Business Intelligence
Data Warehousing
Part I
Objectives
At the end of this lecture, you should be able to:
• Understand the basic definitions and concepts of data
warehouses
• Understand how a data warehouse differs from a database
• Describe the characteristics of data warehouse
• Describe data warehouse process overview
• Describe the different types of data warehouse architectures
Data Warehouse
• A physical repository where relational data are specially
organized to provide enterprise-wide, cleansed data in a
standardized format
• “The data warehouse is a collection of integrated, subject-
oriented databases design to support DSS functions, where
each unit of data is non-volatile and relevant to some moment
in time”
• A data warehouse is a repository of an organization's
electronically stored data, designed to facilitate reporting and
analysis . (Wikipedia)
• In your own words?
Characteristics of
data warehousing
Main
• Subject oriented - Data organized by detailed subject,
containing only information relevant for decision support,
unlike operational database which are product oriented
• Integrated – must place data from different sources into a
consistent format, to do so they must deal with naming
conflict and discrepancies
• Time variant (time series) - maintains historical data. Data
for analysis from multiple sources contain multiple time
points
• Nonvolatile - after data are entered into a data warehouse,
users cannot change or update the data.
Characteristics of
data warehousing (cont..)
Additional
• Relational/multidimensional
• Client/server
• Real-time
• Include metadata
How is a data warehouse different
from a database?
• Technically a data warehouse is a database, with certain
characteristics to facilitate its role in decision support.
• However, it is an “integrated, time-variant, nonvolatile,
subject-oriented repository of detail and summary data used
for decision support and business analytics within an organi-
zation.” - These characteristics, are not necessarily true of
databases in general.
• As a practical matter most databases are highly normalized, in
part to avoid update anomalies.
• Data warehouses are often denormalized for performance
reasons. This is acceptable because their content is never
updated, just added to. (Historical data are static)
Data Warehousing - Concept
Data Mart
– Smaller and focuses on a particular subject or department.
– It is a subset of data warehouse/departmental data
warehouse
– A data mart is a smaller DW designed around one problem,
organizational function, topic, or other focus area.
Can be Dependent data mart
– A subset that is created directly from a data warehouse
– Ensures that the end user is viewing the same version of
the data that are accessed by all other data warehouse
users
Or Independent data mart
– A small data warehouse designed for a strategic business
unit or a department
Data Warehousing - Concept
• Operational Data Stores (ODS)
– It is a type of database often used as an interim area for a
data warehouse, especially for customer information files.
– Use for short term decisions rather than medium and long
term
– Similar to short term memory, stores only recent
information
Data Warehousing - Concept
• Oper Marts
An operational data mart. An oper mart is a small-scale data
mart typically used by a single department or functional area in
an organization
Data Warehousing - Concept
• Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW)
– A large scale data warehouse used across the enterprise
for decision support
– Used to provide data for many types of DSS, including
CRM, supply chain management, BPM, KMS etc
• Metadata
– Data about data. In a data warehouse, metadata describe
the contents of a data warehouse and the manner of its use
Data Warehousing Process
Overview how is works???
• Organizations continuously collect data, information, and
knowledge at an increasingly accelerated rate and store them in
computerized systems
• The number of users needing to access the information
continues to increase as a result of improved reliability and
availability of network access, especially the Internet
• Creating of data warehouse involves the following:
– Data are imported from various internal and external resources
– Cleansed and organized to suit the organization’s needs.
– Data marts can be loaded for specific department/area
(alternatively data marts are created first and later integrated into EDW)
Data Warehousing
Process Overview
The data warehousing process consists of the following steps:
1. Data are imported from various internal and external sources
2. Data are cleansed and organized consistently with the organization’s
needs
3a. Data are loaded into the enterprise data warehouse (EDW)
4a. If desired, data marts are created as subsets of the EDW
—OR—
3b.Data are loaded into data marts
4b.The data marts are consolidated into the EDW
5. Analyses are performed as needed
Data Warehousing - Process
Overview
The major components of a data warehousing process
• Data sources. Data are sourced from operational systems and possibly from
external data sources.
