Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL LAST_INSERT_ID() function to return the first automatically generated integer successfully inserted for an AUTO_INCREMENT column.
Introduction to MySQL LAST_INSERT_ID() function
In database design, we often use a surrogate key to generate unique integer values for the primary key column of a table by using the AUTO_INCREMENT attribute:
CREATE TABLE table_name( id INT AUTO_INCREMENT, ..., PRIMARY KEY(id) );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)When you insert a row into the table without specifying a value for the id column, MySQL automatically generates a sequential unique integer for the id column.
The LAST_INSERT_ID() function returns the first automatically generated integer ( BIGINT UNSIGNED) successfully inserted for an AUTO_INCREMENT column.
If you insert multiple rows into the table using a single INSERT statement, the LAST_INSERT_ID() function returns the first automatically generated value only.
If the insertion fails, the result returned by the LAST_INSERT_ID() remain unchanged.
The LAST_INSERT_ID() function works based on the client-independent principle. It means the value returned by the LAST_INSERT_ID() function for a specific client is the value generated by that client only to ensure that each client can obtain its own unique ID.
MySQL LAST_INSERT_ID function examples
Let’s look at an example of using MySQL LAST_INSERT_ID function.
1) Using MySQL LAST_INSERT_ID() function to get value when inserting one row into a table
First, create a new table named messages that has the id column as the primary key and its value is automatically generated:
CREATE TABLE messages( id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, description VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert a new row into the messages table:
INSERT INTO messages(description) VALUES('MySQL last_insert_id');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, use the LAST_INSERT_ID function to get the inserted value of the id column:
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)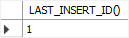
Fourth, attempt to insert a null value into the description column:
INSERT INTO messages(description) VALUES(NULL);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL issued the following error:
Error Code: 1048. Column 'description' cannot be nullCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Finally, use the LAST_INSERT_ID function to get the last automatically inserted value:
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
The result is unchanged.
2) Using MySQL LAST_INSERT_ID() function to get value when inserting multiple rows into a table
First, insert three rows into the messages table:
INSERT INTO messages(description) VALUES ('Insert multiple rows'), ('LAST_INSERT_ID() example'), ('MySQL AUTO_INCREMENT');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, query data from the messages table:
SELECT * FROM messages;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)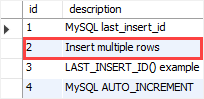
Third, use the LAST_INSERT_ID() function to get the inserted value:
SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID();Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)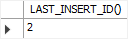
As you can see clearly from the output, the LAST_INSERT_ID() function returns the generated value of the first row successfully inserted, not the last row.
3) Using MySQL LAST_INSERT_ID() function in a stored procedure
First, create two tables accounts and phones for testing:
CREATE TABLE accounts ( account_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, first_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, last_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL ); CREATE TABLE phones ( phone_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT, account_id INT NOT NULL, phone VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL, description VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (phone_id , account_id), FOREIGN KEY (account_id) REFERENCES accounts (account_id) );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, create a stored procedure that inserts an account with a phone number into both tables:
DELIMITER $$ CREATE PROCEDURE CreateAccount( fname VARCHAR(255), lname VARCHAR(255), phone VARCHAR(25), description VARCHAR(255) ) BEGIN DECLARE l_account_id INT DEFAULT 0; START TRANSACTION; -- Insert account data INSERT INTO accounts(first_name, last_name) VALUES(fname, lname); -- get account id SET l_account_id = LAST_INSERT_ID(); -- insert phone for the account IF l_account_id > 0 THEN INSERT INTO phones(account_id, phone, description) VALUES(l_account_id,phone,description); -- commit COMMIT; ELSE ROLLBACK; END IF; END$$ DELIMITER ;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The stored procedure inserts a row into the accounts table, get the account id using the LAST_INSERT_ID() function, and use this account id to insert a phone into the phones table.
A row in the phones table should only exist if there is a corresponding row in the accounts table, therefore, we wrap the insert statements in a transaction.
Third, call the stored procedure CreateAccount to create a new account with a phone number:
CALL CreateAccount( 'John', 'Doe', '(408)-456-4567', 'Emergency Contact' );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Fourth, query data from the accounts and phones tables:
SELECT * FROM accounts;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)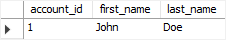
SELECT * FROM phones;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
It works as expected.
Finally, attempt to create a new account with the value of the last name is null:
CALL CreateAccount( 'Jane', null , '(408)-456-1111', 'Emergency Contact');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)MySQL issued an error:
Error Code: 1048. Column 'last_name' cannot be nullCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Summary
- Use the MySQL
LAST_INSERT_IDfunction to get the first automatically generated integer successfully inserted for anAUTO_INCREMENTcolumn.