SUBROUTINE
A subroutine, also known as a function or procedure, is a block of code
that performs a specific task and can be called multiple times within a
program. Subroutines help break down complex tasks into smaller,
manageable parts, making code more organized and reusable.
Key characteristics of subroutines:
Modularization:
Subroutines promote modular programming, allowing developers to
divide a large program into smaller, independent units.
Reusability:
Subroutines can be called multiple times from different parts of the program,
reducing code duplication and improving efficiency.
Readability:
By encapsulating specific tasks within subroutines, the overall code becomes
easier to understand and maintain.
Abstraction:
Subroutines hide the internal details of their implementation, allowing users
to interact with them through a simple interface.
Example:
C
#include <stdio.h>
// Subroutine to calculate the area of a rectangle
float calculateArea(float length, float width) {
return length * width;
}
int main() {
float l = 5.0, w = 10.0;
float area = calculateArea(l, w); // Calling the subroutine
printf("Area of the rectangle: %f\n", area);
return 0;
}
In this example, calculateArea is a subroutine that calculates the area of a
rectangle given its length and width. The main function calls this subroutine to
perform the calculation and print the result.
Common subroutine types:
Functions: Functions typically return a value after performing their task.
Procedures: Procedures do not necessarily return a value.
In summary, subroutines are fundamental building blocks in programming,
promoting code organization, reusability, and maintainability.
In a program, what will be the necessity of using subroutine call
instruction?
1. initialize program counter 2. Clear the accumulator
3. Reset the microprocessor 4. Clear the instruction register
Option 4 : Clear the instruction register
The correct answer is Clear the instruction registers.
Key Points
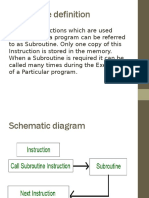
Subroutine call is referred to as the block of instructions which are
used again and again in a program and its sub-programs.
When a program is executing, the subroutine can be called
multiple times as per the requirement of the program.
The subroutine call cleans the instruction registers in the
program.
Thus the correct answer is Clear the instruction registers.
Additional Information
In the memory only one copy of subroutine call instruction is
stored.
The material of the PC has to be Saved with the aid of using the
decision Subroutine Instruction to make an accurate go back to
the calling program.
The subroutine linkage technique is a manner wherein computer
systems call and return the subroutine. The best manner of
subroutine linkage is saving the return deal within a selected
location, inclusive of a check-in which may be referred to as a
hyperlink check in the called subroutine.
Computer Organization Questions and Answers – Subroutines and Nesting
1. The return address of the Sub-routine is pointed to by _______
a) IR b) PC c) MAR d) Special memory registers
2. The location to return to, from the subroutine is stored in _____
a) TLB b) PC c) MAR d) Link registers
3. What is subroutine nesting?
a) Having multiple subroutines in a program
b) Using a linking nest statement to put many subroutines under the same name
c) Having one routine call the other
d) None of the mentioned
4. The order in which the return addresses are generated and used is
______ a) LIFO b) FIFO c) Random d) Highest priority
5. In case of nested subroutines the return addresses are stored in
a) System heap b) Special memory buffers
c) Processor stack d) Registers
6. The appropriate return addresses are obtained with the help of ____ in
case of nested routines.
a) MAR b) MDR c) Buffers d) Stack-pointers
7. When parameters are being passed on to the subroutines they are stored
in _ a) Registers b) Memory locations
c) Processor stacks d) All of the mentioned
8. The most efficient way of handling parameter passing is by using _____
a) General purpose registers b) Stacks
c) Memory locations d) None of the mentioned
9. The most Flexible way of logging the return addresses of the subroutines
is by using _______a) Registers b) Stacks
c) Memory locations d) None of the mentioned
10. The wrong statement/s regarding interrupts and subroutines among the
following is/are ___i) The sub-routine and interrupts have a return statementii)
Both of them alter the content of the PC iii) Both are
software oriented iv) Both can be initiated by the user
a) i, ii and iv b) ii and iii c) iv d) iii and iv
ANSWERS:
1. Answer: b
Explanation: The return address from the subroutine is pointed to by the PC.
2. Answer: d
Explanation: The registers store the return address of the routine and is pointed
to by the PC.
3. Answer: c
Explanation: None.
4. Answer: a
Explanation: That is the routine called first is returned first.
5. Answer: c
Explanation: In this case, there will be more number of return addresses it is
stored on the processor stack.
6. Answer: d
Explanation: The pointers are used to point to the location on the stack where
the address is stored.
7. Answer: d
Explanation: In the case of, parameter passing the data can be stored on any of
the storage space.
8. Answer: a
Explanation: By using general purpose registers for the parameter passing we
make the process more efficient.
