Created by Turbolearn AI
Introduction to Algorithms
What is an Algorithm?
An algorithm is "a finite set of precise instructions for performing a computation or for solving a problem."
A program is one type of algorithm.
All programs are algorithms.
Not all algorithms are programs.
Example: Designing a scheduler for RTOS is an algorithm.
Algorithm Complexity
Some algorithms are easy.
Finding the largest (or smallest) value in a list.
Finding a specific value in a list.
Some algorithms are a bit harder.
Sorting a list.
Some algorithms are very hard.
Finding the shortest path between Miami and Seattle.
Some algorithms are essentially impossible.
Factoring large composite numbers.
Algorithm complexity needs to be considered.
Algorithm 1: Maximum Element
Given a list, how do we find the maximum element in the list?
Pseudocode:
procedure max(a1, a2, …, an: integers)
max := a1
for i := 2 to n
if max < ai then
max := ai
Maximum Element Running Time: If the list has n elements, the worst-case scenario is that it takes n steps. A step is considered
a single step through the list.
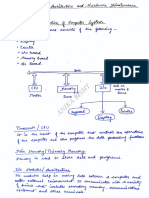
Properties of Algorithms
Algorithms generally share a set of properties:
Input: What the algorithm takes in as input.
Output: What the algorithm produces as output.
Definiteness: The steps are defined precisely.
Correctness: Should produce the correct output.
Finiteness: The steps required should be finite.
Effectiveness: Each step must be able to be performed in a finite amount of time.
Generality: The algorithm should be applicable to all problems of a similar form.
Searching Algorithms
Given a list, find a specific element in the list. Two types of searches will be covered:
Page 1
Created by Turbolearn AI
Linear Search (a.k.a. sequential search)
Binary Search
Algorithm 2: Linear Search
Given a list, find a specific element in the list. The list does NOT have to be sorted!
Pseudocode:
procedure linear_search (x: integer; a1, a2, …, an: integers)
i := 1
while ( i ≤ n and x ≠ ai )
i := i + 1
if i ≤ n then
location := i
else
location := 0
{location is the subscript of the term that equals x, or it is 0 if x is not found}
Linear Search Running Time: If the list has n elements, the worst-case scenario is that it takes n steps. A step is considered a
single step through the list. Complexity is O(N ).
Algorithm 3: Binary Search
Given a list, find a specific element in the list. The list MUST be sorted! Each time it iterates through, it cuts the list in half.
Pseudocode:
procedure binary_search (x: integer; a1, a2, …, an: increasing integers)
i := 1 { i is left endpoint of search interval }
j := n { j is right endpoint of search interval }
while i < j
begin
m := ⌊(i+j)/2⌋ { m is the point in the middle }
if x > am then
i := m+1
else
j := m
end
if x = ai then
location := i
else
location := 0
Binary Search Running Time: How long does this take (worst case)?
If the list has 8 elements, it takes 3 steps.
If the list has 16 elements, it takes 4 steps.
If the list has n elements, it takes log n steps.
2
Sorting Algorithms
Given a list, put it into some order (numerical, lexicographic, etc.). Two types will be covered:
Bubble Sort
Insertion Sort
Algorithm 4: Bubble Sort
One of the most simple sorting algorithms, also one of the least efficient. It takes successive elements and "bubbles" them up the
list.
Pseudocode:
Page 2
Created by Turbolearn AI
procedure bubble_sort (a1, a2, …, an)
for i := 1 to n-1
for j := 1 to n-i
if aj > aj +1 then
interchange aj and aj +1
{ a1, …, an are in increasing order }
Bubble Sort Running Time:
Outer for loop does n-1 iterations.
Inner for loop does n-1 iterations the first time, n-2 iterations the second time, … 1 iteration the last time.
Total: (n − 1) + (n − 2) + (n − 3) + … + 2 + 1 = (n − n)/2
2
We can say that's "about" n time.
2
Algorithm 5: Insertion Sort
Another simple (and inefficient) algorithm. It starts with a list with one element and inserts new elements into their proper place
in the sorted part of the list.
Pseudocode:
procedure insertion_sort (a1, a2, …, an)
for j := 2 to n
begin
i := 1
while aj > ai
i := i +1
m := aj
for k := 0 to j-i-1
aj-k := aj-k-1
ai := m
end
{ a1, a2, …, an are sorted }
Insertion Sort Running Time:
Outer for loop runs n-1 times.
In the inner for loop:
Worst case is when the while keeps i at 1, and the for loop runs lots of times.
If i is 1, the inner for loop runs 1 time (k goes from 0 to 0) on the first iteration, 1 time on the second, up to n-2 times
on the last iteration.
Total is 1 + 2 + … + n − 2 = (n − 1)(n − 2)/2 We can say that’s "about" n time 2
Comparison of Running Times
Algorithm Type Algorithm Running Time
Searching Linear n steps
Searching Binary log2nsteps
Sorting Bubble n steps
2
Sorting Insertion n steps
2
Note: Binary search is about as fast as you can get. There are other, more efficient, sorting techniques. In principle, the fastest are
heap sort, quick sort, and merge sort. These each take take n ∗ log n steps. In practice, quick sort is the fastest, followed by
2
merge sort.
