FUNCTIONS
Functions are the block of code which is used to perform a particular task.
Functions
User defined Predefined/inbuilt
functions functions
Single row Multi row
functions functions
1. SINGLE ROW FUNCTIONS
Single row functions executes row by row.
It takes an input, starts the execution and gives you an output and then it
goes for next input.
If we pass ‘n’ number of inputs to a single row functions, it will return
‘n’ number of outputs.
1 1
2 2
‘n’ 3 3 ‘n’
number . . . number of
of inputs . . . outputs
n n
SRF ()
2. MULTI ROW FUNCTIONS
1. Multi row functions are also known as GROUP Functions/ Aggregate
functions.
2. It takes all the inputs at once aggregates them and starts the executions, gives
you only one output.
3. If you pass ‘n’ number of inputs to the multi row functions, it will return only
one output.
2
‘n’
3
number Single
1
of inputs .
output
.
n
MRF ()
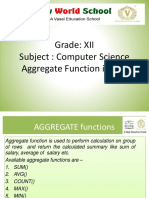
LIST OF MULTI ROW FUNCTIONS
1. MIN ()
2. MAX ()
3. SUM ()
4. AVG ()
5. COUNT ()
Rules of using MRF ()
Multi row functions can accept only a single argument that can be
COL_NAME or an expression.
MAX () and MIN () can accept all the datatype columns.
SUM () and AVG () can accept only numbered datatype columns.
Multi row functions will ignore NULL values.
We cannot use multi row functions in WHERE clause.
We cannot use any columns along with multi row functions in SELECT clause.
COUNT () is the only multi row function which accepts * as an argument.
Examples:
1.WAQTD no of employees, maximum salary, minimum commission, average
salary and total commission of all the employees.
SELECT COUNT (*), MAX(SAL), MIN(COMM), AVG(SAL), SUM(COMM)
FROM EMP;
2.WAQTD no of employees getting salary less than 2000 in dept no 10.
SELECT COUNT (*)
FROM EMP
WHERE SAL<2000 AND DEPTNO=10;
3.WAQTD total salary needed to pay employees working as CLERK.
SELECT SUM(SAL)
FROM EMP
WHERE JOB=’CLERK’;
4.WAQTD average salary needed to pay all the employees.
SELECT AVG(SAL)
FROM EMP;
5.WAQTD no of employees having ‘A’ as their first character.
SELECT COUNT (*)
FROM EMP
WHERE ENAME LIKE ‘A%’;
6.WAQTD no of employees working as clerk or manager.
SELECT COUNT (*)
FROM EMP
WHERE JOB IN (‘CLERK’,’MANAGER’);
7.WAQTD total salary needed to pay employees hired in February.
SELECT SUM(SAL)
FROM EMP
WHERE HIREDATE LIKE ‘%FEB%’;
8.WAQTD no of employees reporting to 7839.
SELECT COUNT (*)
FROM EMP
WHERE MGR IN 7839.
9.WAQTD no of employees getting commission in dept no 30.
SELECT COUNT (*)
FROM EMP
WHERE COMM IS NOT NULL AND DEPTNO=30;
10.WAQTD no of employees having character A in their names.
SELECT COUNT (*)
FROM EMP
WHERE ENAME LIKE ‘%A%’;
GROUP BY CLAUSE
Syntax:
SELECT GROUP FUNCTION/GROUP BY EXPRESSION
FROM EMP
WHERE <filter condition>
GROUP BY COLUMN_NAME/EXPRESSION;
Order of execution
1.FROM
2.WHERE CLAUSE – row by row
3.GROUP BY CLAUSE – row by row
4.SELECT CLAUSE – group by group
1.GROUP BY clause is used to group the records.
2.GROUP BY clause executes row by row.
3.After the execution of GROUP BY clause it will create groups.
4.Any clause which executes after the execution of GROUP BY clause will be
executed group by group.
5.We can use GROUP BY expression along with the multi row function in SELECT
clause.
GROUP BY EXPRESSION
Any column name or expression which is written in inside GROUP BY clause is
known GROUP BY EXPRESSION.
Example
1.WAQTD maximum and minimum salary of the employees where the employees
should not be earning rupees 4000 in each dept.
SELECT MAX(SAL), MIN(SAL)
FROM EMP
WHERE SAL NOT IN 4000
GROUP BY DEPTNO;
2.WAQTD no of employees and job of all the employees present in each job.
SELECT COUNT (*), JOB
FROM EMP
GROUP BY JOB;
Questions on GROUP BY clause
1.WAQTD no of employees working in each dept except ‘PRESIDENT’.
2.WAQTD total salary needed to pay all the employees in each dept.
3.WAQTD no of employees working as manager in each dept.
4.WAQTD average salary needed to pay all the employees in each dept excluding the
employees of dept no 20.
5.WAQTD no of employees having char A in their names in each job.
6.WAQTD no of employees and average salary needed to pay the employees whose
salary is greater than 2000 in each dept.
7.WAQTD no of employees and total salary given to all the salesman in each dept.
8.WAQTD no of employees with their maximum salary in each job.
9.WAQTD maximum salaries given to all employee working in each dept.
10.WAQTD number of times the salary are present in employee table.