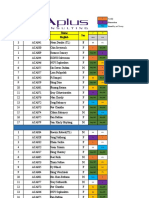
Concepts of Database Management
Chapter 3
The Relational Model 2: SQL
http://sophorn26sun.blogspot.com/
Objectives
• Introduce Structured Query Language (SQL)
• Use simple and compound conditions in SQL
• Use computed fields in SQL
• Use built-in SQL functions
• Use subqueries in SQL
• Group records in SQL
fb.me/SophornDS 2
Objectives
• Join tables using SQL
• Perform union operations in SQL
• Use SQL to update database data
• Use an SQL query to create a table in a database
fb.me/SophornDS 3
Introduction to SQL
• Provides with the capacities of querying a
relational database
• Enter commands to obtain the desired result
• Use commands to create and update tables and
to retrieve data from table
• Developed under the name SEQUEL at the IBM
San Jose research in mid-1970
• It was renamed SQL in 1980
• It is a standard language for relational database
manipulation
fb.me/SophornDS 4
Getting Started with SQL
• If you are completing the work in this chapter using
Microsoft Office Access 2010/2013/2016 or MySQL
version 4.1 or higher (5.7), the following sections
contain specific information about your DBMS
fb.me/SophornDS 5
Getting Started with Microsoft
Office Access 2010/2013 or 2016
• If you are using the Access 2010/2013 or 2016
version of the Premiere Products database
provided with the Data Files for this text:
– Tables in the database have already been created
– You will not need to execute the CREATE TABLE
commands to create the tables or the INSERT
commands to add records to the tables
fb.me/SophornDS 6
Getting Started with Microsoft Office
Access 2010/2013 or 2016 (cont.)
• To execute the SQL commands shown in the
figures in Access 2013/2016
– Open the Premiere Products database
– Click on tab: Create, then click on Query Design
– Click the Close button in the Show Table dialog box
– Click the View button list arrow on the Query Design
tab, and then click SQL View
– The query opens in SQL view, ready for you to type
your SQL commands
fb.me/SophornDS 7
Getting Started with Microsoft Office
Access 2010/2013 or 2016 (cont.)
• To run the SQL command:
• Click the Run button in the Results group on the
Query Tools Design tab.
• To return to SQL view:
• Click the View button arrow in the Views group on the
Home tab, and then click SQL View.
fb.me/SophornDS 8
Getting Started with MySQL
• MySQL is an open-source relational database
management system (RDBMS)
• Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-
founder Michael Widenius's daughter and "SQL", the
abbreviation for Structured Query Language
• Owned and sponsored by the Swedish company
MySQL AB, which was bought by Sun Microsystems
(now Oracle Corporation)
fb.me/SophornDS 9
Getting Started with MySQL
• MySQL Server Installation
fb.me/SophornDS 10
Getting Started with MySQL
• MySQL-Premiere script provided with the
Data Files for this text will:
– Activate the database
– Create the tables
– Insert the records
• To run a script in MySQL:
– Type the SOURCE command followed by the name
of the file
– Press the Enter key
fb.me/SophornDS 11
Getting Started with MySQL (cont.)
• Before typing commands in MySQL, you must
activate the database by typing the USE
command followed by the name of the
database
• The most recent command entered in MySQL
is stored in a special area of memory called the
statement history
fb.me/SophornDS 12
fb.me/SophornDS 13
Table Creation
• SQL CREATE TABLE command
– Creates a table by describing its layout
• Typical restrictions placed on table and column
names by DBMS
– Names cannot exceed 18 characters
– Names must start with a letter
– Names can contain only letters, numbers, and
underscores (_)
– Names cannot contain spaces
fb.me/SophornDS 14
Typical Data Types
• INTEGER
– Numbers without a decimal point
• SMALLINT
– Uses less space than INTEGER
• DECIMAL(p, q)
– P number of digits; q number of decimal places
• CHAR(n)
– Character string n places long
• DATE
– Dates in DD-MON-YYYY or MM/DD/YYYY
fb.me/SophornDS 15
• Use SQL to create the Rep table by
describing its layout.
