Java Programming
Basics of Java
P.Suresh
1
Java is
Object Oriented
Platform independent
Simple :Java is designed to be easy to learn.
Secure
Architectural- neutral
Portable
Robust
Multi-threaded
Distributed
2
Popular Java Editors
Notepad
Netbeans
http://www.netbeans.org/index.html.
Eclipse http://www.eclipse.org/.
3
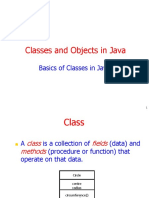
Classes
A class is a collection of fields (data) and
methods (procedure or function) that
operate on that data.
Circle
centre
radius
circumference()
area()
4
Classes
A class is a collection of fields (data) and methods
(procedure or function) that operate on that data.
The basic syntax for a class definition:
class ClassName [extends
SuperClassName]
{
[fields declaration]
[methods declaration]
}
Bare bone class – no fields, no methods
public class Circle {
// my circle class
}
5
Adding Fields: Class Circle with fields
Add fields
public class Circle {
public double x, y; // centre coordinate
public double r; // radius of the
circle
The fields (data) are also called the
instance varaibles.
6
Adding Methods
A class with only data fields has no life. Objects
created by such a class cannot respond to any
messages.
Methods are declared inside the body of the
class but immediately after the declaration of
data fields.
The general form of a method declaration is:
type MethodName (parameter-list)
{
Method-body;
}
7
Adding Methods to Class Circle
public class Circle {
public double x, y; // centre of the circle
public double r; // radius of circle
//Methods to return circumference and area
public double circumference() {
return 2*3.14*r;
}
public double area() {
return 3.14 * r * r; Method Body
}
}
8
Data Abstraction
Declare the Circle class, have created a
new data type – Data Abstraction
Can define variables (objects) of that
type:
Circle aCircle;
Circle bCircle;
9
Class of Circle cont.
aCircle, bCircle simply refers to a Circle
object, not an object itself.
aCircle bCircle
null null
Points to nothing (Null Reference) Points to nothing (Null Reference)
10
Creating objects of a class
Objects are created dynamically using the
new keyword.
aCircle and bCircle refer to Circle objects
aCircle = new bCircle = new Circle() ;
Circle() ;
11
Creating objects of a class
aCircle = new Circle();
bCircle = new Circle() ;
bCircle = aCircle;
12
Creating objects of a class
aCircle = new Circle();
bCircle = new Circle() ;
bCircle = aCircle;
Before Assignment Before Assignment
aCircle bCircle aCircle bCircle
P Q P Q
13
Automatic garbage collection
The object Q
does not have a
reference and cannot be used in future.
Java automatically collects garbage
periodically and releases the memory
used to be used in the future.
14
Accessing Object/Circle Data
Similar to C syntax for accessing data
defined in a structure.
ObjectName.VariableName
ObjectName.MethodName(parameter-list)
Circle aCircle = new Circle();
aCircle.x = 2.0 // initialize center and radius
aCircle.y = 2.0
aCircle.r = 1.0
15
Executing Methods in Object/Circle
Using Object Methods:
sent ‘message’ to
aCircle
Circle aCircle = new
Circle();
double area;
aCircle.r = 1.0;
area = aCircle.area();
16
Using Circle Class
// Circle.java: Contains both Circle class and its user class
//Add Circle class code here
class MyMain
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Circle aCircle; // creating reference
aCircle = new Circle(); // creating object
aCircle.x = 10; // assigning value to data field
aCircle.y = 20;
aCircle.r = 5;
double area = aCircle.area(); // invoking method
double circumf = aCircle.circumference();
System.out.println("Radius="+aCircle.r+" Area="+area);
System.out.println("Radius="+aCircle.r+" Circumference ="+circumf);
}
}
[raj@mundroo]%: java MyMain
Radius=5.0 Area=78.5
Radius=5.0 Circumference =31.400000000000002
17
Basic Syntax
Case Sensitivity
Class Names - For all class names the first letter should
be in Upper Case.
Example class MyFirstJavaClass
Method Names - All method names should start with a
Lower Case letter. If several words are used, then each
inner word's first letter should be in Upper Case.
Example public void myMethodName()
Program File Name - Name of the program file should
exactly match the class name.
public static void main(String args[]) - java
program processing starts from the main() method which
is a mandatory part of every java program..
18
Java Identifiers
All identifiers should begin with a letter (A to Z
or a to z ), currency character ($) or an
underscore (_).
After the first character identifiers can have any
combination of characters.
A key word cannot be used as an identifier.
Most importantly identifiers are case sensitive.
Examples of legal identifiers: age, $salary,
_value, __1_value
Examples of illegal identifiers : 123abc, -salary
19
Java Modifiers
Visible to the package. the default. No
modifiers are needed.
Visible to the class only (private).
Visible to the world (public).
Visible to the package and all subclasses
(protected).
20
Operators
Arithmetic Operators
Relational Operators
Bitwise Operators
Logical Operators
Assignment Operators
Conditional operator
21
Conditional and Looping
Statements
if statements
switch statements
while Loop
do...while Loop
for Loop
22
Arrays
which stores a fixed-size sequential collection of
elements of the same type
Declaring Array Variables:
dataType[] arrayRefVar;
dataType arrayRefVar[];
Example:
double[] myList;
double myList[];
Creating Arrays:
arrayRefVar = new dataType[arraySize];
23
Another way
dataType[] arrayRefVar = new
dataType[arraySize];
Alternatively you can create arrays as
follows:
dataType[] arrayRefVar = {value0, value1,
..., valuek};
Loop: for (double element: myList)
24
Creating a Method
25
Constructors
A constructor with no parameters is referred
to as a default constructor.
Constructors must have the same name as
the class itself.
Constructors do not have a return type—not
even void.
Constructors are invoked using the new
operator when an object is created.
Constructors play the role of initializing
objects.
26
Constructors
Circle(double r) {
radius = r;
}
Circle() {
radius = 1.0;
}
myCircle = new Circle(5.0);
Constructors are a special kind of methods that
are invoked to construct objects.
27