Example: Java Program to Implement Binary Tree
// class to create nodes class Node { int key; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { key = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { Node root; // Traverse tree public void traverseTree(Node node) { if (node != null) { traverseTree(node.left); System.out.print(" " + node.key); traverseTree(node.right); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // create an object of BinaryTree BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); // create nodes of the tree tree.root = new Node(1); tree.root.left = new Node(2); tree.root.right = new Node(3); tree.root.left.left = new Node(4); System.out.print("\nBinary Tree: "); tree.traverseTree(tree.root); } } Output
Binary Tree: 4 2 1 3
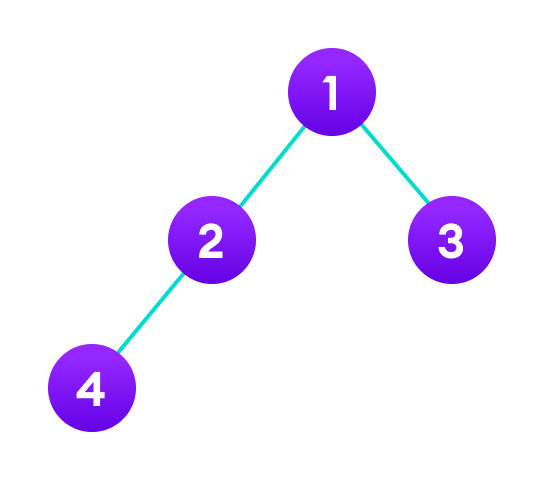
In the above example, we have implemented the binary tree in Java. Unlike other data structures, Java doesn't provide a built-in class for trees.
Here, we have created our own class of BinaryTree. To learn about the binary tree, visit Binary Tree Data Structure.
Also Read: