Eclipse IDE is a platform for developing applications, particularly in Java and other programming languages such as C, C++, Python, Perl, Ruby, etc. It is one of the most powerful and feature-rich IDE used by millions of developers around the world.
Eclipse is a cross-platform IDE that you can install on Linux as well as on Windows and macOS. Let’s see how to install Eclipse IDE on various Linux distributions.
Install Eclipse IDE on Linux via the Installer File
Eclipse provides an official installer file for all Linux distributions which you can install using a few simple commands. Eclipse requires Java to be preinstalled on your Linux distribution, however. Below are the commands to install Java on Linux:
To install Java on Ubuntu and other Debian-based distributions:
sudo apt install -y openjdk-11-jdk On Fedora and other RPM-based distributions:
sudo yum install java-11-openjdk On Arch Linux:
sudo pacman -S jdk11-openjdk On openSUSE:
sudo zypper --non-interactive install java-11-openjdk-devel Once you have installed Java, download the Eclipse IDE installer file.
Download: Eclipse
The installer file will be a TAR.GZ archive that you can extract with:
tar -xvf eclipse-inst-linux64.tar.gz This command will extract the contents of the archive into the eclipse-installer directory. Use the cd command to change the directory:
cd eclipse-installer/ Next, run the installer file using:
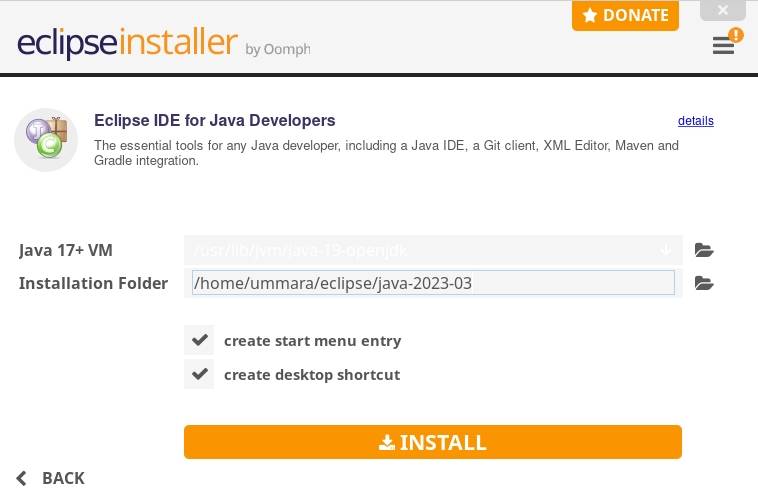
./eclipse-inst This will open the following installer window:
Choose the Eclipse IDE package you want to install. Here, we are installing Eclipse IDE for Java Developers. Next, choose the installation directory for Eclipse IDE or leave the default one selected and click Install.
The installer will now show the software user agreement for you to review and accept if you want to proceed. Click Accept Now.
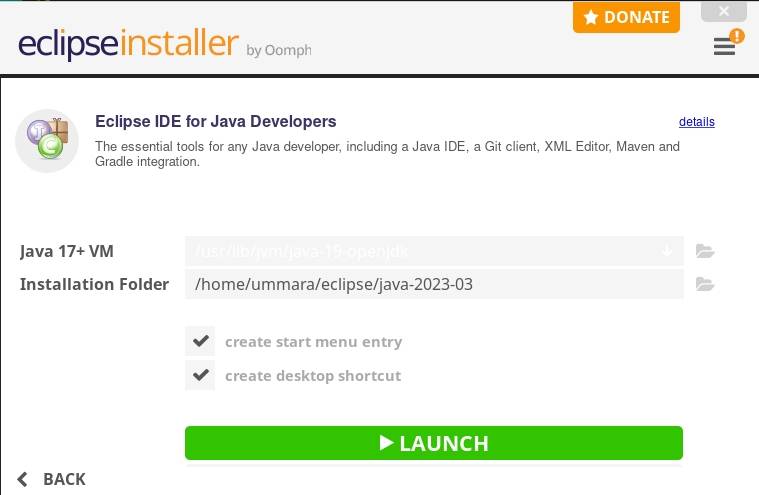
After that, it will start the installation. Once completed, click the Launch button if you want to launch Eclipse right away.