fb.me/SophornDS 16
Simple Retrieval
• SELECT-FROM-WHERE: SQL retrieval command
– SELECT clause: lists fields to display
– FROM clause: lists table or tables that contain data
to display in query results
– WHERE clause (optional): lists any conditions to be
applied to the data to retrieve
• Simple condition: field name, a comparison
operator, and either another field name or a value
fb.me/SophornDS 17
Simple Retrieval
Figures 3.1 - 3.2
fb.me/SophornDS 18
SQL Query to List Part Table
Figures 3.3 - 3.4
fb.me/SophornDS 19
SQL Query with Where Condition
Figures 3.5 - 3.6
fb.me/SophornDS 20
SQL Comparison Operators
Figure 3.7
fb.me/SophornDS 21
SQL Query to Find Customer 148
Figures 3.8 - 3.9
fb.me/SophornDS 22
SQL Query to Find
All Customers in ‘Grove’
Figures 3.10 - 3.11
fb.me/SophornDS 23
Query to find Customers with Credit
Limit Exceeding Balance
Figures 3.12 - 3.13
fb.me/SophornDS 24
Compound Conditions
• Compound condition
– Connecting two or more simple conditions using one
or both of the following operators: AND and OR
– Preceding a single condition with the NOT operator
• Connecting simple conditions using AND operator
– All of the simple conditions must be true for the
compound condition to be true
• Connecting simple conditions using OR operator
– Any of the simple conditions must be true for the
compound condition to be true
fb.me/SophornDS 25
SQL Query with Compound
Condition using ‘AND’
fb.me/SophornDS 26
SQL Query using ‘OR’
fb.me/SophornDS 27
Compound Conditions (continued)
• Preceding a condition by NOT operator
– Reverses the truth or falsity of the original condition
• BETWEEN operator
– Value must be between the listed numbers
fb.me/SophornDS 28
SQL Query using ‘NOT’
Or: WHERE Warehouse!=‘3’;
fb.me/SophornDS 29
Query with ‘BETWEEN’ Operator
Figures 3.20 - 3.21
fb.me/SophornDS 30
Computed Fields
• Computed field or calculated field
– Field whose values you derive from existing fields
– Can involve:
• Addition (+)
• Subtraction (-)
• Multiplication (*)
• Division (/)
• Access: fieldName1 & fieldName2 AS newField
• MySQL: CONCAT(field1, field2, …)
fb.me/SophornDS 31
SQL Query with Computed Field
fb.me/SophornDS 32
SQL Query with Computed
Field and Condition
fb.me/SophornDS 33
Using Special Operators
(LIKE and IN)
• Wildcards in Access SQL
– Asterisk (*): collection of characters
– Question mark (?): any individual character
• Wildcards in MySQL
– Percent sign (%): any collection of characters
– Underscore (_): any individual character
• To use a wildcard, include the LIKE operator in the
WHERE clause
• IN operator provides a concise way of phrasing
certain conditions
fb.me/SophornDS 34
SQL Query with ‘LIKE’ Operator
fb.me/SophornDS 35
SQL Query with ‘IN’ Operator
fb.me/SophornDS 36
Sorting
• Sort data using the ORDER BY clause
• Sort key: field on which to sort data
• When sorting data on two fields:
– Major sort key (or primary sort key): more important
sort key
– Minor sort key (or secondary sort key): less
important sort key
fb.me/SophornDS 37
SQL Query to Sort Data
fb.me/SophornDS 38
SQL Query to Sort on Multiple Fields
fb.me/SophornDS 39
Built-in Functions
• Built-in functions (aggregate functions) in SQL
– COUNT: calculates number of entries
– SUM or AVG: calculates sum or average of all
entries in a given column
– MAX or MIN: calculates largest or smallest values
respectively
fb.me/SophornDS 40
SQL Query to Count Records
