Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to calculate a cumulative distribution of a value in a set of values by using the Oracle CUME_DIST() function.
Introduction to Oracle CUME_DIST() function #
Sometimes, you want to pull the top or bottom x% values from a data set e.g., top 5% salesman by volume. To do this, you can use the CUME_DIST() function.
The CUME_DIST() function is an analytic function that calculates the cumulative distribution of a value in a set of values.
Here’s the basic syntax of CUME_DIST() function:
CUME_DIST() OVER ( [ partition_clause ] order_by_clause )Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The ORDER BY clause specifies the order of rows in each partition or result set. Since CUME_DIST() function is order sensitive, the order_by_clause is mandatory.
The order_by_clause has the following syntax:
ORDER BY expression1 [ASC | DESC ] [NULLS FIRST | LAST] [, expression2 [ASC | DESC ] [NULLS FIRST | LAST],... ] Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The PARTITION BY clause divides the result set into multiple partitions. The partition_clause has the following form:
PARTITION BY expression1 [,expression2,..]Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The partition by clause is optional. If you omit this clause, the CUME_DIST() function will treat the whole result set as a single partition.
The CUME_DIST function uses the following formula for calculation:
CUME_DIST = (number of rows with value <= current value) / total rowsCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)It returns a result that is between 0.0 (0%) and 1.0 (100%). The tied values receive the same cumulative distribution.
Basic Oracle CUME_DIST function example #
First, create a new table called scores with two columns id and score:
CREATE TABLE scores ( id NUMBER GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY, score NUMBER NOT NULL );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert some rows into the scores table:
INSERT INTO scores(score) VALUES(80); INSERT INTO scores(score) VALUES(90); INSERT INTO scores(score) VALUES(90); INSERT INTO scores(score) VALUES(100);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, retrieve data from the scores table:
SELECT * FROM scores;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
ID SCORE ---------- ---------- 1 80 2 90 3 90 4 100Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Finally, calculate the cumulative distribution of a score within a set of scores:
SELECT id, score, CUME_DIST() OVER ( ORDER BY score ) AS cume_dist FROM scores;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
ID SCORE CUME_DIST ---------- ---------- ---------- 1 80 .25 2 90 .75 3 90 .75 4 100 1Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)How it works:
In this example, the result set has 4 rows. The ORDER BY clause in the CUME_DIST function sorts the scores from low to high.
| Row | Score | CUME_DIST | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80 | 1/4 (only 1 row ≤ 80) | 0.25 |
| 2 | 90 | 3/4 (3 rows ≤ 90) | 0.75 |
| 3 | 90 | 3/4 (same as above, tied value) | 0.75 |
| 4 | 100 | 4/4 (all rows ≤ 100) | 1.00 |
Using Oracle CUME_DIST() function over a result set #
The following statement uses CUME_DIST() function to calculate the sales percentile for each salesman in 2017:
SELECT salesman_id, sales, ROUND(CUME_DIST() OVER (ORDER BY sales DESC) * 100,2) || '%' cume_dist FROM salesman_performance WHERE year = 2017;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the result:
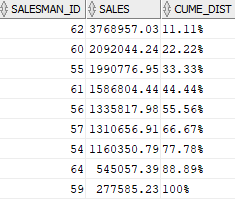
As shown in the output, 33.33 % of salesman have sales amounts greater than 1.99 million.
Using Oracle CUME_DIST() function over partitions #
The following statement uses the CUME_DIST function to calculate the sales percentile for each salesman in 2016 and 2017.
SELECT salesman_id, year, sales, ROUND(CUME_DIST() OVER ( PARTITION BY year ORDER BY sales DESC ) * 100,2) || '%' cume_dist FROM salesman_performance WHERE year in (2016, 2017); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
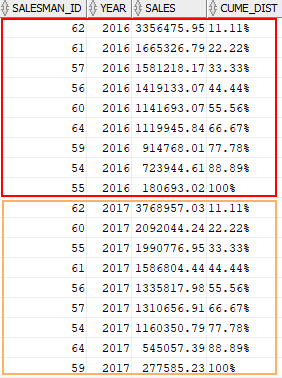
In this example:
- The
PARTITION BYclause divides the result set into two partitions by year, 2016 and 2017. - The
ORDER BYclause sorts the rows in each partition by sales amount in descending order to which theCUME_DIST()function applies.
To get the top 30% of the salesman by sales revenue in 2016 and 2017, you use the following query:
WITH cte_sales AS ( SELECT salesman_id, year, sales, ROUND(CUME_DIST() OVER ( PARTITION BY year ORDER BY sales DESC ),2) cume_dist FROM salesman_performance WHERE year in (2016,2017) ) SELECT * FROM cte_sales WHERE cume_dist <= 0.30; Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
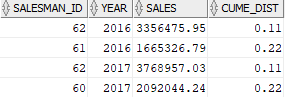
Summary #
- Use the Oracle
CUME_DIST()function to calculate the cumulative distribution of a value in a set of values.