10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
QuickRef.ME Stars 6.3k
JavaScript
A JavaScript cheat sheet with the most important concepts, functions, methods, and more. A
complete quick reference for beginners.
# Getting Started
Introduction
JavaScript is a lightweight, interpreted programming language.
JSON cheatsheet (quickref.me)
Regex in JavaScript (quickref.me)
Console
// => Hello world!
console.log('Hello world!');
// => Hello QuickRef.ME
console.warn('hello %s', 'QuickRef.ME');
// Prints error message to stderr
console.error(new Error('Oops!'));
Numbers
let amount = 6;
let price = 4.99;
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 1/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
Variables
let x = null;
let name = "Tammy";
const found = false;
// => Tammy, false, null
console.log(name, found, x);
var a;
console.log(a); // => undefined
Strings
let single = 'Wheres my bandit hat?';
let double = "Wheres my bandit hat?";
// => 21
console.log(single.length);
Arithmetic Operators
5 + 5 = 10 // Addition
10 - 5 = 5 // Subtraction
5 * 10 = 50 // Multiplication
10 / 5 = 2 // Division
10 % 5 = 0 // Modulo
Comments
// This line will denote a comment
/*
The below configuration must be
changed before deployment.
*/
Assignment Operators
let number = 100;
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 2/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
// Both statements will add 10
number = number + 10;
number += 10;
console.log(number);
// => 120
String Interpolation
let age = 7;
// String concatenation
'Tommy is ' + age + ' years old.';
// String interpolation
`Tommy is ${age} years old.`;
let Keyword
let count;
console.log(count); // => undefined
count = 10;
console.log(count); // => 10
const Keyword
const numberOfColumns = 4;
// TypeError: Assignment to constant...
numberOfColumns = 8;
# JavaScript Conditionals
if Statement
const isMailSent = true;
if (isMailSent) {
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 3/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
console.log('Mail sent to recipient');
Ternary Operator
var x=1;
// => true
result = (x == 1) ? true : false;
Operators
true || false; // true
10 > 5 || 10 > 20; // true
false || false; // false
10 > 100 || 10 > 20; // false
Logical Operator &&
true && true; // true
1 > 2 && 2 > 1; // false
true && false; // false
4 === 4 && 3 > 1; // true
Comparison Operators
1 > 3 // false
3 > 1 // true
250 >= 250 // true
1 === 1 // true
1 === 2 // false
1 === '1' // false
Logical Operator !
let lateToWork = true;
let oppositeValue = !lateToWork;
// => false
console.log(oppositeValue);
Nullish coalescing operator ??
null ?? 'I win'; // 'I win'
undefined ?? 'Me too'; // 'Me too'
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 4/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
false ?? 'I lose' // false
0 ?? 'I lose again' // 0
'' ?? 'Damn it' // ''
else if
const size = 10;
if (size > 100) {
console.log('Big');
} else if (size > 20) {
console.log('Medium');
} else if (size > 4) {
console.log('Small');
} else {
console.log('Tiny');
}
// Print: Small
switch Statement
const food = 'salad';
switch (food) {
case 'oyster':
console.log('The taste of the sea');
break;
case 'pizza':
console.log('A delicious pie');
break;
default:
console.log('Enjoy your meal');
}
== vs ===
0 == false // true
0 === false // false, different type
1 == "1" // true, automatic type conversion
1 === "1" // false, different type
null == undefined // true
null === undefined // false
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 5/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
'0' == false // true
'0' === false // false
# JavaScript Functions
Functions
// Defining the function:
function sum(num1, num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
// Calling the function:
sum(3, 6); // 9
Anonymous Functions
// Named function
function rocketToMars() {
return 'BOOM!';
}
// Anonymous function
const rocketToMars = function() {
return 'BOOM!';
}
Arrow Functions (ES6)
With two arguments
const sum = (param1, param2) => {
return param1 + param2;
};
console.log(sum(2,5)); // => 7
With no arguments
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 6/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
const printHello = () => {
console.log('hello');
};
printHello(); // => hello
With a single argument
const checkWeight = weight => {
console.log(`Weight : ${weight}`);
};
checkWeight(25); // => Weight : 25
Concise arrow functions
const multiply = (a, b) => a * b;
// => 60
console.log(multiply(2, 30));
return Keyword
// With return
function sum(num1, num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
// The function doesn't output the sum
function sum(num1, num2) {
num1 + num2;
}
Calling Functions
// Defining the function
function sum(num1, num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
// Calling the function
sum(2, 4); // 6
Function Expressions
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 7/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
const dog = function() {
Function Parameters
// The parameter is name
function sayHello(name) {
return `Hello, ${name}!`;
}
Function Declaration
function add(num1, num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
# JavaScript Scope
Scope
function myFunction() {
var pizzaName = "Margarita";
// Code here can use pizzaName
// Code here can't use pizzaName
Block Scoped Variables
const isLoggedIn = true;
if (isLoggedIn == true) {
const statusMessage = 'Logged in.';
}
// Uncaught ReferenceError...