Software Technology
Software Development Life Cycle
Page 3
Created by Turbolearn AI
This diagram showcases the cyclical nature of the Software Development Life Cycle, illustrating the iterative progression through
the phases: Requirements Analysis, Design, Development, Testing, and Maintenance. A developer primarily works in the
Development phase.
The stages are:
Page 4
Created by Turbolearn AI
1. Requirement Analysis
Use-case diagrams are used to model system features.
2. Design
Sequence diagrams, flowcharts, state machines, etc.
3. Development
CAD Tools: Github, SourceTree
Software Editors: Visual Studio Code
Project template: MVC model
4. Software Testing
Page 5
Created by Turbolearn AI
Validation and Performance Testing reports This image illustrates
the different levels of software testing, showing Unit Tests as the base, Integration Tests in the middle, and UI Tests at
the top.
5. Maintenance or Operations (DevOps)
This image represents
the DevOps cycle, consisting of two interconnected circles labeled "Dev" and "Ops," illustrating the continuous
integration and continuous deployment processes.
Software Development Framework
Supported libraries, SDK, programming languages for software development and deployment.
Page 6
Created by Turbolearn AI
Dot Net Framework
This image shows
the .NET 5 ecosystem, showcasing its components, tools, and application areas.
Unifies framework for Desktop Applications.
C, C++, and C# are the most popular languages.
Visual Studio IDE: Drag and Drop functionality!
Framework 7 – React JS
https://framework7.io/react/ This
image shows a developer's interface featuring a coding environment on the left and a simulated mobile device on the
right, displaying a code example for creating cards in React.
Framework 7 Web-App development environment
Android Studio and Flutter
This image presents an overview of
Flutter's capabilities, featuring the Flutter logo alongside a list of supported platforms.
Flutter is an Android Studio plug-in: Access to the hardware of the mobile device (Bluetooth, NFC, Wifi, …)
Page 7
Created by Turbolearn AI
Unity 3D
Unity 3D Dashboard This image displays a digital dashboard with various data points, presented in a futuristic and
organized manner.
A product from Microsoft.
Not only for game developers but also a cross-framework for software development.
C# programming language
Unity Asset Store:
https://assetstore.unity.com/templates
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uZaFHx1daLU Data Visualization Dashboard This image showcases a
customizable template designed to effectively communicate data insights through a combination of visual
elements.
Software Programming Language
Programming Concepts
Procedure and OOP Programming Language
Procedural vs Object Oriented Programming
Feature Procedural Programming Object-Oriented Programming
Focus Functions Data
Data Handling Global data shared among functions Data and functions encapsulated within objects
Real-world Resemblance Less resemblance to real-world scenarios More resemblance to real-world scenarios
Basic concepts of OOP
Classes & Objects:
A class is a template which consists of data members.
An object is a variable of type Class.
Inheritance: When one class acquires all the properties and behaviors of the parent class.
Polymorphism: When one task is performed in different ways.
Abstraction: Hiding internal details and showing functionality.
Encapsulation: Binding (or wrapping) code and data together into a single unit.
C/C++ Programming Language
C++ Code Interaction
Finite State Machine (FSM)
Finite-State Machine (FSM) or Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a
mathematical model of computation. Finite State Machine Diagram
This image represents a finite state machine diagram with two states: "Locked" and "Unlocked," connected by transitions
labeled with "Push" and "Coin" events, illustrating the state transitions of a turnstile.
Current State Input Next State
Locked Coin Unlocked
Locked Push Locked
Unlocked Coin Unlocked
Unlocked Push Locked
Finite State Machine Programming:
Page 8
Created by Turbolearn AI
while(1){
switch(status){
case LOCKED:
lock_turnstile(); //operation in a state
if(Coin == true) //transition condition
status = UNLOCKED; //next state
break;
case UNLOCKED:
unlock_turnstile(); //operation in a state
if(Push == true) //transition condition
status = LOCKED; //next state
break;
default:
break;
}
}
Python Programming Language
Python Programming Language
Used in AI, Data science, and Deep Learning.
Interpreted programming language.
Class in Python:
class Student:
def __init__(self, _name, _age):
self.name = _name
self.age = _age
def setName(self, _name):
self.name = _name
Model View Controller
Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern
A pattern for OOP programs
MVC using Python MVC using Python
1. Step 1: Create a new project in Python
Create Model folder: Student.py
Create Controller folder: StudentController.py
The main.py is the View of the project.
2. Step 2: Implement the Student Class
Page 9
Created by Turbolearn AI
class Student:
def __init__(self, _name, _age):
self.name = _name
self.age = _age
def setName(self, _name):
self.name = _name
def getName(self):
return self.name
def setAge(self, _age):
self.age = _age
def getAge(self):
return self.age
The fields are highly related to the database properties.
3. Step 3: Implement the Controller
class StudentController:
def insertStudent(self, student):
print(student.name, student.age)
Data manipulation: insert, update, or delete.
Data storage: database or file management system.
Page 10