Lab ID: 9.9K1014A032.SAI1.
Stand-Alone Lab: Basic Show Commands
Objective
Use basic show commands. These commands are used to display information about the status or
configuration of a Cisco device. Configure Router1 with the appropriate settings.
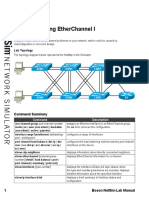
Lab Topology
The topology diagram below represents the NetMap in the Simulator.
Command Summary
Command Description
clock set hh:mm:ss day month year sets the system software clock
configure terminal enters global configuration mode from privileged EXEC mode
enable enters privileged EXEC mode
end ends and exits configuration mode
history size number-of-lines sets the number of previously issued commands that are stored
in the history buffer
hostname host-name sets the device name
line console 0 accesses console line configuration mode
show clock displays the system clock
show flash displays the boot flash or PC card information
show history displays the commands entered in the current EXEC session
show interfaces [type number] displays statistics for all interfaces configured on the router
show ip interface brief displays a brief summary of interface status and configuration
show protocols displays Layer 3 protocols enabled for a device
show running-config displays the active configuration file
show terminal displays the current terminal settings
show version displays hardware platform and software versions
1 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
Lab Tasks
Task 1: Learn the Basic Show Commands
1. On Router1, configure a host name of Router1.
2. Issue the show ? command to use Router1’s help function to view a list of the show commands that
can be issued on Router1. At the ––MORE–– prompt, press the Spacebar key to view the next page
of information.
3. Display the active configuration in memory. At the ––MORE–– prompt, press the Spacebar to view the
next page of information.
4. Display the contents of flash memory.
5. Display the commands that you have issued that are still stored in router memory.
6. Display the number of commands that can be stored in the history buffer on the terminal.
7. How many commands can currently be stored in the history buffer? _________________________
8. Configure the history buffer to store 100 commands.
9. Verify the number of commands can be stored in the history buffer.
10. Press the Ctrl+P key combination or the Up Arrow key to retrieve one of the previous commands
you typed. You can use the Up Arrow key or the Down Arrow key or you can press Ctrl+N or Ctrl+P
to navigate through the list of previously typed commands stored in the history buffer. Commands
stored in the history buffer are deleted each time you log off the device.
2 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
11. View the status of the current Layer 3 routed protocols running on the router. This command displays
the global and interface-specific status of any Layer 3 protocols.
12. Display critical information such as router platform type, operating system (OS) revision, OS last
boot time and file location, amount of memory, number of interfaces, and configuration register.
13. Configure the current date and time on Router1’s clock. Practice using the question mark (?) as you
proceed through the settings.
14. Verify the configuration of Router1’s clock setting.
15. Display detailed information about each interface.
16. Display concise information about interface status on Router1.
3 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
Lab Solutions
Task 1: Learn the Basic Show Commands
1. On Router1, you should issue the following commands to configure a host name of Router1:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname Router1
The enable command places the router into user EXEC mode. The configure terminal command
places the router into global configuration mode. From global configuration mode, you can issue the
hostname host-name command to configure a host name.
2. From user EXEC mode, which can be accessed by issuing the end command, you should issue
the show ? command to use Router1’s help function to view a list of the show commands that can
be issued on Router1. At the ––MORE–– prompt, press the Spacebar key to view the next page of
information.
Router1(config)#end
Router1#show ?
access-lists List access lists
arp ARP table
auto Show Automation Template
bgp BGP information
cdp CDP information
class-map Show QoS Class-Map
clns CLNS network information
clock Display the system clock
compress Show compression statistics
configuration Contents of Non-Volatile memory
controllers Interface controller status
crypto Encryption module
debugging State of each debugging option
dhcp Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol status
dialer Dialer parameters and statistics
etherchannel EtherChannel information
flash: display information about flash: file system
frame-relay Frame-Relay information
history Display the session command history
hosts IP domain-name, nameservers, and host table
interfaces Interface status and configuration
ip IP information
ipv6 IPv6 information
isdn ISDN information
isis IS-IS routing information
key Key information
mpls MPLS information
ntp Network time protocol
<output omitted>
4 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
3. The show running-config command is used to display the active configuration in memory. The
currently active configuration running on the router is referred to as the running-config in the router’s
command-line interface (CLI). At the ––MORE–– prompt, press the Spacebar to view the next page of
information.
Router1#show running-config
Building configuration...
!
Version 12.3
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Router1
!
ip subnet-zero
!
ip cef
no ip domain-lookup
!
interface Serial0/0/0
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
shutdown
<output omitted>
4. You should issue the show flash: command to display flash memory. Sample output is shown
below:
Router1#show flash:
System flash directory:
File Length Name/status
1 5880916 c2800-js-mz.121-9.T.bin
[5880980 bytes used, 2507628 available, 8388608 total]
8192K bytes of processor board System flash (Read/Write)
Flash memory is a special kind of memory that contains the operating system image file(s) on the
router. Unlike regular router memory, flash memory continues to maintain the file image even after
power is lost.
5. You should issue the show history command to display the commands that you have issued that
are still stored in router memory.
Router1#show history
enable
configure terminal
show running-config
show flash
show history
By default, the router’s CLI retains the last 10 commands entered in the history buffer.
