0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views11 pagesGetting Start With Pandas
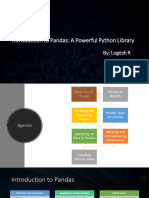
The document provides an introduction to Pandas, a data manipulation library in Python, detailing its primary data structures: Series and DataFrame. It covers creating Series and DataFrames, data manipulation techniques such as filtering, sorting, and grouping, as well as handling missing data, merging DataFrames, and performing descriptive statistics. Additionally, it includes examples of reading from and writing to various file formats and string manipulation methods.
Uploaded by
abhinav.mishraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views11 pagesGetting Start With Pandas
The document provides an introduction to Pandas, a data manipulation library in Python, detailing its primary data structures: Series and DataFrame. It covers creating Series and DataFrames, data manipulation techniques such as filtering, sorting, and grouping, as well as handling missing data, merging DataFrames, and performing descriptive statistics. Additionally, it includes examples of reading from and writing to various file formats and string manipulation methods.
Uploaded by
abhinav.mishraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11