fb.me/SophornDS 41
SQL Query to Count Records and
Calculate a Total
fb.me/SophornDS 42
SQL Query to Perform Calculations
and Rename Fields
fb.me/SophornDS 43
Subqueries
• Subquery: inner query or a query placing inside
another query
• Subquery is evaluated first
• Outer query is evaluated after the subquery
fb.me/SophornDS 44
SQL Query with Subquery
fb.me/SophornDS 45
Grouping
• Create groups of records that share a common
characteristic
• GROUP BY clause indicates grouping in SQL
• HAVING clause is to groups what the WHERE
clause is to rows
fb.me/SophornDS 46
SQL Query to Group Records
GROUP BY ជាឃ្លាមួ យ ដែលនឹ ង
ប្រមូ លផ្ុំតទិនន
ន ័ យដែលែូចគ្នជាប្រុម
នៅរនតង Column ណាមួ យ មត នន្វើការ
សរតរ និ ង សននិដ្ឋាននដ្ឋយ
Aggregate Function ។
fb.me/SophornDS 47
SQL Query to Restrict Groups
HAVING ជាឃ្លាមួយដែលនឹងរុំនត់លរខខ័ណ្ឌ នដ្ឋយ
នប្រើសនរ ើសយរដតរួរនែរមួយចគុំនួន នប្កាយនេល
GROUP BY និង សននិដ្ឋាននដ្ឋយ Aggregate Function ។
fb.me/SophornDS 48
SQL Query with ‘WHERE’
and ‘HAVING’ Clauses
SELECT RepNum, COUNT(*) AS NumCustomers, AVG(Balance) AS
AverageBalance
FROM Customer
WHERE CreditLimit<10000
GROUP BY RepNum
ORDER BY RepNum
;
fb.me/SophornDS 49
Joining Tables
• Queries can locate data from more than one table
• Enter appropriate conditions in the WHERE clause
• To join tables, construct the SQL command as:
1. SELECT clause: list all fields you want to display
2. FROM clause: list all tables involved in the query
3. WHERE clause: give the condition that will restrict
the data to be retrieved to only those rows from the
two tables that match
fb.me/SophornDS 50
SQL Query to Join Tables
Figures 3.48 - 3.49
SELECT CustomerNum, CustomerName, Rep.RepNum, LastName,
FirstName
FROM Customer, Rep
WHERE Customer.RepNum=Rep.RepNum
;
fb.me/SophornDS 51
Query to Restrict Records in Join
Figures 3.50 - 3.51
SELECT CustomerNum, CustomerName, Rep.RepNum, LastName,
FirstName
FROM Customer, Rep
WHERE Customer.RepNum=Rep.RepNum
AND CreditLimit=10000
;
fb.me/SophornDS 52
Query to Join Multiple Tables
Figures 3.52 - 3.53
SELECT Orders.OrderNum, OrderDate, Customer.CustomerNum,
CustomerName, Part.PartNum, Description, NumOrdered, QuotedPrice
FROM Orders, Customer, OrderLine, Part
WHERE Customer.CustomerNum=Orders.CustomerNum
AND Orders.OrderNum=OrderLine.OrderNum
AND OrderLine.PartNum=Part.PartNum
;
fb.me/SophornDS 53
INNER JOIN
SELECT …
FROM T1 [INNER] JOIN T2
ON T1.PK = T2.FK
fb.me/SophornDS 54
OUTER JOIN
SELECT …
FROM T1 LEFT OUTER JOIN T2
ON T1.PK = T2.FK
SELECT …
FROM T1 RIGHT OUTER JOIN T2
ON T1.PK = T2.FK
fb.me/SophornDS 55
Union
• Union of two tables is a table containing all rows in
the first table, the second table, or both tables
• Two tables involved must be union compatible
– Same number of fields
– Corresponding fields must have same data types
fb.me/SophornDS 56
SQL Query to Perform Union
fb.me/SophornDS 57
Intersection
SELECT CustomerNum, CustomerName
FROM Customer
WHERE RepNum=‘35’
AND CustomerNum IN(SELECT Customer.CustomerNum
FROM Customer, Orders
WHERE Customer.CustomerNum=Orders.CustomerNum)
;
fb.me/SophornDS 58
Difference (Subtract)
SELECT CustomerNum, CustomerName
FROM Customer
WHERE RepNum=‘35’
AND CustomerNum NOT IN(SELECT Customer.CustomerNum
FROM Customer, Orders
WHERE Customer.CustomerNum=Orders.CustomerNum)
;
fb.me/SophornDS 59
Example
1. List the number, name and of all customers
that have ordered AND represented by Juan
Perez.