5 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
6. You should issue the show terminal command to determine the number of commands that can be
stored in the history buffer.
Router1#show terminal
<output omitted>
Modem type is unknown
Session limit is not set
Time since activation: 00:01:32
Editing is enabled
History size is enabled, history size is 10
DNS resolution in show commands is enabled
Full user help is disabled
<output omitted>
7. Currently, 10 commands can be stored in the history buffer.
8. You should issue the following commands to configure Router1 to store 100 commands:
Router1#configure terminal
Router1(config)#line console 0
Router1(config-line)#history size 100
The history size number-of-lines command should be issued from line configuration mode. The
history buffer associated with the console and virtual terminal lines can be configured to store up to
256 commands.
9. You should issue the show terminal command to verify the number of commands can be stored in
the history buffer. Sample output is shown below:
Router1(config-line)#end
Router1#show terminal
<output omitted>
Modem type is unknown
Session limit is not set
Time since activation: 00:01:32
Editing is enabled
History size is enabled, history size is 100
DNS resolution in show commands is enabled
Full user help is disabled
<output omitted>
6 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
10. Press Ctrl+P or the Up Arrow key to retrieve one of the previous commands you typed. You can use
the Up Arrow key or the Down Arrow key or you can press Ctrl+N or Ctrl+P to navigate through the
list of previously typed commands stored in the history buffer. Commands stored in the history buffer
are deleted each time you log off the device.
11. You should issue the show protocols command to view the status of the current Layer 3 routed
protocols running on the router. This command displays the global and interface-specific status of
any Layer 3 protocols. Sample output is shown below:
Router1#show protocols
Global values:
Internet Protocol routing is enabled
Serial0/0/0 is administratively down, line protocol is down
Serial0/0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
FastEthernet0/0 is administratively down, line protocol is down
FastEthernet0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
12. You should issue the show version command to display critical information such as router platform
type, OS revision, OS last boot time and file location, amount of memory, number of interfaces, and
configuration register. Sample output is shown below:
Router1#show version
Boson Operating Simulation Software
BOSS (tm) C2800 Software (C2800-Enterprise), Version 12.3, RELEASE SOFTWARE
Copyright (c) 1998-2014 by Boson Software, Inc.
BOSS ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 12.3, RELEASE SOFTWARE
Router1 Uptime Is 0 days, 0 hours, 3 minutes
System restarted by power-on
System image file is “”flash:c2800-enterprise.12.3.boss””, booted via flash
Boson 2800 (BOSS) processor (revision 5.0)
2 Fast Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)
2 Serial network interface(s)
32K bytes of simulated non-volatile configuration memory.
8192K bytes of simulated System flash (Read/Write)
Configuration register is 0X2102
7 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
13. You should issue the following commands to configure the current date and time on Router1’s clock.
Practice using the question mark (?) as you proceed through the settings. The following is sample
output of the process:
Router1#clock set ?
hh:mm:ss Current Time
Router1#clock set 09:12:30 ?
<1-31> Day of the Month
Router1#clock set 09:12:30 19 ?
month Month of the Year
Router1#clock set 09:12:30 19 August ?
<1993-2035> Year
Router1#clock set 09:12:30 19 August 2013
14. You should issue the show clock command to verify your configuration of Router1’s clock setting.
Router1#show clock
09:12:38.501 UTC Wed Aug 19 2013
15. You should issue the show interfaces command displays detailed information about each interface.
Sample output is shown below:
Router1#show interfaces
Serial0/0/0 is administratively down, line protocol is down
Hardware is HD64570
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1544 Kbit, DLY 2000 usec, rely 255/255, load 1/255
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Last input 00:00:00, output 00:00:00, output hang never
Last clearing of “show interface” counters never
Queuing strategy: weighted-fair
Output queue: 0/1000/64/0 (size/max total/threshold/drops)
Conversations 7/35/128 (active/max active/max total)
Reserved Conversations 0/0 (allocated/max allocated)
Available Bandwidth 1158 kilobits/sec
5 minute input rate 1000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 1000 bits/sec, 2 packets/sec
0 packets input, 00 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
0 input packets with dribble condition detected
0 packets output, 00 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 babbles, 0 late collision, 0 deferred
0 lost carrier, 0 no carrier
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Serial0/0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
<output omitted>
8 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
16. You should issue the show ip interface brief command to view concise information about interface
status on Router1. Sample output is shown below:
Router1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Serial0/0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
FastEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Sample Configuration Script
Router1 Router1 (continued)
Router1#show running-config interface FastEthernet0/0
Building configuration... no ip address
Current configuration : 705 bytes no ip directed-broadcast
! shutdown
Version 12.3 !
service timestamps debug uptime interface FastEthernet0/1
service timestamps log uptime no ip address
no service password-encryption no ip directed-broadcast
! shutdown
hostname Router1 !
! ip classless
ip subnet-zero no ip http server
! !
ip cef line con 0
no ip domain-lookup history size 100
! line aux 0
interface Serial0/0/0 line vty 0 4
no ip address !
no ip directed-broadcast no scheduler allocate
shutdown end
!
interface Serial0/0/1
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
shutdown
!
Copyright © 1996–2014 Boson Software, LLC. All rights reserved. NetSim software and documentation are protected by copyright law.
9 Boson NetSim Lab Manual