Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to develop a full Tkinter object-oriented application.
You’ll convert the temperature converter application to a new one that uses object-oriented programming approach:
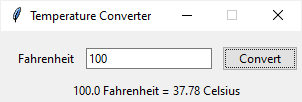
First, define a class called TemperatureConverter. The class has one static method that converts a temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius:
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter.messagebox import showerror class TemperatureConverter: @staticmethod def fahrenheit_to_celsius(f): return (f - 32) * 5 / 9 Code language: Python (python)Second, define a ConverterFrame class that inherits from the ttk.Frame class. The ConverterFrame class will be responsible for creating widgets and handling events:
class ConverterFrame(ttk.Frame): def __init__(self, container): super().__init__(container) # field options options = {'padx': 5, 'pady': 5} # temperature label self.temperature_label = ttk.Label(self, text='Fahrenheit') self.temperature_label.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky=tk.W, **options) # temperature entry self.temperature = tk.StringVar() self.temperature_entry = ttk.Entry(self, textvariable=self.temperature) self.temperature_entry.grid(column=1, row=0, **options) self.temperature_entry.focus() self.convert_button = ttk.Button(self, text='Convert') self.convert_button['command'] = self.convert self.convert_button.grid(column=2, row=0, sticky=tk.W, **options) # result label self.result_label = ttk.Label(self) self.result_label.grid(row=1, columnspan=3, **options) # add padding to the frame and show it self.grid(padx=10, pady=10, sticky=tk.NSEW) def convert(self): """ Handle button click event """ try: f = float(self.temperature.get()) c = TemperatureConverter.fahrenheit_to_celsius(f) result = f'{f} Fahrenheit = {c:.2f} Celsius' self.result_label.config(text=result) except ValueError as error: showerror(title='Error', message=error) Code language: Python (python)How it works:
- The
ConverterFrameneeds a container, therefore, its__init__()method has thecontainerargument. - Inside the
__init__()method of theConverterCFrameclass, call the__init__()method of its superclass. - Assign the widgets to the
selfobject so that you can reference them in other methods of theConverterFrameclass. - Assign the
commandoption of theconvertbutton to theself.convertmethod.
Third, define an App class that inherits from the tk.Tk class:
class App(tk.Tk): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.title('Temperature Converter') self.geometry('300x70') self.resizable(False, False)Code language: Python (python)Finally, bootstrap the application from the if __name__ == "__main__" block:
if __name__ == "__main__": app = App() ConverterFrame(app) app.mainloop() Code language: Python (python)Put it all together:
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter.messagebox import showerror class TemperatureConverter: @staticmethod def fahrenheit_to_celsius(f): return (f - 32) * 5 / 9 class ConverterFrame(ttk.Frame): def __init__(self, container): super().__init__(container) # field options options = {'padx': 5, 'pady': 5} # temperature label self.temperature_label = ttk.Label(self, text='Fahrenheit') self.temperature_label.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky=tk.W, **options) # temperature entry self.temperature = tk.StringVar() self.temperature_entry = ttk.Entry(self, textvariable=self.temperature) self.temperature_entry.grid(column=1, row=0, **options) self.temperature_entry.focus() self.convert_button = ttk.Button(self, text='Convert') self.convert_button['command'] = self.convert self.convert_button.grid(column=2, row=0, sticky=tk.W, **options) # result label self.result_label = ttk.Label(self) self.result_label.grid(row=1, columnspan=3, **options) # add padding to the frame and show it self.grid(padx=10, pady=10, sticky=tk.NSEW) def convert(self): """ Handle button click event """ try: f = float(self.temperature.get()) c = TemperatureConverter.fahrenheit_to_celsius(f) result = f'{f} Fahrenheit = {c:.2f} Celsius' self.result_label.config(text=result) except ValueError as error: showerror(title='Error', message=error) class App(tk.Tk): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.title('Temperature Converter') self.geometry('300x70') self.resizable(False, False) if __name__ == "__main__": app = App() ConverterFrame(app) app.mainloop() Code language: Python (python)In this tutorial, you have learned how to develop a full object-oriented Tkinter application.