CSC 211: COMPUTER PROGRAMMING I
Iteration/Repition/Loop Structure
Iteration structure is for testing certain condition, if
the condition evaluates as true, action statements will
be executed.
The following statements are decision/conditional
statements in C++ programming language:
while statement
do-while statement
for statement
while loop in C++
While loop is also known as a pre-tested loop.
In general, a while loop allows a part of the code to be executed
multiple times depending upon a given boolean condition. It can be
viewed as a repeating if statement.
The while loop is mostly used in the case where the number of
iterations is not known in advance.
Syntax of while loop in C++ language
The syntax of while loop in c language is given below:
while(testExpression){
//code to be executed
}
How while loop works?
The while loop evaluates the testExpression inside the parentheses ().
If testExpression is true, statements inside the body of while loop are
executed. Then, testExpression is evaluated again.
The process goes on until testExpression is evaluated to false.
If testExpression is false, the loop terminates (ends).
WHILE DO and ENDWHILE
WHILE condition (while condition is true, then do
subordinate statements)
statement 1
WHILE (statement2/condition=true)
DO (statement3)
ENDWHILE
The loop is entered if the expression or condition in the
while statement evaluates to true.
If the condition is FALSE, the loop isn't entered. And, if the
condition is TRUE, the body of the loop is executed
WHILE DO and ENDWHILE
Examples:
Write the pseudo code and the code in C to List the figures
between 1 and 100
Input data
Set figure/count initial value
Output data
Figures between 1 to 100
Processing requirement
Increase figure/count by 1
Test if the figure/count is between 1 and 100
Example 1 contd …
For the first time the algorithm will run like the above.
Step1: start
1
Step2: count = 1
Step3: WHILE (count< 99) 2
DO 3
Print count 4
count=count+1
ENDWHILE
Step4: Print “The End”
Step5: stop
Example 1 contd …
The process will continue this way whenever the value of count
increases and its value is any figure from 2 t0 99.
Step1: start
Step2: count = 1 1 2
Step3: WHILE (count< 99) 3
DO
count= count + 1
4
Print count
ENDWHILE
Step4: print “The End”
Step5: stop
Example 1 contd …
When count increases to 100 the process is as follows:
Step1: start
Step2: count = 1
1 2
Step3: WHILE (count< 99)
DO
count= count + 1
Print count
ENDWHILE
Step4: print “The End”
Step5: stop
Example 1 contd …
A pseudocode can be written such that action statements
will be called. This means that the action statement will be
in another step. For example:
Step1: start
Step2: count = 1
Step3: WHILE (count< 99)
DO Process
ENDWHILE
Step4: print “The End”
Step5: Process
count= count + 1
Print count
Step5: stop
simple program of c++ language while loop where we
are printing the table of 1.
#include<iostream>
int main(){
int i=1;
while(i<=10)
{
cout<<i <<endl;
i++;
}
return 0;
}
Program to print table for the given number using
while loop
#include<iostream>
int main(){
int i=1,number;
cout<<"Enter a number: ";
cin>> number;
while(i<=10)
{
cout<<number << “*” << i << (number*i) <<endl;;
i++;
}
return 0;
}
Sum of natural numbers using while loop
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int n, i, sum = 0;
cout<<"Enter a positive integer: ";
cin>> n;
i = 1;
while (i <= n) {
sum += i;
++i;
}
cout<<"Sum = " << sum);
return 0;
}
Using a Sentinel Value
The user can be allowed to keep entering the loop until
he enters a special value that signals that he’s done.
This special signal value is called a sentinel value.
It is also known as flag or signal value.
Its for indicating the end of data entry.
It can also be used when the user does not know the
number of variables to be entered. This means when
the repetition is indefinite.
The sentinel value must not be a legal value for the
problem at hand. For example, we can’t use 0 (zero) as
the sentinel value for an exam score.
14
Classwork
Write a pseudo code to compute the average grade of
students in a class.
Note: the pseudocode should determine the number
of student in the class.
Input data
Output data
Processing requirement
Example:
Step1: start
Step2: count = 0, Total = 0
Step3: Input grade
Step4: WHILE (grade!=-1)
DO
Print student grade
count= count + 1
Total= Total + student grade
Input student grade
ENDWHILE
Step5: average= Total/count
Step6: print count, Total and average
Step7: stop
compute the average grade of students in a class using
while loop
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int stu_grade, count=0, total = 0;
double average;
cout<<"Enter a student grade: ";
cin>> stu_grade;
while (stu_grade != -1) {
++ count;
total+=stu_grade;
cout<<"Enter a student grade: ";
cin>> stu_grade;
}
average = total/count;
cout<<"Total number of Students = " << count);
cout<<"Total grades of Students = " << total);
cout<<"Average grades of Students = " << average;
return 0;
Classwork
Write a pseudo code and C code to calculate the
average grade of students offering COSC 101 using
while loop.
do while loop in C++
The do while loop is a post tested loop.
Using the do-while loop, we can repeat the execution of several parts of
the statements.
The do-while loop is mainly used in the case where we need to execute
the loop at least once.
The do-while loop is mostly used in menu-driven programs where the
termination condition depends upon the end user.
do while loop syntax
The syntax of the C++ language do-while loop is given below:
do {
//code to be executed
}
while(testExpression);
How do...while loop works?
The body of do...while loop is executed once. Only then, the
testExpression is evaluated.
If testExpression is true, the body of the loop is executed again and
testExpression is evaluated once more.
This process goes on until testExpression becomes false.
If testExpression is false, the loop ends.
DO – WHILE statement
What is the output of this pseudo code?
counter = 1
do
Display counter
counter++
while (counter <= 10)
Code in C++ program
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int counter = 1;
do
{
cout<< counter<<endl;
counter++;
}
while (counter <=10);
return 0;
}
Example
Write a pseudo code and code in C++ that prints out
100 level first semester course.
Input data
Output data
Processing requirement
Example
Step1: start
Step2: INPUT semester
Step3: DO
display 100 level first semester courses
WHILE (semester=first)
Step5: stop
Note: for the first iteration this pseudo code will
display 100 level first semester courses even if the value
for semester in step 2 is second.
Program to add numbers until the user enters zero
// Program to add numbers until the user enters zero
#include <iostream>
int main() {
double number, sum = 0;
// the body of the loop is executed at least once
do {
cout<<"Enter a number: ";
cin>> number);
sum += number;
}
while(number != 0.0);
cout<<"Sum = " << sum);
return 0;
}
compute the average grade of students in a class using do….while loop
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int stu_grade, count=0, total = 0;
double average;
cout<<"Enter a student grade: ";
cin>>stu_grade;
do {
++ count;
total+=stu_grade;
cout<<"Enter a student grade: ";
cin>>stu_grade;
} while (stu_grade != -1) ;
average = total/count;
cout<<"Total number of Students = "<< count);
cout<<"Total grades of Students = " << total);
cout<<"Average grades of Students = " << average);
return 0;
}
Example
Write a pseudo code that prints 100 level results for
students in 100 level.
Input data
Output data
Processing requirement
Example
Step1: start
Step2: total number of student=300
Step3: DO
Enter student matric number
Display result
total number of student= total number of
student-1
UNTIL (total number of student=0)
Step4: stop
** Write the C program for this pseudo code
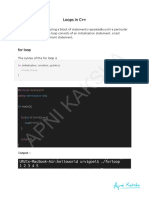
for loop
The for loop in C++ language is used to iterate the statements or a
part of the program several times.
It is frequently used to traverse the data structures like the array and
linked list.
Syntax of for loop in C++
The syntax of for loop in c language is given below:
for (initializationStatement; testExpression; updateStatement)
{
// statements inside the body of loop
}
How for loop works?
The initialization statement is executed only once.
Then, the test expression is evaluated. If the test expression is evaluated to false,
the for loop is terminated.
However, if the test expression is evaluated to true, statements inside the body
of the for loop are executed, and the update expression is updated.
Again the test expression is evaluated.
This process goes on until the test expression is false. When the test expression
is false, the loop terminates.
Program of c language that prints numbers from 1 to 10
using for loop
// Print numbers from 1 to 10
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int i;
for (i = 1; i < 11; ++i) //for (i = 1; i <=10; ++i)
{
cout<< i << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Program to calculate the sum of natural numbers
using for loop
// Program to calculate the sum of first n natural numbers
// Positive integers 1,2,3...n are known as natural numbers
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int num, count, sum = 0;
cout<<"Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%d", &num);
// for loop terminates when num is less than count
for(count = 1; count <= num; ++count)
{
sum += count;
}
printf("Sum = %d", sum);
return 0;
}
Example
Write a pseudocode to print the even numbers from 1 to 10.
Step1: start
Step2: for(i = 0; i <=10; i = i + 2)
Print i
Step3: stop
Program of c language that prints numbers from 1 to 10
using for loop
// Print numbers from 1 to 10
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int i;
for (i = 0; i <=10; i=i+2)
{
cout<< i << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Classwork/ Assignment
How many times does each loop run?
1. for (j = 1; j <= 100; j++)
2. for (j = 100; j >= 1; j--)
3. for (j = 7; j <= 77; j += 7)
4. for (j = 20; j >= 2; j -= 2)
5. for (j = 2; j <= 20; j += 3)
6. for (j = 99; j >= 0; j -= 11)