How to Uninstall Eclipse IDE From Linux
If you no longer want to use Eclipse IDE, you can remove it from your Linux machine. To uninstall Eclipse, go to the home directory and use the rm command to delete the Eclipse folder:
sudo rm -r eclipse* To remove the application shortcut, run the following two commands:
cd .local/share/applications/ sudo rm *eclipse*.desktop epp*.desktop Install Eclipse IDE From the Snap Store
On all Linux distributions that support Snap, you can install Eclipse IDE via its Snap package.
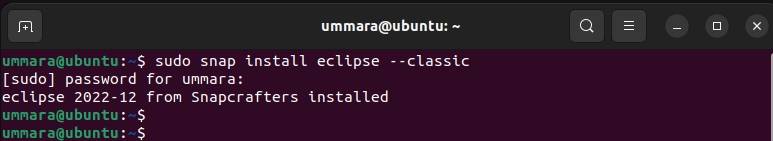
To do so, first, install snapd on your Linux system and then use the following command to install Eclipse:
sudo snap install eclipse --classic After installing the Eclipse snap package, you can launch it from the applications menu or use the following command:
eclipse Uninstall the Eclipse Snap Package
To remove the Eclipse snap application when you're done, run:
sudo snap remove eclipse Install Eclipse IDE on Linux via Flatpak
If your Linux distribution supports Flatpak, you can also install Eclipse using its Flatpak package. For this, you will need to install Flatpak on your system if it's not already installed.
Next, add the Flathub repository using the following command:
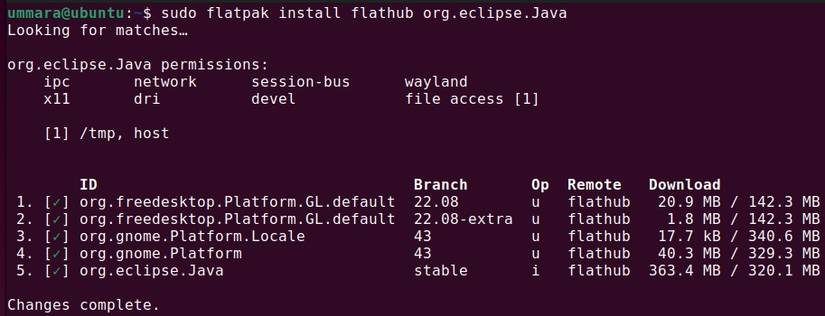
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo You can now install the Eclipse IDE Flatpak package with:
sudo flatpak install flathub org.eclipse.java Launch Eclipse IDE from the applications menu or run the following command:
flatpak run org.eclipse.java Uninstall the Eclipse Flatpak Package
To uninstall the Eclipse IDE Flatpak, run:
sudo flatpak remove org.eclipse.Java Using Eclipse IDE for the First Time
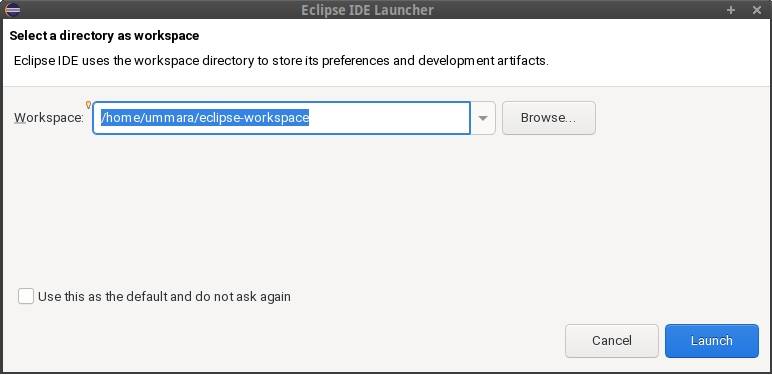
After launching Eclipse IDE for the first time, it will ask you to select a workspace directory to store your projects. You can either leave the default workspace selected by Eclipse or choose a different directory. Then, click the Launch button to start working on the IDE.
Develop Java Applications on Linux Using Eclipse IDE
Using this guide, you will be able to install Eclipse IDE on your Linux machine. Once you have installed Eclipse IDE, you are ready to write, build, and run your code. It comes with a lot of features to help you structure your code in a readable and understandable manner.
For Linux users, there are other IDEs and code editors available as well, such as Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, Atom, Apache NetBeans, etc. You can also try out these editors to determine which one best suits your requirements and preferences.