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 8/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
console.log(statusMessage);
Global Variables
// Variable declared globally
const color = 'blue';
function printColor() {
console.log(color);
}
printColor(); // => blue
let vs var
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// This is the Max Scope for 'let'
// i accessible ✔️
}
// i not accessible ❌
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// i accessible ✔️
}
// i accessible ✔️
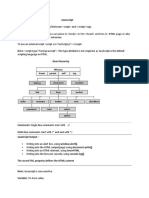
var is scoped to the nearest function block, and let is scoped to the nearest enclosing block.
Loops with closures
// Prints 3 thrice, not what we meant.
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
setTimeout(_ => console.log(i), 10);
}
// Prints 0, 1 and 2, as expected.
for (let j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
setTimeout(_ => console.log(j), 10);
}
The variable has its own copy using let, and the variable has shared copy using var.
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 9/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
# JavaScript Arrays
Arrays
const fruits = ["apple", "orange", "banana"];
// Different data types
const data = [1, 'chicken', false];
Property .length
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
numbers.length // 4
Index
// Accessing an array element
const myArray = [100, 200, 300];
console.log(myArray[0]); // 100
console.log(myArray[1]); // 200
Mutable chart
add remove start end
push ✔ ✔
pop ✔ ✔
unshift ✔ ✔
shift ✔ ✔
Method .push()
// Adding a single element:
const cart = ['apple', 'orange'];
cart.push('pear');
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 10/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
// Adding multiple elements:
const numbers = [1, 2];
numbers.push(3, 4, 5);
Add items to the end and returns the new array length.
Method .pop()
const fruits = ["apple", "orange", "banana"];
const fruit = fruits.pop(); // 'banana'
console.log(fruits); // ["apple", "orange"]
Remove an item from the end and returns the removed item.
Method .shift()
let cats = ['Bob', 'Willy', 'Mini'];
cats.shift(); // ['Willy', 'Mini']
Remove an item from the beginning and returns the removed item.
Method .unshift()
let cats = ['Bob'];
// => ['Willy', 'Bob']
cats.unshift('Willy');
// => ['Puff', 'George', 'Willy', 'Bob']
cats.unshift('Puff', 'George');
Add items to the beginning and returns the new array length.
Method .concat()
const numbers = [3, 2, 1]
const newFirstNumber = 4
// => [ 4, 3, 2, 1 ]
[newFirstNumber].concat(numbers)
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 11/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
// => [ 3, 2, 1, 4 ]
numbers.concat(newFirstNumber)
if you want to avoid mutating your original array, you can use concat.
# JavaScript Loops
While Loop
while (condition) {
// code block to be executed
}
let i = 0;
while (i < 5) {
console.log(i);
i++;
}
Reverse Loop
const fruits = ["apple", "orange", "banana"];
for (let i = fruits.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
console.log(`${i}. ${fruits[i]}`);
}
// => 2. banana
// => 1. orange
// => 0. apple
Do…While Statement
x = 0
i = 0
do {
x = x + i;
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 12/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
console.log(x)
i++;
} while (i < 5);
// => 0 1 3 6 10
For Loop
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i += 1) {
console.log(i);
};
// => 0, 1, 2, 3
Looping Through Arrays
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++){
console.log(array[i]);
}
// => Every item in the array
Break
for (let i = 0; i < 99; i += 1) {
if (i > 5) {
break;
}
console.log(i)
}
// => 0 1 2 3 4 5
Continue
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i === 3) { continue; }
text += "The number is " + i + "<br>";
}
Nested
for (let i = 0; i < 2; i += 1) {
for (let j = 0; j < 3; j += 1) {
console.log(`${i}-${j}`);
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 13/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
}
}
for...in loop
const fruits = ["apple", "orange", "banana"];
for (let index in fruits) {
console.log(index);
}
// => 0
// => 1
// => 2
for...of loop
const fruits = ["apple", "orange", "banana"];
for (let fruit of fruits) {
console.log(fruit);
}
// => apple
// => orange
// => banana
# JavaScript Iterators
Functions Assigned to Variables
let plusFive = (number) => {
return number + 5;
};
// f is assigned the value of plusFive
let f = plusFive;
plusFive(3); // 8
// Since f has a function value, it can be invoked.
