Use requirements.txt
PyCharm provides integration with the major means of requirements management and makes it possible to track the unsatisfied requirements in your projects and create a virtual environment based on the requirements.txt file .
Create requirements file
If you do not have a requirements file in your project yet, you can create it yourself:
Do one of the following:
In the Project tool window (Alt+1), select the directory or package in which you want to create a new file, and then choose from the main menu.
Right-click the directory or package and select New from the context menu.
Select the directory and press Alt+Insert.
Select from the list.
Specify the name of the requirements file. The recommended name for the requirements file is requirements.txt. When a file with this name is added to the root project directory, it is automatically detected by Python Integrated tools.
Click OK. The new file will be created under the target location.
You can also run pip freeze > requirements.txt in the command line to generate a requirements.txt file for your project. See https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/reference/pip_freeze/ for more details.
If the name of the requirements file differs from requirements.txt or when you have several requirements files in one project, you have to notify PyCharm about the requirements file you want to apply.
Configure the default requirements file
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
In the Package requirements file field, type the name of the requirements file or click the browse button and locate the file.
Click OK to save the changes.
PyCharm provides quick fixes that enable populating requirements file.
Define requirements
Open the requirements.txt file in the editor.
If your requirements.txt file is empty, and you have imported packages in your project, PyCharm provides quick fix to update the requirements file.
Click link:

In the opened dialog, specify the name of the requirements file.
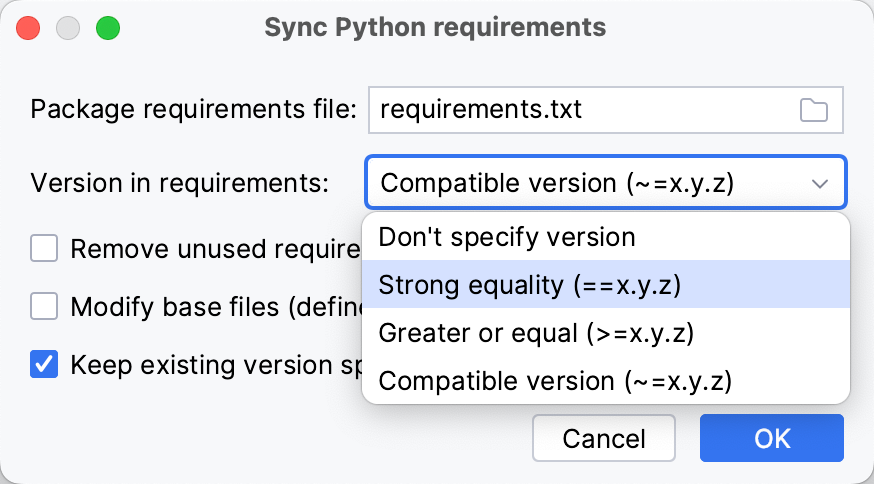
Select the method of handling versions of the required libraries. The version numbers can be defined:
Method
Example
Strong equality
Django==3.0.3Greater or equal
Django>=3.0.3Compatible version
Django~=3.0.3Define the requirements management policy:
Policy
Action
Remove unused requirements
Deletes records that correspond to unused libraries and packages.
Modify base files
Allows modifications in the base requirements files (if any is referenced in the requirements.txt file).
Keep existing version specifier if it matches the current version
Leaves the version number unchanged if it satisfied the selected method versions handling.
Click OK and inspect the updated file.
Update the requirements file
In an
importstatement of a Python file, place the caret on the highlighted package and press Alt+Enter. Use the quick-fix suggested by PyCharm: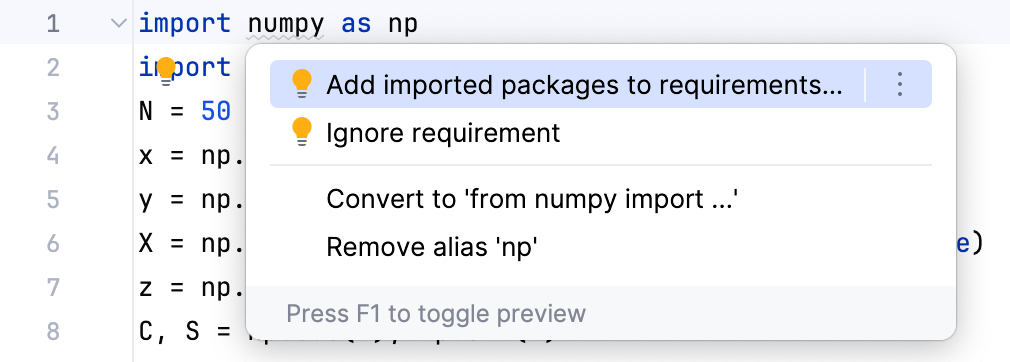
Specify project dependencies
Open requirements.txt in the editor.
