Aggrega&on
Defini&on
• Represents a “has-‐a” rela&onship between two classes
• Class W is an “aggregate” if it has an a:ribute of type P
and P is not a primi&ve type
• A:ribute P is called the “aggregated part”, “part”,
“aggregated component”, or just “component”
EECS1021 W18 2
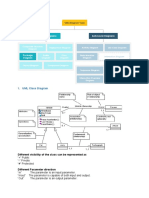
UML Diagram
Whole Part
RFIDTag Worker
• The Whole class has an a:ribute of type Part
• The class Whole aggregates Part
• The RFIDTag class has a Worker a:ribute
• The class RFIDTag aggregates Worker
EECS1021 W18 3
Aggrega&on Example
• Suppose a Person has a name and a date of birth
public class Person
{
private String name;
private Date birthDate;
public Person(String name, Date birthDate) {
this.name = name;
this.birthDate = birthDate;
}
public Date getBirthDate()
{
return birthDate;
}
}
EECS1021 W18 4
UML Class Diagram for Aggrega&on
number of Date number of String
objects each Person has objects each Person has
1 1
Date Person String
open diamonds
indicate aggrega&on
EECS1021 W18 5
Another Aggrega&on Example
• 3D videogames use models that are a three dimensional
representa&ons of geometric data
• Models may be represented by:
• Three-‐dimensional points (par&cle systems)
• Simple polygons (triangles, quadrilaterals)
• Smooth, con&nuous surfaces (splines, parametric surfaces)
• An algorithm (procedural models)
• Rendering the objects to the screen usually results in
drawing triangles
• Graphics cards have specialized hardware that does this very fast
EECS1021 W18 6
EECS1021 W18 7
EECS1021 W18 8
Aggrega&on Example
• A Triangle has 3 three-‐dimensional Points
3
Triangle Point
Triangle Point
+ Triangle(Point, Point, Point) + Point(double, double, double)
+ getA() : Point + getX() : double
+ getB() : Point + getY() : double
+ getC() : Point + getZ() : double
+ setA(Point) : void + setX(double) : void
+ setB(Point) : void + setY(double) : void
+ setC(Point) : void + setZ(double) : void
EECS1021 W18 9
Triangle (a:ributes and constructor)
public class Triangle {
private Point pA;
private Point pB;
private Point pC;
public Triangle(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
this.pA = a;
this.pB = b;
this.pC = c;
}
}
EECS1021 W18 10
Triangle (accessors)
public Point getA() {
return this.pA;
}
public Point getB() {
return this.pB;
}
public Point getC() {
return this.pC;
}
EECS1021 W18 11
Triangle (mutators)
public void setA(Point p) {
this.pA = p;
}
public void setB(Point p) {
this.pB = p;
}
public void setC(Point p) {
this.pC = p;
}
EECS1021 W18 12
Triangle Aggrega&on
• Implemen&ng Triangle is very easy
• A:ributes (3 Point references)
• References to exis&ng objects provided by the user of the class
• Accessors
• Give users of a class access to an a:ribute
• Mutators
• Allows users of a class to change an a:ribute
• We say that the Triangle a:ributes are aliases
(i.e., references to the Point objects)
EECS1021 W18 13
Client code – the user of a class
Point a = new Point(-1.0, -1.0, -3.0);
Point b = new Point(0.0, 1.0, -3.0);
Point c = new Point(2.0, 0.0, -3.0);
Triangle tri = new Triangle(a, b, c);
EECS1021 W18 14
Collec&ons as A:ributes
• O`en you will want to implement a class that has-‐a
collec&on as an a:ribute
• A university has-‐a collec&on of facul&es and each faculty has-‐a
collec&on of schools and departments
• A molecule has-‐a collec&on of atoms
• A person has-‐a collec&on of acquaintances
• A student has-‐a collec&on of GPAs and has-‐a collec&on of courses
• A polygonal model has-‐a collec&on of triangles
EECS1021 W18 15
What Does a Collec&on Hold?
• A collec&on holds references (i.e., memory addresses) to
its elements (i.e., objects)
• It does not hold the elements themselves
• Allows an object to be held by mul&ple collec&ons
List1:
Object2
Object1 Object3
List2:
EECS1021 W18 16
Student Class
• A Student has-‐a:
• String name and id
• Collec&on of yearly GPAs
• Collec&on of courses
1 1
List<Double> Student Set<Course>
gpas courses
4 name
1 1 id *
Double String Course
EECS1021 W18 17
PolygonalModel Class
• A polygonal model has-‐a List of Triangles
1
PolygonalModel List<Triangle>
tri
*
Triangle
EECS1021 W18 18
PolygonalModel
public class PolygonalModel
{
private List<Triangle> tri;
public PolygonalModel()
{
tri = new ArrayList<Triangle>();
}
…
EECS1021 W18 19