9. Answer: b
Explanation: The stacks are used as Logs for return addresses of the
subroutines.
10. Answer: d
Explanation: None.
Memory Stack & Subroutines - MCQs with answers
Q1. Which register holds the address for a stack whose value is
supposed to be directed at the topmost position?
a. Stack Pointer b. Stack Register
c. Both a & b d. None of the above
Q2. The instructions based on the stack operations are also
known as 'zero address' or 'implied instructions', because ______
a. address gets updated automatically in stack pointer
b. processor can refer a memory stack without specifying the address
c. both a & b d. none of the above
Q3. What is another name of memory stack especially given for
the fundamental function performed by it?
a. Last-in-first-out (LIFO) b. First-in-last-out (FILO)
c. First-in-first-out (FIFO) d. Last-in-last-out (LILO)
Q4. What does the last instruction of each subroutine that
transfer the control to the instruction in the calling program with
temporary address storage , called as?
a. jump to subroutine b. branch to subroutine
c. return from subroutine d. call subroutine
1. a. Stack Pointer 2. c. both a & b
3. a. Last-in-first-out (LIFO) 4. c. return from subroutine
1.What is a subroutine?
1. A named self-contained section of code that performs a specific task
2. Another name for pseudocode
3. A routine that has no connection at all to the main routine
4 A word used exclusively in movies to sound cool
2.What is the difference between a function and a procedure?
1. Procedures just carry out instructions, functions always return values
2. Functions carry out instructions and procdures return values
3. Trick question: they are the same thing
4. Both always return values but in different data types
3.Define a paramater
1. A variable named in the subroutine heading that uses values you give it
2. Instructions that stop functions from working if theyaren't followed by the
user
3. Boolean logic used exclsuively in functions
4. An instruction that will return a value if it is followed through
4.Define a local variable
1. A variable defined in a function
2. A variable declared at the beginning of the main program
3. A variable declared in the main program
4. A vaiable declared right at the end of the main program
5. variable
1. A variable declared in the main program
2. A variable declared at the beginning of the main program
3. A variable declared in a function
4. A vaiable declared right at the end of the main program
6.What makes a local variable special?
1. It can only be called in the subroutine it is declared in
2. The computer is unable to understand it without third-party software
3. Its value is unique to your LAN
4. Trick question: it's the same as a global variable
7.What is an advantage of using a local variable?
1. The function can be used with different variables for the same purpose
2. The code is harder to disrrupt
3. It's easier for the user to call back to it outside the function
4. Trick question: local variables are useless
8.How do you call a subroutine?
1. By using the variable it is assigned to in the code
2. With a landline
3. By calling one of its local variables
4. By calling its parameters
9.Why are subroutines useful?
1. To avoid repeating code and reduce length
2. Only to make debugging easier
3. Only to reduce the number of memory used
4. Trick question: functions are always disadvantageous
10.Why are parameters useful?
1. It makes the subroutine more dynamic
2. It always makes the subroutine run faster
3. It makes the subroutine easier to call
4. It makes the subroutine easier to understand by the machine
11.How does a subroutine return data?
1. If its a procedure it depends on how it was coded, functions return values
through a return statement
2. Through return statements
3. Through a text document created by the code
4. Into a variable generated by the function being called
12.How many values does a subroutine have to return?
1. As many as it is programmed to return 2. 1 3. 10 4. 1024
13.What is the maximum amount of parameters a subroutine can have?
1. As many as you want 2. 64
3. As many as the amount of variables in the code 4. 2
14.Can you create a subroutine in a subroutine in Python?
1. Yes, they are nested functions 2. Not unless you define a parameter
3. No 4.Yes, they are called subsubroutines
15.A subroutine may be disadvantageous in which situation?
1. If it is only needed once 2. If it is needed more than 10 times
3. If it is needed more than 100 times
4. If it is needed more than 1x10^1024 times
16.How does a subroutine conserve memory
1. By reducing the number of lines of code needed
2. By reducing the number of global variables needed
3. Witchcraft
4. By reducing the number of local variables needed
17.In what scenario could you use a subroutine?
1. To use a prewritten mathematical formula on a variable
2. To define global variables
3. To accurately predict the name of the user without and prior information
given
4. To hack into the mainframe
18.How many local variables must be used in a subroutine?
1. As few or as many as you want to
2. As many as there are global variables
3. Less than the amount of global variables
4. At least 1
19.How would a person declare the function functionName in Python?
1. def functionName(): 2.fun functionName():
3. def functionName() 4. def functionName{}:
20.Why does a subroutine need parameters
1. Trick question: they don't always need them
2. To stop the code from crashing
3. To give the subroutine instructions on how to function
4. To prevent it from gaining sentience