f(9); // 14
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 14/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
Callback Functions
const isEven = (n) => {
return n % 2 == 0;
}
let printMsg = (evenFunc, num) => {
const isNumEven = evenFunc(num);
console.log(`${num} is an even number: ${isNumEven}.`)
}
// Pass in isEven as the callback function
printMsg(isEven, 4);
// => The number 4 is an even number: True.
Array Method .reduce()
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const sum = numbers.reduce((accumulator, curVal) => {
return accumulator + curVal;
});
console.log(sum); // 10
Array Method .map()
const members = ["Taylor", "Donald", "Don", "Natasha", "Bobby"];
const announcements = members.map((member) => {
return member + " joined the contest.";
});
console.log(announcements);
Array Method .forEach()
const numbers = [28, 77, 45, 99, 27];
numbers.forEach(number => {
console.log(number);
});
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 15/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
Array Method .filter()
const randomNumbers = [4, 11, 42, 14, 39];
const filteredArray = randomNumbers.filter(n => {
return n > 5;
});
# JavaScript Objects
Accessing Properties
const apple = {
color: 'Green',
price: { bulk: '$3/kg', smallQty: '$4/kg' }
};
console.log(apple.color); // => Green
console.log(apple.price.bulk); // => $3/kg
Naming Properties
// Example of invalid key names
const trainSchedule = {
// Invalid because of the space between words.
platform num: 10,
// Expressions cannot be keys.
40 - 10 + 2: 30,
// A + sign is invalid unless it is enclosed in quotations.
+compartment: 'C'
}
Non-existent properties
const classElection = {
date: 'January 12'
};
console.log(classElection.place); // undefined
Mutable
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 16/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
const student = {
name: 'Sheldon',
score: 100,
grade: 'A',
}
console.log(student)
// { name: 'Sheldon', score: 100, grade: 'A' }
delete student.score
student.grade = 'F'
console.log(student)
// { name: 'Sheldon', grade: 'F' }
student = {}
// TypeError: Assignment to constant variable.
Assignment shorthand syntax
const person = {
name: 'Tom',
age: '22',
};
const {name, age} = person;
console.log(name); // 'Tom'
console.log(age); // '22'
Delete operator
const person = {
firstName: "Matilda",
age: 27,
hobby: "knitting",
goal: "learning JavaScript"
};
delete person.hobby; // or delete person[hobby];
console.log(person);
/*
{
firstName: "Matilda"
age: 27
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 17/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
goal: "learning JavaScript"
}
*/
Objects as arguments
const origNum = 8;
const origObj = {color: 'blue'};
const changeItUp = (num, obj) => {
num = 7;
obj.color = 'red';
};
changeItUp(origNum, origObj);
// Will output 8 since integers are passed by value.
console.log(origNum);
// Will output 'red' since objects are passed
// by reference and are therefore mutable.
console.log(origObj.color);
Shorthand object creation
const activity = 'Surfing';
const beach = { activity };
console.log(beach); // { activity: 'Surfing' }
this Keyword
const cat = {
name: 'Pipey',
age: 8,
whatName() {
return this.name
}
};
console.log(cat.whatName()); // => Pipey
Factory functions
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 18/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
// A factory function that accepts 'name',
// 'age', and 'breed' parameters to return
// a customized dog object.
