Write a function to get Nth node in a Linked List
Last Updated : 23 Aug, 2024
Given a LinkedList and an index (1-based). The task is to find the data value stored in the node at that kth position. If no such node exists whose index is k then return -1.
Example:
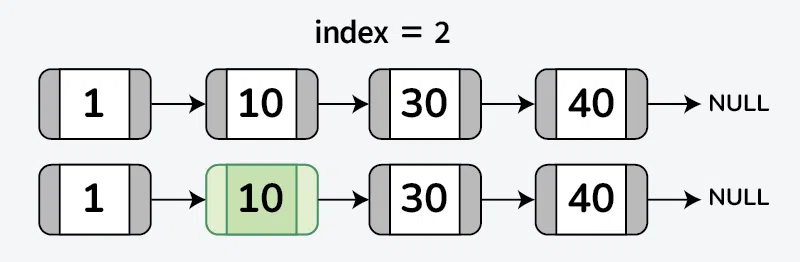
Input: 1->10->30->14, index = 2
Output: 10
Explanation: The node value at index 2 is 10
Input: 1->32->12->10->30->14->100, index = 8
Output: -1
Explanation: No such node exists at index = 8.
[Naive Approach] Recursive Method - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to use the recursive method to find the value of index node (1- based) . Call the function GetNth(head,index) recusively, where head will represent the current head node . Decrement the index value by 1 on every recursion call. When the n reaches 1 ,we will return the data of current node.
Below is the implementation of above approach:
C++ //C++ program to find the data at nth node //recursively #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; Node* next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = NULL; } }; // Takes head pointer of the linked list and index // as arguments and returns data at index. int GetNth(Node* head, int index) { // If the list is empty or index is out of bounds if (head == NULL) return -1; // If index equals 1, return node's data if (index == 1) return head->data; // Recursively move to the next node return GetNth(head->next, index - 1); } int main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node* head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); cout << "Element at index 3 is " << GetNth(head, 3) << endl; return 0; } // C program to find the data at nth node // recursively #include <stdio.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; }; // Takes head pointer of the linked list and index // as arguments and returns data at index. int GetNth(struct Node *head, int index) { // If the list is empty or index is out of bounds if (head == NULL) return -1; // If index equals 1, return node's data if (index == 1) return head->data; // Recursively move to the next node return GetNth(head->next, index - 1); } struct Node *createNode(int new_data) { struct Node *new_node = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = new_data; new_node->next = NULL; return new_node; } int main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 struct Node *head = createNode(1); head->next = createNode(2); head->next->next = createNode(3); head->next->next->next = createNode(4); head->next->next->next->next = createNode(5); printf("Element at index 3 is %d\n", GetNth(head, 3)); return 0; } // Java program to find n'th node in linked list // using recursion import java.io.*; class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x){ data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Takes head pointer of the linked list and index // as arguments and return data at index*/ static int GetNth(Node head, int index) { if (head == null) return -1; // if index equal to 1 return node.data if (index == 1) return head.data; // recursively decrease n and increase // head to next pointer return GetNth(head.next, index - 1); } public static void main(String args[]) { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); System.out.printf("Element at index 3 is %d", GetNth(head, 3)); } } # Python program to find the Nth node in # linked list using recursion class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None # Recursive method to find the Nth node def get_nth_node(head, index): # Helper function to handle recursion #and count tracking if head is None: print(-1) if index == 1: print(head.data) else: get_nth_node(head.next, index-1) if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a linked list: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) print("Element at index 3 is", end=" ") get_nth_node(head, 3) // C# program to find the Nth node in // linked list using recursion using System; class Node { public int Data; public Node Next; public Node(int x) { Data = x; Next = null; } } class GfG { // Takes head pointer of the linked list and index // as arguments and returns data at index static int GetNth(Node head, int index) { // Base Condition if (head == null) return -1; // If n equals 0, return the node's data if (index == 1) return head.Data; // Recursively move to the next node return GetNth(head.Next, index - 1); } public static void Main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.Next = new Node(2); head.Next.Next = new Node(3); head.Next.Next.Next = new Node(4); head.Next.Next.Next.Next = new Node(5); Console.WriteLine("Element at index 3 is {0}", GetNth(head, 3)); } } // JavaScript program to find the n'th node in // a linked list using recursion class Node { constructor(new_data) { this.data = new_data; this.next = null; } } function GetNth(head, index) { // Base case: if the list is empty or index is out of // bounds if (head === null) { return -1; } // Base case: if count equals n, return node's data if (index === 1) { return head.data; } // Recursive case: move to the next node and decrease // index return GetNth(head.next, index - 1); } // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); console.log("Element at index 3 is", GetNth(head, 3)); OutputElement at index 3 is 3
Time Complexity : O(n) ,where n is the nth node of linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(n), for recursive call stack
[Expected Approach-2] Iterative Method - O(n) Time and O(1) Space
The idea is similar to recursive approach to find the value at index node (1- based) .We will use a variable say, count = 1 to track the nodes. Traverse the list until curr != NULL . Increment the count if count is not equal to index node (1- based) , else if count equals to the index node, return data at current node.
