Microcontroller Sheet
1) What is a microcontroller?
Answer: A microcontroller is an Integrated Chip (IC) that includes onboard memory, programmable
peripheral Inputs and Outputs, Timers, Serial Communication, and many more features that I will
cover below.
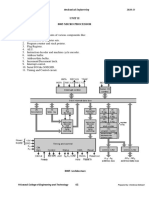
2) Draw a diagram to show difference between microcontroller and microprocessor?
Answer:
3) Difference between Microprocessor and Microcontroller?
Answer:
4) List example of Embedded Systems that use a Microcontroller.
Answer:
Electronic Development boards (Ardunio)
Consumer Electronics (mobile phones, Laptops, gaming systems)
Household appliances (washing machines, toaster, microwaves)
Medical
Aviation
5) What is Harvard architecture?
Answer:
Harvard Architecture is the digital computer architecture whose design is based on the concept
where there are:
a. Separate storage and separate buses (signal path) for instruction and data.
It was basically developed to overcome the bottleneck of Von Neumann Architecture.
6) Compare between Harvard and Von Neumann architectures?
Answer:
7) Compare between RISC and CISC?
Answer:
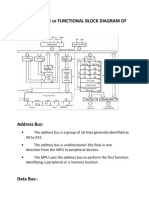
8) Draw simplified overview of AVR Microcontroller?
Answer:
9) Give three examples of the AVR special purpose registers?
Answer:
a) Program counter
b) Stack Pointer
c) Status Register:
It is the flag register in the AVR micro-controller.
It is a 8 – bit register. Only 6 of these 8 bits are called conditional flags. They are C, Z, N, V,
S, H.
The value of these bits indicates some conditions that result after the execution of an
instruction.
C – Carry Flag :
This flag is set whenever there is a carryout from the D7 bit.
This flag bit is affected after an 8-bit addition or subtraction.
Z – Zero Flag :
The zero flag reflects the result of an arithmetic or logic operation.
If the result is zero, then Z = 1. Therefore, Z = 0 if the result is not zero.
N – Negative Flag :
Binary representation of signed numbers uses D7 as the sign bit.
The negative flag reflects the result of an arithmetic operation. If the D7
bit of the result is zero.
Then N = 0 and the result is positive. If the D7 bit is one, then N = 1 and
the result is negative.
V – Overflow Flag :
This flag is set whenever the result of a signed number operation is too
large.
S – Sign Flag :
This flag is the result of Exclusive-ORing of N and V flags.
H – Half Carry Flag :
If there is a carry from D3 to D4 during an ADD or SUB operation, this
bit is set; otherwise, it is cleared.
10) What are the two kinds of memory space in AVR?
Answer:
Code memory space: our program is stored in code memory space.
Data memory space: stores data.
The data memory is composed of three parts:
GPRs (general purpose registers).
I/O memory.
Internal data SRAM.
11) What are the general purpose registers?
Answer: The GPRs use 32 bytes of data memory space.
They always take the address location $00—$lF in the data memory space, regardless of the
AVR chip number.
The GPRs do not have any specific function and are used for storing general data.
12) What are the I/O memory registers?
Answer:
The I/O memory is dedicated to specific functions such as status register, timers, serial
communication, I/O ports, ADC, and so on.
I/O memory can be accessed as the Data Space locations those of the Register File, $20 -$5F.
13) What is the difference between SRAM and EEPROM?
Answer:
The AVR has an EEPROM memory that is used for storing data.
EEPROM does not lose its data when power is off, whereas SRAM does.
EEPROM is used for storing data that should rarely be changed and should not be lost when the
power is off (e.g., options and settings).
SRAM is used for storing data and parameters that are changed frequently.