Structured Query Language (SQL) is the standard language used to interact with relational databases.
- It allows users to store, retrieve, update and manage data efficiently through simple commands.
- It is known for its user-friendly syntax and powerful capabilities, SQL is widely used across industries.
How Does SQL Work?
We interact with databases using SQL queries. DBMS tools like MySQL and SQL Server have their own SQL engine and an interface where users can write and execute SQL queries.

Below are the detailed steps involved in the SQL query execution.
- Input: The user submits a query (e.g., SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) via an application or interface.
- Parsing: The query processor breaks the query into parts (tokens) and checks for syntax and schema correctness.
- Optimization: The optimizer finds the most efficient way to run the query using indexes, statistics and available resources.
- Execution: The execution engine runs the query using the chosen plan, accessing or modifying the database as needed.
- Output: Results are returned to the user, either data (for SELECT) or a success message (for other operations).
Key Components of a SQL System
- Databases : A database is a structured collection of data. It organizes data into tables, which are like spreadsheets with rows (records) and columns (fields) .
- Tables: Each table enforces rules and relationships among its columns for data integrity.
- Indexes: Indexes speed up queries by allowing the database to quickly locate data without scanning the entire table.
- Views: A view is a virtual table basically a saved SELECT statement you can query like a table.
- Stored Procedures: These are pre-written SQL scripts stored inside the database. They can receive inputs, run complex logic and return results boosting performance, reusability and security.
- Transactions: A transaction groups multiple SQL operations into a single unit. It ensures all changes are applied successfully or none are, preserving data integrity (ACID properties)
- Security and Permissions: SQL includes tools to restrict access, letting DBAs assign who can do what whether it's accessing tables, executing procedures, or changing structures.
- Joins: Joins combine data from multiple tables based on relationships essential for querying across related datasets.
Rules for Writing SQL Queries
There are certain rules for SQL which would ensure consistency and functionality across databases. By following these rules, queries will be well formed and well executed in any database.
- End with Semicolon (
;): Each SQL statement must end with a semicolon to execute properly. - Case Insensitivity: SQL keywords (e.g., SELECT, INSERT) are not case-sensitive. However, table or column names may be case-sensitive depending on the DBMS.
- Whitespace Allowed: Queries can span multiple lines, but use spaces between keywords and names.
- Reserved Words: Avoid using SQL keywords as names. If needed, wrap them in quotes (
" ") or backticks (`).
Comments
- Single-line: -- comment
- Multi-line: /* comment */
Data Constraints: Use NOT NULL, UNIQUE, PRIMARY KEY, etc., to ensure data accuracy.
String Values: Enclose strings in single quotes ('text').
Naming Rules:
- We Start with a letter
- We can only use Max 30 characters
- We only use letters, numbers and underscores (_)
What are Different SQL Commands or Queries?
Structured Query Language (SQL) commands are standardized instructions used by developers to interact with data stored in relational databases. These commands allow for the creation, manipulation, retrieval and control of data, as well as database structures. SQL commands are categorized based on their specific functionalities:
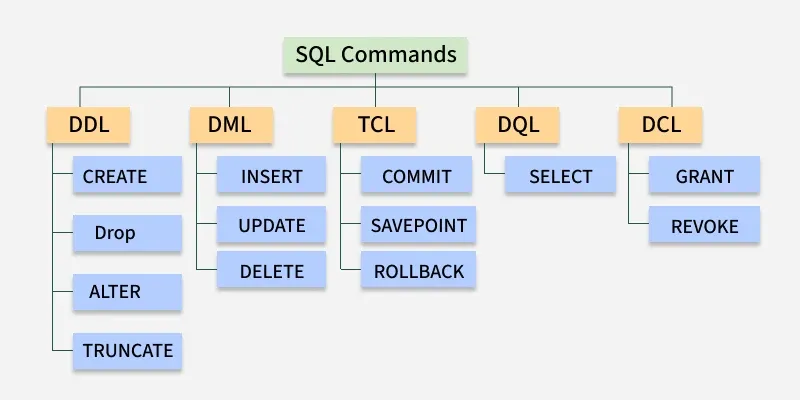 Different SQL Commands or Queries
Different SQL Commands or Queries1. Data Definition Language
These commands are used to define the structure of database objects by creating, altering and dropping the database objects. Based on the needs of the business, database engineers create and modify database objects using DDL. The CREATE command, for instance, is used by the database engineer to create database objects like tables, views and indexes.
Command | Description |
|---|
CREATE | Creates a new table, a view on a table, or some other object in the database. |
|---|
ALTER | Modifies an existing database object, such as a table |
|---|
DROP | Deletes an entire table, a view of a table, or other objects in the database |
|---|
TRUNCATE | Removes all records from a table but keeps the table structure intact. |
|---|
RENAME | It is used to change the name of an existing database object, such as a table. |
|---|
2. Data Manipulation Language
A relational database can be updated with new data using data manipulation language (DML) statements. The INSERT command, for instance, is used by an application to add a new record to the database.
Command | Description |
|---|
INSERT | Creates a record. |
|---|
UPDATE | Modifies records. |
|---|
DELETE | Deletes records. |
|---|
3. Data Query Language
Data retrieval instructions are written in the data query language (DQL), which is used to access relational databases. The SELECT command is used by software programs to filter and return particular results from a SQL table.
4. Data Control language
DCL commands manage user access to the database by granting or revoking permissions. Database administrators use DCL to enforce security and control access to database objects.
Command | Description |
|---|
GRANT | Gives a privilege to the user. |
|---|
REVOKE | Takes back privileges granted by the user. |
|---|
5. Transaction Control Language
TCL commands manage transactions in relational databases, ensuring data integrity and consistency. These commands are used to commit changes or roll back operations in case of errors.
Command | Description |
|---|
COMMIT | Saves all changes made during the current transaction on a permanent basis. Some databases provide an auto-commit feature, which can be configured using settings. |
|---|
ROLLBACK | Reverts changes made during the current transaction, ensuring no unwanted changes are saved. |
|---|
SAVEPOINT | Sets a point within a transaction to which changes can be rolled back, allowing partial rollbacks |
|---|
Benefits of SQL
- Efficiency: SQL is designed to handle complex queries and large datasets with optimal performance, making data retrieval and manipulation seamless.
- Standardization: As an ANSI and ISO standard language, SQL provides a universal method to interact with relational databases across platforms.
- Scalability: SQL supports databases ranging from small-scale applications to enterprise-level systems, ensuring smooth operations regardless of size.
- Flexibility: SQL can be extended with procedural programming (e.g., PL/SQL, T-SQL) to build complex business logic and custom functions.
Limitations of SQL
- Complexity in Advanced Operations: Advanced functionalities such as indexing, query optimization and performance tuning require in-depth technical knowledge.
- Scalability Concerns: SQL performs best with structured data but handling unstructured data or massive distributed systems can pose challenges.
- Platform-Specific Variations: While SQL is standardized, many databases implement unique extensions, leading to portability and compatibility issues.
- Lack of Real Time Analytics: Traditional SQL databases are not optimized for real-time data ingestion and analysis.
Real-World Applications of SQL
- E-Commerce: Manage customer orders, product catalogs and inventory.
- Healthcare: Maintain patient records and appointment schedules.
- Banking: Analyze transaction histories and generate financial reports.
- Web Development: Power dynamic websites with user-specific content.
- Machine Learning and Data Science: Combine SQL databases with tools like Python, R and TensorFlow to streamline machine learning workflows.
Explore
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security
My Profile