const dogFactory = (name, age, breed) => {
return {
name: name,
age: age,
breed: breed,
bark() {
console.log('Woof!');
}
};
};
Methods
const engine = {
// method shorthand, with one argument
start(adverb) {
console.log(`The engine starts up ${adverb}...`);
},
// anonymous arrow function expression with no arguments
sputter: () => {
console.log('The engine sputters...');
},
};
engine.start('noisily');
engine.sputter();
Getters and setters
const myCat = {
_name: 'Dottie',
get name() {
return this._name;
},
set name(newName) {
this._name = newName;
}
};
// Reference invokes the getter
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 19/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
console.log(myCat.name);
// Assignment invokes the setter
myCat.name = 'Yankee';
# JavaScript Classes
Static Methods
class Dog {
constructor(name) {
this._name = name;
}
introduce() {
console.log('This is ' + this._name + ' !');
}
// A static method
static bark() {
console.log('Woof!');
}
}
const myDog = new Dog('Buster');
myDog.introduce();
// Calling the static method
Dog.bark();
Class
class Song {
constructor() {
this.title;
this.author;
}
play() {
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 20/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
console.log('Song playing!');
}
}
const mySong = new Song();
mySong.play();
Class Constructor
class Song {
constructor(title, artist) {
this.title = title;
this.artist = artist;
}
}
const mySong = new Song('Bohemian Rhapsody', 'Queen');
console.log(mySong.title);
Class Methods
class Song {
play() {
console.log('Playing!');
}
stop() {
console.log('Stopping!');
}
}
extends
// Parent class
class Media {
constructor(info) {
this.publishDate = info.publishDate;
this.name = info.name;
}
}
// Child class
class Song extends Media {
constructor(songData) {
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 21/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
super(songData);
this.artist = songData.artist;
}
}
const mySong = new Song({
artist: 'Queen',
name: 'Bohemian Rhapsody',
publishDate: 1975
});
# JavaScript Modules
Export
// myMath.js
// Default export
export default function add(x,y){
return x + y
}
// Normal export
export function subtract(x,y){
return x - y
}
// Multiple exports
function multiply(x,y){
return x * y
}
function duplicate(x){
return x * 2
}
export {
multiply,
duplicate
}
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 22/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
Import
// main.js
import add, { subtract, multiply, duplicate } from './myMath.js';
console.log(add(6, 2)); // 8
console.log(subtract(6, 2)) // 4
console.log(multiply(6, 2)); // 12
console.log(duplicate(5)) // 10
// index.html
<script type="module" src="main.js"></script>
Export Module
// myMath.js
function add(x,y){
return x + y
}
function subtract(x,y){
return x - y
}
function multiply(x,y){
return x * y
}
function duplicate(x){
return x * 2
}
// Multiple exports in node.js
module.exports = {
add,
subtract,
multiply,
duplicate
}
Require Module
// main.js
const myMath = require('./myMath.js')
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 23/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
console.log(myMath.add(6, 2)); // 8
console.log(myMath.subtract(6, 2)) // 4
console.log(myMath.multiply(6, 2)); // 12
console.log(myMath.duplicate(5)) // 10
# JavaScript Promises
Promise states
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const res = true;
// An asynchronous operation.
if (res) {
resolve('Resolved!');
}
else {
reject(Error('Error'));
}
});
promise.then((res) => console.log(res), (err) => console.error(err));
Executor function
const executorFn = (resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Resolved!');
};
const promise = new Promise(executorFn);
setTimeout()
const loginAlert = () =>{
console.log('Login');
};
setTimeout(loginAlert, 6000);
.then() method
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 24/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Result');
}, 200);
});
promise.then((res) => {
console.log(res);
}, (err) => {
console.error(err);
});
.catch() method
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(Error('Promise Rejected Unconditionally.'));
}, 1000);
});
promise.then((res) => {
console.log(value);
});
promise.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
});
Promise.all()
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(3);
}, 300);
});
const promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(2);
}, 200);
});
Promise.all([promise1, promise2]).then((res) => {
console.log(res[0]);
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 25/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
console.log(res[1]);
});
Avoiding nested Promise and .then()
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('*');
}, 1000);
});
const twoStars = (star) => {
return (star + star);
};
const oneDot = (star) => {
return (star + '.');
};
const print = (val) => {
console.log(val);
};
// Chaining them all together
promise.then(twoStars).then(oneDot).then(print);
Creating
const executorFn = (resolve, reject) => {
console.log('The executor function of the promise!');
};