Below is the implementation of above approach :
C++ // C++ program to find n'th // node in linked list (iteratively) #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; // Function to find the nth node in the list int GetNth(Node *head, int index) { Node *curr = head; int count = 1; while (curr != nullptr) { if (count == index) return curr->data; count++; curr = curr->next; } return -1; } int main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node *head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); cout << "Element at index 3 is " << GetNth(head, 3) << endl; return 0; } // C program to find n'th // node in linked list (iteratively) #include <stdio.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; }; // Function to find the nth node in the list int GetNth(struct Node *head, int index) { struct Node *curr = head; int count = 1; while (curr != NULL) { if (count == index) return curr->data; count++; curr = curr->next; } return -1; } struct Node *createNode(int new_data) { struct Node *new_node = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = new_data; new_node->next = NULL; return new_node; } int main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 struct Node *head = createNode(1); head->next = createNode(2); head->next->next = createNode(3); head->next->next->next = createNode(4); head->next->next->next->next = createNode(5); printf("Element at index 3 is %d\n", GetNth(head, 3)); } // Java program to find the Nth node in // a linked list iteratively class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to find the nth node in the list iteratively static int getNthNodeIterative(Node head, int index) { Node current = head; int count = 1; // Traverse the list until the end or until the nth // node is reached while (current != null) { if (count == index) { return current.data; } count++; current = current.next; } // Return -1 if the index is out of bounds return -1; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); int index = 3; int result = getNthNodeIterative(head, index); if (result != -1) { System.out.println("Element at index " + index + " is " + result); } else { System.out.println("Index " + index + " is out of bounds"); } } } # Python program to find the Nth node in # a linked list iteratively class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None # Function to find the nth node in the list iteratively def get_nth_node_iterative(head, n): current = head count = 1 # Traverse the list until the end or until the nth node is reached while current is not None: if count == n: return current.data count += 1 current = current.next # Return -1 if the index is out of bounds return -1 if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a hard-coded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) index = 3 result = get_nth_node_iterative(head, index) if result != -1: print(f"Element at index {index} is {result}") else: print(f"Index {index} is out of bounds") // Iterative C# program to find the nth node in // a linked list using System; class Node { public int Data; public Node Next; public Node(int x) { Data = x; Next = null; } } class GfG { // Given the head of a list and index, find the nth node // and return its data static int GetNthNode(Node head, int n) { Node current = head; int count = 1; // Traverse the list until the nth node is found or // end of the list is reached while (current != null) { if (count == n) { return current.Data; } count++; current = current.Next; } // Return -1 if the index is out of bounds return -1; } public static void Main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.Next = new Node(2); head.Next.Next = new Node(3); head.Next.Next.Next = new Node(4); head.Next.Next.Next.Next = new Node(5); int index = 3; int result = GetNthNode(head, index); if (result != -1) { Console.WriteLine($"Element at index {index} is {result}"); } else { Console.WriteLine($"Index {index} is out of bounds"); } } } // Iterative JavaScript program to find the Nth node in a // linked list class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; } } // Given the head of a list and an index, return the data at // the index function getNth(head, index) { let current = head; let count = 1; // Traverse the linked list while (current !== null) { if (count === index) { // Return data at the current // node if index matches return current.data; } count++; current = current.next; } // Return -1 if index is out of bounds return -1; } // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); let index = 3; let result = getNth(head, index); if (result !== -1) { console.log(`Element at index ${index} is ${result}`); } else { console.log(`Index ${index} is out of bounds`); } OutputElement at index 3 is 3
Time Complexity : O(n), where n is the nth node of linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Similar Reads
Linked List Data Structure A linked list is a fundamental data structure in computer science. It mainly allows efficient insertion and deletion operations compared to arrays. Like arrays, it is also used to implement other data structures like stack, queue and deque. Here’s the comparison of Linked List vs Arrays Linked List:
