Summary: In this tutorial, you will learn how to calculate the cumulative distribution of a value in a set of values by using the Oracle PERCENT_RANK() function.
Introduction to Oracle PERCENT_RANK() function #
The PERCENT_RANK() is an analytic function that calculates the relative rank of a row within a result set. It returns a value as a percentage between 0 and 1, inclusive.
Tie values evaluate to the same cumulative distribution value.
Here’s the basic syntax of the PERCENT_RANK() function:
PERCENT_RANK() OVER ( [ partition_clause ] order_by_clause )Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Since PERCENT_RANK() is order sensitive, the order_by_clause is mandatory.
The order_by_clause specifies the order of rows in each partition and has the following form:
ORDER BY expression1 [ASC | DESC ] [NULLS FIRST | LAST] [, expression2 [ASC | DESC ] [NULLS FIRST | LAST],... ]Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The PARTITION BY clause divides the result set into multiple partitions. It is an optional clause. Omitting this clause means that the function will treat the whole result set as a single partition.
The partition_clause has the following syntax:
PARTITION BY expression1 [,expression2,..]Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The PERCENT_RANK() function uses the following formula to calculate the percent rank:
percent_rank = (rank - 1) / (total_rows - 1)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this formula:
rankis the rank of a value, i.e., the result of the RANK() function.total_rowsis the number of rows in the result set.
The PERCENT_RANK function returns 0 (0%) for the highest-ranked rows and 1 (or 100%) for the lowest ranked rows. It returns NULL if the result set (or partition) has only one row because the denominator becomes 0 (total_rows - 1).
In practice, you use the PERCENT_RANK function to find how a value compares relatively to others or to create percentile-based analysis.
Basic Oracle PERCENT_RANK() function example #
First, create a new table called scores with two columns id and score:
CREATE TABLE scores( id NUMBER GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY, score NUMBER NOT NULL );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert some rows into the scores table:
INSERT INTO scores(score) VALUES(100); INSERT INTO scores(score) VALUES(90); INSERT INTO scores(score) VALUES(90); INSERT INTO scores(score) VALUES(80);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, retrieve data from the scores table:
SELECT * FROM scores;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
ID SCORE ---------- ---------- 1 100 2 90 3 90 4 80Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Finally, calculate the ranks and percent ranks of scores:
SELECT id, score, RANK() OVER ( ORDER BY score DESC ) AS rank, PERCENT_RANK() OVER ( ORDER BY score DESC ) AS percent_rank FROM scores;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
ID SCORE RANK PERCENT_RANK ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ 1 100 1 0 2 90 2 .333333333 3 90 2 .333333333 4 80 4 1Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The scores table has four rows:
- Score 100, rank 1.
- Score 90, rank 2 ( second and third rows).
- Score 80, rank 4.
The PERCENT_RANK function calculates the percent rank of each score based on the following formula:
percent_rank = (rank - 1) / (total_rows - 1)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)So:
- Score 100, rank 1, percent rank 0 ( or 0%).
- Score 90, rank 2, the percent rank is (2-1) / (4 -1) = 1/3 ~ 0.33 ( or 33%)
- Score 80, rank 4, the percent rank is (4 – 1) / (4 – 1) = 3 /3 = 1 (or 100%)
Using the Oracle PERCENT_RANK() function over the result set example #
The following statement uses the PERCENT_RANK function to calculate the sales percentile for each salesman in 2017:
SELECT salesman_id, sales, ROUND( PERCENT_RANK() OVER ( ORDER BY sales DESC ) * 100, 2 ) || '%' percent_rank FROM salesman_performance WHERE year = 2017;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
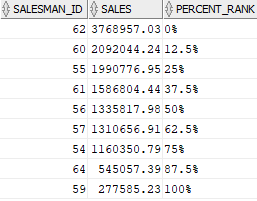
Using Oracle PERCENT_RANK() function over partition example #
The following statement uses the PERCENT_RANK function to calculate the sales percentile for each salesman in 2016 and 2017.
SELECT salesman_id, year, sales, ROUND(PERCENT_RANK() OVER ( PARTITION BY year ORDER BY sales DESC ) * 100,2) || '%' percent_rank FROM salesman_performance WHERE year in (2016,2017); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
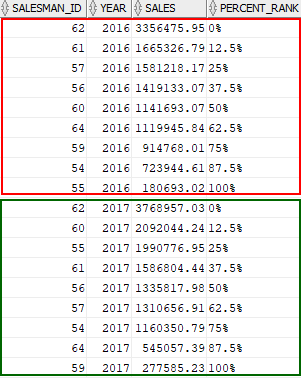
In this example:
- The
PARTITION BYclause divides the result set into two partitions by year, 2016 and 2017. - The
ORDER BYclause sorts rows in each partition by sales amount from high to low. - The
PERCENT_RANK()function calculates the percent rank value of each row in each partition.
Summary #
- Use the
PERCENT_RANK()function to calculate the cumulative distribution of a value in a set of values.