2. List the number, name and of all customers
that have ordered OR represented by Juan
Perez.
3. List the number, name and of all customers
that have ordered BUT NOT represented by
Juan Perez.
fb.me/SophornDS 60
Updating Tables
• UPDATE command makes changes to existing data
• INSERT command adds new data to a table
• DELETE command deletes data from the database
fb.me/SophornDS 61
SQL Query to Update Data
fb.me/SophornDS 62
SQL Query to Delete Rows
Figure 3.58
fb.me/SophornDS 63
Creating a Table from a Query
• INTO clause
– Saves the results of a query as a table
– Specified before FROM and WHERE clauses
• MySQL
1.Create the new table using a CREATE TABLE
command
2.Use an INSERT command to insert the appropriate
data into the new table
OR: Use a SELECT command to insert the appropriate
data in CREATE TABLE command
fb.me/SophornDS 64
SQL Query to Create New Table from
Existing Table In Access
fb.me/SophornDS 65
Creating a Table from a Query in
MySQL/Oracle
FIGURE 3-59b: Query to create a new table (MySQL)
fb.me/SophornDS 66
SQL Query to Create New Table from
Existing Table in MySQL
mysql> CREATE TABLE SmallCust
-> SELECT * FROM Customer;
fb.me/SophornDS 67
SQL Query to Append Record from One
Table to Another Table in Access
fb.me/SophornDS 68
Alter table to add more column to
a table
fb.me/SophornDS 69
Alter table to delete a column
from a table
fb.me/SophornDS 70
Alter table to modify a column in
a table
mysql> ALTER TABLE Customer MODIFY RepNum INTEGER;
fb.me/SophornDS 71
Alter table to add a primary key
to a table
fb.me/SophornDS 72
CREATE INDEX command to
create a primary key to a table
fb.me/SophornDS 73
DROP INDEX Command to
remove primary key from a table
fb.me/SophornDS 74
DROP a table from a database
fb.me/SophornDS 75
Summary
• Structured Query Language (SQL) is a language
that is used to manipulate relational databases
• Basic form of an SQL query: SELECT-FROM-
WHERE
• Use CREATE TABLE command to describe table
layout to the DBMS, which creates the table
• In SQL retrieval commands, fields are listed after
SELECT, tables are listed after FROM, and
conditions are listed after WHERE
• In conditions, character values must be enclosed in
single quotation marks
fb.me/SophornDS 76
Summary (continued)
• Compound conditions are formed by combining
simple conditions using either or both of the
following operators: AND and OR
• Sorting is accomplished using ORDER BY clause
• When the data is sorted in more than one field, can
have a major and minor sort keys
• Grouping: use the GROUP BY clause
• HAVING clause: restricts the rows to be displayed
fb.me/SophornDS 77
Summary (continued)
• Joining tables: use a condition that relates
matching rows in the tables to be joined
• Built-in (aggregate) functions: COUNT, SUM, AVG,
MAX, and MIN
• One SQL query can be placed inside another; the
subquery is evaluated first
• UNION operator: unifies the results of two queries
fb.me/SophornDS 78
Summary (continued)
• Calculated fields: include the calculation, the word
AS, the name of the calculated field
• INSERT command adds a new row to a table
• UPDATE command changes existing data
• DELETE command deletes records
• INTO clause is used in a SELECT command to
create a table containing the results of the query
fb.me/SophornDS 79