Specify the names of the required packages and their versions.
When you start typing the package name, PyCharm provides completion options:
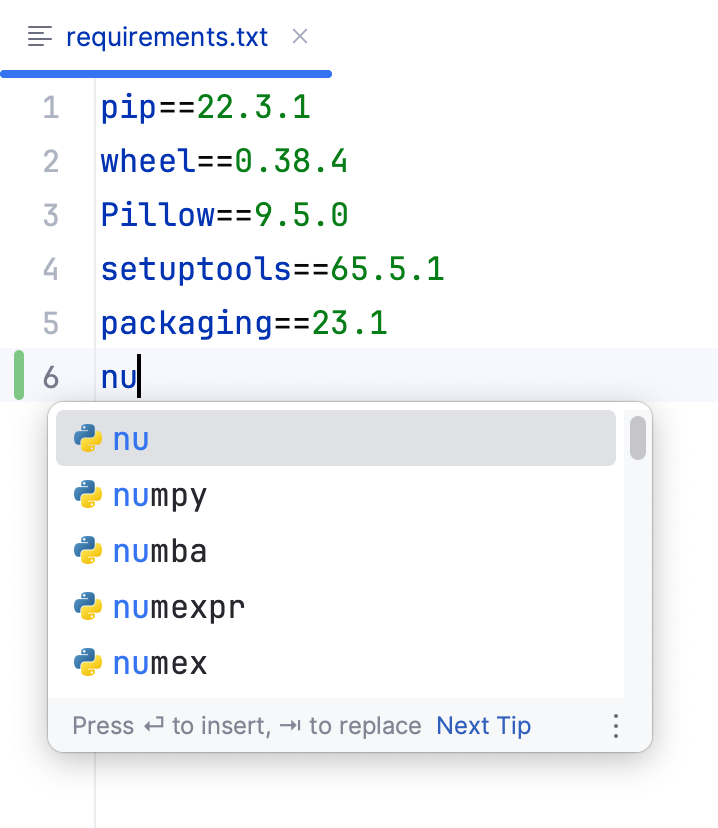
Press Enter to insert the suggestion.
PyCharm provides quick fixes and notifications related to the unsatisfied dependencies.
Install the required packages from requirements.txt
When you open requirements.txt or a Python file on a project that contains requirements.txt, PyCharm checks whether all the packages specified in requirements.txt are installed for the current Python interpreter.
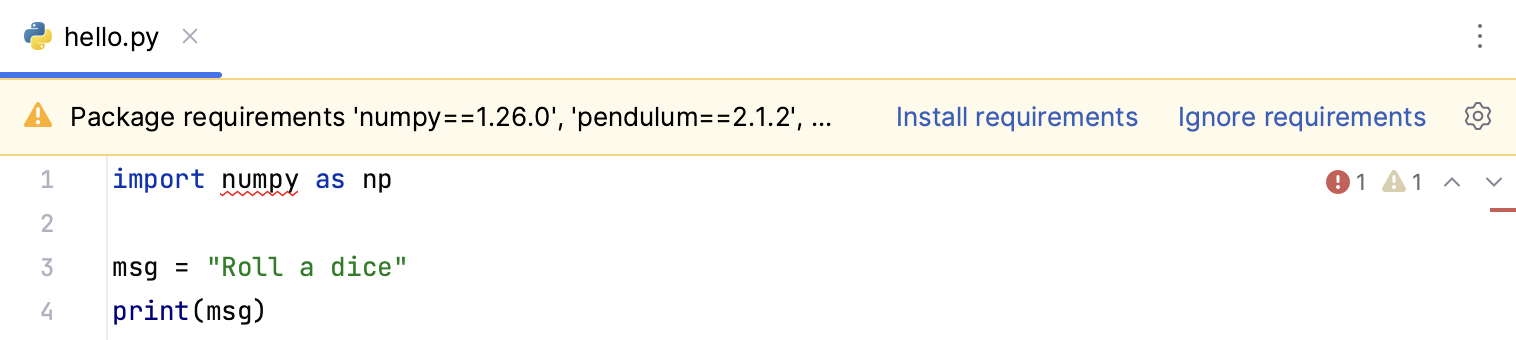
If any packages are missing, a notification bar is displayed at the top of the editor. Click Install requirements.