const promise = new Promise(executorFn);
Chaining multiple .then()
const promise = new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve('dAlan'), 100));
promise.then(res => {
return res === 'Alan' ? Promise.resolve('Hey Alan!') : Promise.reject('Who are you
}).then((res) => {
console.log(res)
}, (err) => {
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 26/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
console.error(err)
});
Fake http Request with Promise
const mock = (success, timeout = 1000) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if(success) {
resolve({status: 200, data:{}});
} else {
reject({message: 'Error'});
}
}, timeout);
});
}
const someEvent = async () => {
try {
await mock(true, 1000);
} catch (e) {
console.log(e.message);
}
}
# JavaScript Async-Await
Asynchronous
function helloWorld() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Hello World!');
}, 2000);
});
}
const msg = async function() { //Async Function Expression
const msg = await helloWorld();
console.log('Message:', msg);
}
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 27/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
const msg1 = async () => { //Async Arrow Function
const msg = await helloWorld();
console.log('Message:', msg);
}
msg(); // Message: Hello World! <-- after 2 seconds
msg1(); // Message: Hello World! <-- after 2 seconds
Resolving Promises
let pro1 = Promise.resolve(5);
let pro2 = 44;
let pro3 = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(resolve, 100, 'foo');
});
Promise.all([pro1, pro2, pro3]).then(function(values) {
console.log(values);
});
// expected => Array [5, 44, "foo"]
Async Await Promises
function helloWorld() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Hello World!');
}, 2000);
});
}
async function msg() {
const msg = await helloWorld();
console.log('Message:', msg);
}
msg(); // Message: Hello World! <-- after 2 seconds
Error Handling
let json = '{ "age": 30 }'; // incomplete data
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 28/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
try {
let user = JSON.parse(json); // <-- no errors
console.log( user.name ); // no name!
} catch (e) {
console.error( "Invalid JSON data!" );
}
Aysnc await operator
function helloWorld() {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Hello World!');
}, 2000);
});
}
async function msg() {
const msg = await helloWorld();
console.log('Message:', msg);
}
msg(); // Message: Hello World! <-- after 2 seconds
# JavaScript Requests
JSON
const jsonObj = {
"name": "Rick",
"id": "11A",
"level": 4
};
Also see: JSON cheatsheet
XMLHttpRequest
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 29/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
xhr.open('GET', 'mysite.com/getjson');
XMLHttpRequest is a browser-level API that enables the client to script data transfers via JavaScript, NOT
t f th J S i t l
GET
const req = new XMLHttpRequest();
req.responseType = 'json';
req.open('GET', '/getdata?id=65');
req.onload = () => {
console.log(xhr.response);
};
req.send();
POST
const data = {
fish: 'Salmon',
weight: '1.5 KG',
units: 5
};
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('POST', '/inventory/add');
xhr.responseType = 'json';
xhr.send(JSON.stringify(data));
xhr.onload = () => {
console.log(xhr.response);
};
fetch api
fetch(url, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-type': 'application/json',
'apikey': apiKey
},
body: data
}).then(response => {
if (response.ok) {
return response.json();
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 30/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
}
throw new Error('Request failed!');
}, networkError => {
console.log(networkError.message)
})
}
JSON Formatted
fetch('url-that-returns-JSON')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(jsonResponse => {
console.log(jsonResponse);
});
promise url parameter fetch api
fetch('url')
.then(
response => {
console.log(response);
},
rejection => {
console.error(rejection.message);
);
Fetch API Function
fetch('https://api-xxx.com/endpoint', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({id: "200"})
}).then(response => {
if(response.ok){
return response.json();
}
throw new Error('Request failed!');
}, networkError => {
console.log(networkError.message);
}).then(jsonResponse => {
console.log(jsonResponse);
})
async await syntax
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 31/32
10/13/24, 6:04 PM JavaScript Cheat Sheet & Quick Reference
const getSuggestions = async () => {
const wordQuery = inputField.value;
const endpoint = `${url}${queryParams}${wordQuery}`;
try{
const response = await fetch(endpoint, {cache: 'no-cache'});
if(response.ok){
const jsonResponse = await response.json()
}
}
catch(error){
console.log(error)
}
}
Related Cheatsheet
jQuery Cheatsheet CSS 3 Cheatsheet
Quick Reference Quick Reference
HTML Cheatsheet Laravel Cheatsheet
Quick Reference Quick Reference
Recent Cheatsheet
Remote Work Revolution Cheatsheet Homebrew Cheatsheet
Quick Reference Quick Reference
PyTorch Cheatsheet Taskset Cheatsheet
Quick Reference Quick Reference
© 2023 QuickRef.ME, All rights reserved.
https://quickref.me/javascript.html 32/32