Unit 5: Interacting with
Database
CO:Develop a program using database
(Marks :12)
ODBC
• ODBC stands for Open Database
Connectivity
• A standard or open application
programming interface (API) for accessing a
database.
• ODBC provides a C interface for database
access on Windows environment.
2
JDBC
• JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity.
• It is a standard Java API for connecting
programs written in Java to the data in
relational databases.
• JDBC works with Java on a variety of
platforms, such as Windows, Mac OS, and
the various versions of UNIX.
3
JDBC Driver
• JDBC Driver is a software component that
enables java application to interact with the
database. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
Native-API driver (partially java driver)
JDBC-Net pure Java/ Network-Protocol driver (fully
java driver)
Pure Java Driver / Thin driver / Database-Protocol
driver(fully java driver)
4
JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
• The JDBC type 1 driver, also known as the JDBC-ODBC
bridge driver.
• The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver uses ODBC driver to connect
to the database. The JDBC-ODBC bridge driver converts
JDBC method calls into the ODBC function calls.
5
Advantages:
• easy to use.
• can be easily connected to any database.
Disadvantages:
• Performance degraded because JDBC method
call is converted into the ODBC function calls.
• The ODBC driver needs to be installed on the
client machine.
6
Native API driver
• The JDBC type 2 driver, also known as the Native-API driver
• The Native API driver uses the client-side libraries of the
database. The driver converts JDBC method calls into native
calls of the database API. It is not written entirely in java.
7
Advantage:
• performance upgraded than JDBC-ODBC
bridge driver.
Disadvantage:
• The Native driver needs to be installed on the
each client machine.
• The Vendor client library needs to be installed
on client machine.
8
JDBC-Net pure Java Driver
• The JDBC type 3 driver, also known as the Pure Java driver for
database middleware. It is a database driver implementation
which makes use of a middle tier between the calling program and
the database.
• The middle-tier (application server) converts JDBC calls directly or
indirectly into a vendor-specific database protocol. It is fully
written in java.
9
Advantage:
• No client side library is required because of
application server that can perform many tasks
like auditing, load balancing, logging etc.
Disadvantages:
• Network support is required on client machine.
• Requires database-specific coding to be done in
the middle tier.
• Maintenance of Network Protocol driver
becomes costly because it requires database-
specific coding to be done in the middle tier.
10
Thin driver
• The JDBC type 4 driver, also known as the Direct to Database Pure
Java Driver, is a database driver implementation that
converts JDBC calls directly into a vendor- specific database protocol.
• That is why it is known as thin driver. It is fully written in Java
language.
11
Advantage:
• Better performance than all other drivers.
• No software is required at client side or server
side.
Disadvantage:
• Drivers depend on the Database.
12
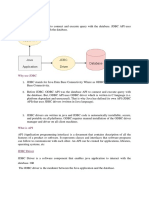
JDBC two tier model
• In a two-tier model, a Java application communicates
directly with the database, via the JDBC driver.
13
JDBC three tier model
• In a three-tier model, a Java application communicates
with a middle tier component that functions as an
application server. The application server talks to a
given database using JDBC.
14
Common JDBC Components
• The JDBC API provides the following interfaces
and classes −
• DriverManager Class
• Driver Interface
• Connection Interface
• Statement Interface
• ResultSet Interface
15
Common JDBC Components
DriverManager Class
• The DriverManager class acts as an interface
between user and drivers.
• It keeps track of the drivers that are available and
handles establishing a connection between a
database and the appropriate driver.
• The DriverManager class maintains a list of Driver
classes that have registered themselves by calling
the method DriverManager.registerDriver().
16
Commonly used methods of DriverManager class
Method Description
public static void registerDriver(Driver driver); is used to register the given driver
with DriverManager.
is used to deregister the given
public static void deregisterDriver(Driver driver); driver (drop the driver from the
list) with DriverManager.
public static Connection getConnection(String url); is used to establish the connection
with the specified url.
public static Connection getConnection(String is used to establish the connection
url,String userName,String password); with the specified url, username
and password.
17
Common JDBC Components (cont’d..)
• Driver Interface
This interface handles the communications
with the database server. You will very rarely
interact directly with Driver objects. Instead,
you use DriverManager objects, which
manages objects of this type. It also abstracts
the details associated with working with
Driver objects.
18
Common JDBC Components (cont’d..)
• Connection Interface
A Connection is the session between java
application and database. The Connection
interface is a factory of Statement,
PreparedStatement, and DatabaseMetaData.
The Connection interface provide many
methods for transaction management like
commit(),rollback() etc.
19
Commonly used methods of Connection interface
Method Description
public Statement createStatement(); creates a statement object that can be
used to execute SQL queries.
public void setAutoCommit(boolean status); It is used to set the commit status. By
default it is true.
public void commit(); It saves the changes made since the
previous commit/rollback permanent.
public void rollback(); Drops all changes made since the
previous commit/rollback.
closes the connection and Releases a
public void close(); JDBC resources immediately.