You can also click Ignore requirements. In this case, you will be able to remove the packages from the list of the ignored packages.
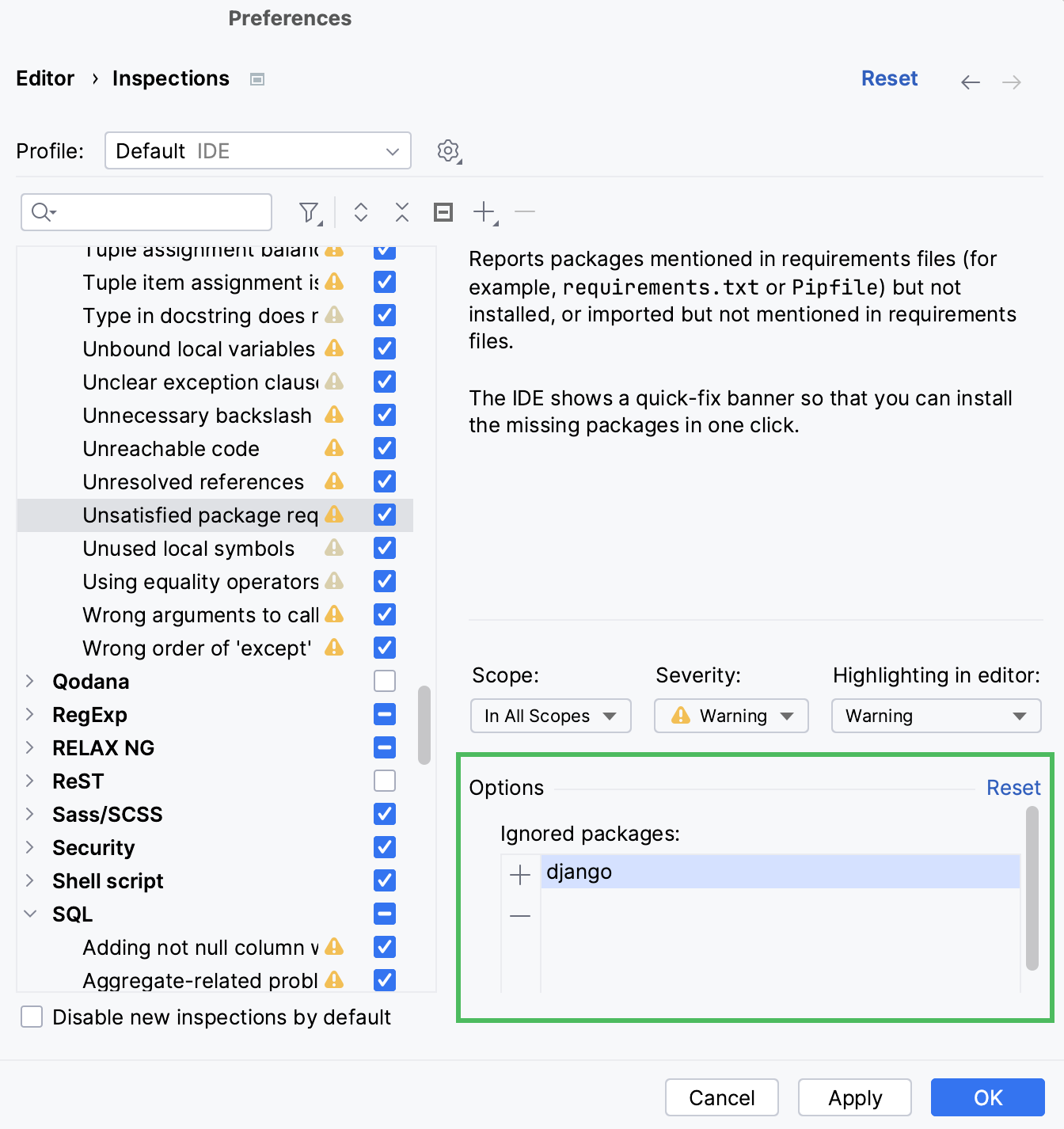
Manage the ignored dependencies
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open project Settings.
In the main menu, go to .
In the list of the inspections, select Unsatisfied package requirements.
Preview the list of the ignored requirements and click the Add icon (
) to add them.