Entity Relationship model
ER (Entity Relationship) Diagram in DBMS
o ER model stands for an Entity-Relationship model. It is a high-level data
model. This model is used to define the data elements and relationship for a
specified system.
o It develops a conceptual design for the database. It also develops a very
simple and easy to design view of data.
o In ER modeling, the database structure is portrayed as a diagram called an
entity-relationship diagram.
For example, Suppose we design a school database. In this database, the student will
be an entity with attributes like address, name, id, age, etc. The address can be another
entity with attributes like city, street name, pin code, etc and there will be a relationship
between them.
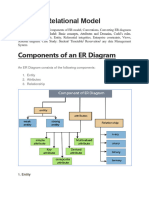
Component of ER Diagram
What is Entity?
An Entity may be an object with a physical existence – a particular person,
car, house, or employee – or it may be an object with a conceptual
existence – a company, a job, or a university course.
What is Entity Set?
An Entity is an object of Entity Type and a set of all entities is called an
entity set. For Example, E1 is an entity having Entity Type Student and
the set of all students is called Entity Set. In ER diagram, Entity Type is
represented as:
Entity Set
We can represent the entity set in ER Diagram but can‟t represent entity
in ER Diagram because entity is row and column in the relation and ER
Diagram is graphical representation of data.
Types of Entity
There are two types of entity:
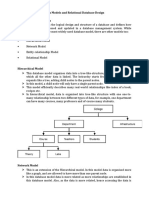
1. Strong Entity
A Strong Entity is a type of entity that has a key Attribute. Strong Entity
does not depend on other Entity in the Schema. It has a primary key, that
helps in identifying it uniquely, and it is represented by a rectangle. These
are called Strong Entity Types.
2. Weak Entity
An Entity type has a key attribute that uniquely identifies each entity in the
entity set. But some entity type exists for which key attributes can‟t be
defined. These are called Weak Entity types .
For Example, A company may store the information of dependents
(Parents, Children, Spouse) of an Employee. But the dependents can‟t
exist without the employee. So Dependent will be a Weak Entity Type and
Employee will be Identifying Entity type for Dependent, which means it
is Strong Entity Type .
A weak entity type is represented by a Double Rectangle. The
participation of weak entity types is always total. The relationship between
the weak entity type and its identifying strong entity type is called
identifying relationship and it is represented by a double diamond.
Strong Entity and Weak Entity
What is Attributes?
Attributes are the properties that define the entity type. For example,
Roll_No, Name, DOB, Age, Address, and Mobile_No are the attributes
that define entity type Student. In ER diagram, the attribute is represented
by an oval.
Attribute
Types of Attributes
1. Key Attribute
The attribute which uniquely identifies each entity in the entity set is called
the key attribute. For example, Roll_No will be unique for each student. In
ER diagram, the key attribute is represented by an oval with underlying
lines.
Key Attribute
2. Composite Attribute
An attribute composed of many other attributes is called a composite
attribute. For example, the Address attribute of the student Entity type
consists of Street, City, State, and Country. In ER diagram, the composite
attribute is represented by an oval comprising of ovals.
Composite Attribute
3. Multivalued Attribute
An attribute consisting of more than one value for a given entity. For
example, Phone_No (can be more than one for a given student). In ER
diagram, a multivalued attribute is represented by a double oval.
Multivalued Attribute
4. Derived Attribute
An attribute that can be derived from other attributes of the entity type is
known as a derived attribute. e.g.; Age (can be derived from DOB). In ER
diagram, the derived attribute is represented by a dashed oval.
Derived Attribute
The Complete Entity Type Student with its Attributes can be represented
as:
Entity and Attributes
Relationship Type and Relationship Set
A Relationship Type represents the association between entity types. For
example, „Enrolled in‟ is a relationship type that exists between entity type
Student and Course. In ER diagram, the relationship type is represented
by a diamond and connecting the entities with lines.
Entity-Relationship Set
A set of relationships of the same type is known as a relationship set. The
following relationship set depicts S1 as enrolled in C2, S2 as enrolled in
C1, and S3 as registered in C3.
Relationship Set
Degree of a Relationship Set
The number of different entity sets participating in a relationship set is
called the degree of a relationship set.
1. Unary Relationship: When there is only ONE entity set participating in a
relation, the relationship is called a unary relationship. For example, one
person is married to only one person.
Unary Relationship
2. Binary Relationship: When there are TWO entities set participating in a
relationship, the relationship is called a binary relationship. For example, a
Student is enrolled in a Course.
Binary Relationship
3. Ternary Relationship: When there are three entity sets participating in a
relationship, the relationship is called a ternary relationship.
4. N-ary Relationship: When there are n entities set participating in a
relationship, the relationship is called an n-ary relationship.
What is Cardinality?
The number of times an entity of an entity set participates in a relationship
set is known as cardinality . Cardinality can be of different types:
1. One-to-One: When each entity in each entity set can take part only
once in the relationship, the cardinality is one-to-one. Let us assume that
a male can marry one female and a female can marry one male. So the
relationship will be one-to-one.
the total number of tables that can be used in this is 2.
one to one cardinality
Using Sets, it can be represented as:
Set Representation of One-to-One
2. One-to-Many: In one-to-many mapping as well where each entity can
be related to more than one entity and the total number of tables that can
be used in this is 2. Let us assume that one surgeon department can
accommodate many doctors. So the Cardinality will be 1 to M. It means
one department has many Doctors.
total number of tables that can used is 3.
one to many cardinality
Using sets, one-to-many cardinality can be represented as:
Set Representation of One-to-Many
3. Many-to-One: When entities in one entity set can take part only once in
the relationship set and entities in other entity sets can take part more
than once in the relationship set, cardinality is many to one. Let us
assume that a student can take only one course but one course can be
taken by many students. So the cardinality will be n to 1. It means that for
one course there can be n students but for one student, there will be only
one course.
The total number of tables that can be used in this is 3.
many to one cardinality
Using Sets, it can be represented as:
Set Representation of Many-to-One
In this case, each student is taking only 1 course but 1 course has been
taken by many students.
4. Many-to-Many: When entities in all entity sets can take part more than
once in the relationship cardinality is many to many. Let us assume that a
student can take more than one course and one course can be taken by
many students. So the relationship will be many to many.
the total number of tables that can be used in this is 3.
many to many cardinality
Using Sets, it can be represented as:
Many-to-Many Set Representation
In this example, student S1 is enrolled in C1 and C3 and Course C3 is
enrolled by S1, S3, and S4. So it is many-to-many relationships.
Difference Between Entity, Entity Set and Entity
Type
Entity Entity Type Entity Set
A thing in the real world Set of all entities of a
A category of a particular
with independent particular entity
entity
existence type.
Any particular row (a
The name of a relation All rows of a relation
record) in a relation
(table) in RDBMS is an (table) in RDBMS is
(table) is known as an
entity type entity set
entity.
Represents a
Entities can be tangible Defines attributes shared snapshot of all
or intangible. by entities of that type. entities at a given
time.
It can grow or shrink
It is identified uniquely It represents the structure
as entities are added
through a key attribute. of the table without data.
or removed.
Example: A student Example: “Student” table Example: All records
with ID 1. schema. in the “Student” table.