example: Microsoft Windows, Solaris,
Linux, MAC OS, Ubuntu, Apple’s i-Phone OS etc.
HOW AN OPERATING SYSTEM WORKS
In any computer or mobile device, the operating system can be termed as the back bone when it comes
to software. This is because it has to be there before other programs can be run. It works as a
middleman (interface) between machine and user. At the simplest level, an operating system does two
things:
• It manages the hardware resources of the computer system. These resources include such things as
the processor, memory, disk space, etc.
• It provides a stable, consistent way for applications to deal with the hardware without having to know
all the details of the hardware.
FUNCTIONS OF OPERATING SYSTEM
• Processor management Loads, schedules and execute process/programs.
• Memory management Allocates /De-allocation of memory for program execution.
• Device management Communicate and controls various I/O devices.
• Storage management Manages and controls the storage device to provide space to program for
execution & data save.
• Application interface API/drivers provide a way for applications to make use of hardware
• User interface structure for interaction between a user and the computer
TYPE OF OPERATING SYSTEM
* Single-User, Single Task Operating System: These operating systems work on single task & single user at
a time. E.g. DOS
* Single-User, Multi-Task Operating System: These operating systems works on more than one task and
process them concurrently at a time. E.g. windows 95 or later version of windows
* Multiuser Operating System: In these OS, multiple users are allowed to access the same data or
information at a time via a network. E.g. Unix, Linux, Windows7.
* Multiprocessing Operating System: Here, a single process runs on two or more processors. All the
processing and their management takes place in a parallel way, hence this OS are also called as Parallel
Processing. E.g. Linux, UNIX and Windows 7.
* Embedded Operating System: These are embedded in a device, which is located in ROM. E.g. OS of
microwaves, washing machine.
* Distributed Operating System: In these OS, the computers work in co-operation with each other.
Language processor/Programming tool
As the computer understand machine language (0/1) where as Humans understand High level/Human
Lang. Language Processors does the conversion task (high level to machine lang.) These are of 3 types
Language processors
1.Compilers-It convert high-level language code to machine code in one session. It takes time because it
has to translate high-level code to lower-level machine language all at once and then save the executable
object code to memory.
2. Interpreters-It translates code like a compiler but reads the code and immediately executes that code,
and therefore it is faster than a compiler.
3. Assemblers-It translates an assembly language program into machine language. One-pass assemblers
go through the source code once. Any symbol used before it is defined will require "errata" at the end of
the object telling the linker or the loader to "go back" and overwrite a placeholder which had been left
where the as yet undefined symbol was used. Multi-pass assemblers create a table with all symbols and
their values in the first passes, then use the table in later passes to generate code.
(2) Application software
* General Purpose application software
These are ready to use software for daily use purpose e.g. word processor, spread sheet, presentation,
DBMS etc.
* Specific Purpose application software
Softwares which are designed for specific task e.g. Payroll, Hotel Mgmt, Hospital Mgmt, Stock Mgmt etc.
(3) Utility software/System
Utilities that assist OS in carrying out certain specialized tasks are called utility software.
▪ Antivirus - An anti-virus scans the system for any virus and if detected, gets rid of it by deleting or
isolating it.
▪ Compression tools - Compression tools are utilities that assist operating systems in shortening files so
that they take less space
▪ Disk Cleanup - Disk cleanup tools assist users in freeing up disk space.
▪ Disk Defragmenter - Disk defragmenter is a disk management utility that increases file access speeds
by rearranging fragmented files on contiguous locations.
▪ Backup - Backup utility enables backing up of files, folders, databases or complete disks. ▪ File
management tools - Utility software providing regular file management tasks like browse, search,
update, preview, etc. are called file management tools.
▪ Restore – This utility restores the backup earlier taken.
▪ Device driver or hardware driver is a group of files that enable one or more hardware devices to
communicate with the computer's operating system. Without drivers, the computer would not be able
to send and receive data correctly to hardware devices, such as a printer.