• Data extraction. Data are extracted using custom-written or commercial
software called ETL.
• Data loading. Data are loaded into a staging area, where they are
transformed and cleansed. The data are then ready to load into the data
warehouse.
• Comprehensive database. This is the EDW that supports decision analysis by
providing relevant summarized and detailed information.
• Metadata. Metadata are maintained for access by IT personnel and users.
Metadata include rules for organizing data summaries that are easy to index
and search.
• Middleware tools. Middleware tools enable access to the data warehouse
from a variety of front-end applications.
Data Warehousing - Process Overview
Data Warehousing Architectures
• There are several basic architectures for data warehousing
• To distinguished the architectures data warehouse is divided
into three (3) parts:
• The data warehouse itself
• Data acquisition (back-end) software, which extracts data
from legacy systems and external sources, consolidates and
loads into the data warehouse
• Client (front-end) software, which allows users access and
analyze data from the warehouse
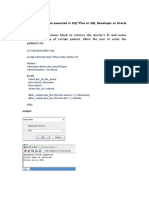
1) Three-tier DW architecture
• 1st tier : operational systems contain data and software for
data acquisition
• 2nd tier : the data warehouse
• 3rd tier : DSS/BI/BA engines
• Data from data warehouse are processed and deposited in
multidimensional database and organized for easy analysis
and presentation
• Advantage: its separation of the functions of the data
warehouse, which eliminates resource constraints and makes
it easy to create data marts
Data Warehousing Architectures
Tier 1: Tier 2: Tier 3:
Client workstation Application server Database server
2) Two-tier DW architecture
• 1st tier : operational systems contain data and software for
data acquisition (i.e the server)
• 2nd tier : DSS/BI/BA engines and the data warehouse
• DSS engines run on the same hardware platform as the data
warehouse, hence more economical
• Advantage: economical
• Disadvantage: performance problem for large data warehouse
with data intensive applications for decision support
Data Warehousing Architectures
Tier 1: Tier 2:
Client workstation Application & database server
3) Web-based DW architecture
• Data warehousing and the Internet are two key technologies
that offer important solutions for managing corporate data
• The integration of these two produced WEB-BASED data
warehousing
• On the client side, the user needs an Internet connection and
a Web browser using GUI
• The Internet/Intranet/Extranet is the communication medium
between client and servers
• On the server side, a Web server is used to manage the flow
of info between client and server
• Advantage: ease of access, platform independence, lower cost
• Disadvantage: server capacity must be well planned carefully,
page loading speed
Data Warehousing Architectures
Data Warehousing Architectures
Data Warehousing Architectures
Data Warehousing Architectures
Data Warehousing Architectures
Data Warehousing Architectures
Data Warehousing Architectures
Data Warehousing Architectures
Data Warehousing Architectures
• Issues to consider when deciding which architecture to use:
– Which database management system (DBMS) should be
used? Most are built using RDBMS (Oracle, SQL server, DB2
are commonly used) Each supports client/server and Web-
based architecture
– Will parallel processing and/or partitioning be used? Parallel
processing enables multiple CPUs to process data warehouse
requests simultaneously and provide scalability. Partitioning
will split into smaller tables for access efficiency
– Will data migration tools be used to load the data
warehouse?
– What tools will be used to support data retrieval and
analysis?
Data Warehousing Architectures
Ten (10) factors that potentially affect the architecture
selection decision:
1. Information 1. 5. Constraints on resources
interdependence between 2. 6. Strategic view of the data
organizational units warehouse prior to
2. Upper management’s implementation
information needs 3. 7. Compatibility with existing
3. Urgency of need for a data systems
warehouse 4. 8. Perceived ability of the in-
4. Nature of end-user tasks house IT staff
5. 9. Technical issues
6. 10. Social/political factors
Now ask if ..
You are able to:
• Understand the basic definitions and concepts of data
warehouses
• Understand how a data warehouse differs from a database
• Describe the characteristics of data warehouse
• Describe data warehouse process overview
• Describe the different types of data warehouse architectures