3 min read
Basic Terminologies of Linked List Linked List is a linear data structure, in which elements are not stored at a contiguous location, rather they are linked using pointers. Linked List forms a series of connected nodes, where each node stores the data and the address of the next node.Node Structure: A node in a linked list typically
2 min read
Introduction to Linked List - Data Structure and Algorithm Tutorials Linked List is basically chains of nodes where each node contains information such as data and a pointer to the next node in the chain. It is a popular data structure with a wide range of real-world applications. Unlike Arrays, Linked List elements are not stored at a contiguous location. In the lin
9 min read
Applications, Advantages and Disadvantages of Linked List A Linked List is a linear data structure that is used to store a collection of data with the help of nodes. Please remember the following points before moving forward.The consecutive elements are connected by pointers / references.The last node of the linked list points to null.The entry point of a
4 min read
Linked List vs Array Array: Arrays store elements in contiguous memory locations, resulting in easily calculable addresses for the elements stored and this allows faster access to an element at a specific index.Data storage scheme of an arrayLinked List: Linked lists are less rigid in their storage structure and element
2 min read
Types of Linked List
Basic Operations on Linked List
Insertion in Linked ListInsertion in a linked list involves adding a new node at a specified position in the list. There are several types of insertion based on the position where the new node is to be added:At the front of the linked list Before a given node.After a given node.At a specific position.At the end of the link
4 min read
Search an element in a Linked List (Iterative and Recursive)Given a linked list and a key, the task is to check if key is present in the linked list or not. Examples:Input: 14 -> 21 -> 11 -> 30 -> 10, key = 14Output: YesExplanation: 14 is present in the linked list.Input: 6 -> 21 -> 17 -> 30 -> 10 -> 8, key = 13Output: NoExplanatio
12 min read
Find Length of a Linked List (Iterative and Recursive)Given a Singly Linked List, the task is to find the Length of the Linked List.Examples:Input: LinkedList = 1->3->1->2->1Output: 5Explanation: The linked list has 5 nodes.Input: LinkedList = 2->4->1->9->5->3->6Output: 7 Explanation: The linked list has 7 nodes.Input: Lin
11 min read
Reverse a Linked ListGiven a linked list, the task is to reverse the linked list by changing the links between nodes.Examples: Input: head: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> NULLOutput: head: 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULLExplanation: Reversed Linked List: Input: head: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULLOut
15+ min read
Deletion in Linked ListDeleting a node in a Linked List is an important operation and can be done in three main ways: removing the first node, removing a node in the middle, or removing the last node.In this article, we will explore deletion operation on Linked List for all the above scenarios. Types of Deletion in Linked
3 min read
Delete a Linked List node at a given positionGiven a singly linked list and a position (1-based indexing), the task is to delete a linked list node at the given position.Note: Position will be valid (i.e, 1 <= position <= linked list length)Example: Input: position = 2, Linked List = 8->2->3->1->7Output: Linked List = 8->3
8 min read
Write a function to delete a Linked ListGiven a linked list, the task is to delete the linked list completely.Examples:Input: head: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULLOutput: NULLExplanation: Linked List is Deleted.Input: head: 1 -> 12 -> 1 -> 4 -> 1 -> NULLOutput: NULLExplanation: Linked List is Deleted.Table of C
9 min read
Write a function to get Nth node in a Linked ListGiven a LinkedList and an index (1-based). The task is to find the data value stored in the node at that kth position. If no such node exists whose index is k then return -1.Example:Â Input: 1->10->30->14, index = 2Output: 10Explanation: The node value at index 2 is 10 Input: 1->32->12
11 min read
Program for Nth node from the end of a Linked ListGiven a Linked List of M nodes and a number N, find the value at the Nth node from the end of the Linked List. If there is no Nth node from the end, print -1.Examples:Input: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4, N = 3Output: 2Explanation: Node 2 is the third node from the end of the linked list.Input: 35 ->
14 min read
Top 50 Problems on Linked List Data Structure asked in SDE Interviews A Linked List is a linear data structure that looks like a chain of nodes, where each node is a different element. Unlike Arrays, Linked List elements are not stored at a contiguous location. Here is the collection of the Top 50 list of frequently asked interview questions on Linked Lists. Problems
3 min read