20
Common JDBC Components (cont’d..)
• Statement Interface
The Statement interface provides methods to
execute queries with the database. It provides
factory method to get the object of ResultSet.
21
Commonly used methods of Statement interface
Method Description
public ResultSet executeQuery(String sql); used to execute SELECT query. It returns
the object of ResultSet.
public int executeUpdate(String sql); used to execute specified query, it may be
create, drop, insert, update, delete etc.
public boolean execute(String sql); used to execute queries that may return
multiple results.
public int[] executeBatch(); used to execute batch of commands.
22
Prepared Statement
• The PreparedStatement interface is a subinterface of
Statement. It is used to execute parameterized query.
• Example:
String sql="insert into emp values(?,?,?)";
Here, we are passing parameter (?) for the values. Its value will
be set by calling the setter methods of PreparedStatement.
• to get the instance of PreparedStatement the
prepareStatement() method of Connection interface is used
to return the object of PreparedStatement.
• Syntax:
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String query)throws SQLExce
ption{}
23
Methods of PreparedStatement interface
Method Description
public void setInt(int paramIndex, int sets the integer value to the given
value) parameter index.
public void setString(int paramIndex, sets the String value to the given
String value) parameter index.
public void setFloat(int paramIndex, sets the float value to the given
float value) parameter index.
public void setDouble(int paramIndex, sets the double value to the given
double value) parameter index.
public int executeUpdate() executes the query. It is used for
create, drop, insert, update, delete etc.
public ResultSet executeQuery() executes the select query. It returns an
instance of ResultSet.
24
Common JDBC Components (cont’d..)
• ResultSet Interface
The object of ResultSet maintains a cursor
pointing to a particular row of data. Initially,
cursor points to before the first row.
25
Commonly used methods of ResultSet interface
Method Description
public boolean next(); is used to move the cursor to the one row next from
the current position.
public boolean previous(); is used to move the cursor to the one row previous
from the current position.
public boolean first(); is used to move the cursor to the first row in result set
object.
public boolean last(); is used to move the cursor to the last row in result set
object.
public boolean absolute(int row); is used to move the cursor to the specified row number
in the ResultSet object.
public int getInt(int columnIndex); is used to return the data of specified column index of
the current row as int.
public int getInt(String columnName); is used to return the data of specified column name of
the current row as int.
public String getString(int columnIndex); is used to return the data of specified column index of
the current row as String.
public String getString(String is used to return the data of specified column name of
columnName); the current row as String.
26
Connecting to Database
• There are 5 steps to connect any java
application with the database in java using
JDBC. They are as follows:
1. Register the driver class
2. Creating connection
3. Creating statement
4. Executing queries
5. Closing connection
27
1.Register the driver class
• The Class.forName() method is used to register the
driver class. This method is used to dynamically load
the driver class.
• Syntax of forName() method
public static void forName(String className)throws ClassNotFoundException
• Example to register with JDBC-ODBC Driver
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
28
2. Creating connection
• The DriverManager .getConnection() method is used
to establish connection with the database.
• Syntax of getConnection() method
public static Connection getConnection(String url)throws SQLException
public static Connection getConnection(String url,String name,String password)
throws SQLException
• Example establish connection with Oracle Driver
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection
("jdbc:odbc:DemoDB","username","password");
29
3. Creating statement
• The createStatement() method of Connection
interface is used to create statement. The
object of statement is responsible to execute
queries with the database.
• Syntax of createStatement() method
public Statement createStatement()throws SQLException
• Example to create the statement object
Statement stmt=con.createStatement();
30
4. Executing queries
• The executeQuery() method of Statement interface is used
to execute queries to the database. This method returns
the object of ResultSet that can be used to get all the
records of a table.
• Syntax of executeQuery() method
public ResultSet executeQuery(String sql)throws SQLException
• Example to execute query
ResultSet rs=stmt.executeQuery("select * from emp");
while(rs.next())
{
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)+" "+rs.getString(2));
}
31
5. Closing connection
• By closing connection object statement and
ResultSet will be closed automatically. The close()
method of Connection interface is used to close
the connection.
• Syntax of close() method
public void close()throws SQLException
• Example to close connection
con.close();
32
Example to Connect Java Application
with mysql database
33
import java.sql.*;
class MysqlCon{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try
{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sun","root",“123");
//here sun is database name, root is username and password
Statement stmt=con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs=stmt.executeQuery("select * from emp");
while(rs.next())
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)+" "+rs.getString(2)+" "+rs.getString(3));
con.close();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
} //C:\Program Files\Java\jre1.6.0\lib\ext
34
Prepared Statement Example
import java.sql.*;
class InsertPrepared{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sun","root",“123");
PreparedStatement stmt=con.prepareStatement("insert into Emp values(?,?)");
stmt.setInt(1,101);//1 specifies the first parameter in the query
stmt.setString(2,"Ratan"); //2 specifies the second parameter in the query
int i=stmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(i+" records inserted");
con.close();
}catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e);}
}
}
35