DATA MINING WITH
CLUSTERING
AND
CLASSIFICATION
DATA MINING
Data Mining is the process of discovering new
correlations, patterns, and trends by digging into
(mining) large amounts of data stored in warehouses,
using artificial intelligence, statistical and
mathematical techniques.
It is currently used in a wide range of profiling
practices, such as marketing ,fraud detection, and
scientific discovery.
From a managerial perspective:
Analyzing trends
Wealth generation
Security
Strategic decision making
MODELS OF DATA MINING
Predictive Model: Predictive models can be used to
forecast explicit values, based on patterns determined
from known results. For example, from a database of
customers who have already responded to a particular
offer, a model can be built that predicts which prospects
are likeliest to respond to the same offer.
Predictive data mining is further categorized into:
Classification
Regression
CONT…
Descriptive Model: Descriptive models describe
patterns in existing data, and are generally used to
create meaningful subgroups such as demographic
clusters. They are generally used to create meaningful
subgroups.
Descriptive data mining is further classified into
Clustering
Association
Sequential analysis.
CLUSTERING
• Clustering can be considered the most important
unsupervised learning technique; so, as every other
problem of this kind, it deals with finding a structure
in a collection of unlabeled data.
• Clustering is “the process of organizing objects into
groups whose members are similar in some way”.
• A cluster is therefore a collection of objects which
are “similar” between them and are “dissimilar” to
the objects belonging to other clusters.
CONT…
Where to use clustering?
Data mining
Information retrieval
text mining
Web analysis
marketing
medical diagnostic
Major clustering methods
Distance-based
Hierarchical
Partitioning
Probabilistic
CLASSIFICATION
predicts categorical class labels
classifies data (constructs a model) based on the
training set and the values (class labels) in a classifying
attribute and uses it in classifying new data
Classification—A Two-Step Process
Model construction: describing a set of predetermined classes
Each tuple is assumed to belong to a predefined class, as determined
by the class label attribute (supervised learning)
The set of tuples used for model construction: training set
The model is represented as classification rules, decision trees, or
mathematical formulae
Model usage: for classifying previously unseen objects
Estimate accuracy of the model using a test set
The known label of test sample is compared with the classified
result from the model
Accuracy rate is the percentage of test set samples that are correctly
classified by the model
Test set is independent of training set, otherwise over-fitting will
occur
Classification Process: Model
Construction
Classification
Algorithms
Training
Data
NAME RANK YEARS TENURED Classifier
(Model)
Mike Assistant Prof 3 no
Mary Assistant Prof 7 yes
Bill Professor 2 yes
Jim Associate Prof 7 yes
IF rank = ‘professor’
Dave Assistant Prof 6 no OR years > 6
Anne Associate Prof 3 no THEN tenured = ‘yes’
Classification Process: Model
usage in Prediction
Classifier
Testing
Data Unseen Data
(Jeff, Professor, 4)
NAME RANK YEARS TENURED
Tom Assistant Prof 2 no Tenured?
Merlisa Associate Prof 7 no
George Professor 5 yes
Joseph Assistant Prof 7 yes
Classification Techniques
Classification by Decision Tree
Bayesian Classification
Classification by Backpropogation
Classification based on Association Rule Mining
Classification vs Clustering
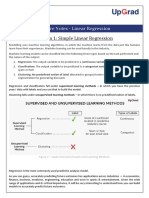
Supervised learning (classification)
Supervision: The training data (observations,
measurements, etc.) are accompanied by labels
indicating the class of the observations
New data is classified based on the training set
Unsupervised learning (clustering)
The class labels of training data is unknown
Given a set of measurements, observations, etc. the
aim is to establish the existence of classes or clusters in
the data